Wind Speed Estimation Method of Low-altitude Wind Shear Based on CL-KA-STAP in Complex Terrain Environment
-
摘要: 针对机载气象雷达在复杂的地形环境下探测低空风切变时,地杂波呈现的非均匀特征导致难以准确获得杂波统计特性,进而影响杂波抑制效果,使得风切变风速估计不准的问题,该文提出一种色加载知识辅助STAP(CL-KA-STAP)的低空风切变风速估计方法。该方法首先构造降维联合时空变换矩阵,并对待检测距离单元的回波信号进行降维处理,然后将由数字高程模型(DEM)和国家土地覆盖数据库(NLCD)获取的先验知识融入到组合空时主通道自适应处理器(CMCAP)中,构造色加载系数优化函数求解色加载系数,最后构造滤波器,实现杂波自适应滤波并准确估计风速。后续仿真结果证明了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: When the airborne weather radar detects low-altitude wind shear in a complex terrain environment, the non-uniform characteristics of ground clutter make it difficult to accurately obtain clutter statistical characteristics, which in turn affects the clutter suppression effect, and makes the wind speed estimation of wind shear inaccurate. A Colored-Loading Knowledge-Aided STAP (CL-KA-STAP) wind speed estimation method of low-altitude wind shear is proposed. This method first constructs a dimensionality reduction joint space-time transformation matrix, and performs dimensionality reduction processing on the echo signal of the distance unit to be detected, and then integrates the prior knowledge obtained by