Approach for Dynamic Flight Pricing Based on Strategy Learning
-
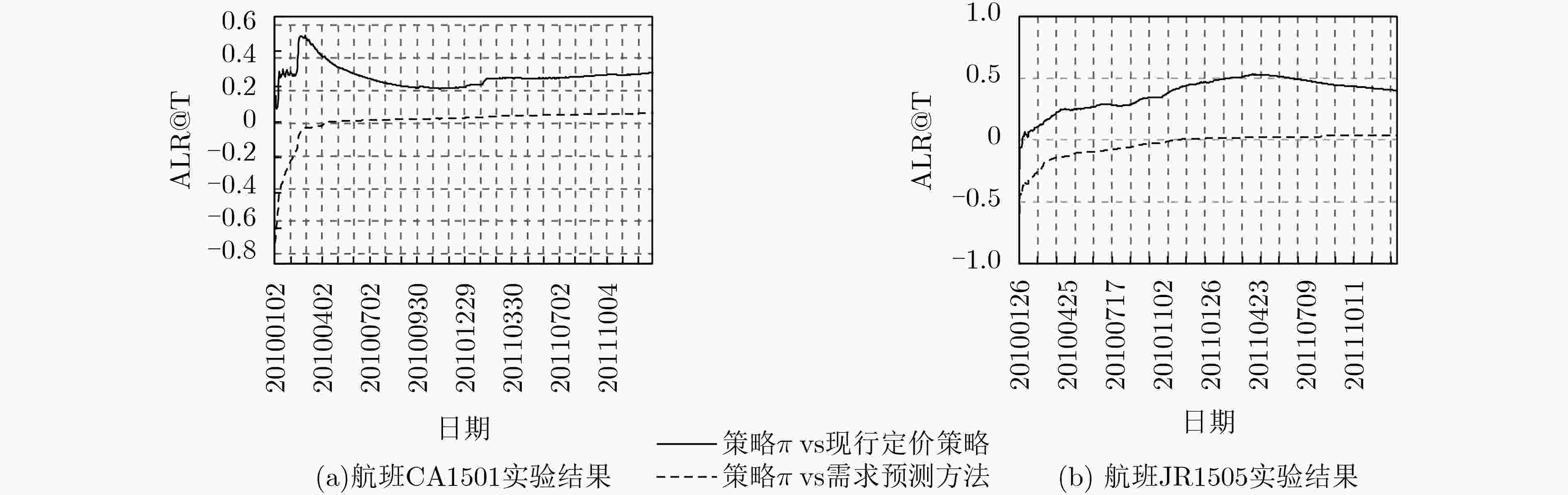
摘要: 机票动态定价旨在构建机票售价策略以最大化航班座位收益。现有机票定价算法都建立在提前预测各票价等级的需求量基础之上,会因票价等级需求量的预测偏差而降低模型性能。为此,提出基于策略学习的机票动态定价算法,其核心是不再预测各票价等级的需求量,而是将机票动态定价问题建模为离线强化学习问题。通过设计定价策略评估和策略更新的方式,从历史购票数据上学习具有最大期望收益的机票动态定价策略。同时设计了与现行定价策略和需求量预测方法的对比方法及评价指标。在两趟航班的多组定价结果表明:相比于现行机票销售策略,策略学习算法在座位收益上的提升率分别为30.94%和39.96%,且比基于需求量预测方法提升了6.04%和3.36%。Abstract: The core of the dynamic flight pricing is to yield a pricing strategy with maximum seat revenue. The state-of-the-art flight pricing approaches are built on forecasting the fare demand. They suffer low profit due to the inaccurate prediction. To tackle the above issue, an approach for dynamic flight pricing based on strategy learning is proposed. That approach resorts to reinforcement learning to output pricing strategy with the highest expected return. That strategy is learned by iteratively policy evaluation and policy improvement. The rate of profit improvement on the two flights is empirically 30.94% and 39.96% over the existing pricing strategy, while that rate is 6.04% and 3.36% over the demand forecasting algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Revenue management /
- Dynamic flight pricing /
- Reinforcement learning /
- Strategy learning
-
表 1 机票动态定价策略学习算法
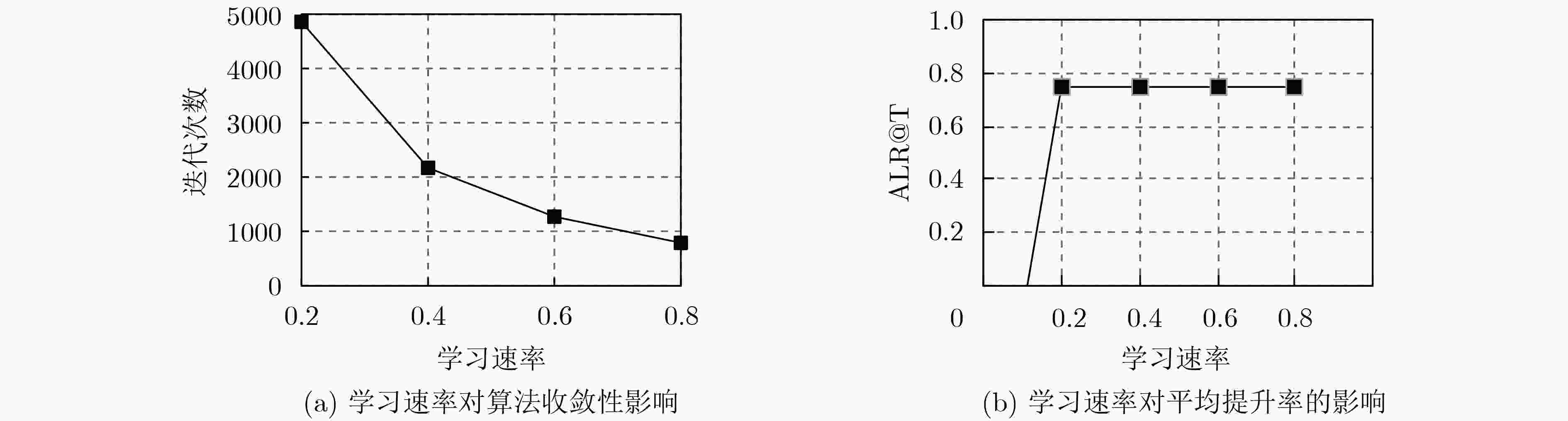
输入 学习速率$\eta $,折扣因子$\gamma $,最大迭代次数${\rm{episodes}}$,航班总座位数$N$ 航班第1天到$T - 1$天的历史销售序列${\rm{\{ }}s_{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{(}}n)},a_{\rm{0}}^{(n)},r_{\rm{0}}^{(n)}, ··· ,s_v^{(n)},a_v^{(n)},r_v^{(n)}{\rm{\} }}_{n = {\rm{1}}}^{T - {\rm{1}}}$ 初始化 对于任何状态$s$和$\alpha ,$$q(s,\alpha ) = 0,k = 0,n = 1$ Repeat: Repeat (对于第1天到$T - 1$天的每趟离港航班): Repeat (对于此趟航班历史销售序列的每一步$(s_t^{(n)},a_t^{(n)},r_t^{(n)},s_{t + {\rm{1}}}^{(n)})$): 策略评估:据式(3)更新动作值函数$q(s_t^{(n)},a_t^{(n)})$ 策略更新:按式(4)调整策略$\pi (s_t^{(n)}) = \arg {\rm{ma}}{{\rm{x}}_\alpha }q(s_t^{(n)},a)$ Until 航班没有剩余座位或售票时间截止 $n \leftarrow n + 1$ Until $n > T - 1$ $k \leftarrow k + 1$ Until $k > {\rm{episodes}}$ 输出 第$T$天的机票动态定价策略$\pi (s) = \arg {\max _\alpha }q(s,\alpha )$ 表 2 旅客订票记录示例
身份证号 航空公司 航班号 出发机场 到达机场 出发日期 订单编号 票价等级 52893787 CA 1501 PEK SHA 20100308 2273651247 0.5213 55503718 CA 1501 PEK SHA 20100308 2745812364 0.8212 表 3 实验数据集的统计信息
航班 售票记录
总数销售
序列数状态、动作等
四元组数原始票价等级
(精确到万分位)预处理后的票价
等级(精确到千分位)预处理后的票价
等级(精确到百分位)票价
等级数各等级
平均票数票价
等级数各等级
平均票数票价
等级数各等级
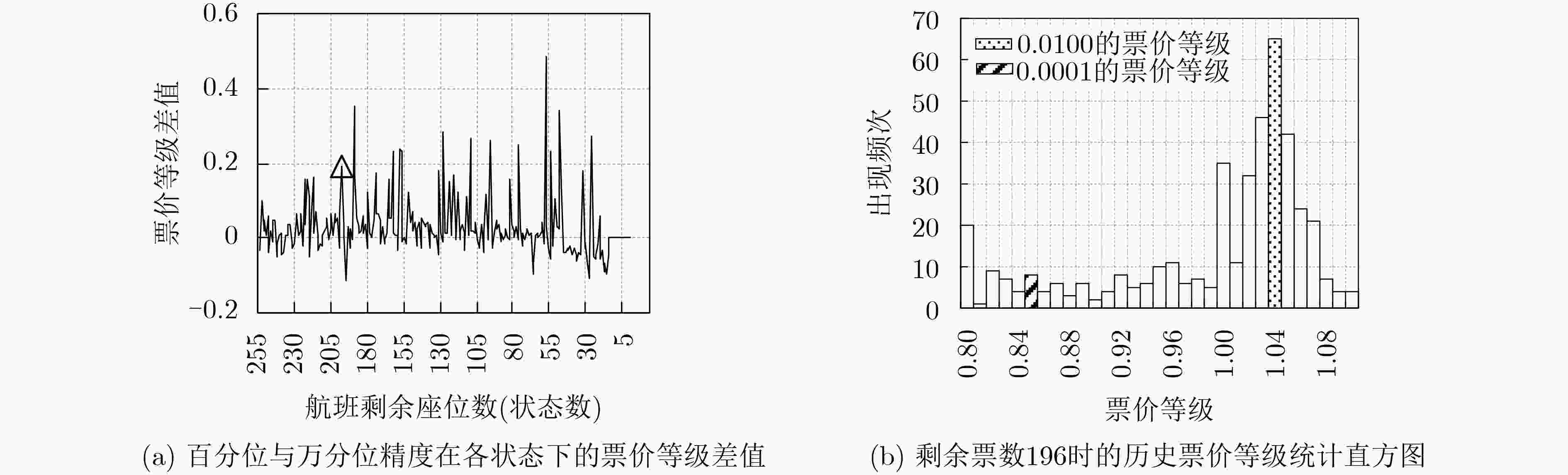
平均票数CA1501 130118 718 102809 5737 22.68 1087 119.70 150 867.45 JR1505 22691 611 17102 2359 9.62 745 30.46 90 254.96 表 4 票价等级精确度影响分析
票价等级
精度训练集中票价
等级总数定价策略中出现
票价等级总数收益平均提升率
${\rm{ALR@T}}$(%)0.0001 4590 128 13.21 0.0100 120 16 16.38 -
SMITH B C, LEIMKUHLER J F, and DARROW R M. Yield management at American airlines[J]. Interfaces, 1992, 22(1): 8–31. doi: 10.1287/inte.22.1.8 GALLEGO G and VAN RYZIN G. Optimal dynamic pricing of inventories with stochastic demand over finite horizons[J]. Management Science, 1994, 40(8): 999–1020. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.40.8.999 OTERO D F and AKHAVAN-TABATABAEI R. A stochastic dynamic pricing model for the multiclass problems in the airline industry[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2015, 242(1): 188–200. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2014.09.038 DELAHAYE T, ACUNA-AGOST R, BONDOUX N, et al. Data-driven models for itinerary preferences of air travelers and application for dynamic pricing optimization[J]. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management, 2017, 16(6): 621–639. doi: 10.1057/s41272-017-0095-z 高金敏, 乐美龙, 曲林迟, 等. 基于时变需求的机票动态定价研究[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 50(4): 570–576. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2018.04.020GAO Jinmin, LE Meilong, QU Linchi, et al. Dynamic pricing of air tickets based on time-varying demand[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics &Astronautics, 2018, 50(4): 570–576. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2018.04.020 SELC̣UK A M and AVṢAR Z M. Dynamic pricing in airline revenue management[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2019, 478(2): 1191–1217. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2019.06.012 LIN K Y and SIBDARI S Y. Dynamic price competition with discrete customer choices[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 197(3): 969–980. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2007.12.040 施飞, 陈森发. 随时间变化的机票折扣定价研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010, 10(1): 112–116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2010.01.017SHI Fei and CHEN Senfa. Air ticket discount pricing based on time varying[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2010, 10(1): 112–116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2010.01.017 LEE J, LEE E and KIM J. Electric vehicle charging and discharging algorithm based on reinforcement learning with data-driven approach in dynamic pricing scheme[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(8): 1950. doi: 10.3390/en13081950 CHENG Yin, ZOU Luobao, ZHUANG Zhiwei, et al. An extensible approach for real-time bidding with model-free reinforcement learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 360: 97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.009 陈前斌, 谭颀, 魏延南, 等. 异构云无线接入网架构下面向混合能源供应的动态资源分配及能源管理算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1428–1435. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190499CHEN Qianbin, TAN Qi, WEI Yannan, et al. Dynamic resource allocation and energy management algorithm for hybrid energy supply in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1428–1435. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190499 GOSAVII A, BANDLA N, and DAS T K. A reinforcement learning approach to a single leg airline revenue management problem with multiple fare classes and overbooking[J]. IIE Transactions, 2002, 34(9): 729–742. doi: 10.1080/07408170208928908 SHIHAB S A M, LOGEMANN C, THOMAS D G, et al. Autonomous airline revenue management: A deep reinforcement learning approach to seat inventory control and overbooking[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 132–139. QIU Qinfu and CHEN Xiong. Behaviour-driven dynamic pricing modelling via hidden Markov model[J]. International Journal of Bio-Inspired Computation, 2018, 11(1): 27–33. doi: 10.1504/IJBIC.2018.090071 LAWHEAD R J and GOSAVI A. A bounded actor-critic reinforcement learning algorithm applied to airline revenue management[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 82: 252–262. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.04.008 RAMASWAMY A and BHATNAGAR S. Stability of stochastic approximations with “controlled markov” noise and temporal difference learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(6): 2614–2620. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2874687 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
