Multi-scale Underwater Image Enhancement Network Based on Attention Mechanism
-
摘要: 水下图像往往会因为光的吸收和散射而出现颜色退化与细节模糊的现象,进而影响水下视觉任务。该文通过水下成像模型合成更接近水下图像的数据集,以端到端的方式设计了一个基于注意力的多尺度水下图像增强网络。在该网络中引入像素和通道注意力机制,并设计了一个多尺度特征提取模块,在网络开始阶段提取不同层次的特征,通过带跳跃连接的卷积层和注意力模块后得到输出结果。多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在处理合成水下图像和真实水下图像时都能有很好的效果,与现有方法相比能更好地恢复图像颜色和纹理细节。Abstract: Due to the absorption and scattering, color degradation and detail blurring often occur in underwater images, which will affect the underwater visual tasks. A multi-scale underwater image enhancement network based on attention mechanism is designed in an end-to-end manner by synthesizing dataset closer to underwater images through underwater imaging model. In the network, pixel and channel attention mechanisms are introduced. A new multi-scale feature extraction module is designed to extract the features of different levels at the beginning of the network, and the output results are obtained via a convolution layer and an attention module with skip connections. Experimental results on multiple datasets show that the proposed method is effective in processing both synthetic and real underwater images. It can better recover the color and texture details of images compared with the existing methods.
-
Key words:
- Underwater image enhancement /
- Deep learning /
- Attention mechanism /
- Multi-scale features
-
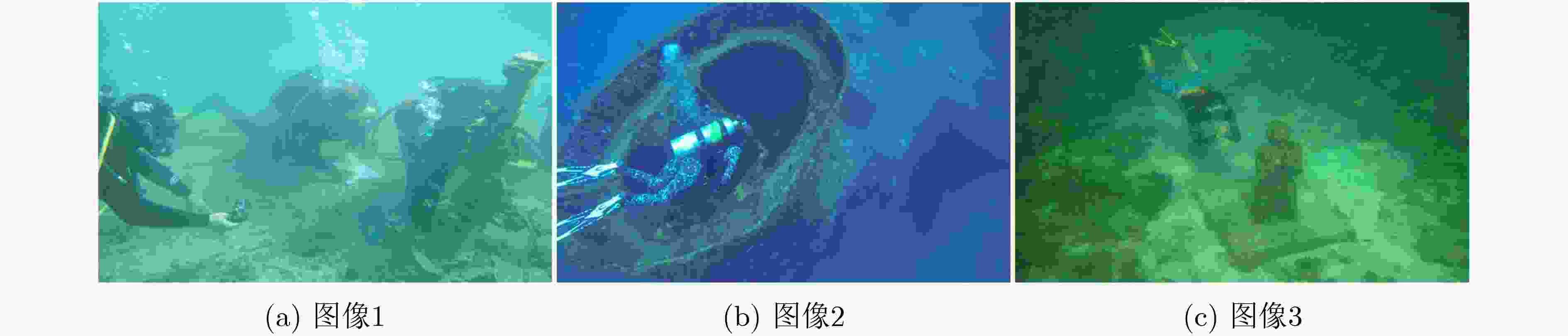
表 1 不同水体中红(R),绿(G),蓝(B)通道中参数设置[23]
水体类型 参数 R G B (1) ${\rm{Nrer}}(\lambda )$ 0.79+0.06rand() 0.92+0.06rand() 0.94+0.05rand() ${B_\lambda }$ 0.05+0.15rand() 0.60+0.30rand() 0.70+0.29rand() (2) ${\rm{Nrer}}(\lambda )$ 0.71+0.04rand() 0.82+0.06rand() 0.80+0.07rand() ${B_\lambda }$ 0.05+0.15rand() 0.60+0.30rand() 0.70+0.29rand() (3) ${\rm{Nrer}}(\lambda )$ 0.67 0.73 0.67 ${B_\lambda }$ 0.15 0.80 0.75 表 2 网络参数表
