Research on Background Ionospheric Impacts Imposed by Spatio-temporal Variations on Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar Azimuth Imaging
-
摘要: 对于星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)成像,方位向信号的相关性可能会因时-空变化的背景电离层而遭到破坏,特别是对于低波段系统。该文将孔径内方位时变的斜距电子总量(STEC)归结于3个因素:垂向电子总量(VTEC)的时间变化、空间变化以及电磁波传播路径的变化,分别分析了每个因素造成的时变STEC各阶系数。该文建立了统一的分析模型,即时变STEC影响下的SAR方位向信号3阶泰勒展开模型,推导了方位向偏移和相位误差解析表达式,并基于此得到了不同星载SAR系统的时变STEC各阶系数容限。利用实测的VTEC数据以及国际参考电离层(IRI)模型,开展了信号级仿真。数值分析和信号级仿真的结果表明,对于低轨P波段SAR系统,空变VTEC与传播路径变化是导致方位时变STEC的主要因素;而对于中高轨SAR系统,时变VTEC是导致方位时变STEC的主要因素。随着载频的下降与合成孔径时间的增加,方位向成像性能更加容易受到方位时变STEC的影响。
-
关键词:
- 星载合成孔径雷达 /
- 方位向成像 /
- 电离层 /
- 时-空变化的背景电离层
Abstract: In spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging, the coherence of azimuth signals might be degraded by spatio-temporal variations of the background ionosphere, especially for low-frequency systems. In this paper, the azimuth temporal-varying Slant Total Electron Content (STEC) is attributed to three factors: the spatial- and temporal-varying Vertical Total Electron Content (VTEC), and the propagation path variation. Derivative of each order of the azimuth-varying STEC is analyzed as to each factor. A uniform analytical model is established, that is the third-order Taylor expansion model of SAR azimuth signals influenced by the temporal-varying STEC. The analytical expressions of the azimuth shift and phase errors are derived. Based on