the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and the National Land Cover Database (NLCD) into the combined space. In the Combined space-time Main Channel Adaptive Processor (CMCAP), the color loading coefficient optimization function is constructed to solve the color loading coefficient, and finally the filter is constructed to realize the adaptive filtering of clutter and accurately estimate the wind speed. The subsequent simulation results prove the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 不同地貌类型的参数值
编码 地貌类型 ${\sigma _{\rm{c}}}$ $\rho $ $\chi $ ${\beta _0}$ ${{\rm{La}}_1}$ 农田 1 0.004000 ${{\pi} } /2$ 0.200 ${{\rm{La}}_2}$ 丘陵 1 0.012600 ${\rm{\pi} } /2$ 0.400 ${{\rm{La}}_3}$ 高山 1 0.040000 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.500 ${{\rm{La}}_4}$ 泥地 1 0.001945 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.155 ${{\rm{La}}_5}$ 雪地 1 0.002630 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.170 ${{\rm{La}}_6}$ 草地 1 0.005720 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.240 ${{\rm{La}}_7}$ 庄稼地 1 0.007440 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.280 ${{\rm{La}}_8}$ 树林 1 0.009160 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.320 ${{\rm{La}}_9}$ 裸石地 1 0.010880 ${{\pi}} /2$ 0.360 表 2 飞机与雷达参数
参数 值 参数 值 载机高度(m) 600 阵元数 8 载机速度(m/s) 75 采样脉冲数 64 雷达波长(m) 0.032 主瓣方向(°) (90, 0) 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 7000 杂噪比(dB) 40 距离分辨率(m) 150 信噪比(dB) 5 表 3 不同风速估计方法结果对比
样本数 风速估计方法 均方根误差(m/s) 0.5系统自由度 空时最优 17.5174 CMCAP 14.8567 本文方法CL-KA-STAP 1.8328 0.25系统自由度 EFA 14.8756 FA 6.0765 本文方法CL-KA-STAP 1.9073 表 4 不同误差情况下
${\alpha _{\rm{CPW}}}$ 的取值不同误差情况 0.5系统自由度
${\alpha _{\rm{CPW}}}$取值0.25系统自由度
${\alpha _{\rm{CPW}}}$取值0 0.6854 0.6749 0.1 0.4312 0.5213 0.3 0.2155 0.2432 0.5 0.0902 0.1059 -
[1] DESHPANDE M D and STATON L. Determination of windspeed within a weather storm using airborne Doppler radar[C]. IEEE Southeastcon’91, Williamsburg, USA, 1991: 508–519. doi: 10.1109/SECON.1991.147807. [2] LAI Y C and BAXA E G. On the application of the LMS-based adaptive noise canceller in nonstationary environment associated with airborne Doppler weather radar[C]. 1993 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Minneapolis, USA, 1993, 3: 25–28. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1993.319426. [3] BAXA E J. Signal processing techniques for clutter filtering and wind shear detection[R]. NASA Report N91–24154, 1990. [4] WARD J. Space-time adaptive processing for airborne radar[R]. Report of Lincoln Laboratory, Lexington, MA, USA, 1998. [5] 吴仁彪, 张彪, 李海, 等. 基于空时自适应处理的低空风切变风速估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(3): 631–636. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140697WU Renbiao, ZHANG Biao, LI Hai, et al. Wind speed estimation for low-attitude windshear based on space-time adaptive processing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(3): 631–636. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140697 [6] 李海, 周盟, 陈筱浅, 等. 基于多通道联合自适应处理的微下击暴流中心风速估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1619–1625. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161094LI Hai, ZHOU Meng, CHEN Xiaoqian, et al. Multiple Doppler channels joint adaptive processing based central wind speed estimation for microburst[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1619–1625. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161094 [7] 李海, 王杰. 基于CMCAP的低空风切变风速估计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(3): 529–533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.03.10LI Hai and WANG Jie. Low-altitude wind-shear wind speed estimation based on CMCAP[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(3): 529–533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.03.10 [8] MELVIN W, WICKS M, ANTONIK P, et al. Knowledge-based space-time adaptive processing for airborne early warning radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 1998, 13(4): 37–42. doi: 10.1109/62.666835 [9] CAPRARO C T, CAPRARO G T, BRADARIC I, et al. Implementing digital terrain data in knowledge-aided space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 1080–1099. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248199 [10] RIEDL M and POTTER L C. Knowledge-aided Bayesian space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(4): 1850–1861. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2805141 [11] KANG Naixin, SHANG Zheran, and DU Qinglei. Knowledge-aided structured covariance matrix estimator applied for radar sensor signal detection[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(3): 664. doi: 10.3390/s19030664 [12] RIEDL M and POTTER L C. Multimodel shrinkage for knowledge-aided space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2601–2610. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2813898 [13] BERGIN J S, TEIXEIRA C M, TECHAU P M, et al. STAP with knowledge-aided data pre-whitening[C]. The 2004 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37509), Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 289–294. doi: 10.1109/NRC.2004.1316437. [14] LI Hai, WANG Jie, FAN Yi, et al. High-fidelity inhomogeneous ground clutter simulation of airborne phased array PD radar aided by digital elevation model and digital land classification data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): 2925. doi: 10.3390/s18092925 [15] BRINGI V N and CHANDRASEKAR V. Polarimetric, Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2005: 1–100. [16] BOYER E, LARZABAL P, ADNET C et al. Parametric spectral moments estimation for wind profiling radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(8): 1859–1868. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.813487 [17] 姚晖. 分布式信号源参数估计技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 解放军信息工程大学, 2013: 9–25.YAO Hui. Research on parameter estimation method for distributed sources[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], PLA Information Engineering University, 2013: 9–25. [18] 刘青光, 彭应宁, 孙欣, 等. 机载雷达自适应杂波抑制的联合通道变换方法[J]. 电子学报, 1994, 22(6): 1–9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1994.06.001LIU Qingguang, PENG Yingning, SUN Xin, et al. Adaptive clutter suppression in airborne radar by a combined channel transformation approach[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1994, 22(6): 1–9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1994.06.001 [19] 张圣鹋. 机载认知雷达中的KA-STAP研究[D]. [博士学位论文], 电子科技大学, 2017: 91–102.ZHANG Shenghu. Study on KA-STAP of the airborne cognitive radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017: 91–102. [20] MORCHIN W C. Airborne Early Warning Radar[M]. Fitchburg: Artech House, 1990: 20–100. [21] 乌拉比 F T, 穆尔 R K, 冯健超, 黄培康, 汪一飞, 译. 微波遥感-第二卷-雷达遥感和面目标的散射、辐射理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 1–50.ULABY F T, MOORE R K, FUNG A K, HUANG Peikang, WANG Yifei, translation. Microwave Remote Sensing. Volume II Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 1–50. [22] ZHU Xumin, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Knowledge-aided space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1325–1336. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751261 [23] 王晓明, 李军, 张圣鹋, 等. 基于稀疏恢复谱相似度的自适应样本筛选算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(5): 976–981. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.03WANG Xiaoming, LI Jun, ZHANG Shenghu, et al. Adaptive sample selection algorithm based on sparse recovery spectral similarity[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(5): 976–981. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.03 [24] 张圣鹋, 何子述, 李军, 等. 一种稳健的知识辅助STAP色加载系数优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 1942–1949. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151335ZHANG Shenghu, HE Zishu, LI Jun, et al. A robust colored-loading factor optimization approach for KA-STAP[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 1942–1949. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151335 -






 下载:
下载:
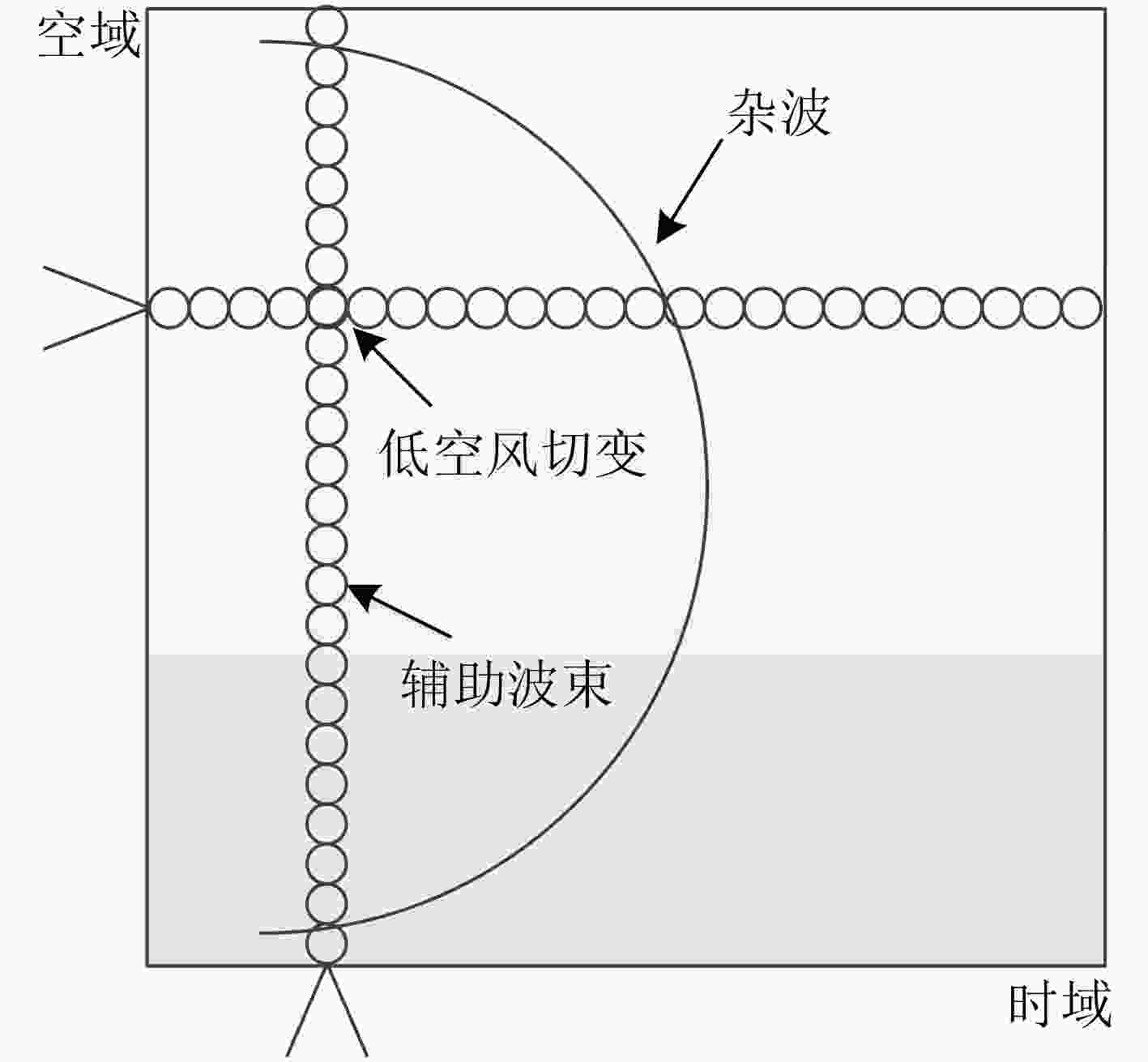
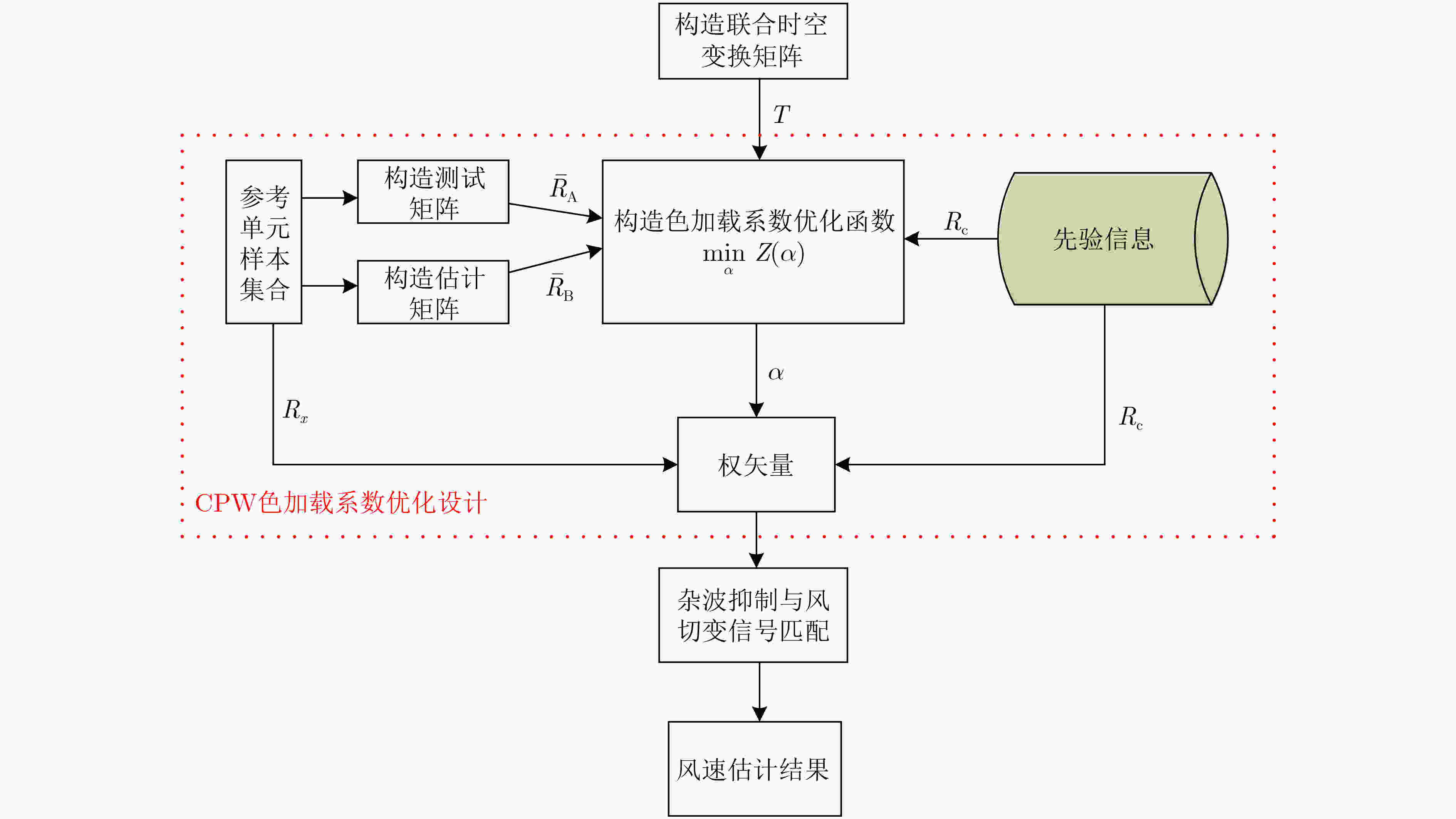
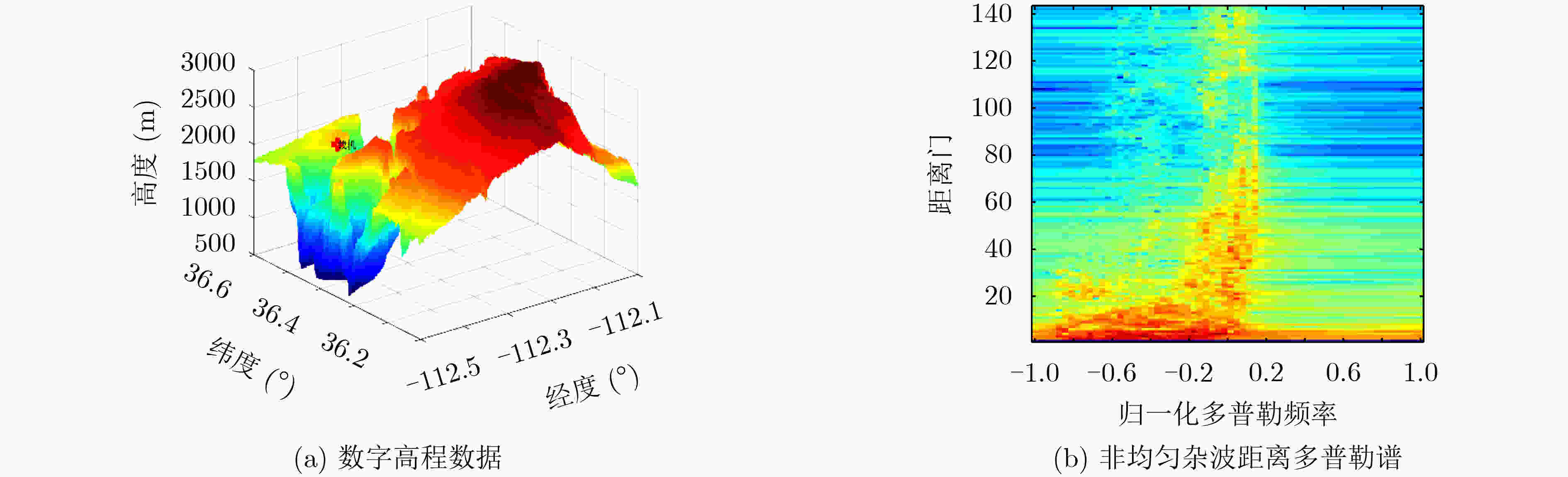
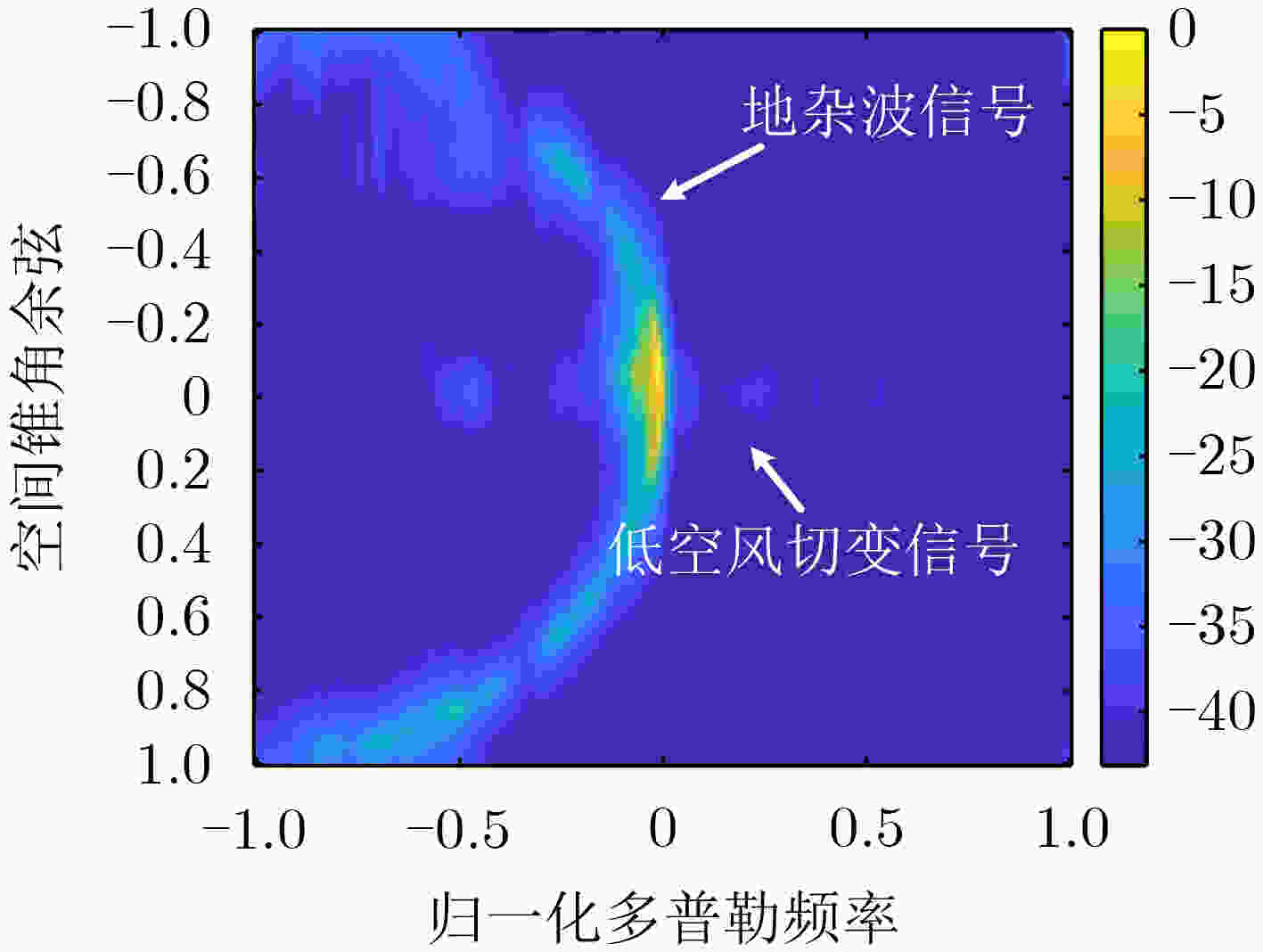
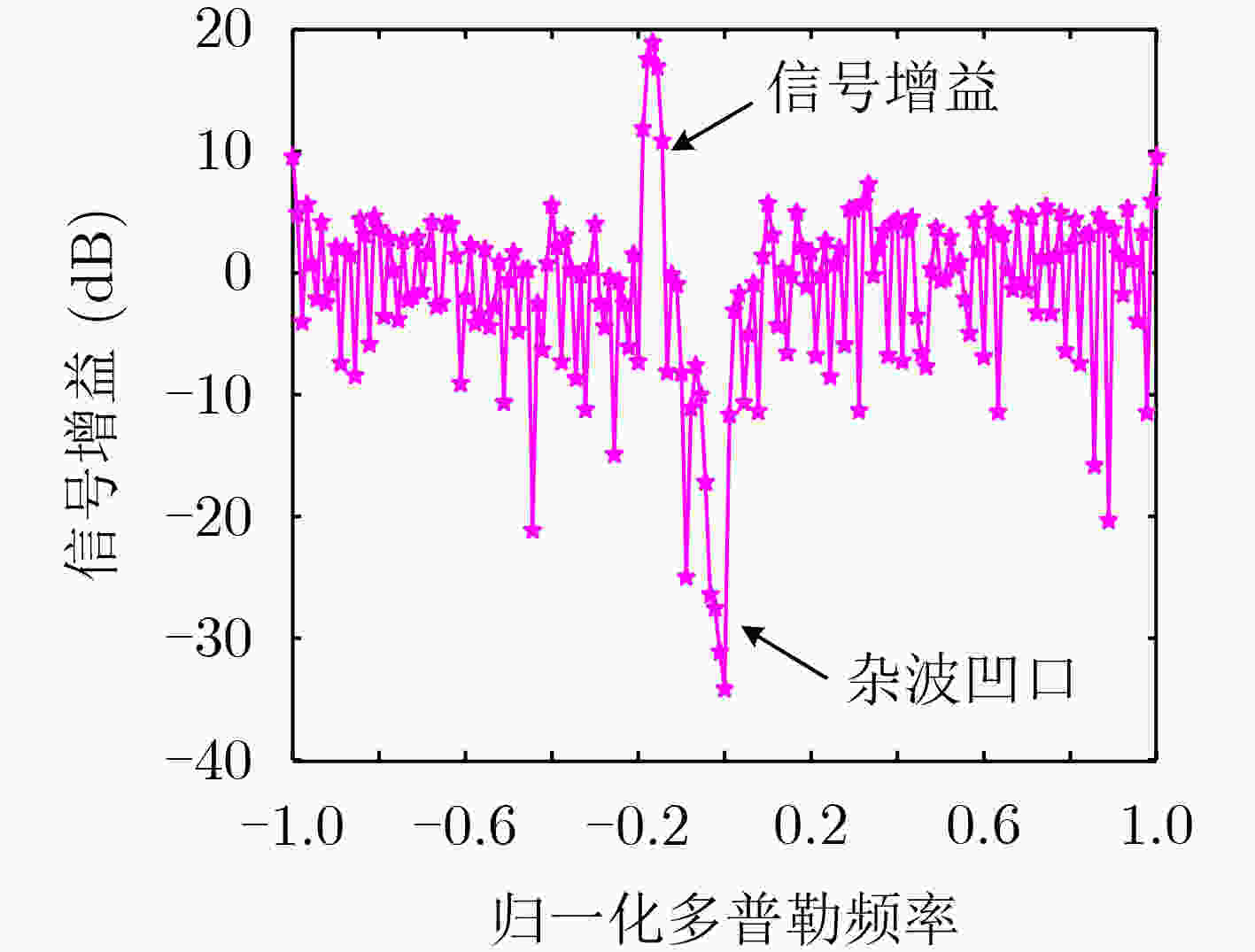
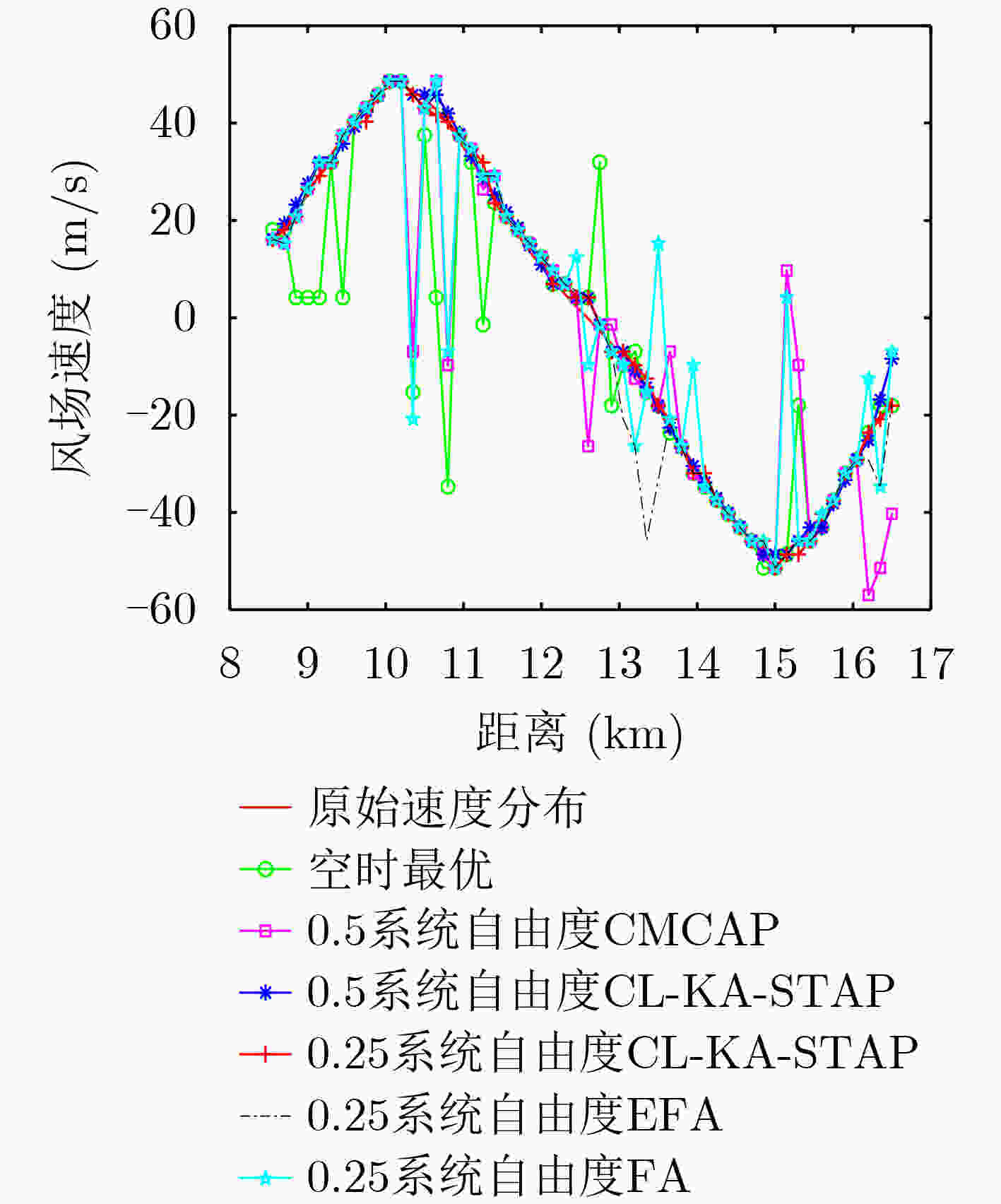
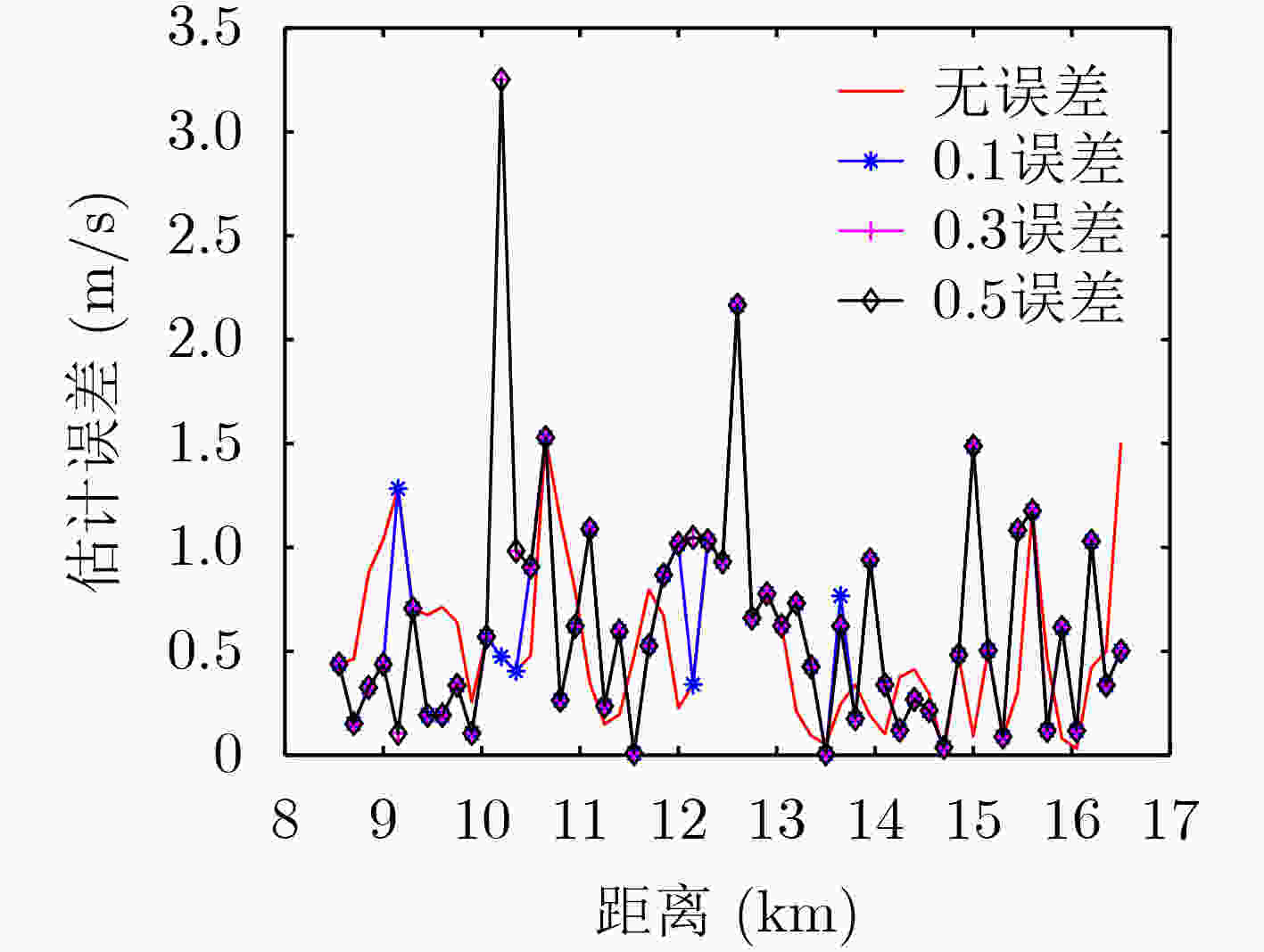



 下载:
下载:
