A Three-level Name Lookup Method Based on Deep Bloom Filter for Named Data Networking
-
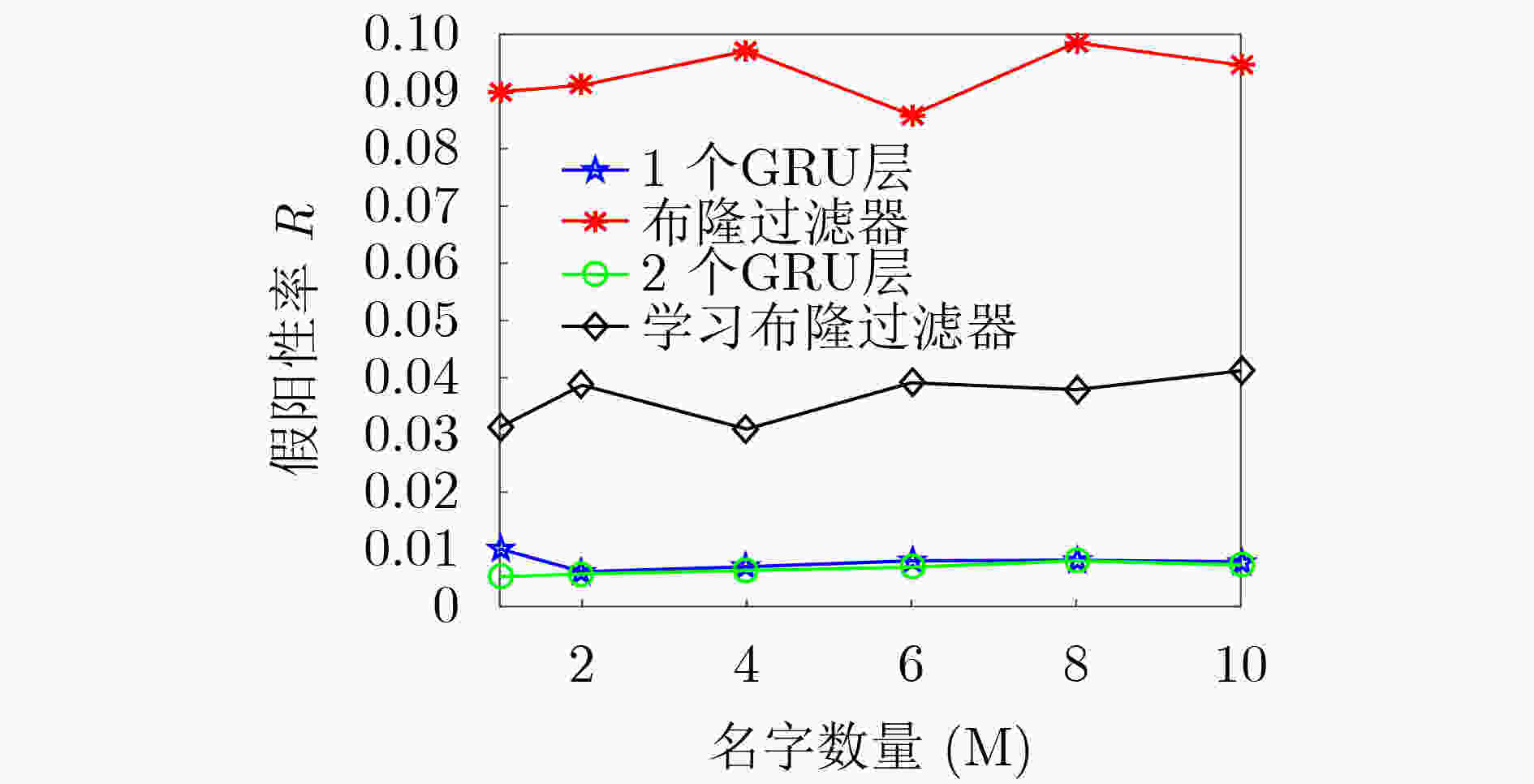
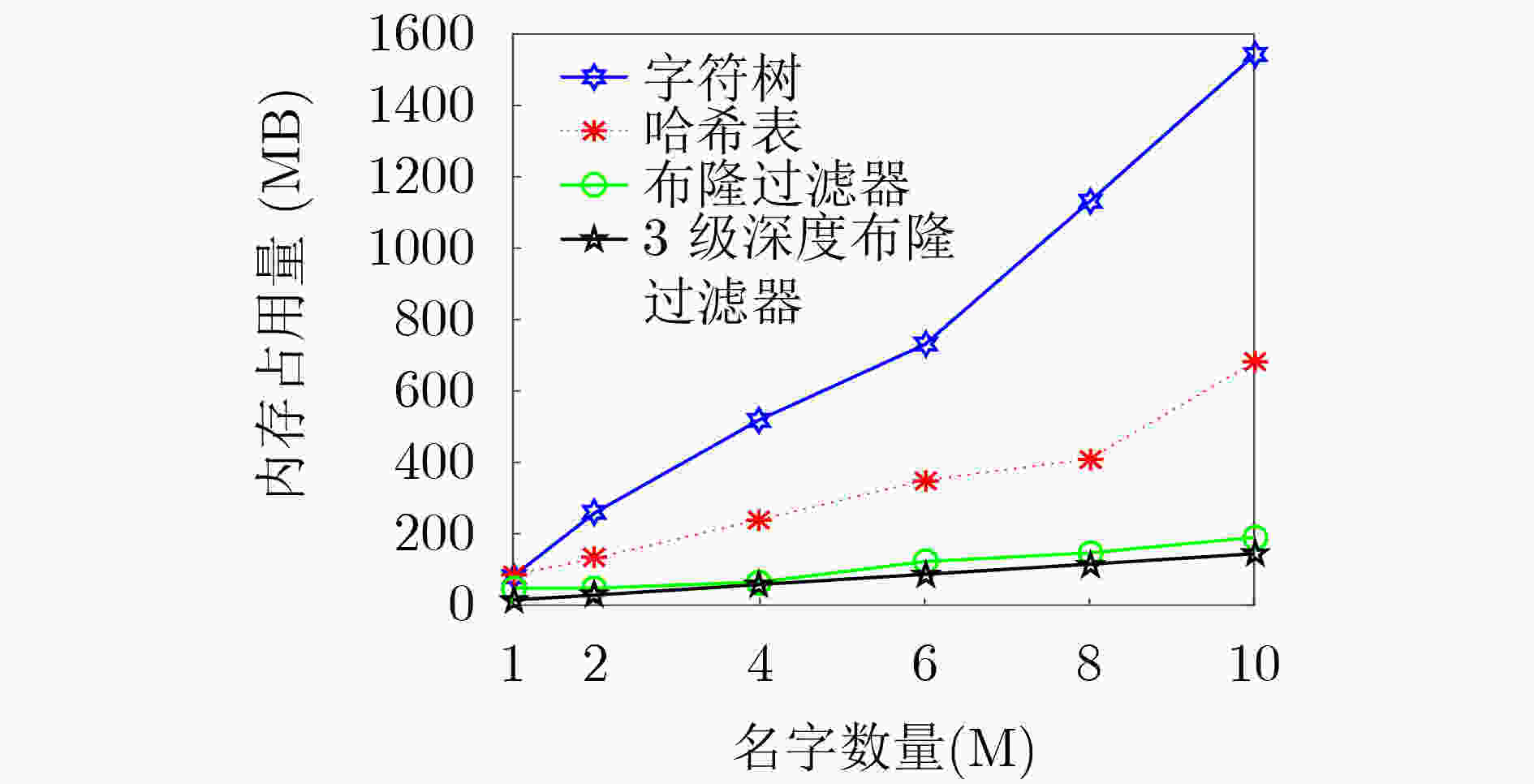
摘要: 为提高命名数据网络(Name Data Networking, NDN)路由过程中内容名字查找的效率,该文提出一种基于深度布隆过滤器的3级名字查找方法。该方法使用长短记忆神经网络(Long Short Term Memory, LSTM)与标准布隆过滤器相结合的方法优化名字查找过程;采用3级结构优化内容名字在内容存储器(Content Store, CS)、待定请求表(Pending Interest Table, PIT)中的精确查找过程,提高查找精度并降低内存消耗。从理论上分析了3级名字查找方法的假阳性率,并通过实验验证了该方法能够有效节省内存、降低查找过程的假阳性。Abstract: A three-level name lookup method based on deep Bloom filter is proposed to improve the searching efficiency of content name in the routing progress of the Named Data Networking (NDN). Firstly, in this method, the Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) is combined with standard Bloom filter to optimize the name searching progress. Secondly, a three-level structure is adopted to optimize the accurate content name lookup progresses in the Content Store (CS) and the Pending Interest Table (PIT) to promote lookup accuracy and reduce memory consumption. Finally, the