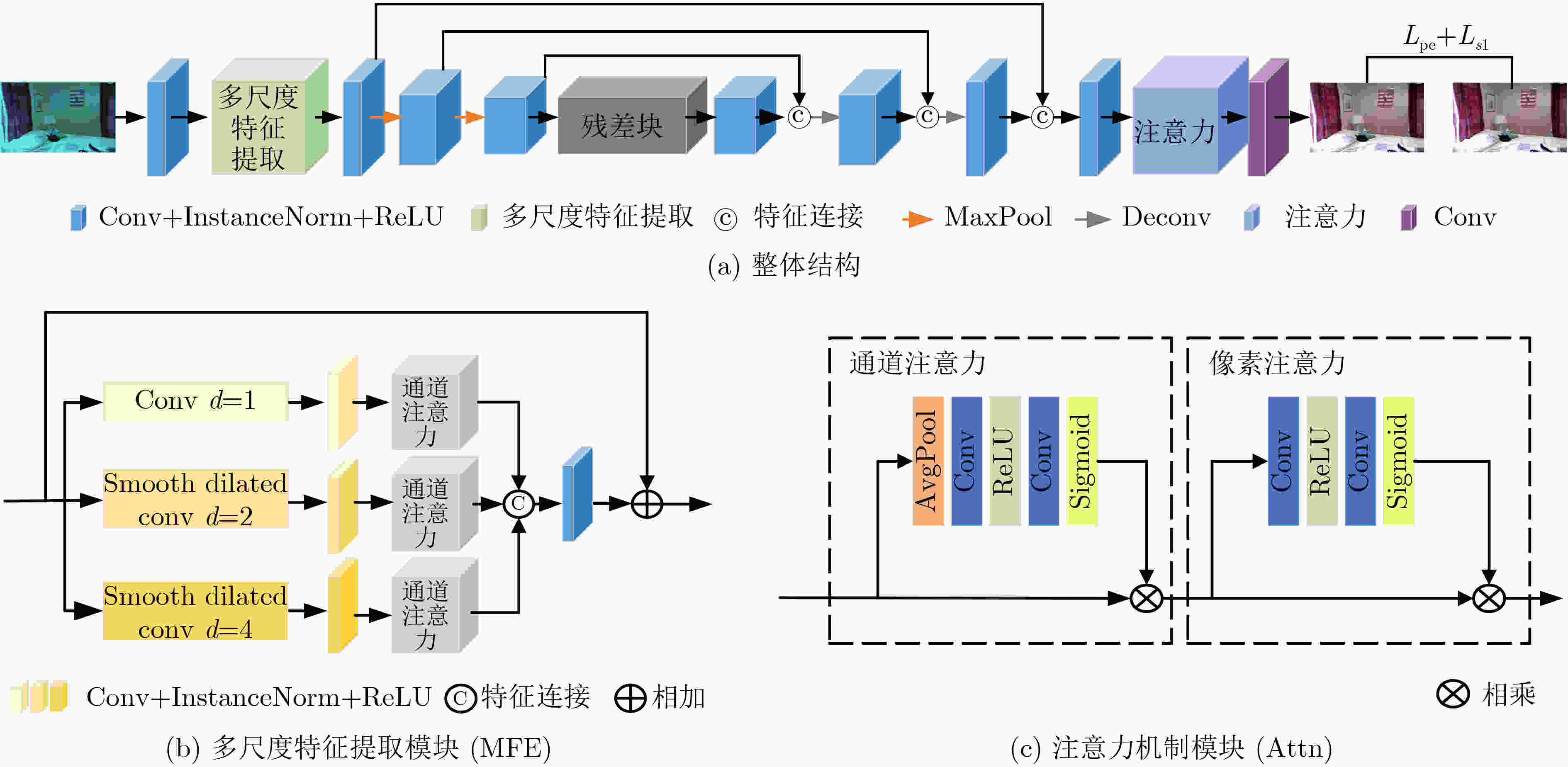
CINR MFE CINR Maxpool CINR Maxpool CINR ResBlocks CINR Deconv CINR Deconv CINR CINR Attn Conv 卷积核大小 3,1,1 3,1,1 2,2,0 3,1,1 2,2,0 3,1,1 3,1,1 3,1,1 4,2,1 3,1,1 4,2,1 3,1,1 3,1,1 3,1,1 输出通道数 64 64 64 64 128 128 256 256 256 128 128 64 64 64 64 64 表 3 不同方法在合成数据集上的PSNR和SSIM值
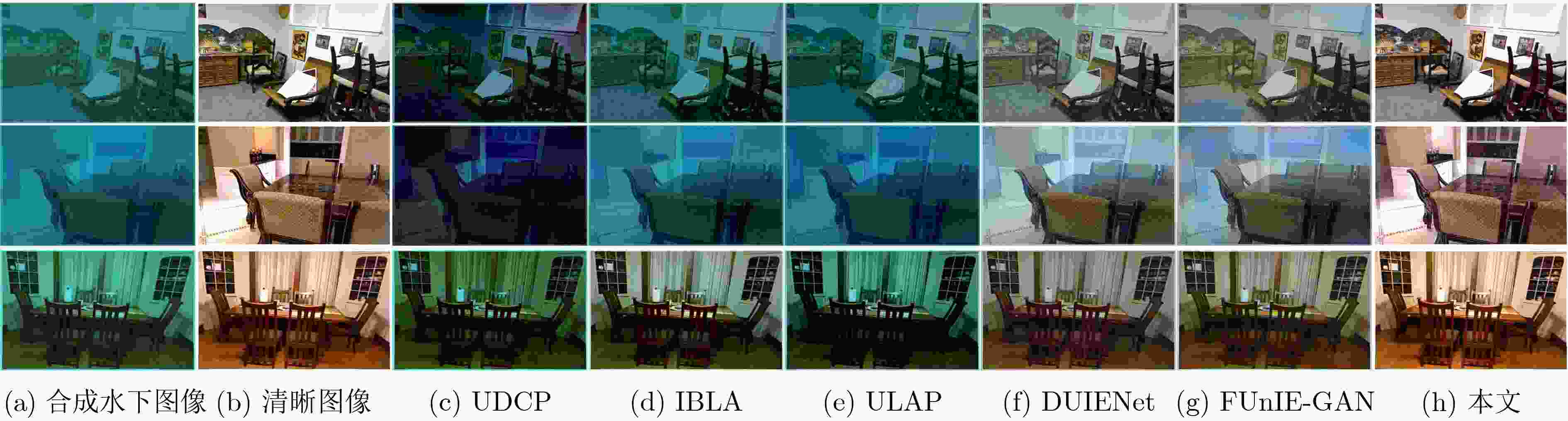
UDCP IBLA ULAP DUIENet FUnIE-GAN 本文 PSNR 10.3134 14.8764 14.3421 15.6875 16.7233 28.4583 SSIM 0.5022 0.7225 0.7058 0.7889 0.7601 0.9110 表 4 图6中图片的不同方法的UIQM值
图像 UDCP IBLA ULAP DUIENet FUnIE-GAN 本文 UIQM 第1幅 3.5135 3.8244 3.8666 4.1049 4.3301 4.8344 第2幅 3.3235 3.5484 3.6567 3.7669 3.3144 3.9077 第3幅 3.3387 3.2753 3.1166 3.7438 3.9245 4.2782 第4幅 3.7411 4.1643 3.8395 4.3814 4.4317 4.6122 表 5 不同方法在真实数据集上的UIQM值
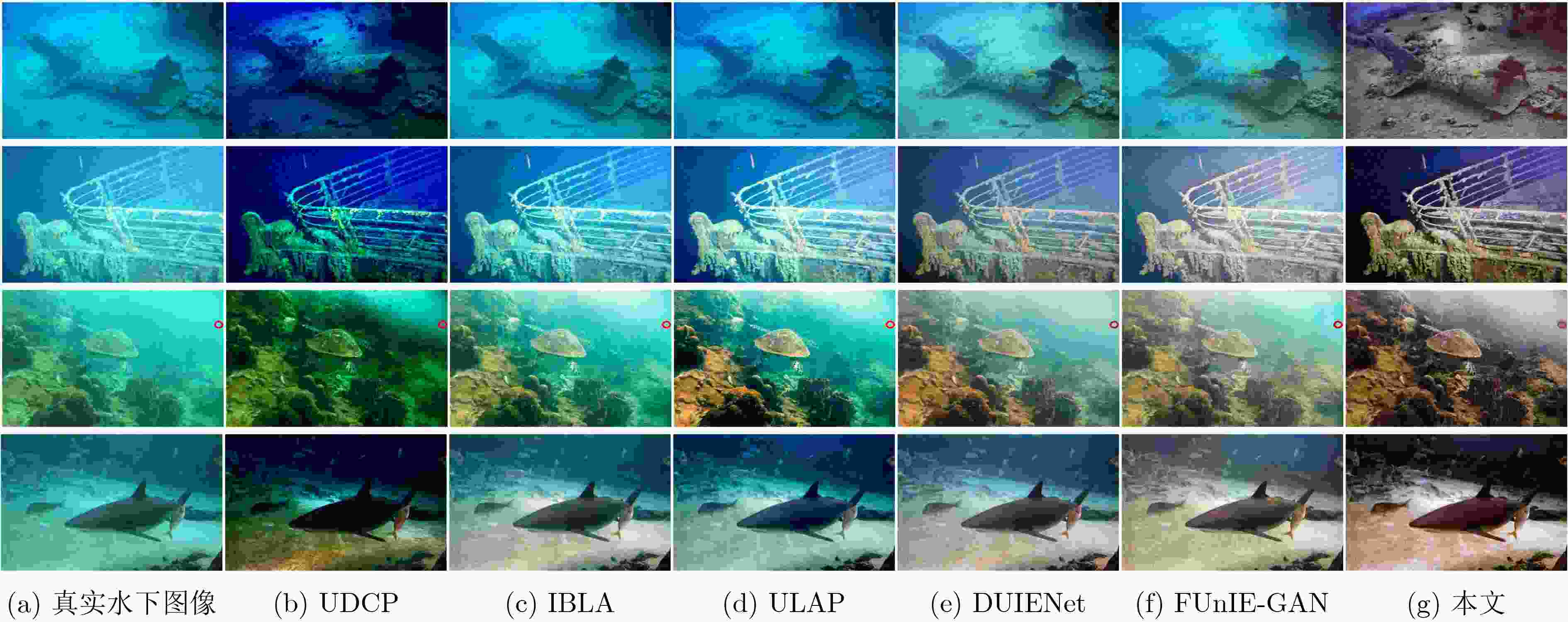
UDCP IBLA ULAP DUIENet FUnIE-GAN 本文 UICM 3.8090 3.8621 3.8424 3.5210 4.2954 2.3348 UISM 4.4584 4.7460 4.8385 5.2352 5.2672 5.1937 UIConM 0.7023 0.5915 0.6202 0.6888 0.6779 0.7278 UIQM 3.9349 3.6251 3.7548 4.1079 4.1002 4.2016 表 6 网络结构消融实验数值结果
MFE Attn 感知损失 PSNR SSIM 无MFE, Attn模块 √ 27.8182 0.9057 无Attn模块 √ √ 27.8408 0.9092 无感知损失 √ √ 28.1272 0.8967 本文完整网络 √ √ √ 28.4583 0.9110 表 7 不同方法运行时间表(s)
UDCP IBLA ULAP DUIENet FUnIE-GAN 本文 运行时间 16.81 34.75 2.23 15.30 1.01 15.93 -
[1] ZUIDERVELD K. Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization[M]. Graphics Gems IV, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1994: 474–485. [2] ANCUTI C, ANCUTI C O, HABER T, et al. Enhancing underwater images and videos by fusion[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, USA, 2012: 81–88. [3] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, and TANG Xiaoou. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [4] LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, CONG Runmin, et al. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664–5677. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2612882 [5] 杨爱萍, 郑佳, 王建, 等. 基于颜色失真去除与暗通道先验的水下图像复原[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(11): 2541–2547. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150483YANG Aiping, ZHENG Jia, WANG Jian, et al. Underwater image restoration based on color cast removal and dark channel prior[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(11): 2541–2547. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150483 [6] DREWS P L J, NASCIMENTO E R, BOTELHO S S C, et al. Underwater depth estimation and image restoration based on single images[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2016, 36(2): 24–35. doi: 10.1109/MCG.2016.26 [7] REN Wenqi, LIU Si, ZHANG Hua, et al. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Kingdom of the Netherlands, 2016: 154–169. [8] AKKAYNAK D and TREIBITZ T. A revised underwater image formation model[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6723–6732. [9] ANWAR S and LI Chongyi. Diving deeper into underwater image enhancement: A survey[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.07863, 2019. [10] LI Jie, SKINNER K A, EUSTICE R M, et al. WaterGAN: Unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(1): 387–394. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2730363 [11] HASHISHO Y, ALBADAWI M, KRAUSE T, et al. Underwater color restoration using u-net denoising autoencoder[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.09000. 2019. [12] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, REN Wenqi, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.05495, 2019. [13] FABBRI C, ISLAM M J, and SATTAR J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 7159–7165. [14] ISLAM M J, XIA Y Y, and SATTAR