Beamforming Algorithm for MIMO-based Heterogeneous Networks with Hardware Impairments
-
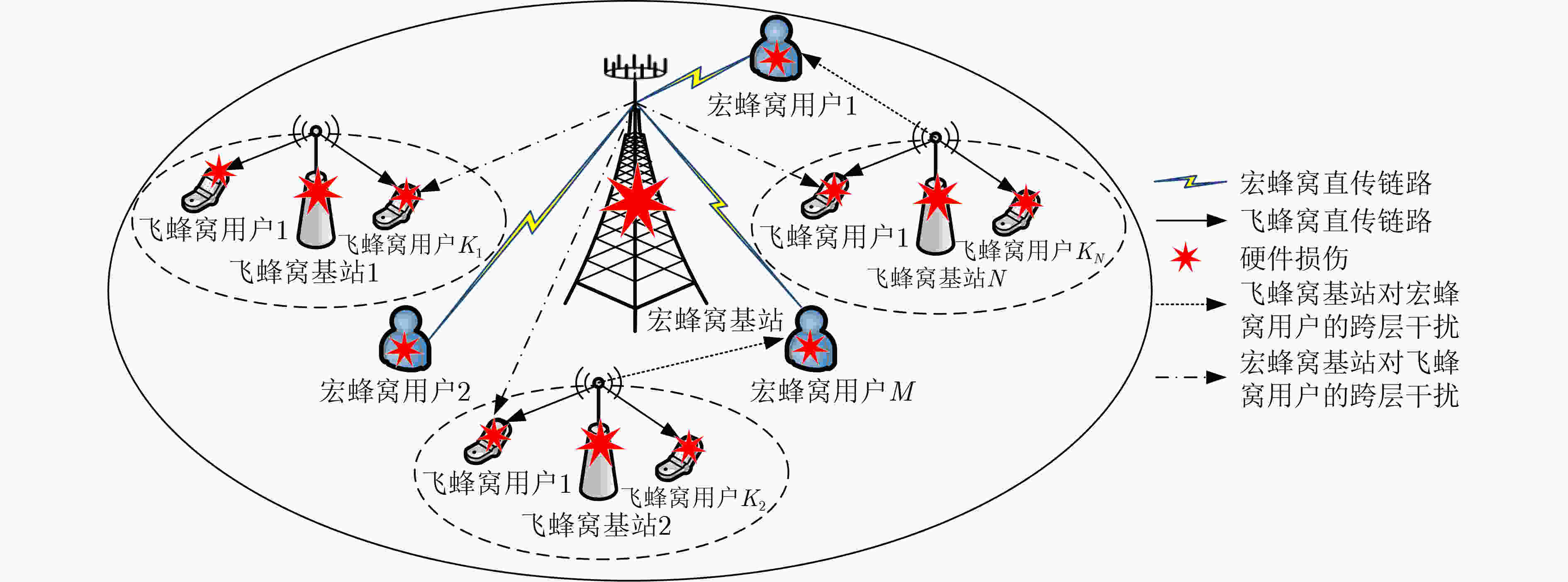
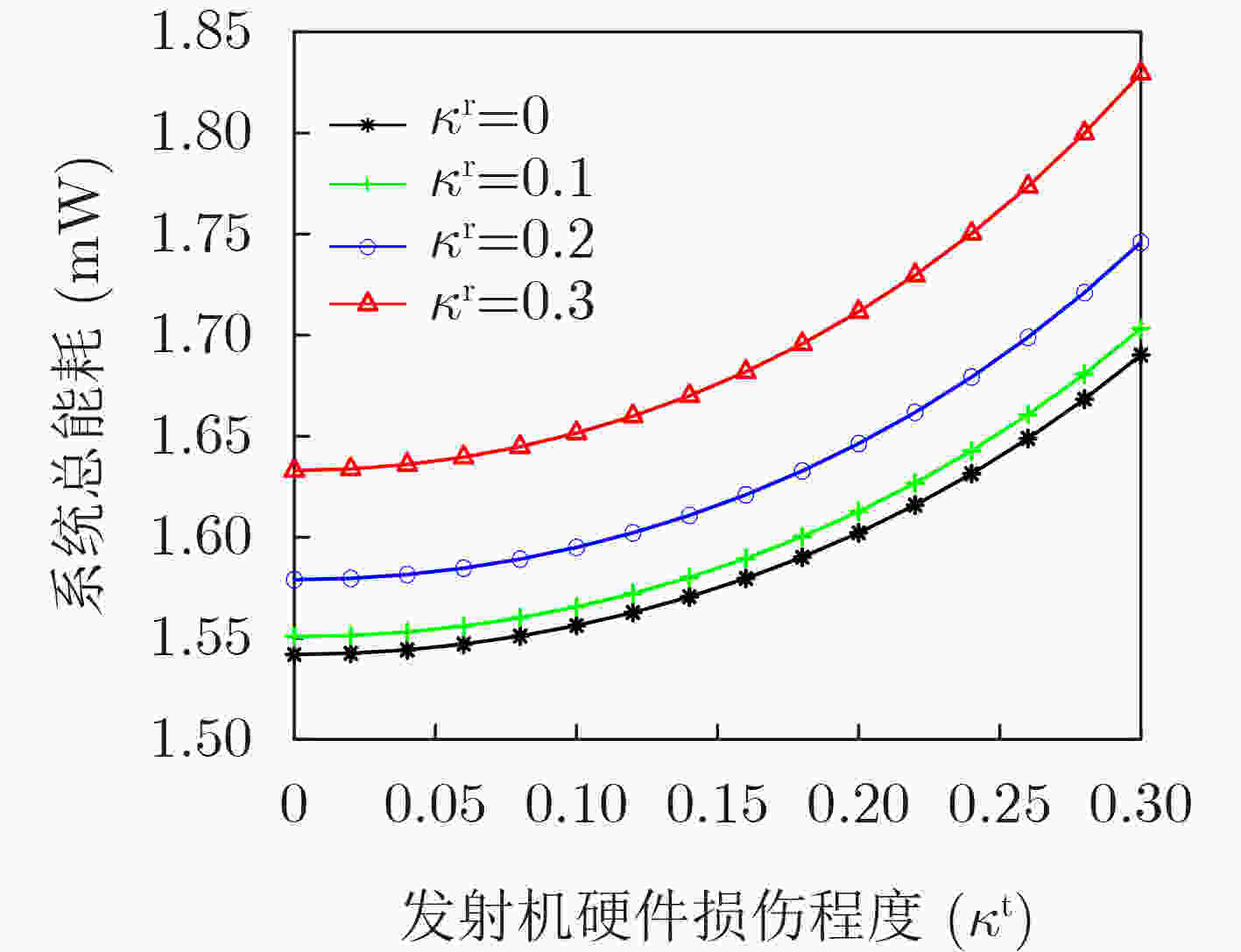
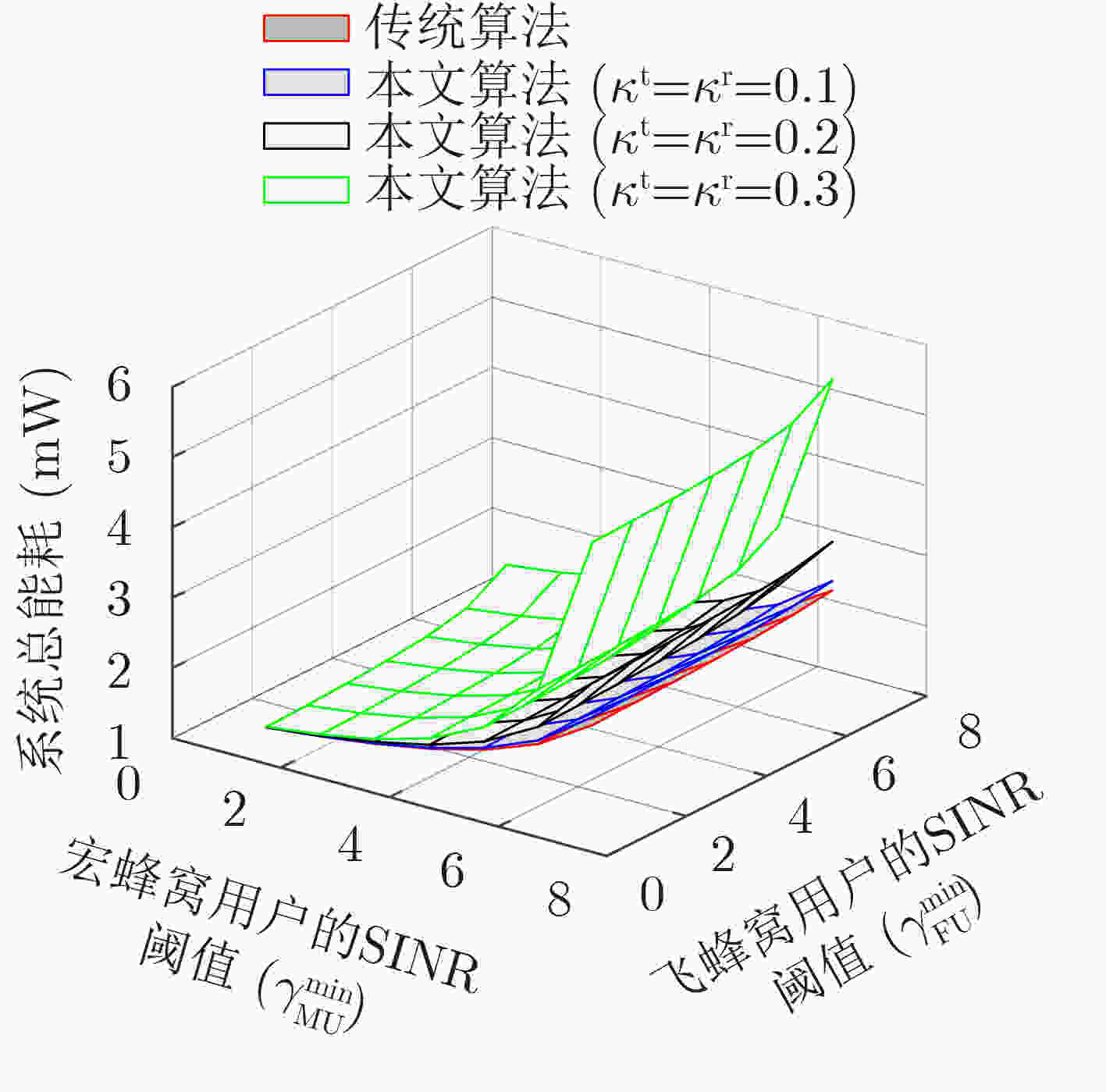
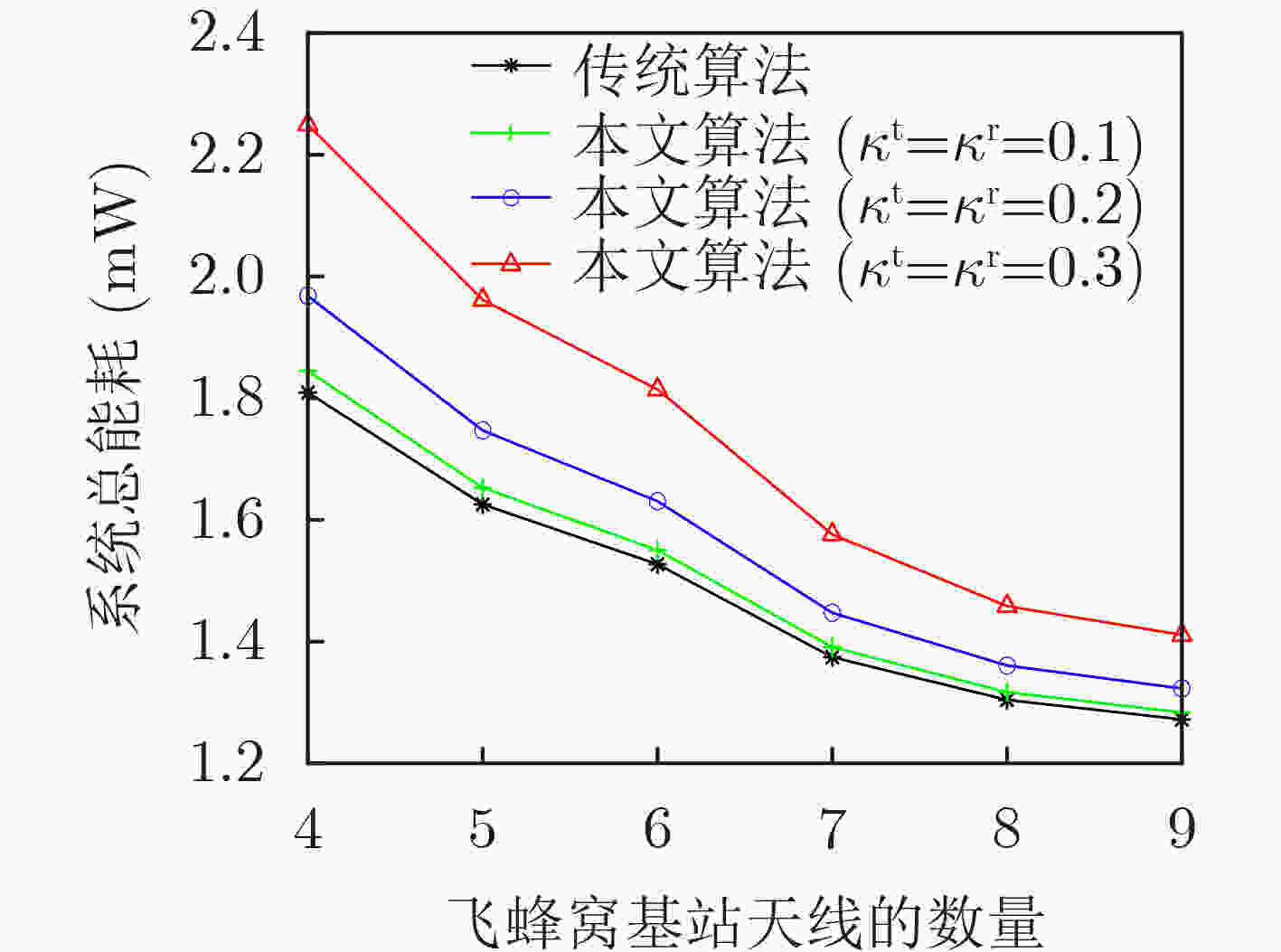
摘要: 由于多输入多输出(MIMO)异构网络能够提高系统容量和实现更多的用户接入,因此受到了学术界和工业界的广泛关注,从而成为下一代通信系统的关键技术之一。然而,由于放大器非线性、相位噪声和I/Q不均衡等因素的影响,这类硬件损伤成为制约当前MIMO异构网络波束成形性能进一步提升的瓶颈。为了解决该问题,该文提前将硬件损伤考虑到MIMO异构网络波束成形算法设计当中。首先,考虑了每个基站的最大发射功率约束和每个用户的最小信干噪比约束,建立了一个含硬件损伤参数的系统总能耗最小的资源优化问题。其次,利用等价变换和半正定松弛方法,将原非凸问题转化为凸优化问题进行求解。仿真结果表明,与完美硬件条件下的波束成形算法对比,所提算法具有较好的抗硬件损伤能力和较低的中断概率。Abstract: Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO)-based Heterogeneous Network (HetNet) can improve system capacity and achieve more connectivity, which is dramatically concerned by academia and industry. Therefore, it becomes one of the key technologies in the next-generation communication system. However, due to the effect of factors such as amplifier nonlinearities, phase noise, and I/Q imbalance, these impairments become the bottlenecks for further improving the performance of beamforming in MIMO-based HetNets. In order to solve this problem, this paper studies the beamforming design in MIMO-based HetNets by considering hardware impairments ahead of time. Firstly, the resource allocation problem is formulated as the total transmit power minimization of the system with hardware impairments under the constraints of the maximum transmit power of each base station and the minimum signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio of each user. Then, the original non-convex problem is transformed into an equivalent convex optimization problem by using the methods of the equivalent transformation and the semidefinite programming relaxation. Simulation results verify that the proposed algorithm has a low outage probability and can overcome the impact of hardware impairments by comparing it with the traditional beamforming algorithm with perfect hardware.
-
表 1 仿真参数
参数 值 参数 值 $ {P^{\max }}({\text{W}}) $ 10 $ P_n^{\max }({\text{W}}) $ 0.1 ${ {{P} }_{\text{C} } }({\text{mW} })$ 1 $ \gamma _m^{\min } $ 1 $ \gamma _{n,k}^{\min } $ 1 $ \zeta $ 5 $ {\delta ^2}({\text{W}}) $ 10-8 $ M $ 2 $ N $ 2 $ {K_1},{K_2} $ 2 -
[1] 徐勇军, 彭瑶, 余晓磊, 等. 面向5G协作通信系统的资源分配技术综述[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 31(2): 143–157. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.02.001XU Yongjun, PENG Yao, YU Xiaolei, et al. Survey on resource allocation techniques for 5G cooperative communication networks[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 31(2): 143–157. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.02.001 [2] 李国权, 徐勇军, 陈前斌. 基于干扰效率多蜂窝异构无线网络最优基站选择及功率分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 957–964. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190419LI Guoquan, XU Yongjun, and CHEN Qianbin. Interference efficiency-based base station selection and power allocation algorithm for multi-cell heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 957–964. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190419 [3] NGUYEN L D, TUAN H, DUONG T Q, et al. Downlink beamforming for energy-efficient heterogeneous networks with massive MIMO and small cells[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(5): 3386–3400. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2811472 [4] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [5] STUDER C, WENK M, and BURG A. MIMO transmission with residual transmit-RF impairments[C]. Proceedings of 2010 International ITG Workshop on Smart Antennas (WSA), Bremen, Germany, 2010: 189–196. [6] ZHANG Jiayi, XUE Xipeng, BJÖRNSON E, et al. Spectral efficiency of multipair massive MIMO two-way relaying with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(1): 14–17. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2017.2750162 [7] TLEBALDIYEVA L, MAHAM B, and TSIFTSIS T A. Capacity analysis of device-to-device mmWave networks under transceiver distortion noise and imperfect CSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(5): 5707–5712. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2983417 [8] BALLTI E, GUIZANI M, HAMDAOUI B, et al. Aggregate hardware impairments over mixed RF/FSO relaying systems with outdated CSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(3): 1110–1123. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2776261 [9] SHARMA P K and UPADHYAY P K. Cognitive relaying with transceiver hardware impairments under interference constraints[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(4): 820–823. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2533500 [10] SOLANKI S, UPADHYAY P, DA COSTA D B, et al. Joint impact of RF hardware impairments and channel estimation errors in spectrum sharing multiple-relay networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(9): 3809–3824. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2832623 [11] LI Xingwang, LI Jingjing, LIU Yuanwei, et al. Residual transceiver hardware impairments on cooperative NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(1): 680–695. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2947670 [12] BJÖRNSON E, HOYDIS J, KOUNTOURIS M, et al. Massive MIMO systems with non-ideal hardware: Energy efficiency, estimation, and capacity limits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(11): 7112–7139. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2354403 [13] ZHU Jun, NG D W K, WANG Ning, et al. Analysis and design of secure massive MIMO systems in the presence of hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(3): 2001–2016. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2659724 [14] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A, CLERCKX B, and RATNARAJAH T. Rate-splitting to mitigate residual transceiver hardware impairments in massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(9): 8196–8211. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2691014 [15] BOSHKOVSKA E, NG D W K, DAI Linglong, et al. Power-efficient and secure WPCNs with hardware impairments and non-linear EH circuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(6): 2642–2657. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2783628 [16] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A K and RATNARAJAH T. Downlink MIMO HCNs with residual transceiver hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(10): 2023–2026. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2593480 [17] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A and RATNARAJAH T. Toward a realistic assessment of multiple antenna HCNs: Residual additive transceiver hardware impairments and channel aging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(10): 9061–9073. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2710188 [18] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A, RATNARAJAH T, KOURTESSIS P, et al. Nuts and bolts of a realistic stochastic geometric analysis of mmWave HetNets: Hardware impairments and channel aging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5657–5671. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2908044 [19] DAMNJANOVIC A, MONTOJO J, WEI Yongbin et al. A survey on 3GPP heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2011, 18(3): 10–21. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2011.5876496 [20] FANG Fang, CHENG Julian, and DING Zhiguo. Joint energy efficient subchannel and power optimization for a downlink NOMA heterogeneous network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(2): 1351–1364. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2881314 [21] SHENG Min, WANG Liang, WANG Xijun, et al. Energy efficient beamforming in MISO heterogeneous cellular networks with wireless information and power transfer[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(4): 954–968. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2544538 [22] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [23] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019 [24] WANG Kunyu, SO A M C, CHANG T H, et al. Outage constrained robust transmit optimization for multiuser MISO downlinks: Tractable approximations by conic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5690–5705. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2354312 [25] CHU Zheng, ZHU Zhengyu, JOHNSTON M, et al. Simultaneous wireless information power transfer for MISO secrecy channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(9): 6913–6925. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2499439 -





 下载:
下载:
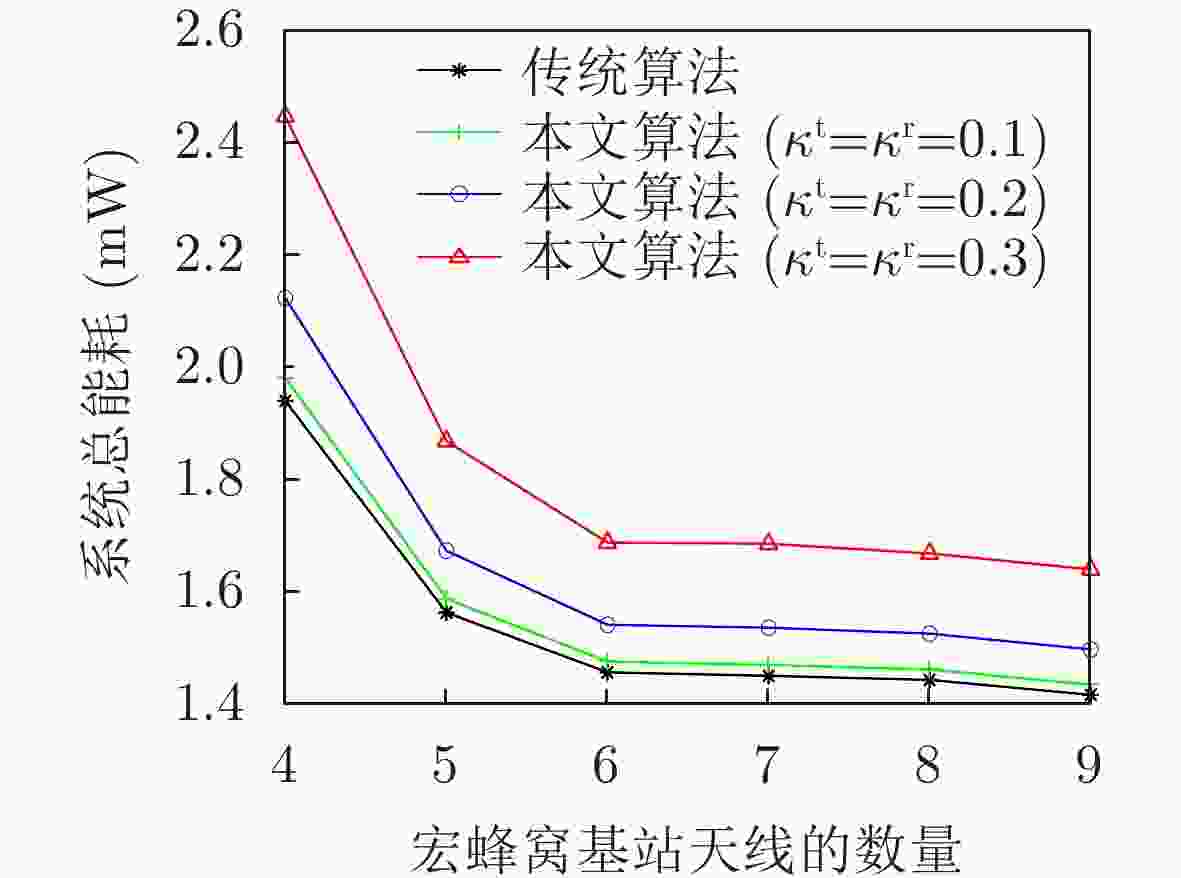
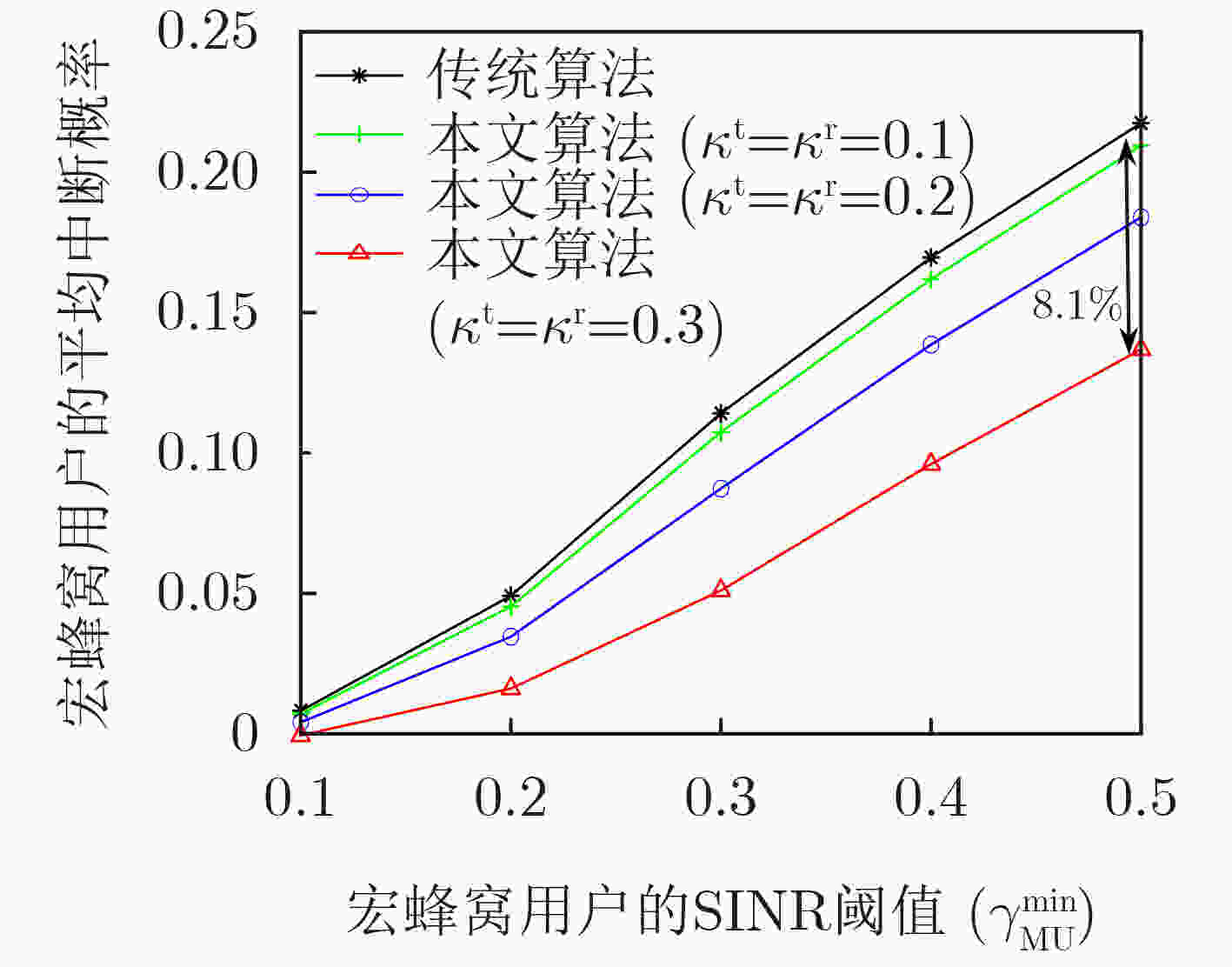

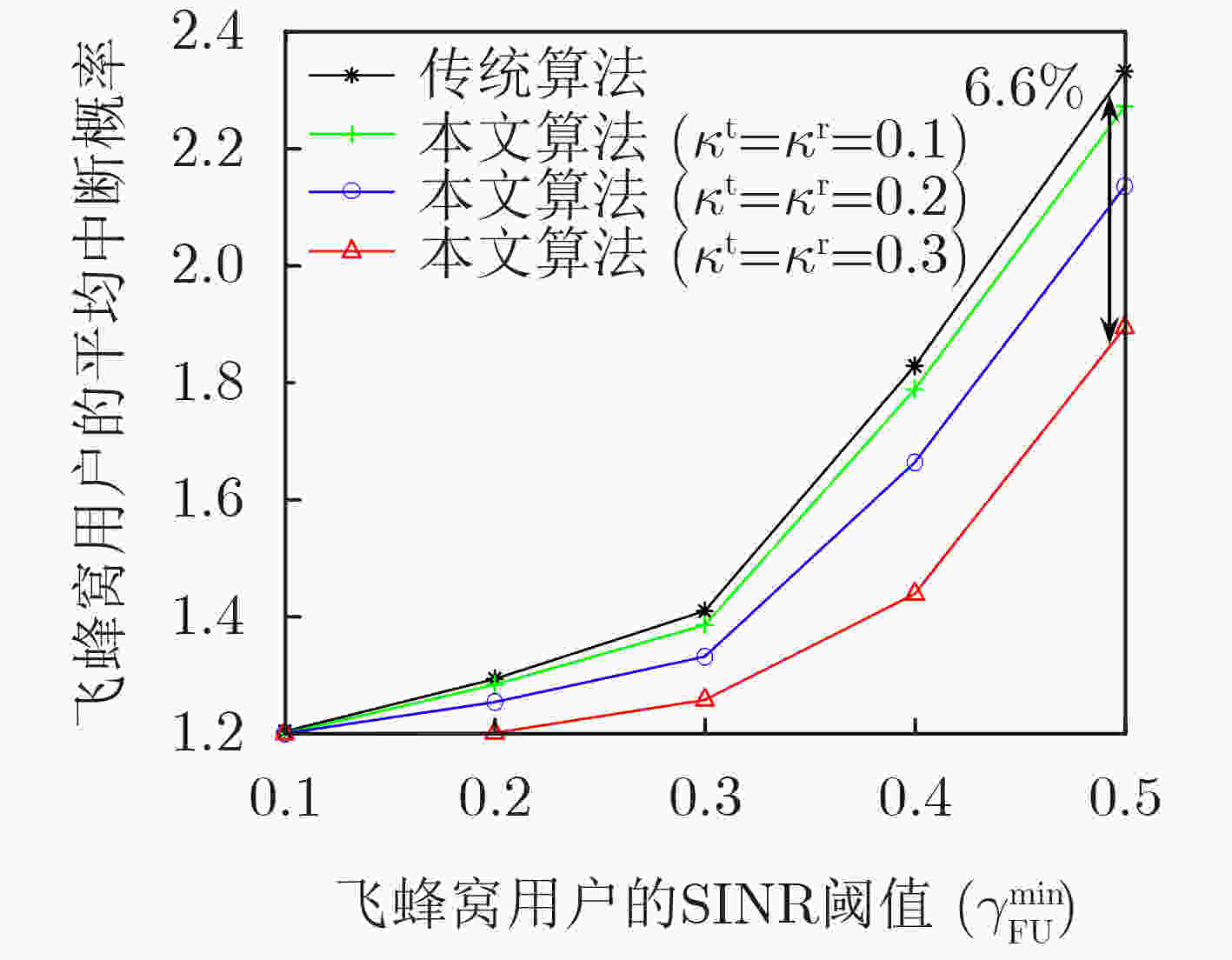



 下载:
下载:
