Multi-stream Architecture and Multi-scale Convolutional Neural Network for Remote Sensing Image Fusion
-
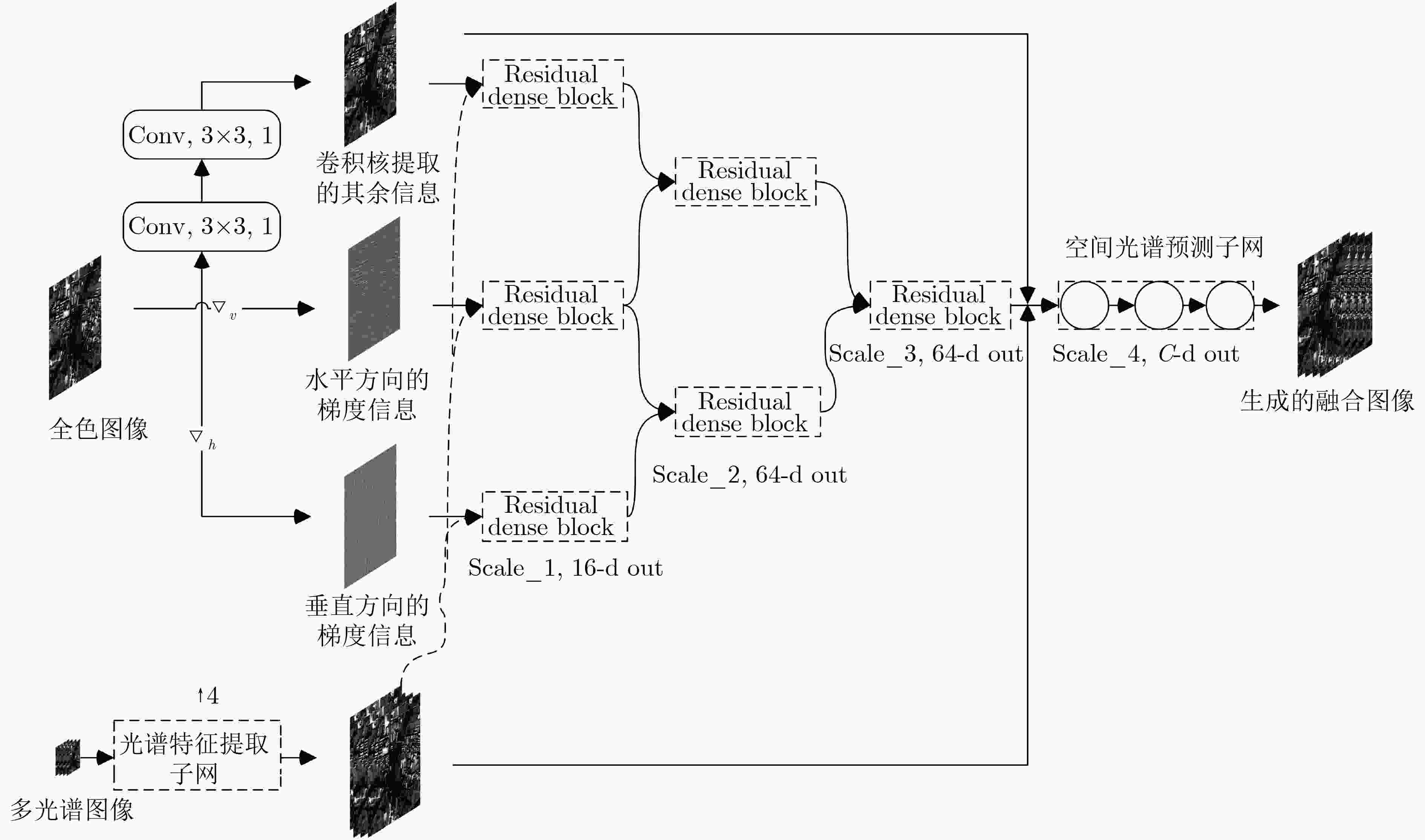
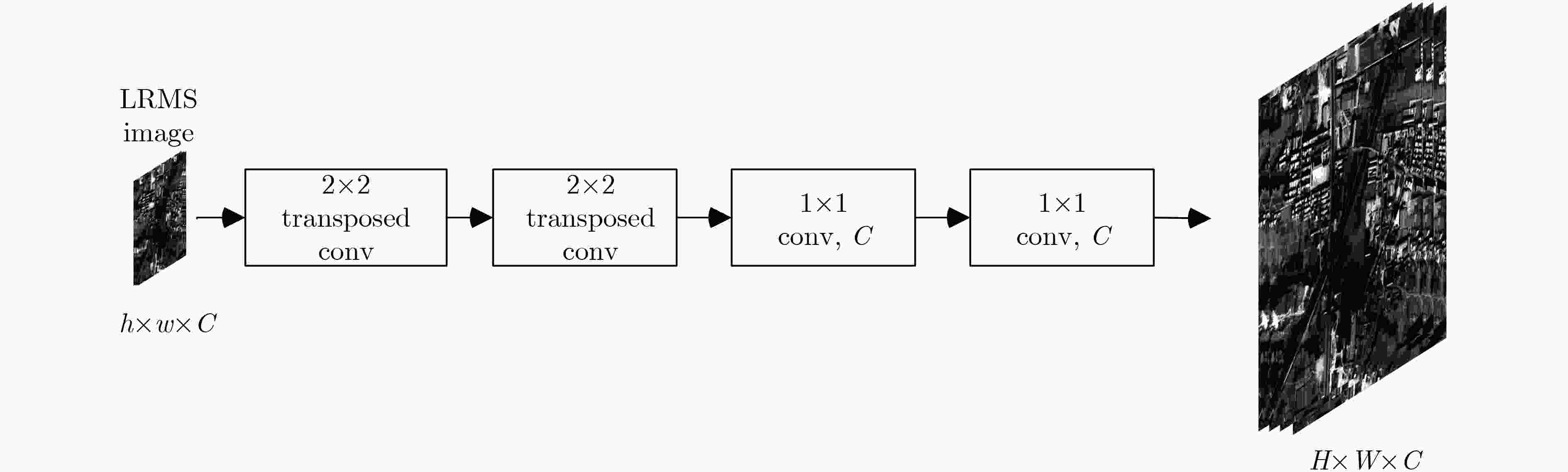
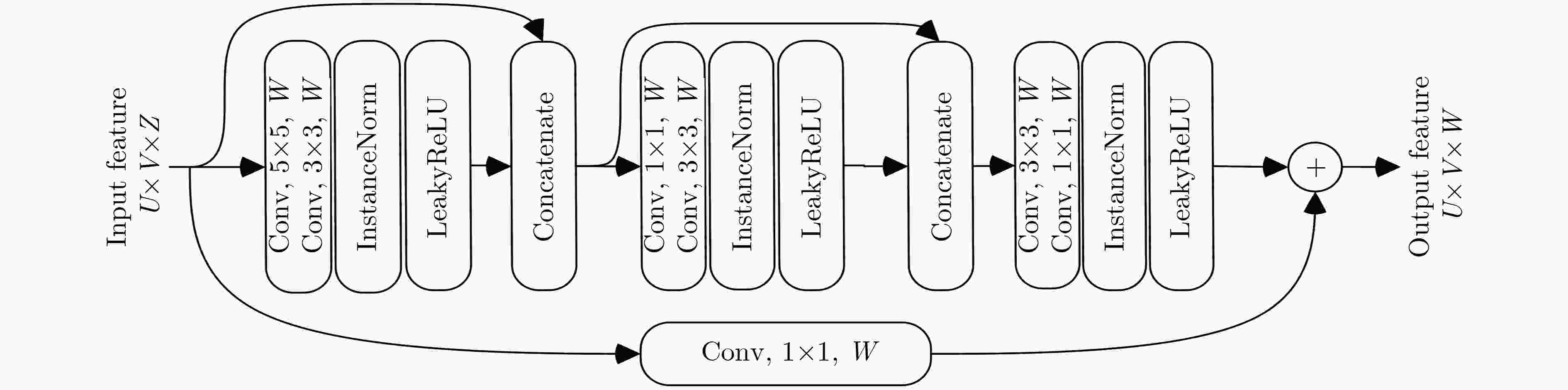
摘要: 为尽可能保持原始低分辨率多光谱(LRMS)图像光谱信息的同时,显著提高融合后的多光谱图像的空间分辨率,该文提出一种联合多流融合和多尺度学习的卷积神经网络遥感图融合方法。首先将原始MS图像输入频谱特征提取子网得到其光谱特征,然后分别将通过梯度算子处理全色图像得到的梯度信息和通过卷积后的全色图像与得到的光谱特征图在通道上拼接输入到具有多流融合架构的金字塔模块进行图像重构。金字塔模块由多个骨干网络组成,可以在不同的空间感受野下进行特征提取,能够多尺度学习图像信息。最后,构建空间光谱预测子网融合金字塔模块输出的高级特征和网络前端的低级特征得到具有高空间分辨率的MS图像。结合WorldView-3卫星获取的图像进行实验,结果表明,所提方法生成的融合图像在主观目视检验和客观评价指标上都优于大多先进的遥感图像融合方法。Abstract: In order to make the fused multispectral images preserve the spectral information of the original Low-Resolution Multi-Spectral (LRMS) images as much as possible, and improve the spatial resolution effectively, a new pan-sharpening method based on multi-stream architecture and multi-scale is proposed. Firstly, This paper inputs the original MS image into the spectral feature extraction subnet to obtain its spectral features, and extracts the multi-directional gradient information and spatial structure information from the panchromatic images by the gradient operator and the convolution kernel. Then the extracted feature is added into the pyramid module with multi-stream fusion architecture for image reconstruction. The pyramid module is composed of multiple backbone networks, which can perform feature extraction under different spatial receptive fields, and can learn image information at multiple scales. Finally, a spatial spectrum prediction subnet is constructed to fuse the