this model, thresholds of the varying STEC derivatives are derived for different spaceborne SAR systems. Signal-level simulations are performed by means of the VTEC real data and the International Reference Ionosphere (IRI) model. Numerical analyses and signal-level simulations indicate that the spatial-varying VTEC and the propagation path variation highlight in the low-orbit P-band SAR system, while the temporal-varying VTEC becomes a predominant factor that results in the azimuth temporal-varying STEC in the medium- or high-orbit SAR system. As the carrier frequency decreases and the synthetic aperture time increases, the azimuth imaging performance is more susceptible to the azimuth temporal-varying STEC. -
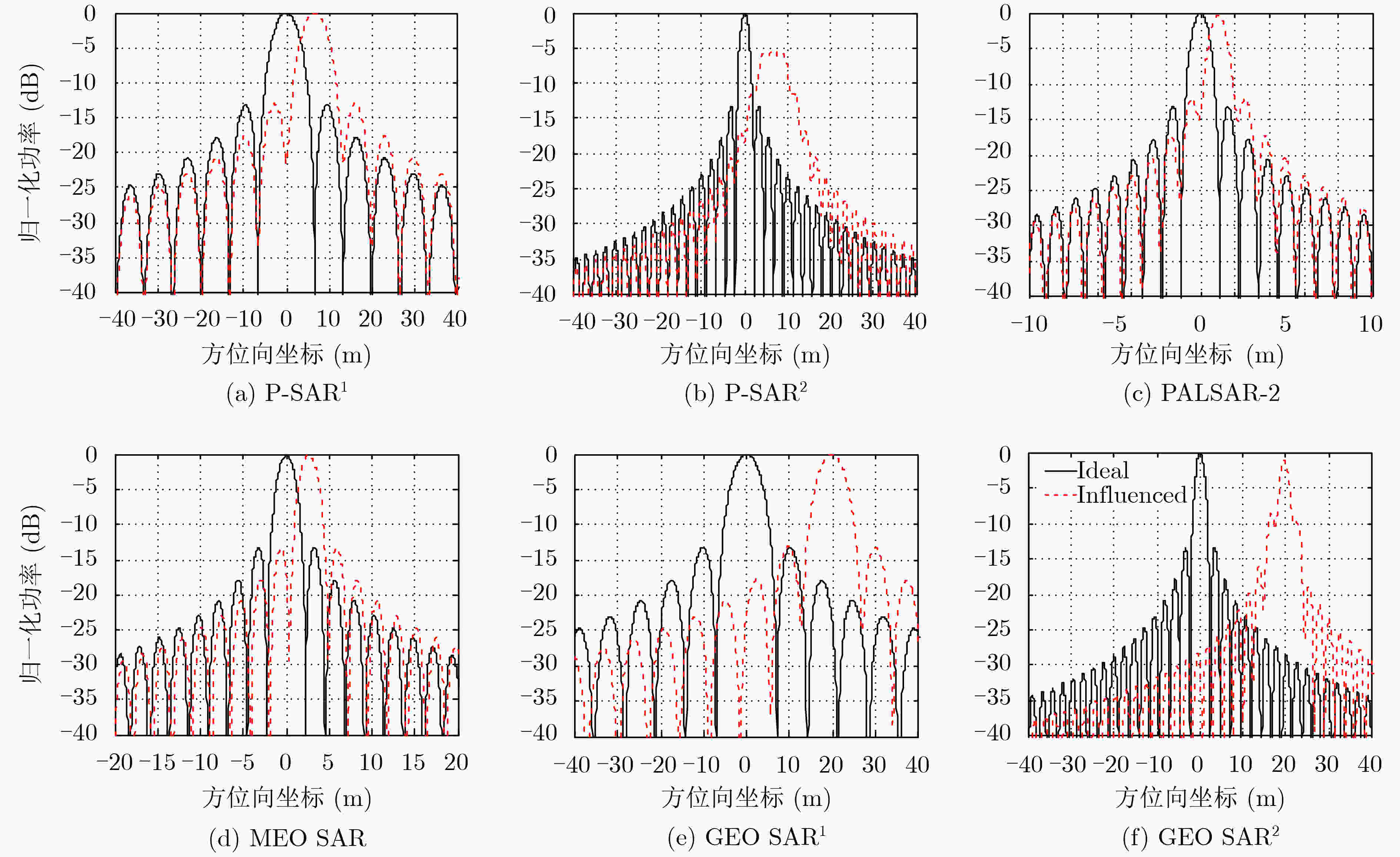
表 1 不同星载SAR系统对应的时变STEC各阶系数容限
P-SAR1 P-SAR2 PALSAR-2 MEO SAR GEO SAR1 GEO SAR2 中心频率 (GHz) 0.50 0.50 1.27 1.25 1.25 1.25 方位分辨率 (m) 4.96 1.98 ≈1.00 2.10 6.30 2.10 轨道高度 (km) 700 700 636 7000 35793 35793 合成孔径时间 (s) 5.65 14.11 ≈10.00 75.00 200.00 600.00 $\left| {{k_1}} \right|$容限(TECU/s) 2.9×10–2 1.2×10–2 4.2×10–2 5.6×10–3 2.1×10–3 7.0×10–4 $\left| {{k_2}} \right|$容限(TECU/s2) 3.0×10–3 4.7×10–4 2.3×10–3 4.2×10–5 5.9×10–6 6.6×10–7 $\left| {{k_3}} \right|$容限(TECU/s3) 1.3×10–4 8.3×10–6 5.9×10–5 1.4×10–7 7.4×10–9 2.7×10–10 表 2 仿真中各因素导致的时变STEC各阶系数值