J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227–3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [15] ZHANG Tingting, LI Yujie, and TAKAHASHI S. Underwater image enhancement using improved generative adversarial network[J]. Concurrency and Computation Practice and Experience, 2020: e5841. doi: 10.1002/cpe.5841 [16] PARK J, HAN D K, and KO H. Adaptive weighted multi-discriminator CycleGAN for underwater image enhancement[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2019, 7(7): 200. doi: 10.3390/jmse7070200 [17] ANWAR S, LI Chongyi, and PORIKLI F. Deep underwater image enhancement[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03528, 2018. [18] LI Chongyi, ANWAR S, and PORIKLI F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107038 [19] SILBERMAN N, HOIEM D, KOHLI P, et al. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 746–760. [20] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. [21] CHIANG J Y and CHEN Y C. Underwater image enhancement by wavelength compensation and dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1756–1769. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2179666 [22] DING Xueyan, WANG Yafei, YAN Yang, et al. Jointly adversarial network to wavelength compensation and dehazing of underwater images[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.05595, 2019. [23] ZHOU Yuan and YAN Kangming. Domain adaptive adversarial learning based on physics model feedback for underwater image enhancement[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.09315, 2020. [24] QIN Xu, WANG Zhilin, BAI Yuanchao, et al. FFA-Net: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.07559, 2019. [25] 柳长源, 王琪, 毕晓君, 等. 基于多通道多尺度卷积神经网络的单幅图像去雨方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2285–2292. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190755LIU Changyuan, WANG Qi, BI Xiaojun, et al. Research on rain removal method for single image based on multi-channel and multi-scale CNN[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2285–2292. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190755 [26] WANG Zhengyang and JI Shuiwang. Smoothed dilated convolutions for improved dense prediction[C]. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery& Data Mining, London, UK, 2018: 2486–2495. [27] CHEN Dongdong, HE Mingming, FAN Qingnan, et al. Gated context aggregation network for image dehazing and deraining[C]. 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1375–1383. [28] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, and LI Feifei. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Kingdom of the Netherlands, 2016: 694–711. [29] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–5. [30] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [31] PANETTA K, GAO C, and AGAIAN S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(3): 541–551. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2015.2469915 [32] DREWS P JR, DO NASCIMENTO E, MORAES F, et al. Transmission estimation in underwater single images[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 825–830. [33] PENG Y T and COSMAN P C. Underwater image restoration based on image blurriness and light absorption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1579–1594. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2663846 [34] SONG Wei, WANG Yan, HUANG Dongmei, et al. A rapid scene depth estimation model based on underwater light attenuation prior for underwater image restoration[C]. The 19th Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia, Hefei, China, 2018: 678–688. -





 下载:
下载:
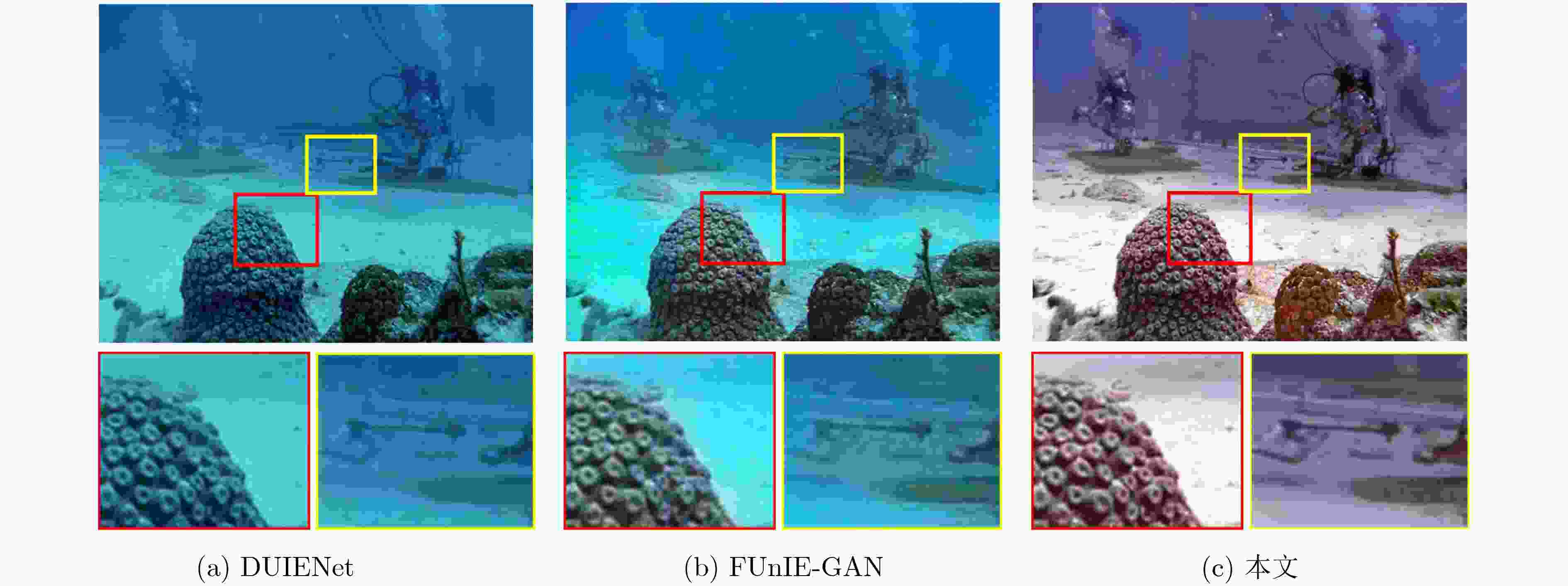


 下载:
下载:
