Recommendation Model Combining Deep Sentiment Analysis and Scoring Matrix
-
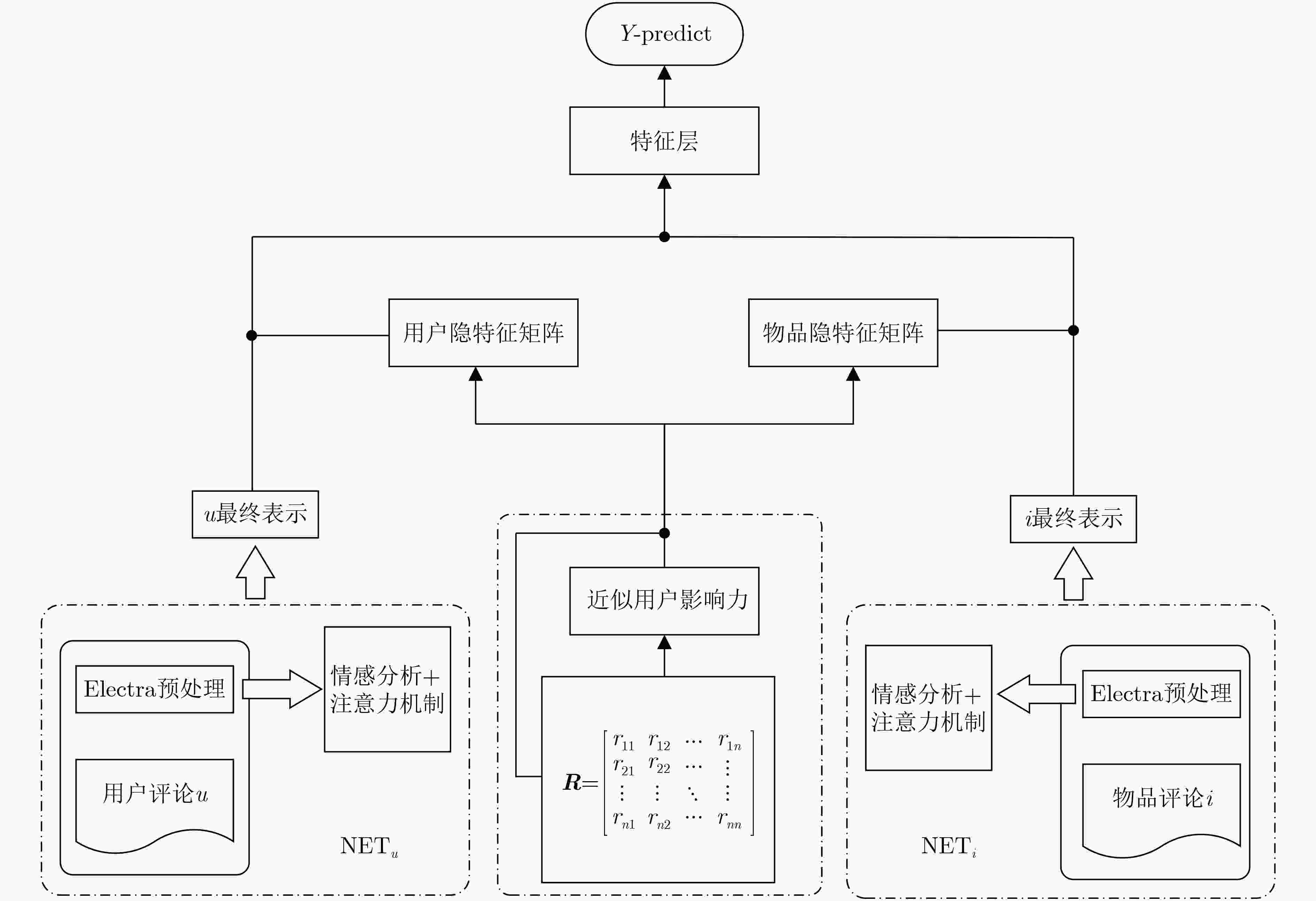
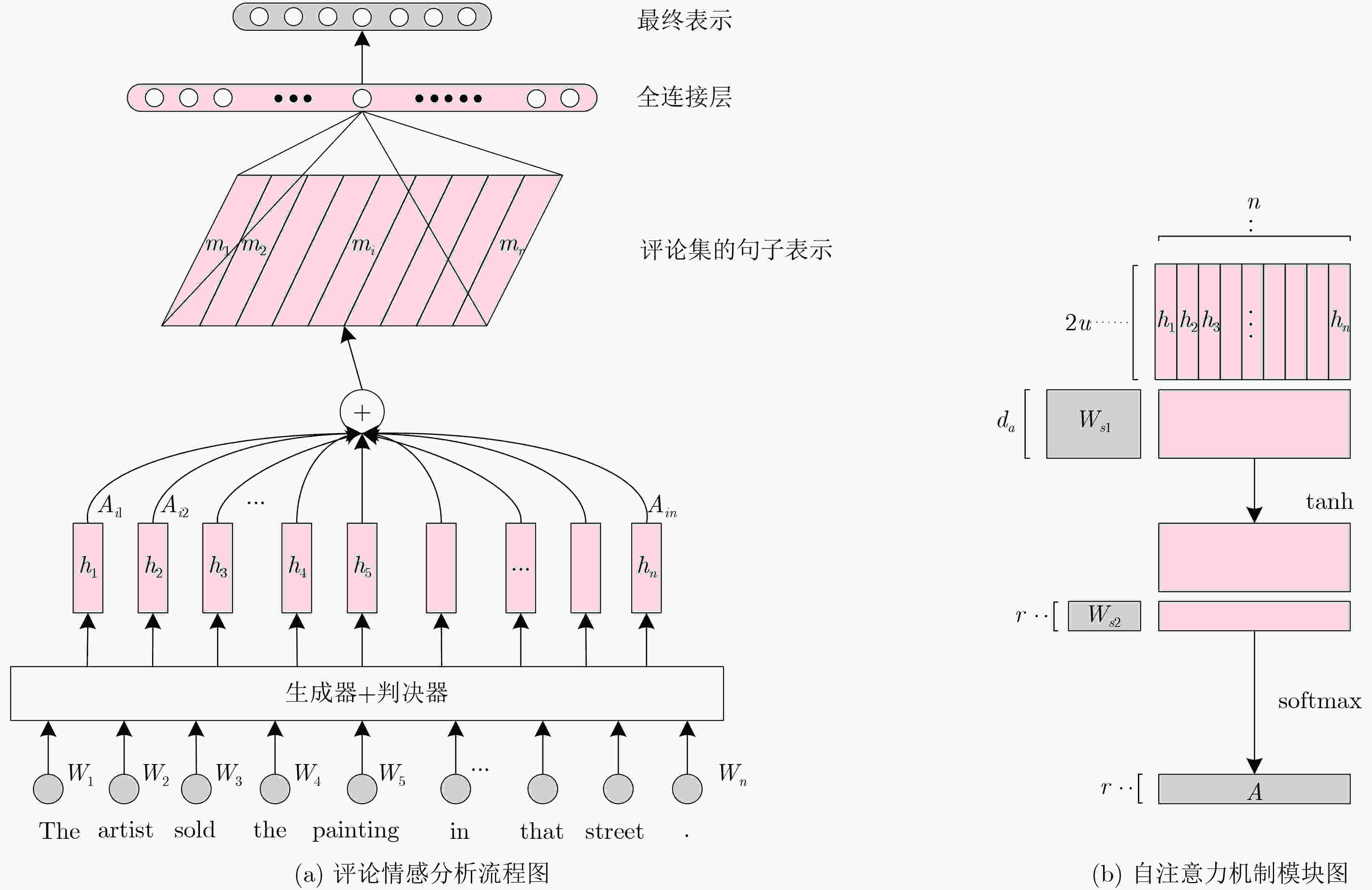
摘要: 目前,大多数推荐系统都具有评分数据稀疏性的问题,它会限制模型的有效性。而用户对于某件商品撰写的评论中隐含了很多信息,对评论文本进行情感分析并提取关键的因素来用于模型的学习,可以有效地缓解数据稀疏问题,但仅使用评论数据而忽略了评分数据的主要因素会影响推荐精度。对此,为了进一步提高推荐精度,该文提出一个评论文本和评分矩阵交互(RTRM)的深度模型,该模型能够提取评论文本和评分矩阵的深层次特征,并结合它们进行评分预测;其次,通过使用预训练的Electra模型得到每条评论的隐表达,并结合深度情感分析及注意力机制实现从上下文语义层面对评论文本的分析,解决了短文本的语义难以分析的问题;同时,在融合层模块中,用户(物品)评论和评分矩阵进行交互,最终预测出用户对商品的评分;最后,在6组数据集上,采用均方误差(MSE)进行性能对比实验,实验结果表明该文模型性能优于其他系统,且平均预测误差最大降低了12.821%,该模型适用于向用户推荐精确的物品。Abstract: Most recommendation systems have a data sparsity problem, which limits the validity of the model that they use. However, the user’s comments on a commodity contain a lot of information. Emotional analysis of the comment text and the extraction of key factors for model learning can effectively alleviate the data sparsity problem, but only the use of comment data and ignore the main factors of the scoring data will affect the recommendation accuracy. To improve further the precision of recommendations, a deep model for the processing of Review Texts and Rating Matrices (RTRM) is proposed. The model extracts deep-level features and combines them to make rating predictions. Then, by using the pre-trained Electra model, the implicit expression of each comment is get, and combining with the deep emotion analysis and attention mechanism, the analysis of the comment text is realized from the context semantic level. It solves the problem that it is difficult to analyze the semantics of short text; User (item) reviews interact with a rating matrix to predict the user’s rating of a product in the fusion layer module. Finally, the Mean Square Error (MSE) is used to perform performance comparison experiments on 6 sets of data sets. Experimental results show that the performance of the proposed model outperforms significantly other systems on a variety of datasets, and the average prediction error is reduced by a maximum of 12.821%, the model is suitable for recommending accurate items to users.
-
Key words:
- Recommendation system /
- Matrix decomposition /
- Review text /
- Scoring data /
- Deep learning
-
表 1 数据集基本信息
Arts and Crafts Digital Music Software Kindle Store Luxury Beauty Video Games 平均数 用户 33423 19819 3864 167569 5228 36789 44448 物品 29800 12876 1293 76438 1578 25212 24532 评论数目 494485 169781 12805 2222983 34278 497577 571984 表 2 RTRM模型与其他模型的性能比较
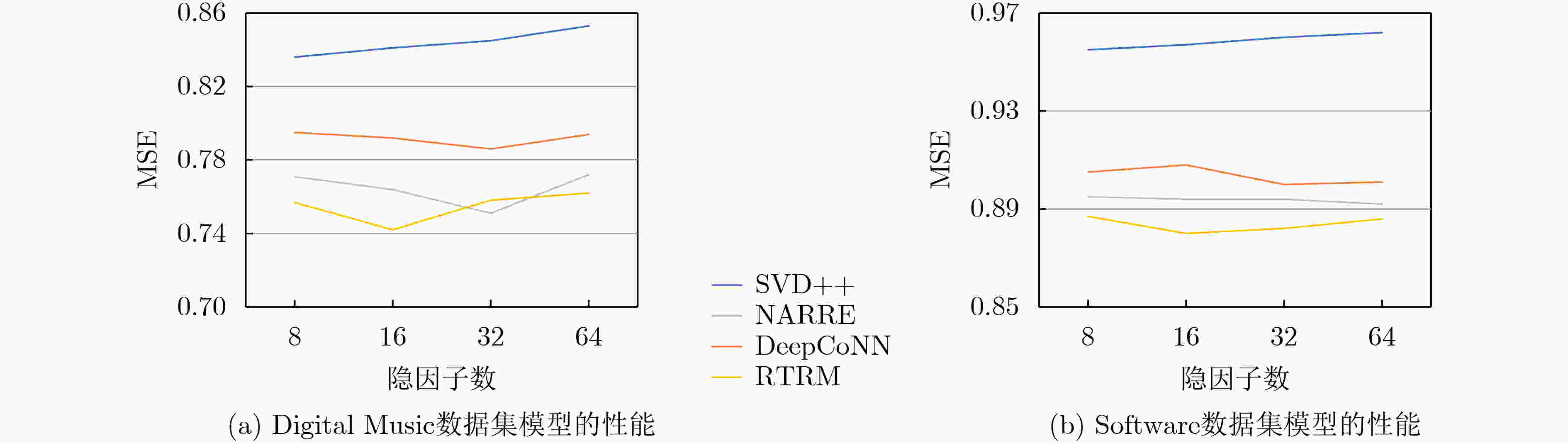
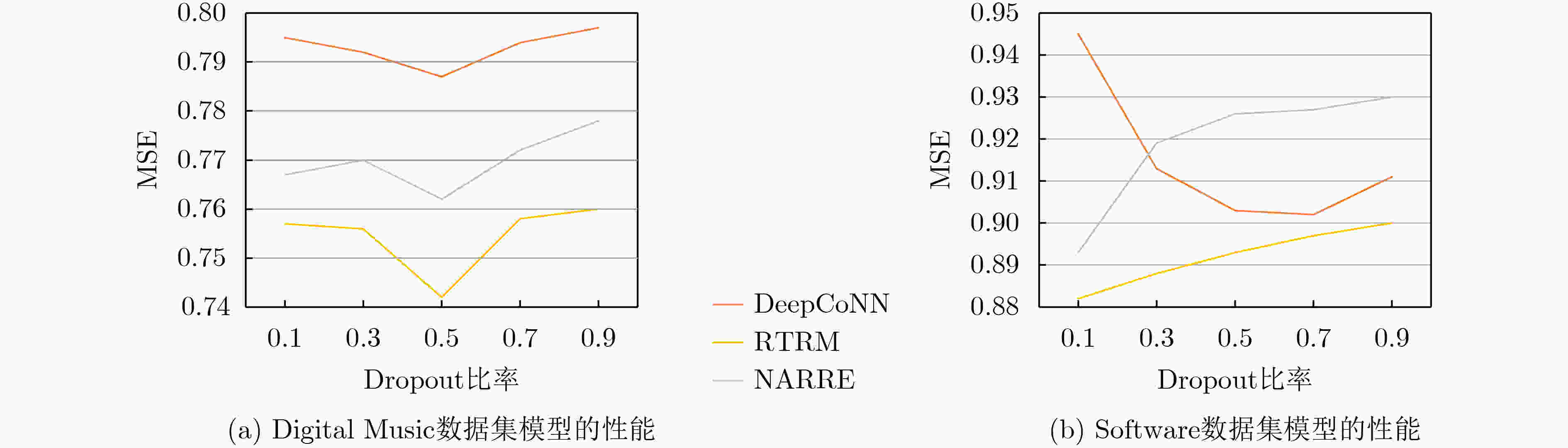
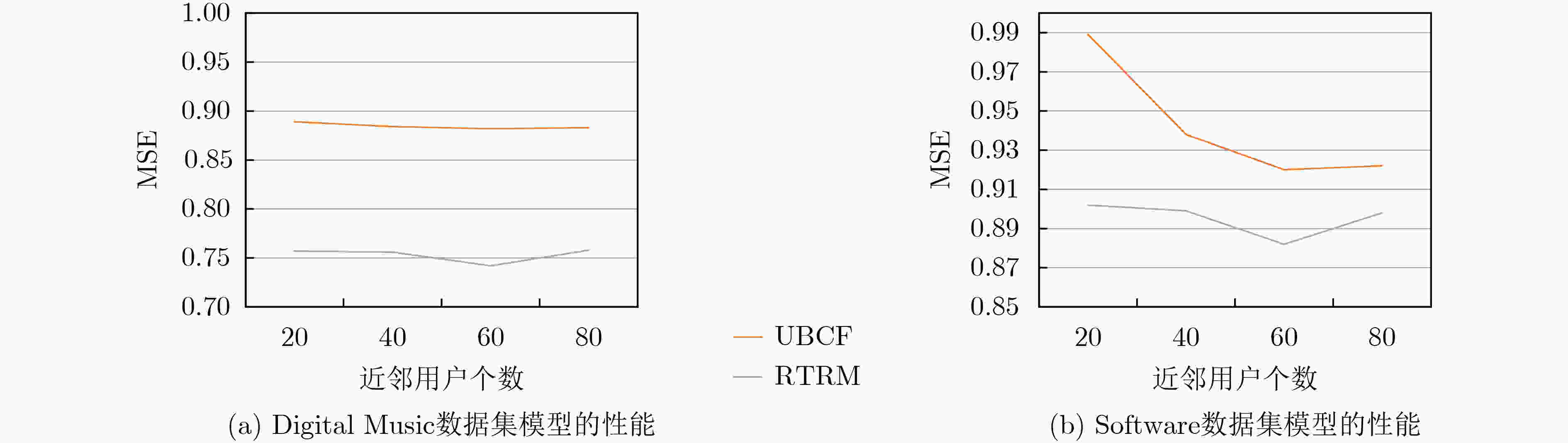
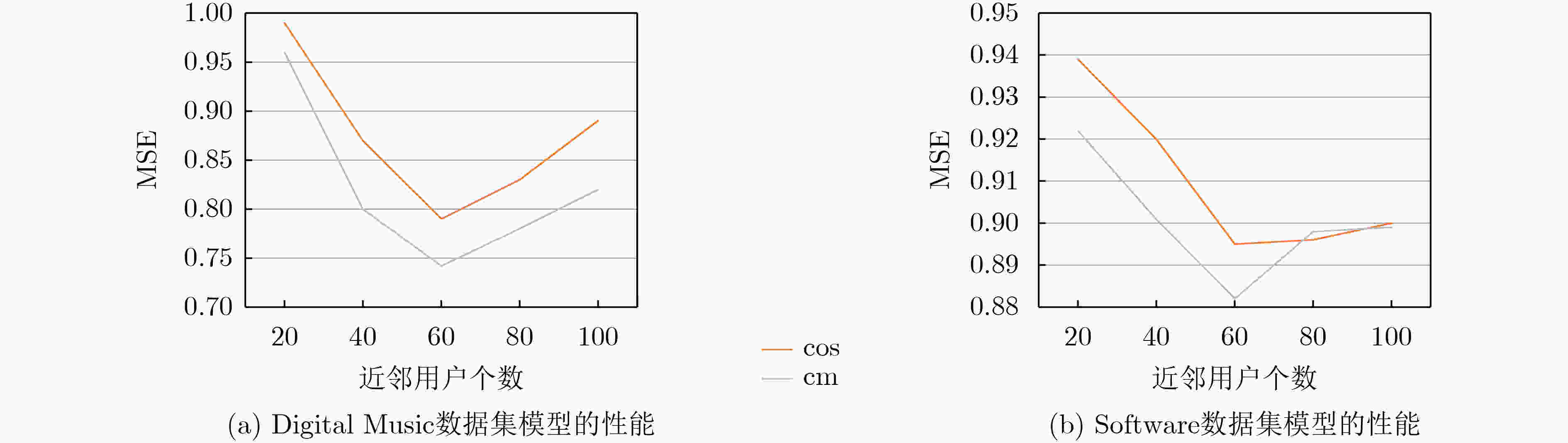
数据集 SVD ++ HFT PMF Deep CoNN NA RRE RTRM 提升(%) 提升(%) 提升(%) a b c d e f f vs a f vs c f vs e Arts and Crafts 0.862 0.809 0.794 0.776 0.738 0.699 18.910 11.965 5.285 Digital Music 0.835 0.816 0.803 0.787 0.763 0.742 11.138 7.597 2.752 Software 0.956 0.961 0.916 0.902 0.893 0.882 7.741 3.712 1.232 Kindle Store 1.371 1.313 1.105 1.084 0.993 0.972 29.103 12.036 2.115 Luxury Beauty 0.941 0.938 0.929 0.912 0.901 0.887 5.739 4.521 1.554 Video Games 0.675 0.698 0.681 0.662 0.655 0.646 4.296 5.147 1.374 AVG 0.940 0.923 0.871 0.854 0.824 0.805 12.821 7.496 2.385 -
[1] BOBADILLA J, ORTEGA F, HERNANDO A, et al. Recommender systems survey[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2013, 46: 109–132. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2013.03.012 [2] 黄立威, 江碧涛, 吕守业, 等. 基于深度学习的推荐系统研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(7): 1619–1647. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01619HUANG Liwei, JIANG Bitao, LÜ Shouye, et al. Survey on deep based recommender systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(7): 1619–1647. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01619 [3] KOREN Y, BELL R, and VOLINSKY C. Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems[J]. Computer, 2009, 42(8): 30–37. doi: 10.1109/MC.2009.263 [4] 张光卫, 李德毅, 李鹏, 等. 基于云模型的协同过滤推荐算法[J]. 软件学报, 2007, 18(10): 2403–2411. doi: 10.1360/jos182403ZHANG Guangwei, LI Deyi, LI Peng, et al. A collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on cloud model[J]. Journal of Software, 2007, 18(10): 2403–2411. doi: 10.1360/jos182403 [5] SUNDERMANN C V, DOMINGUES M A, SINOARA R A, et al. Using opinion mining in context-aware recommender systems: A systematic review[J]. Information, 2019, 10(2): 42. doi: 10.3390/info10020042 [6] CHEN Li, CHEN Guanliang, and WANG Feng. Recommender systems based on user reviews: The state of the art[J]. User Modeling And User-adapted Interaction, 2015, 25(2): 99–154. doi: 10.1007/s11257-015-9155-5 [7] MCAULEY J and LESKOVEC J. Hidden factors and hidden topics: Understanding rating dimensions with review text[C]. The 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 165–172. doi: 10.1145/2507157.2507163. [8] REN Zhaochun, LIANG Shangsong, LI Piji, et al. Social collaborative viewpoint regression with explainable recommendations[C]. The Tenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Cambridge, UK, 2017: 485–494. doi: 10.1145/3018661.3018686. [9] ZHENG Lei, NOROOZI V, and YU P S. Joint deep modeling of users and items using reviews for recommendation[C]. The Tenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Cambridge, UK, 2017: 425–434. doi: 10.1145/3018661.3018665. [10] LI Piji, WANG Zihao, REN Zhaochun, et al. Neural rating regression with abstractive tips generation for recommendation[C]. The 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Tokyo, Janpan, 2017: 345–354. doi: 10.1145/3077136.3080822. [11] SEO S, HUANG Jing, YANG Hao, et al. Interpretable convolutional neural networks with dual local and global attention for review rating prediction[C]. The Eleventh ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Como, Italy, 2017: 297–305. doi: 10.1145/3109859.3109890. [12] CHEN Chong, ZHANG Min, LIU Yiqun, et al. Neural attentional rating regression with review-level explanations[C]. The 2018 World Wide Web Conference, Lyon, France, 2018: 1583–1592. doi: 10.1145/3178876.3186070. [13] CHO K, VAN MERRIENBOER B, BAHDANAU D, et al. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1259, 2014. [14] CLARK K, LUONG M T, LE Q V, et al. ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations 2020, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 1–13. [15] 赵衎衎, 张良富, 张静, 等. 因子分解机模型研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(3): 799–821. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005698ZHAO Kankan, ZHANG Liangfu, ZHANG Jing, et al. Survey on factorization machines model[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(3): 799–821. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005698 [16] 李琳, 朱阁, 解庆, 等. 一种潜在特征同步学习和偏好引导的推荐方法[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(11): 3382–3396. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005542LI Lin, ZHU Ge, XIE Qing, et al. Recommendation approach by simultaneous learning latent features and preferences guidance[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(11): 3382–3396. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005542 [17] KIM D, PARK C, OH J, et al. Convolutional matrix factorization for document context-aware recommendation[C]. The 10th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Boston, USA, 2016: 233–240. doi: 10.1145/2959100.2959165. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