LEO SAR ${k'_1}$(TECU/s) ${k'_2}$(TECU/s2) ${k'_3}$(TECU/s3) ${k''_1}$(TECU/s) ${k''_2}$(TECU/s2) 6.2×10–3 –2.8×10–6 –1.3×10–9 3.3×10–2 2.1×10–3 ${\rm{VTE}}{{\rm{C}}_0}$ ${\rm{STE}}{{\rm{C}}_0}$ ${k_1}$(TECU/s) ${k_2}$(TECU/s2) ${k_3}$(TECU/s3) 42.9 49.1 3.9×10–2 2.1×10–3 2.6×10–7 MEO SAR ${k'_1}$(TECU/s) ${k'_2}$(TECU/s2) ${k'_3}$(TECU/s3) ${k''_1}$(TECU/s) ${k''_2}$(TECU/s2) 6.2×10–3 –2.7×10–6 –1.3×10–9 2.2×10–3 1.1×10–5 ${\rm{VTE}}{{\rm{C}}_0}$ ${\rm{STE}}{{\rm{C}}_0}$ ${k_1}$(TECU/s) ${k_2}$(TECU/s2) ${k_3}$(TECU/s3) 42.9 49.1 8.4×10–3 8.5×10–6 1.6×10–11 GEO SAR ${k'_1}$(TECU/s) ${k'_2}$(TECU/s2) ${k'_3}$(TECU/s3) ${k''_1}$(TECU/s) ${k''_2}$(TECU/s2) 6.2×10–3 –2.6×10–6 –1.3×10–9 2.6×10–4 1.7×10–7 ${\rm{VTE}}{{\rm{C}}_0}$ ${\rm{STE}}{{\rm{C}}_0}$ ${k_1}$(TECU/s) ${k_2}$(TECU/s2) ${k_3}$(TECU/s3) 42.9 49.1 6.5×10–3 –2.4×10–6 –1.2×10–9 表 3 不同星载SAR系统对应的时变STEC各阶系数容限
分辨率 (m) 展宽系数 PSLR (dB) ISLR (dB) 峰值功率损失 (dB) 偏移 (m) P-SAR1 4.99 1.01 –12.58 –9.04 0.13 6.67 P-SAR2 6.81 3.44 –6.13 –7.15 5.34 6.64 PALSAR-2 1.01 1.02 –11.73 –8.31 0.30 1.04 MEO SAR 2.10 1.00 –13.20 –9.62 0.01 3.21 GEO SAR1 6.30 1.02 –13.01 –9.52 0.03 19.82 GEO SAR2 2.20 1.05 –7.59 –5.59 1.03 19.65 -
[1] CUMMING I, WONG F H, 洪文, 胡东辉, 译. 合成孔径雷达成像: 算法与实现[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 2–11.CUMMING I, WONG F, HONG Wen, HU Donghui, translation. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 2–11. [2] TOAN T L, BEAUDOIN A, RIOM J, et al. Relating forest biomass to SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(2): 403–411. doi: 10.1109/36.134089 [3] CARREIRAS J M B, QUEGAN S, TOAN T L, et al. Coverage of high biomass forests by the ESA BIOMASS mission under defense restrictions[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 196: 154–162. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.05.003 [4] SHIMADA M, ITOH T, MOTOOKA T, et al. New global forest/non-forest maps from ALOS PALSAR data (2007–2010)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 155: 13–31. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.04.014 [5] 梁甸农, 周智敏, 常文革. 叶簇穿透超宽带成像雷达技术发展动态[J]. 国防科技参考, 1999, 20(3): 1–6.LIANG Diannong, ZHOU Zhimin, and CHANG Wenge. Technological development trend of the foliage-penetrating ultra-wideband imaging radar[J]. Reference of National Defense Technology, 1999, 20(3): 1–6. [6] 杨淋, 赵宁, 姚佰栋, 等. 高分辨率星载P波段SAR系统参数设计[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2017, 15(1): 19–28.YANG Lin, ZHAO Ning, YAO Baidong, et al. Parameter design of a high resolution space-borne P-band SAR system[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2017, 15(1): 19–28. [7] WANG Cheng, CHEN Liang, and LIU Lu. A new analytical model to study the ionospheric effects on VHF/UHF wideband SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4545–4557. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2693396 [8] TOMIYASU K and PACELLI J L. Synthetic aperture radar imaging from an inclined geosynchronous orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1983, 21(3): 324–329. [9] 李德鑫. 地球同步轨道合成孔径雷达信号处理与仿真技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2017.LI Dexin. Research on the technology of signal processing and simulation of geosynchronous SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2017. [10] LONG Teng, HU Cheng, DING Zegang, et al. Geosynchronous SAR: System and Signal Processing[M]. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd, 2018: 129–186. [11] MEYER F, BAMLER R, JAKOWSKI N, et al. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(4): 560–564. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.882148 [12] JI Yifei, ZHANG Qilei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging degradations imposed by ionospheric irregularities[J]. Science China Information Science, 2017, 60(6): 060308. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-9064-1 [13] JI Yifei, ZHANG Yongsheng, DONG Zhen, et al. Impacts of ionospheric irregularities on L-band geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 3941–3954. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2959702 [14] JI Yifei, ZHANG Qilei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Spaceborne P-band SAR imaging degradation by anisotropic ionospheric irregularities: A comprehensive numerical study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5516–5526. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2966710 [15] QUEGAN S and LAMONT J. Ionospheric and tropospheric effects on synthetic aperture radar performance[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1986, 7(4): 525–539. doi: 10.1080/01431168608954707 [16] ISHIMARU A, KUGA Y, LIU J, et al. Ionospheric effects on synthetic aperture radar at 100 MHz to 2 GHz[J]. Radio Science, 1999, 34(1): 257–268. doi: 10.1029/1998RS900021 [17] XU Zhengwen, WU Jian, and WU Zhensen. A survey of ionospheric effects on space-based radar[J]. Waves in Random Media, 2004, 14(2): S189–S273. doi: 10.1088/0959-7174/14/2/008 [18] 李亮, 洪峻, 明峰, 等. 电离层时空变化对中高轨SAR成像质量的影响分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 915–922.LI Liang, HONG Jun, MING Feng, et al. Study on ionospheric effects induced by spatio-temporal variability on medium-earth-orbit SAR imaging quality[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 915–922. [19] 李雨龙, 张弘毅, 黄丽佳, 等. 同步轨道SAR电离层影响分析与仿真研究[J]. 电子测量技术, 2014, 37(9): 14–22, 27.LI Yulong, ZHANG Hongyi, HUANG Lijia, et al. Analysis and simulation on GEO SAR ionosphere effects[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2014, 37(9): 14–22, 27. [20] TIAN Ye, HU Cheng, DONG Xichao, et al. Theoretical analysis and verification of time variation of background ionosphere on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 721–725. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2360235 [21] HU Cheng, TIAN Ye, YANG Xiaopeng, et al. Background ionosphere effects on geosynchronous SAR focusing: Theoretical analysis and verification based on the BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS)[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1143–1162. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2475283 [22] DONG Xichao, HU Cheng, TIAN Weiming, et al. Design of validation experiment for analysing impacts of background ionosphere on geosynchronous SAR using GPS signals[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(20): 1604–1606. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.1545 [23] DONG Xichao, HU Cheng, TIAN Ye, et al. Experimental study of ionospheric impacts on geosynchronous SAR using GPS signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2171–2183. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2537401 [24] 李力. 星载P波段合成孔径雷达中的电离层效应研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2014.LI Li. Research on ionospheric effects in spaceborne P band synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014. [25] JI Yifei, ZHANG Qilei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Analysis of background ionospheric effects on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. Radioengineering, 2017, 26(1): 130–138. doi: 10.13164/re.2017.0130 -





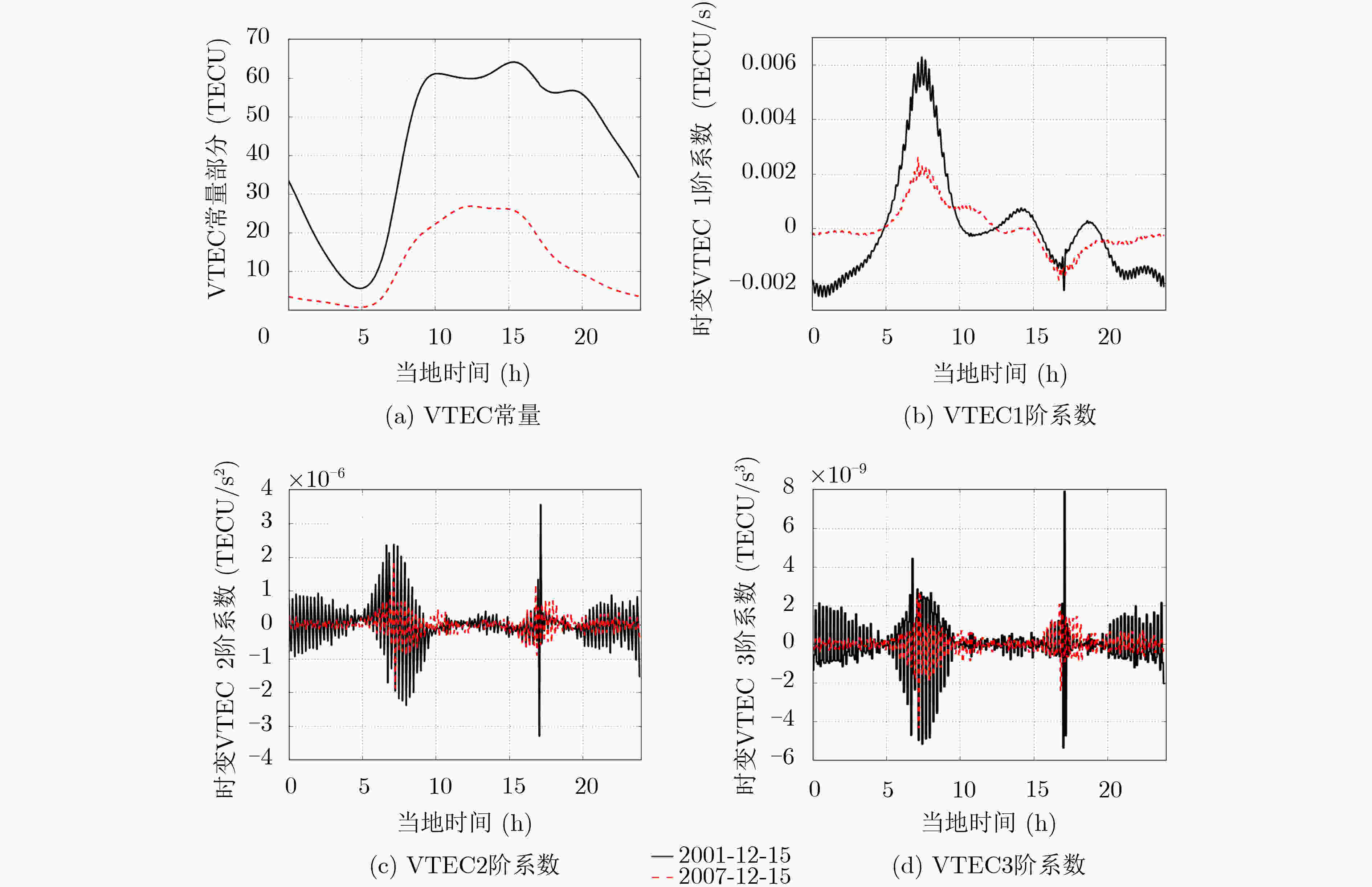
 下载:
下载:
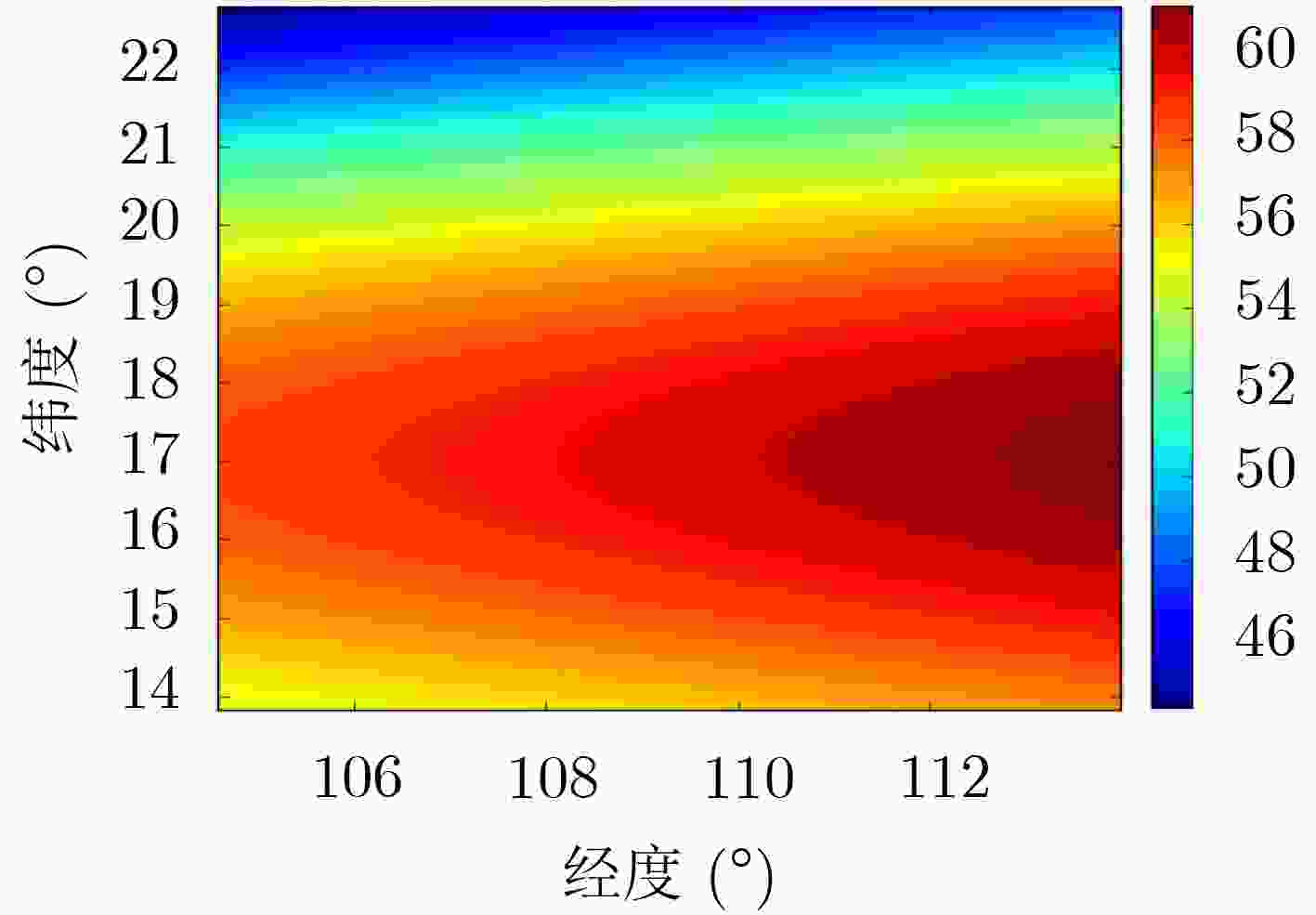
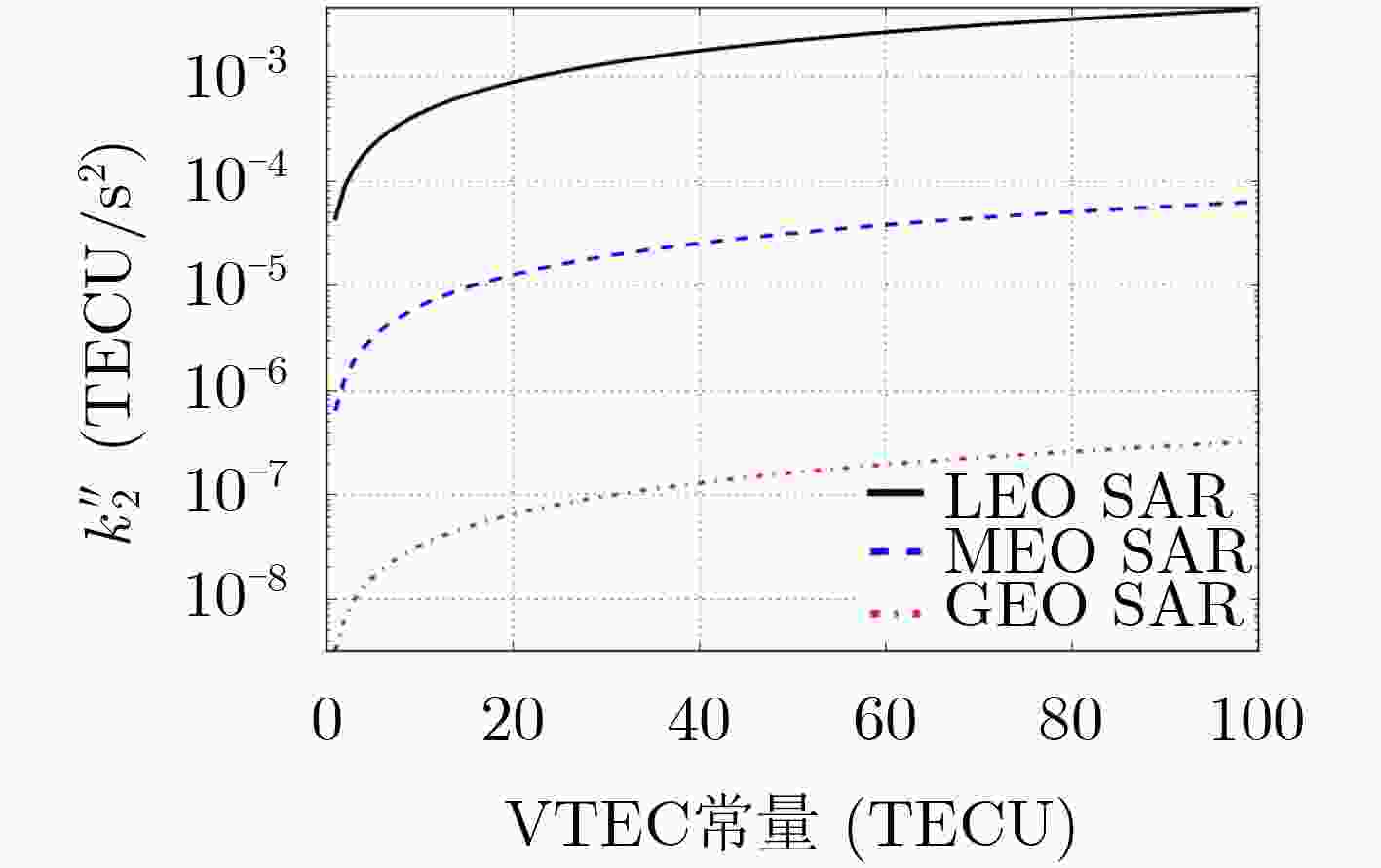
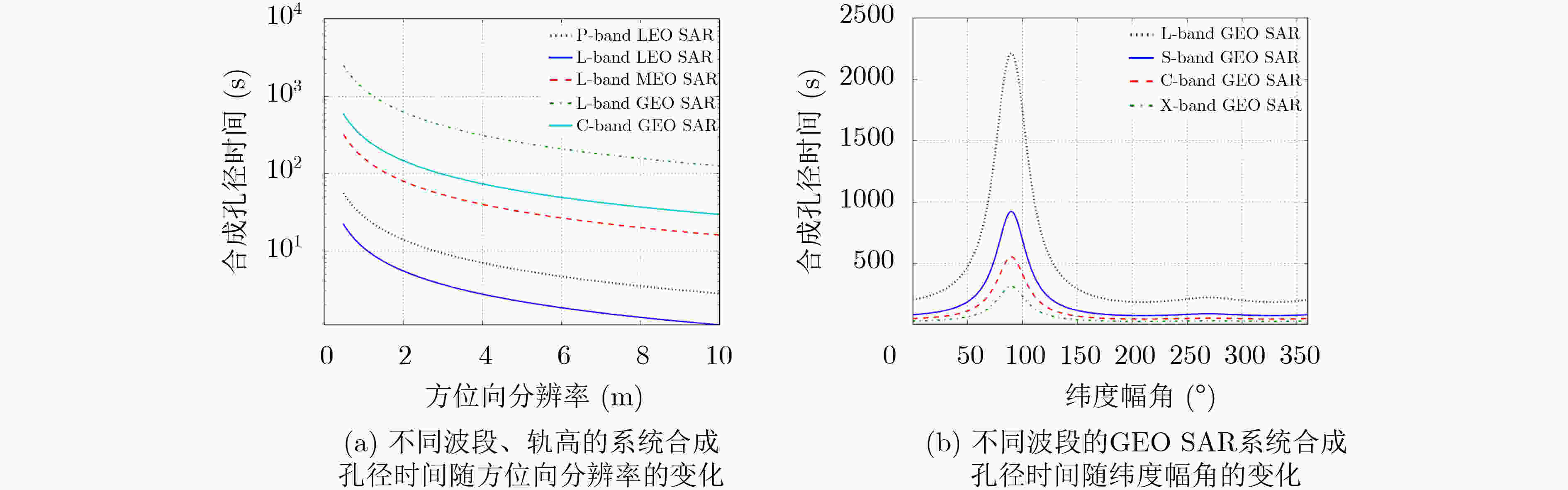



 下载:
下载:
