Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in Spaceborne Squinted Multichannel Synthetic Aperture Radar
-
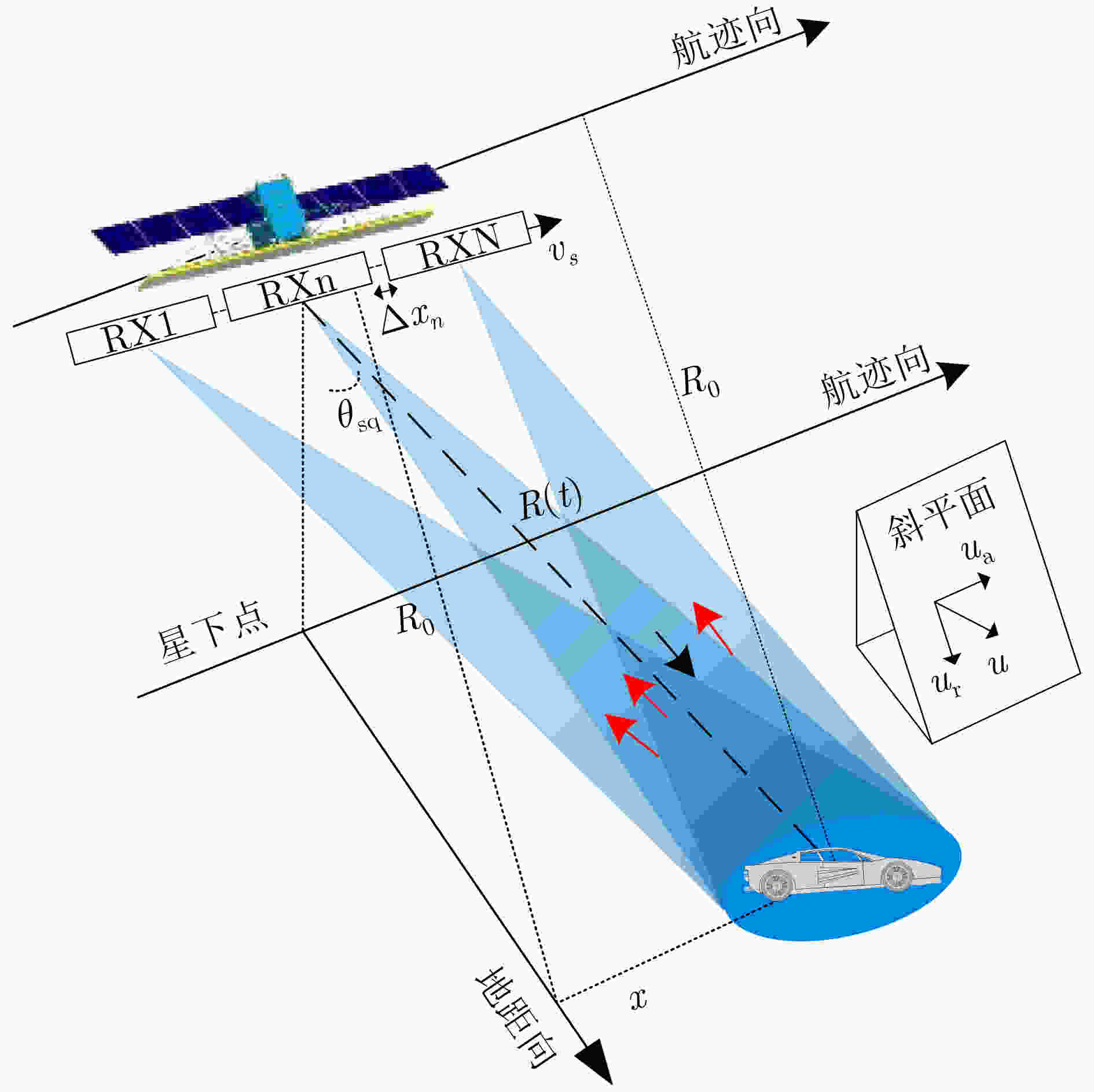
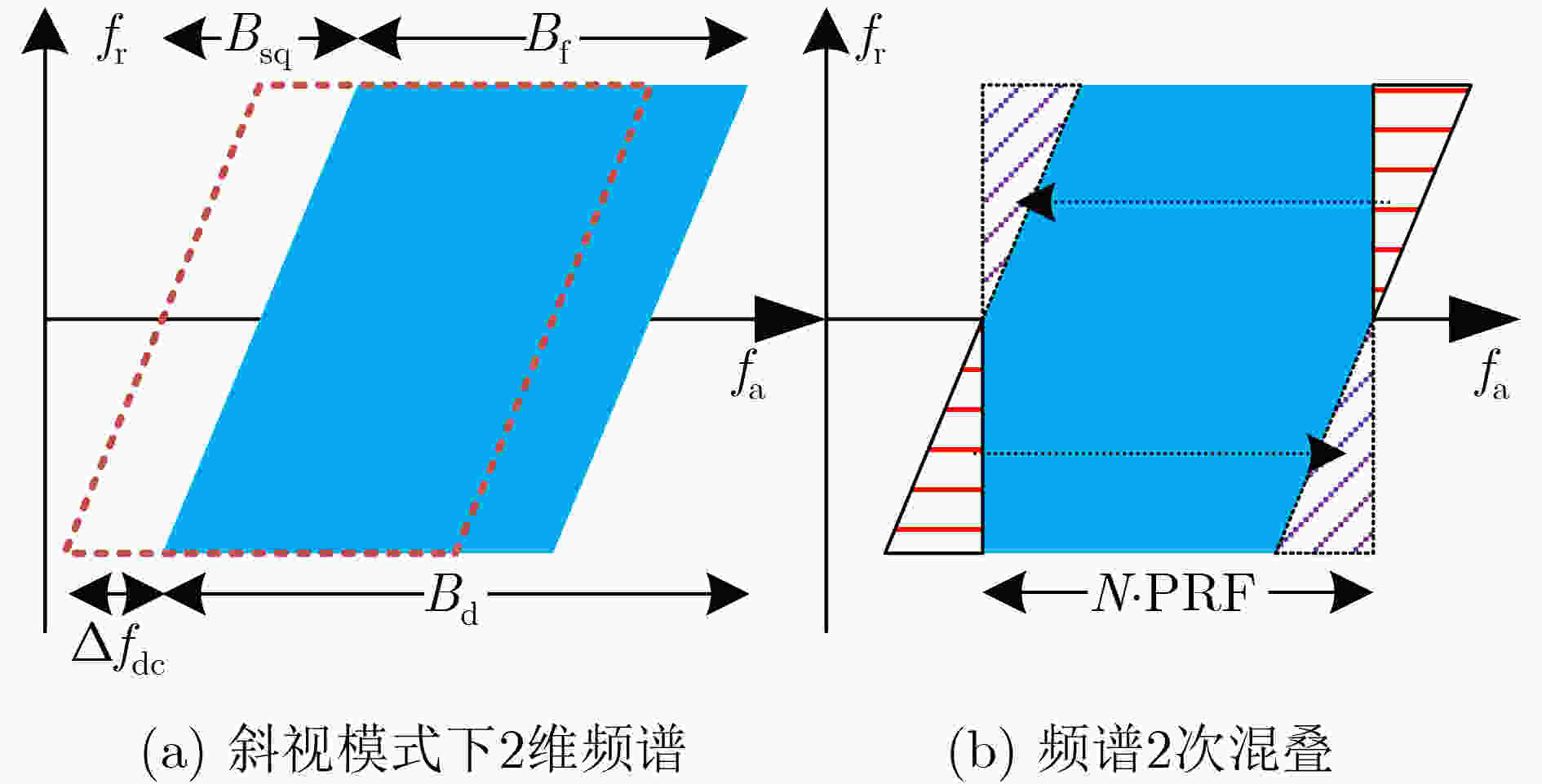
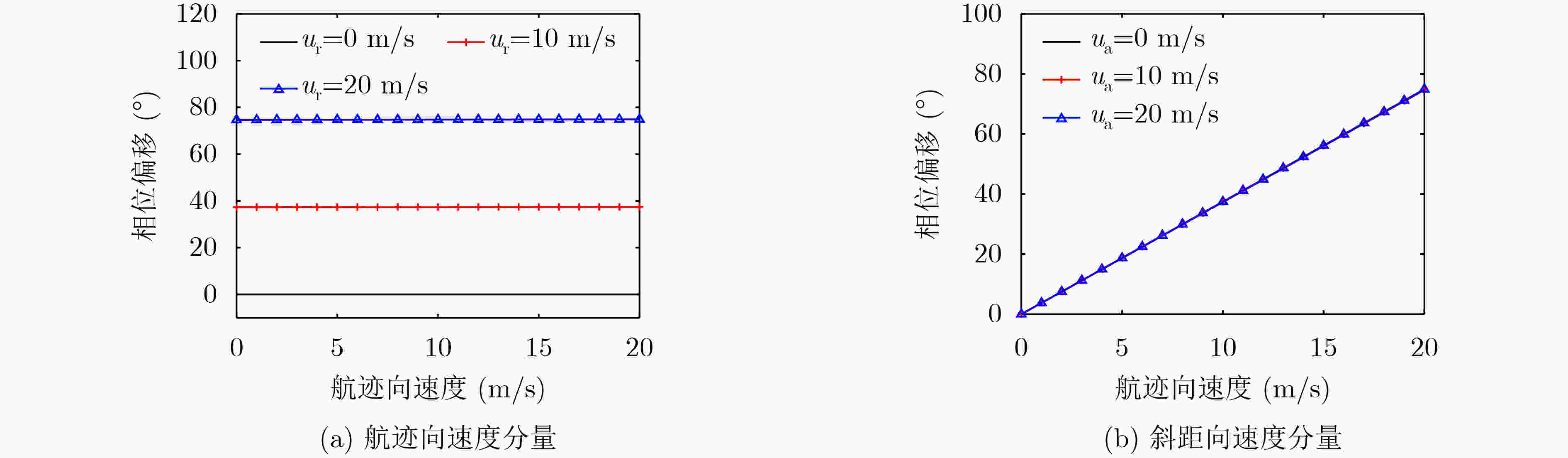
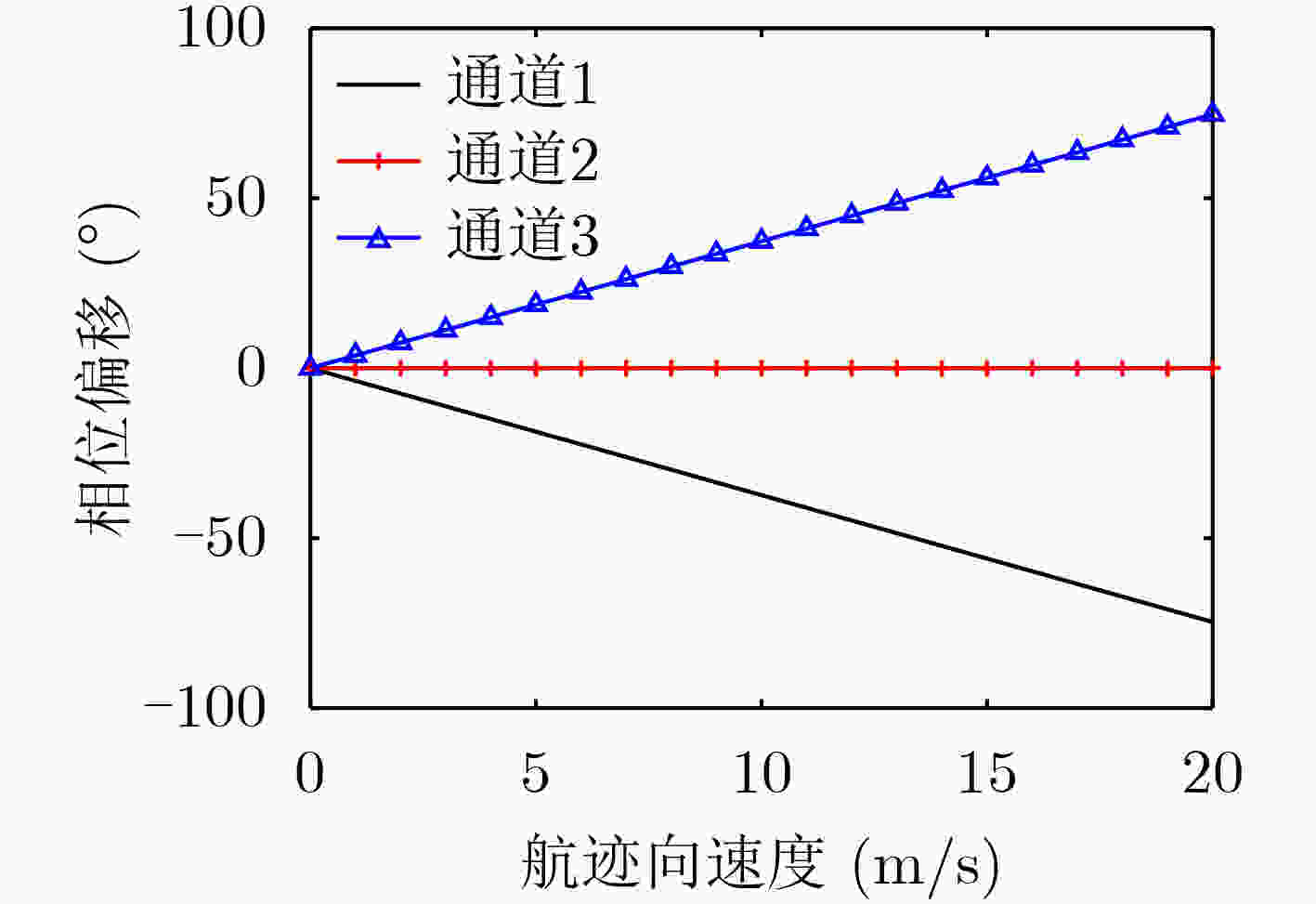
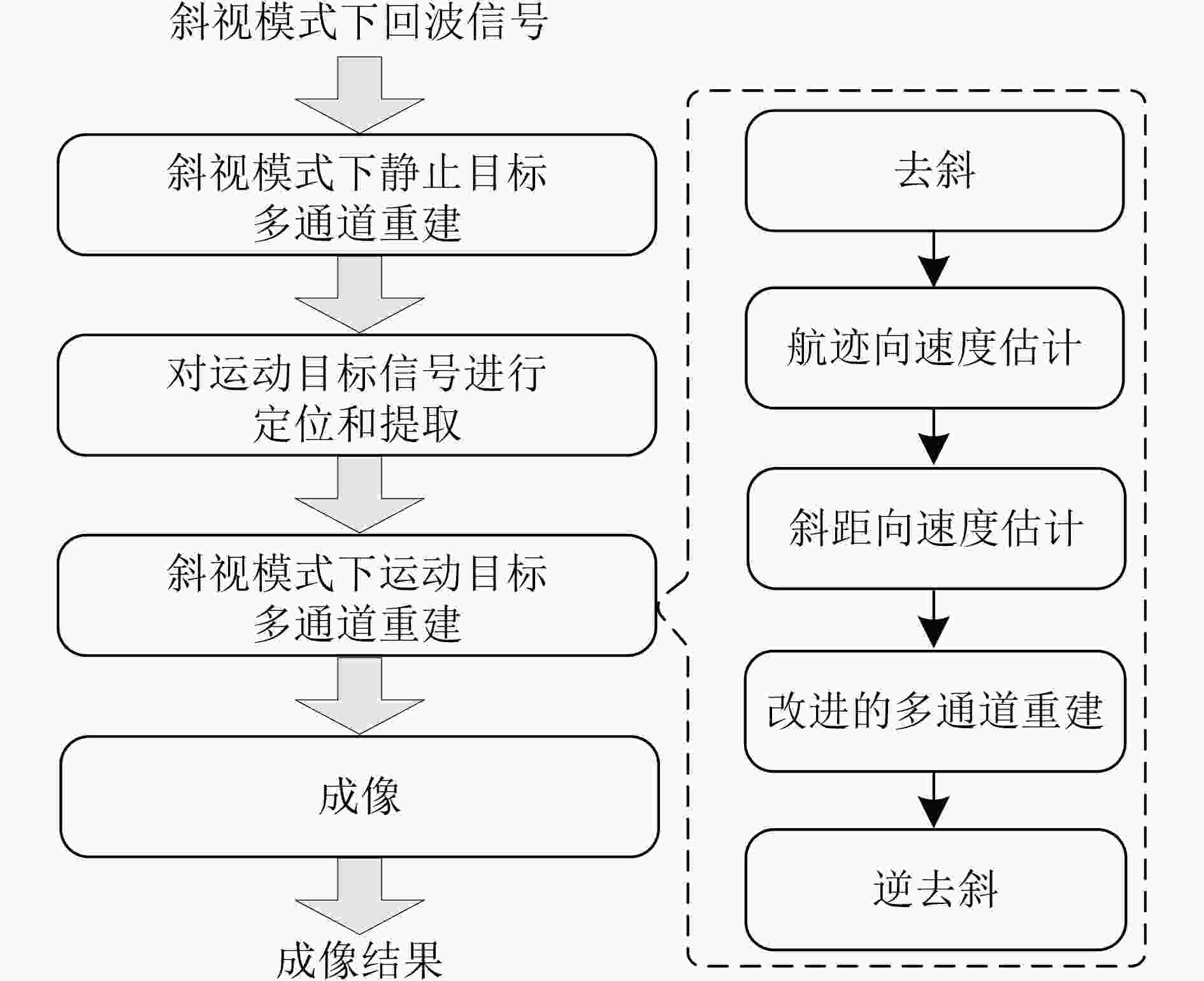
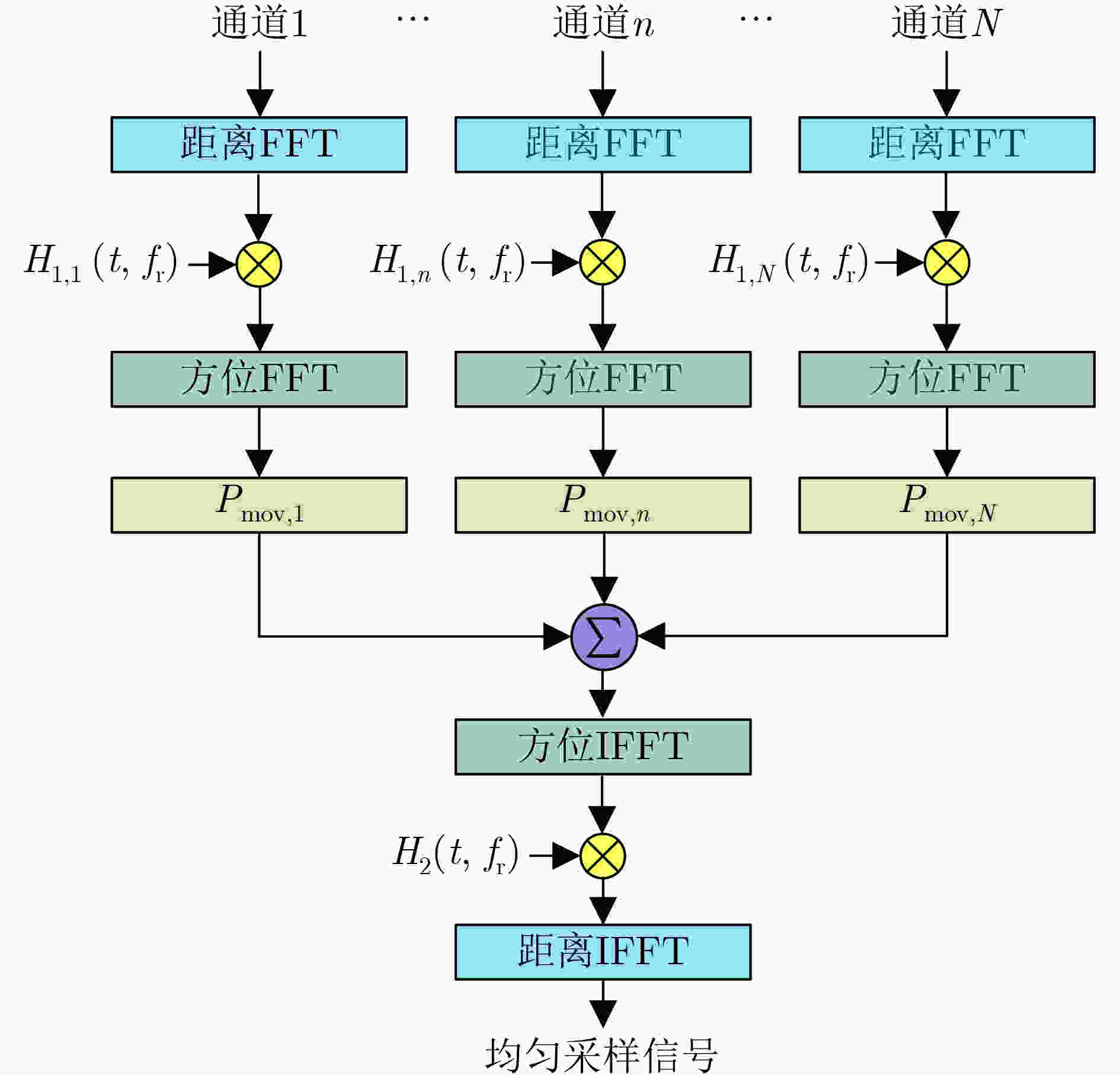
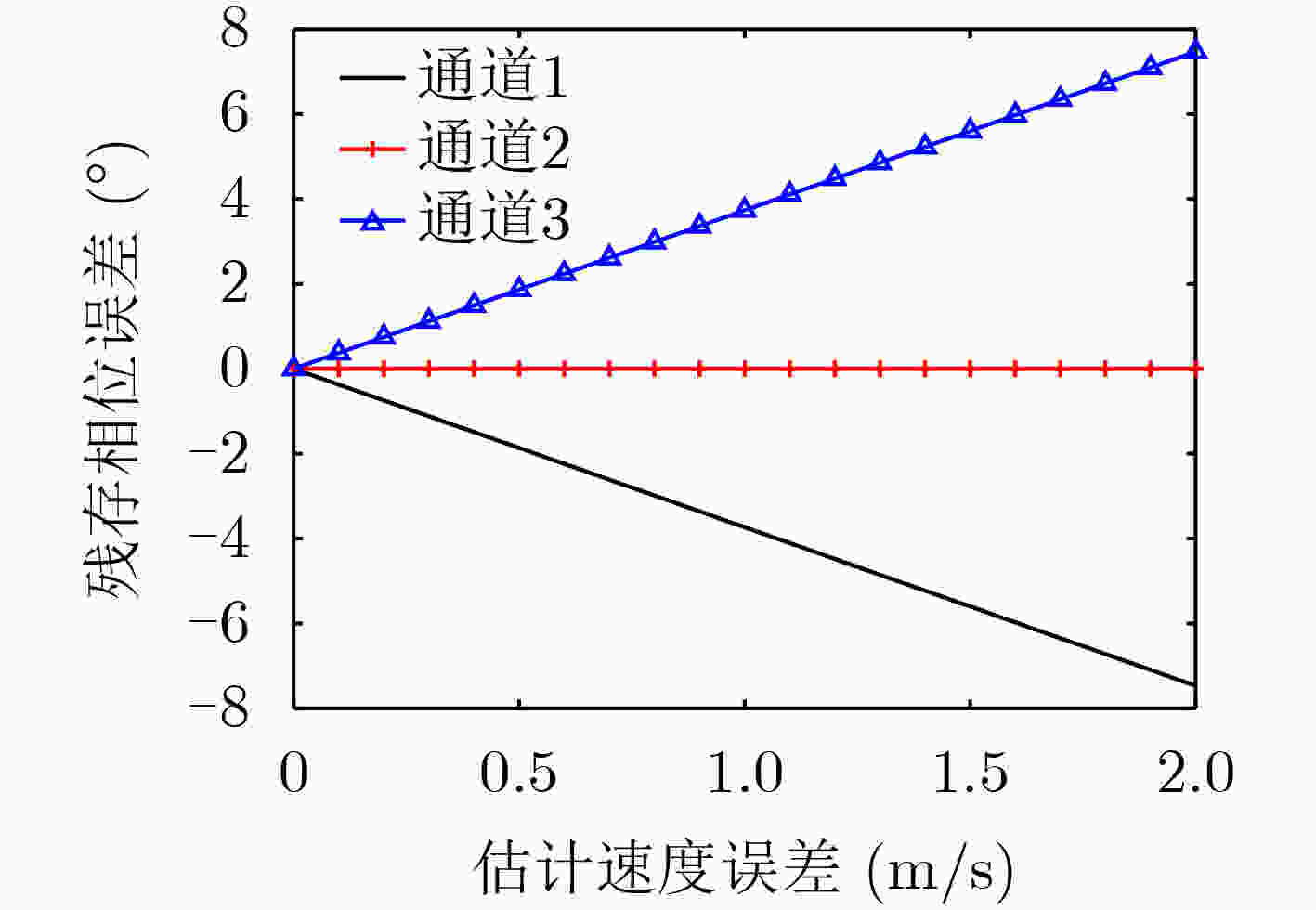
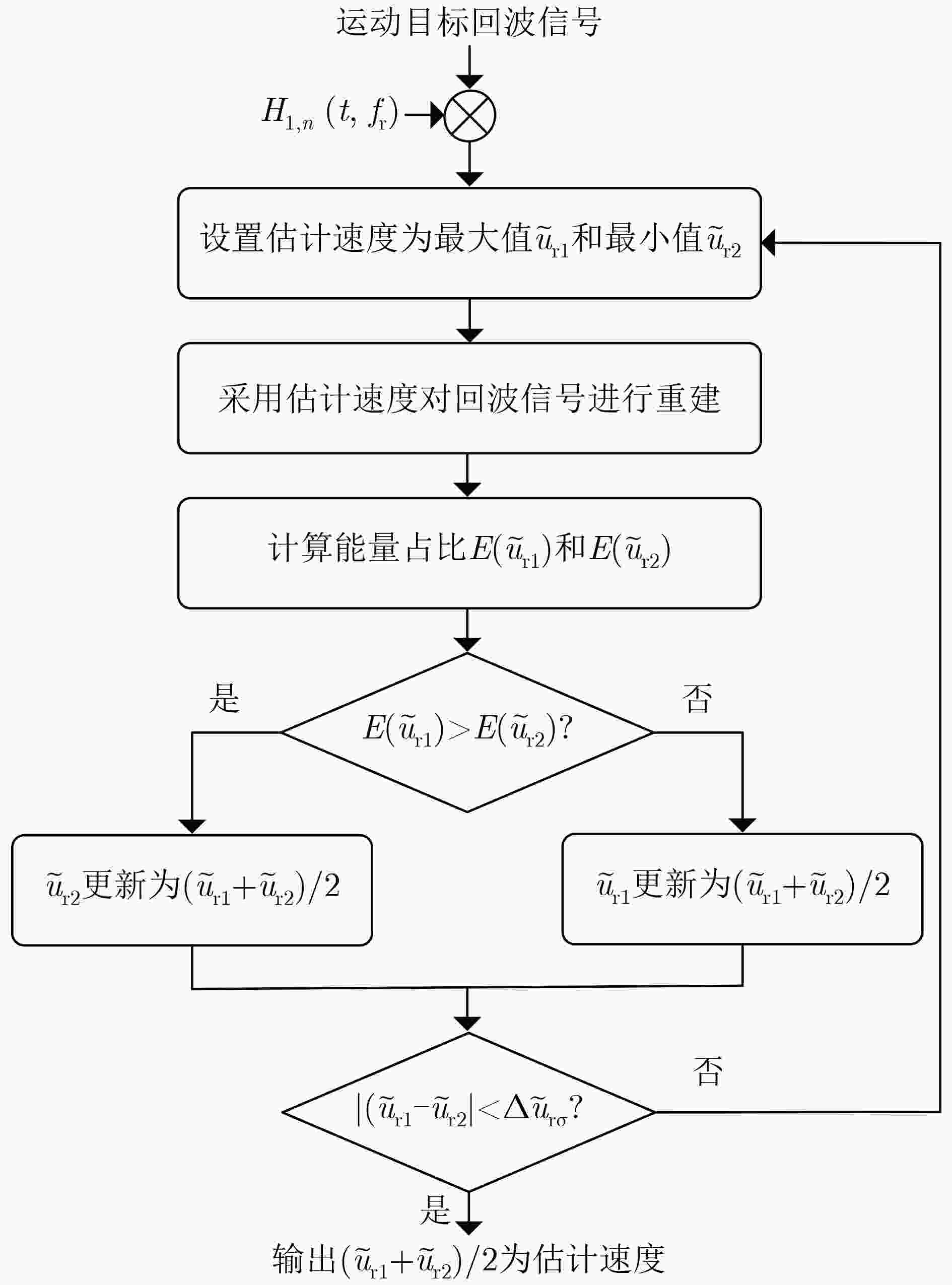
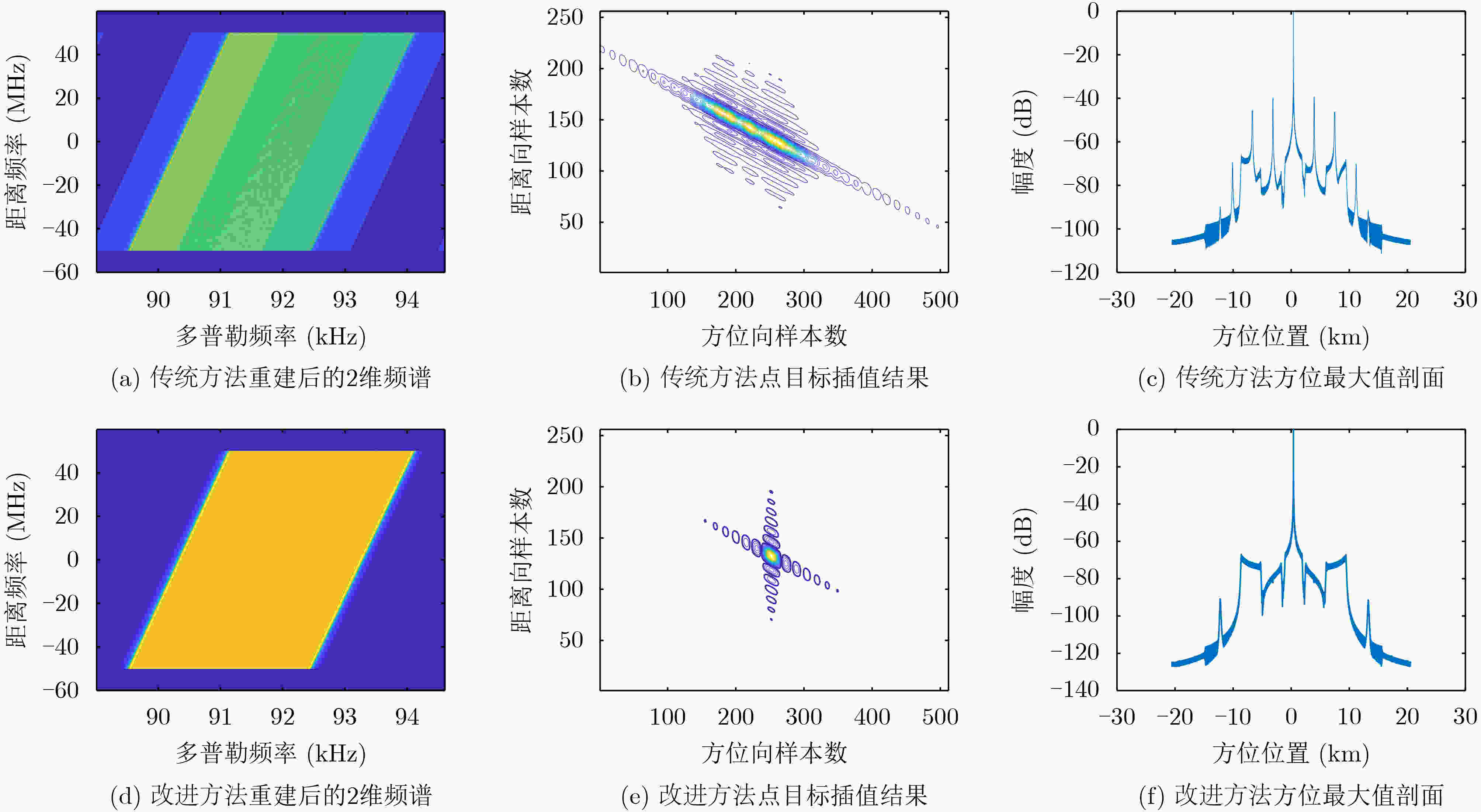
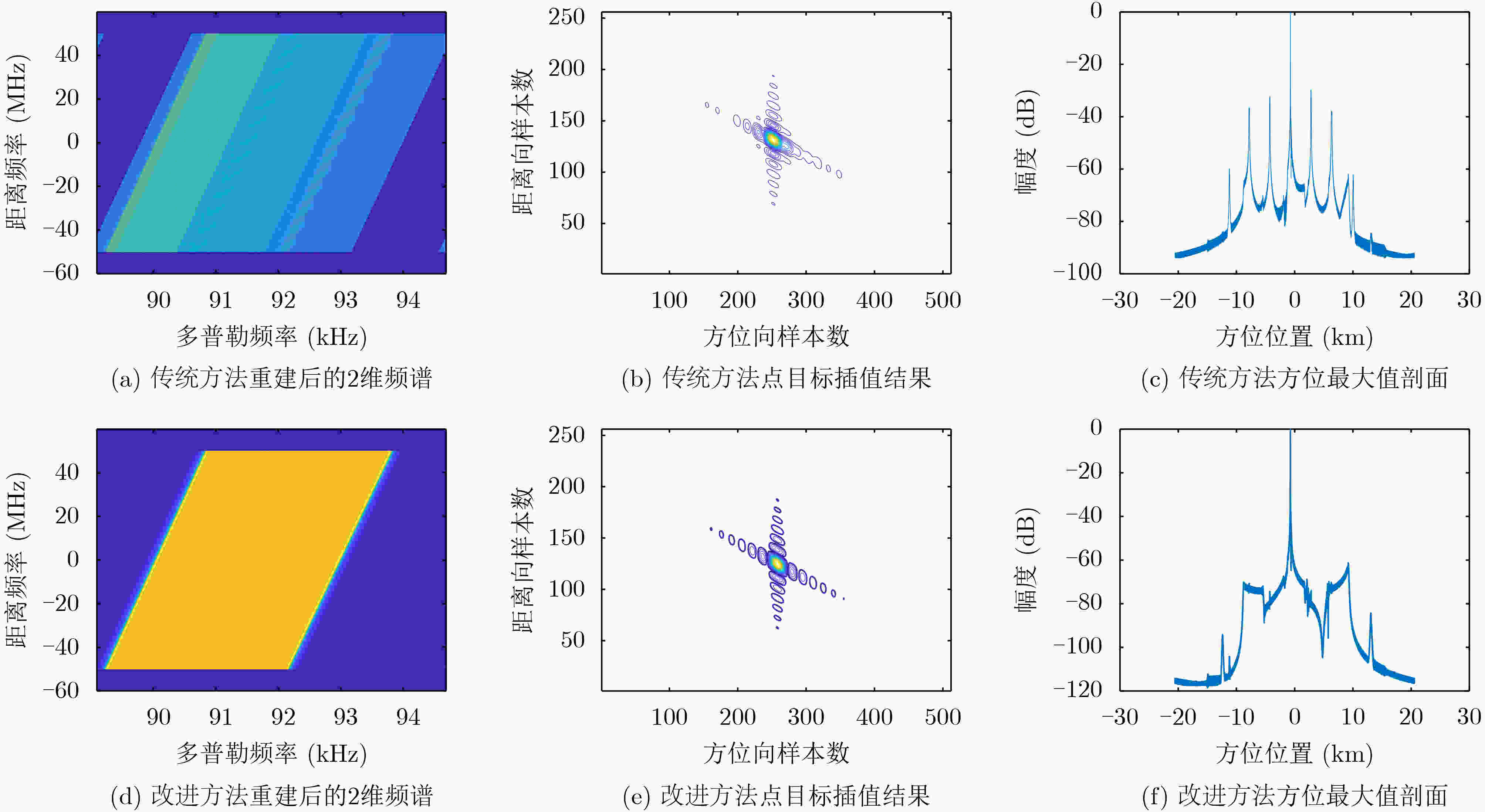
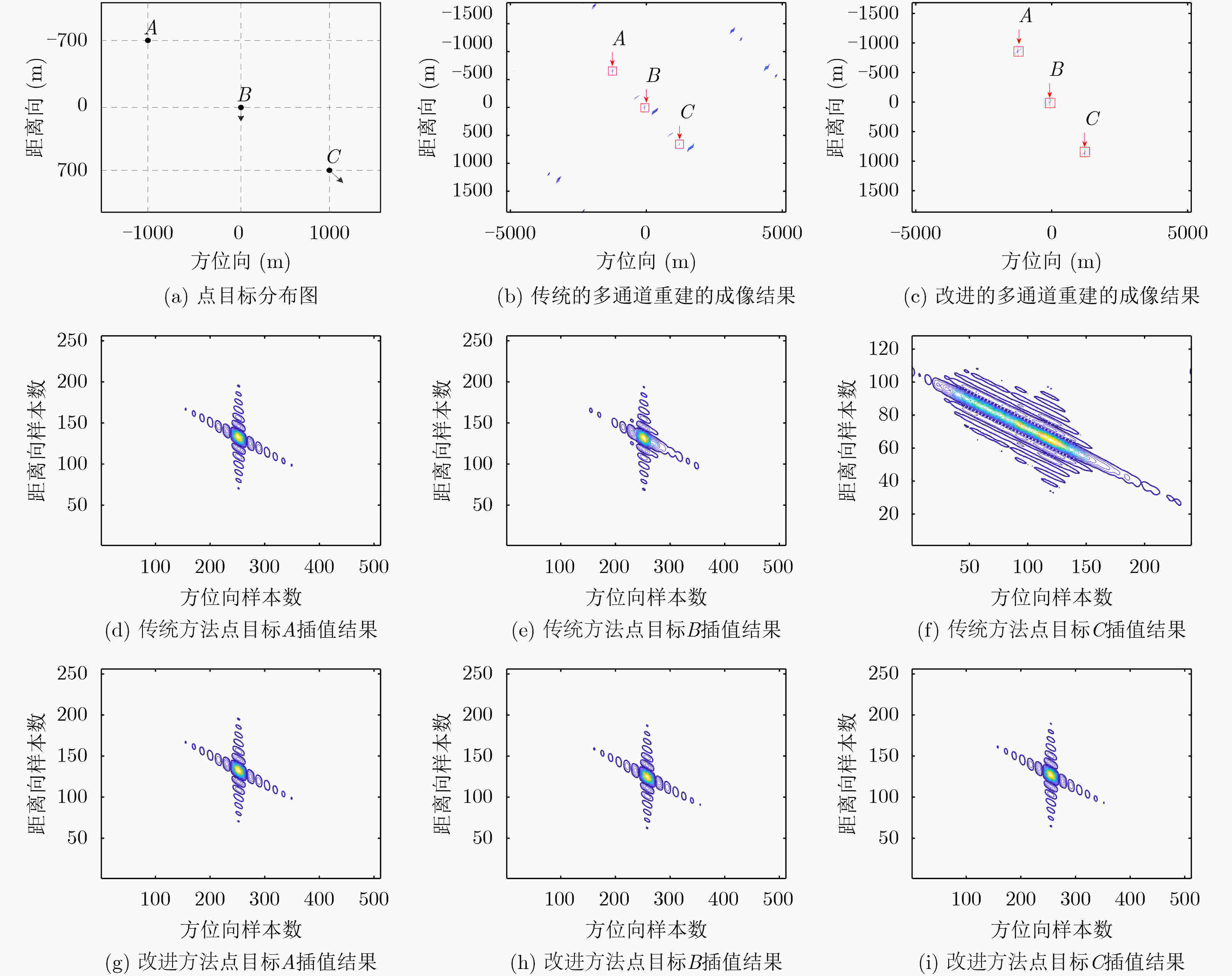
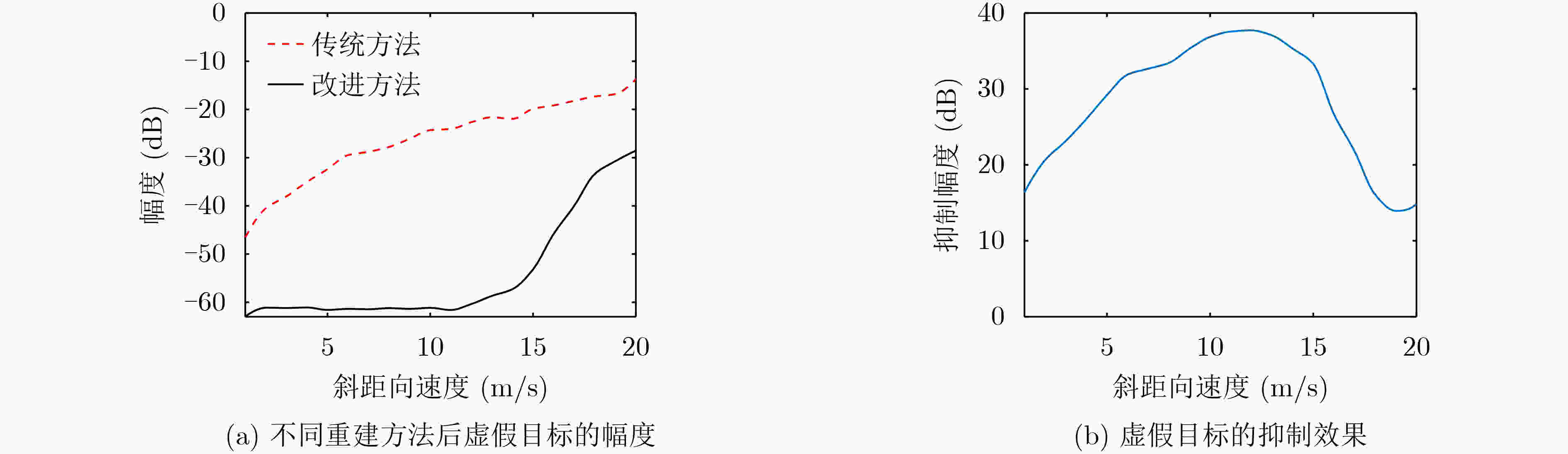
摘要: 在星载方位多通道SAR斜视模式下,方位斜视角度和运动目标的速度分别导致回波多普勒频谱发生2次混叠和通道失衡,影响运动目标方位多通道信号重建。针对该问题,该文提出一种适用于多通道斜视模式下的运动目标的重建方法。首先通过方位向去斜预处理消除了斜视导致的2次多普勒混叠,然后通过修正的多通道重建矩阵来解决目标速度导致的通道失衡。此外,该文还研究了通道冗余情况下的杂波抑制能力,分析了估计速度误差带来的残余相位误差,给出了一种星载方位多通道SAR斜视模式下的运动目标速度快速估计搜索方法。最后,通过点目标仿真验证了方法的有效性。Abstract: In the spaceborne azimuth multichannel SAR squinted mode, the squint angle and the velocity of moving target will cause the 2-D spectrum of echo signal to be aliased and the multichannel imbalance, respectively. Both phenomena would affect the azimuth multichannel reconstruction for moving targets. To resolve this problem, an azimuth multichannel reconstruction method for moving targets in the azimuth multichannel squinted mode is proposed. It eliminates the secondary Doppler aliasing problem caused by the squint angle through azimuth de-ramp preprocessing, and then the multichannel imbalance caused by the moving target velocity is resolved by the improved multichannel reconstruction matrix. The clutter suppression ability in the case of channel redundancy is analyzed, and the residual phase error caused by the estimated velocity error is discussed. Furthermore, an effect moving target velocity estimate approach is proposed. Finally, the simulation results on point targets validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
-
表 1 仿真参数
参数 值 载频 5.6 GHz 子孔径长度 4 m 子孔径数目 3 斜视角度 20° 系统PRF 1400 Hz 发射脉冲宽度 4 μs 发射脉冲带宽 100 MHz 采样频率 120 MHz 卫星速度 7200 m/s 最短斜距 600 km 表 2 性能指标
方法 点目标 航迹向 斜距向 Res(m) PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) MFTA(dB) Res(m) PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) 传统 P1 2.83 –13.22 –9.77 –63.59 1.42 –12.97 –9.40 P2 2.99 –15.17 –3.55 –24.29 1.72 –11.74 –5.94 P3 9.54 –18.61 –5.95 –22.12 4.57 –13.41 –5.56 改进 P1 2.83 –13.22 –9.77 –63.59 1.42 –12.97 –9.40 P2 2.81 –13.25 –9.69 –61.15 1.41 –12.79 –9.37 P3 2.82 –13.24 –9.69 –62.08 1.43 –13.02 –9.49 -
[1] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 2–4. [2] LUO Yin, ZHAO Fengjun, LI Ning, et al. A modified cartesian factorized back-projection algorithm for highly squint spotlight synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 902–906. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2885196 [3] LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. Highly squinted MEO SAR focusing based on extended omega-k algorithm and modified joint time and doppler resampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9188–9200. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2925385 [4] XING Mengdao, WU Yufeng, ZHANG Y D, et al. Azimuth resampling processing for highly squinted synthetic aperture radar imaging with several modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4339–4352. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281454 [5] XU Wei, DENG Yunkai, HUANG Pingping, et al. Full-aperture SAR data focusing in the spaceborne squinted sliding-spotlight mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4596–4607. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282863 [6] 孙宁霄, 吴琼之, 孙林. 基于局部最优匹配的斜视SAR子孔径成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2851–2859. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170466SUN Ningxiao, WU Qiongzhi, and SUN Lin. Local optimal matching algorithm for subaperture imaging of squint synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2851–2859. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170466 [7] HUANG Pingping, LI Shenyang, and XU Wei. Investigation on full-aperture multichannel azimuth data processing in TOPS[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(4): 728–732. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2278183 [8] 赵庆超, 张毅, 王宇, 等. 基于多帧超分辨率的方位向多通道星载SAR非均匀采样信号重建方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 408–419. doi: 10.12000/JR17035ZHAO Qingchao, ZHANG Yi, WANG Yu, et al. Signal reconstruction approach for multichannel SAR in azimuth based on multiframe super resolution[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 408–419. doi: 10.12000/JR17035 [9] HUANG Pingping, XU Wei, and LI Shenyang. Spaceborne squinted multichannel synthetic aperture radar data focusing[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(9): 1073–1080. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0332 [10] ZHANG Shuangxi, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A robust imaging algorithm for squint mode multi-channel high-resolution and wide-swath SAR with hybrid baseline and fluctuant terrain[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1583–1598. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2464182 [11] XU Wei, WEI Zhengbin, HUANG Pingping, et al. Azimuth multichannel reconstruction for moving targets in geosynchronous spaceborne–airborne bistatic SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(11): 1703. doi: 10.3390/rs12111703 [12] 王玉莹, 张志敏, 李宁, 等. 高分宽幅SAR系统下的方位多通道运动目标成像算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 541–546. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190211WANG Yuying, ZHANG Zhimin, LI Ning, et al. A moving target imaging approach for the multichannel in azimuth high resolution wide swath SAR system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 541–546. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190211 [13] TAN Weixian, XU Wei, HUANG Pingping, et al. Investigation of azimuth multichannel reconstruction for moving targets in high resolution wide swath SAR[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): 1270. doi: 10.3390/s17061270 [14] ZHANG Ying, XIONG Wei, DONG Xichao, et al. A novel azimuth spectrum reconstruction and imaging method for moving targets in geosynchronous spaceborne–airborne bistatic multichannel SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5976–5991. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2974531 [15] 郜参观, 邓云凯, 冯锦. 通道不平衡对偏置相位中心多波束SAR性能影响的理论分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(8): 1828–1832. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01257GAO Canguan, DENG Yunkai, and FENG Jin. Theoretical analysis on the mismatch influence of displaced phase center multiple-beam SAR systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(8): 1828–1832. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01257 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