high-level features output by the pyramid module and the low-level features of the network front end to obtain multispectral images with high spatial resolution. Experiments on images obtained by WorldView-3 satellites show that the fusion images generated by the proposed method are superior to the most of advanced remote sensing image pan-sharpening methods in both subjective visual and objective evaluation indicators.
-
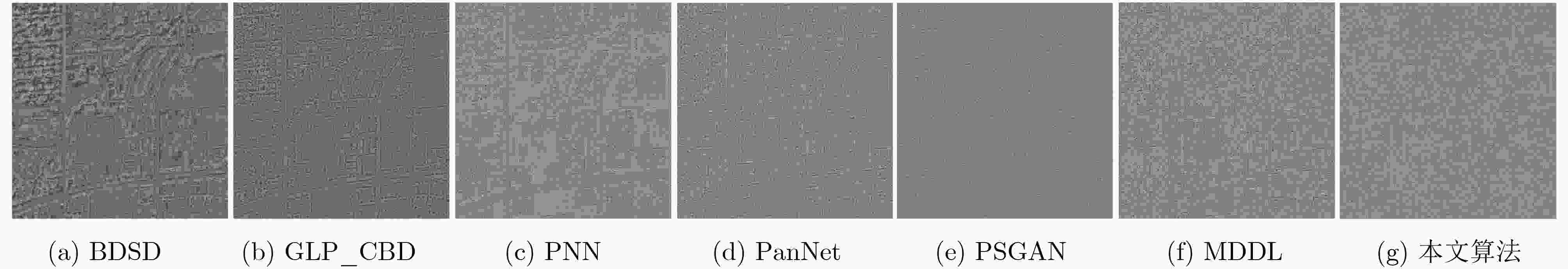
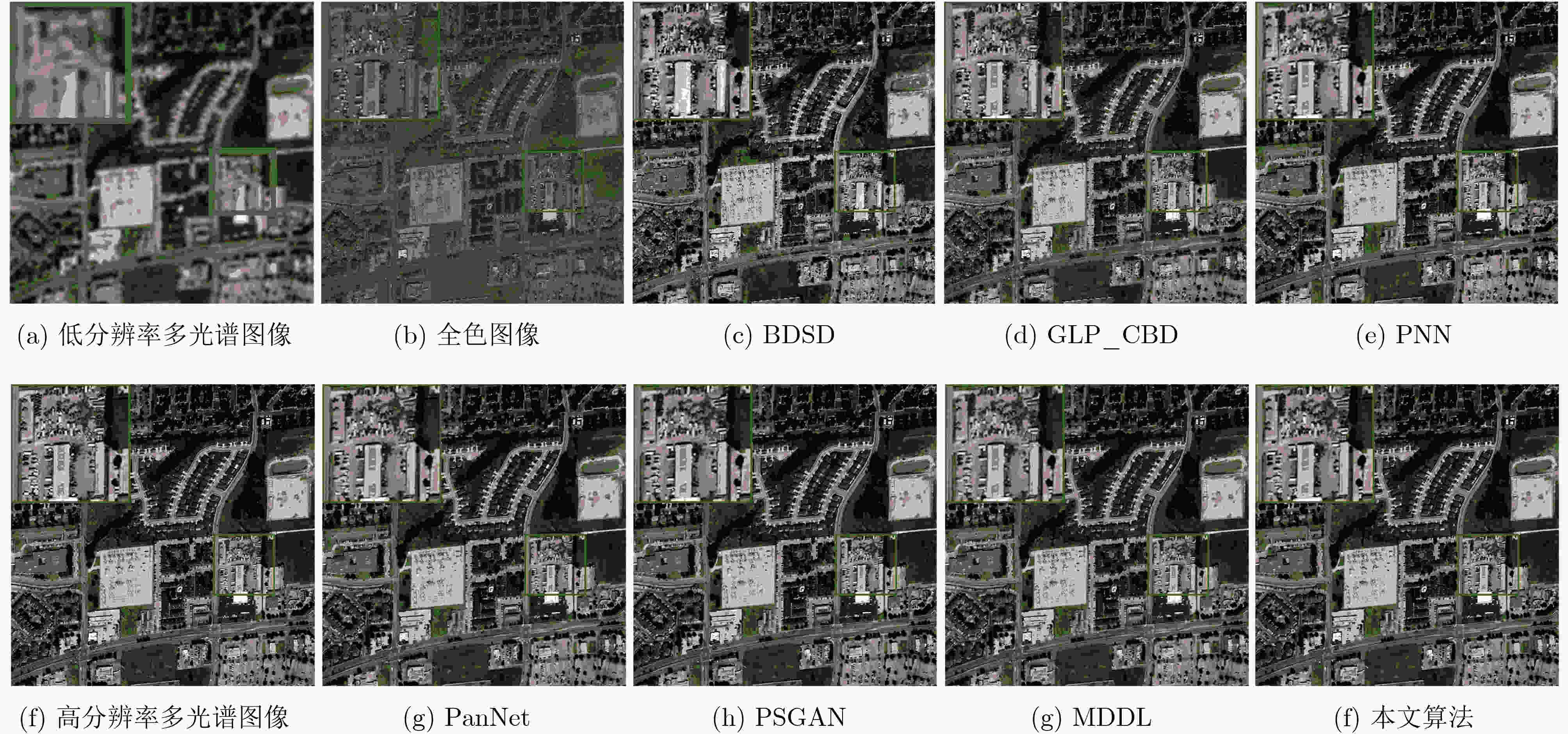
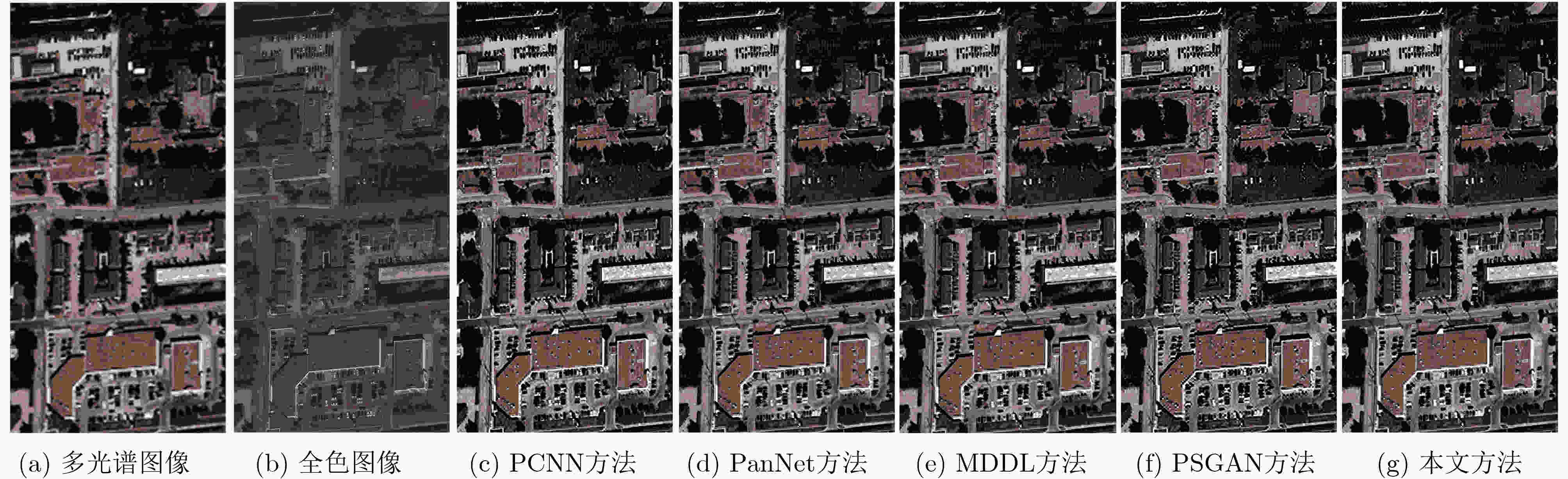
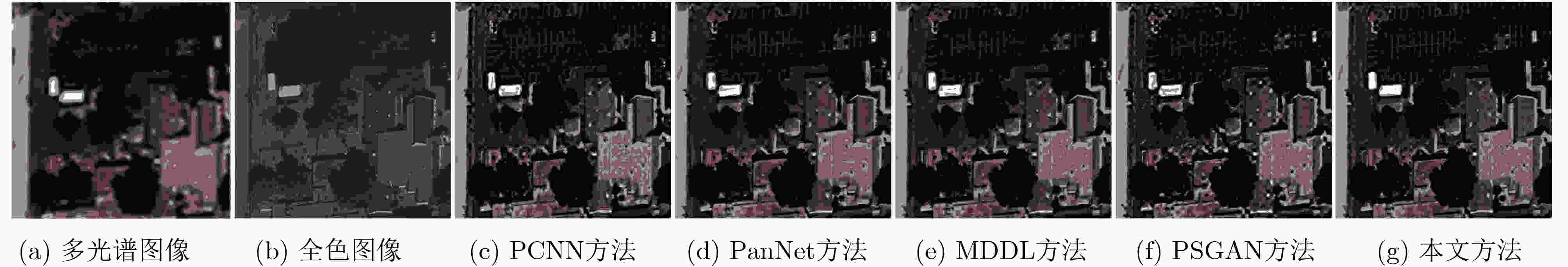
图 5 图4中各方法与真实图像对比的残差图
表 1 基于WorldView-3卫星的仿真实验融合结果评价
融合方法 SAM ERGAS $ {Q}_{8} $ SCC BDSD 8.0948 7.5179 0.5055 0.6817 GLP-CBD 6.8215 7.4179 0.6512 0.6580 PNN 5.3811 5.1357 0.8231 0.8602 PanNet 5.2177 5.0017 0.8129 0.8571 PSGAN 4.8744 4.3600 0.8668 0.9089 MDDL 5.1238 4.7812 0.8223 0.8684 本文算法 4.7676 4.3351 0.8677 0.9092 参考值 0 0 1 1 表 2 基于WorldView-3卫星的真实数据实验融合结果评价
融合方法 $ {D}_{\lambda } $ $ {D}_{s} $ QNR BDSD 0.0155 0.1060 0.8800 GLP-CBD 0.0379 0.0849 0.8805 PNN 0.0223 0.0483 0.9305 PanNet 0.0087 0.0648 0.9270 PSGAN 0.0152 0.0436 0.9419 MDDL 0.0098 00589 0.9318 本文算法 0.0175 0.0293 0.9537 参考值 0 0 1 表 3 基于WorldView-3卫星仿真数据集的消融实验融合结果评价
融合方法 SAM ERGAS $ {{Q}}_{8} $ SCC 缺少空间光谱预测子网的本文算法 4.7598 4.5692 0.8563 0.8974 缺少频谱特征提取子网的本文算法 4.8191 4.3818 0.8651 0.9073 缺少金字塔模块的本文算法 4.8602 4.4388 0.8614 0.9049 上采样LRMS输入的本文算法 4.7940 4.3434 0.8661 0.9091 本文算法 4.7676 4.3351 0.8677 0.9092 参考值 0 0 1 1 -
[1] THOMAS C, RANCHIN T, WALD L, et al. Synthesis of multispectral images to high spatial resolution: A critical review of fusion methods based on remote sensing physics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(5): 1301–1312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.912448 [2] CHOI M. A new intensity-hue-saturation fusion approach to image fusion with a tradeoff parameter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1672–1682. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.869923 [3] 纪峰, 李泽仁, 常霞, 等. 基于PCA和NSCT变换的遥感图像融合方法[J]. 图学学报, 2017, 38(2): 247–252. doi: 10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2017020247JI Feng, LI Zeren, CHANG Xia, et al. Remote sensing image fusion method based on PCA and NSCT transform[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2017, 38(2): 247–252. doi: 10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2017020247 [4] 刘静, 李小超, 祝开建, 等. 基于分布式压缩感知的遥感图像融合算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(10): 2374–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161393LIU Jing, LI Xiaochao, ZHU Kaijian, et al. Distributed compressed sensing based remote sensing image fusion algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(10): 2374–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161393 [5] GARZELLI A, NENCINI F, and CAPOBIANCO L. Optimal MMSE Pan sharpening of very high resolution multispectral images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 228–236. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907604 [6] 贺康建, 金鑫, 聂仁灿, 等. 基于简化脉冲耦合神经网络与拉普拉斯金字塔分解的彩色图像融合[J]. 计算机应用, 2016, 36(S1): 133–137.HE Kangjian, JIN Xin, NIE Rencan, et al. Color image fusion based on simplified PCNN and Laplace pyramid decomposition[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2016, 36(S1): 133–137. [7] AIAZZI B, ALPARONE L, BARONTI S, et al. Context-driven fusion of high spatial and spectral resolution images based on oversampled multiresolution analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(10): 2300–2312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803623 [8] WANG Xianghai, SHEN Yutong, ZHOU Zhiguang, et al. An image fusion algorithm based on lifting wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Optics, 2015, 17(5): 055702. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/17/5/055702 [9] ZHOU J, CIVCO D L, and SILANDER J A. A wavelet transform method to merge Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 19(4): 743–757. doi: 10.1080/014311698215973 [10] AIAZZI B, ALPARONE L, BARONTI S, et al. MTF-tailored multiscale fusion of high-resolution MS and Pan imagery[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2006, 72(5): 591–596. doi: 10.14358/PERS.72.5.591 [11] CHEN Chen, LI Yeping, LIU Wei, et al. Image fusion with local spectral consistency and dynamic gradient sparsity[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 2760–2765. [12] LIU Yu, CHEN Xun, WANG Zengfu, et al. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 42: 158–173. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.10.007 [13] YANG Junfeng, FU Xueyang, HU Yuwen, et al. PanNet: A deep network architecture for pan-sharpening[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1753–1761. [14] SCARPA G, VITALE S, COZZOLINO D. Target-adaptive CNN-based pansharpening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5443–5457. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2817393 [15] XIANG Zhikang, XIAO Liang, LIU Pengfei, et al. A multi-scale densely deep learning method for pansharpening[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 2786–2789. [16] LIU Xiangyu, WANG Yunhong, and LIU Qingjie. Psgan: A generative adversarial network for remote sensing image Pan-sharpening[C]. The 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Athens, Greece, 2018: 873–877. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2018.8451049. [17] 雷大江, 张策, 李智星, 等. 基于多流融合生成对抗网络的遥感图像融合方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1942–1949. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190273LEI Dajiang, ZHANG Ce, LI Zhixing, et al. Remote sensing image fusion based on generative adversarial network with multi-stream fusion architecture[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1942–1949. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190273 [18] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [19] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 630–645. [20] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4700–4708. [21] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295–307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [22] ZHANG Yulun, TIAN Yapeng, KONG Yu, et al. Residual dense network for image super-resolution[C]. 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2472–2481. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00262. [23] WALD L, RANCHIN T, and MANGOLINI M. Fusion of satellite images of different spatial resolutions: Assessing the quality of resulting images[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1997, 63(6): 691–699. [24] VIVONE G, ALPARONE L, CHANUSSOT J, et al. A critical comparison among pansharpening algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(5): 2565–2586. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2361734 [25] WALD L. Data Fusion: Definitions and Architectures—Fusion of Images of Different Spatial Resolutions[M]. Pairs, France: Les Presses de l’ Écoledes Mines, 2002: 165–189. [26] GARZELLI A and NENCINI F. Hypercomplex quality assessment of multi/hyperspectral images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(4): 662–665. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2022650 [27] 张新曼, 韩九强. 基于视觉特性的多尺度对比度塔图像融合及性能评价[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2004, 38(4): 380–383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-987X.2004.04.013ZHANG Xinman and HAN Jiuqiang. Image fusion of multiscale contrast pyramid-Based vision feature and its performance evaluation[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2004, 38(4): 380–383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-987X.2004.04.013 [28] ALPARONE L, AIAZZI B, BARONTI S, et al. Multispectral and panchromatic data fusion assessment without reference[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2008, 74(2): 193–200. doi: 10.14358/PERS.74.2.193 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