error rate generated by content name searching method based on deep Bloom filter structure is analyzed in theory, and the experiment results prove that the proposed the three-level lookup structure can compress memory and decrease the error effectively.
-
表 1 面向深度布隆过滤器的名字查找算法
输入:内容集合S,非内容集合U,阈值$\tau $ 输出:内容名字x 1: 调用LSTM架构使用集合S和集合U获得一个集合D; 2: 查找x在初始过滤器中进行精确匹配; 3: while 对每一个$x \in S$ do 4: If b[i]=1 then 5: 将匹配内容x发送到深度学习模型中; 6: else 7: 将未匹配的x发送到FIB表中进行最长前缀匹配查找; 8: end while 9: if $(x, y) \in D $ then//在第2级深度学习模型中进行精确匹配查找 10: 计算$f(x)=\dfrac{1}{1+{ \rm{e} }^{-x} }$; 11: end if 12: if $x \in S $且$ f(x) < \tau $ then 13: 将查找获得的内容名x在路由表中对应的数据包进行转发; 14: else if $x \in S $且$f(x) < \tau $ then 15: 将未匹配的内容名字x发送到第3级备份过滤器进行查找; 16: while在备份布隆过滤器查找b[i]=1 do 17: 将查找获得的内容名x在路由表中对应的数据包进行转发; 18: end while 19: else 20: 将第3级未匹配的内容发送到FIB表中进行最长前缀匹配查找; 21: end if 表 2 服务器配置
主要模块 具体配置 主板 LENOVO-LNVNB161216 CPU Intel Core™ i7-9750H (6核,主频2.60 GHz) 内存 DDR4 8GB (内存频率 2667 MHz) 表 3 GRU和隐藏层参数配置与编号
配置编号 参数配置 配置编号 参数配置 配置编号 参数配置 I型 GRU大小=32,隐藏层大小=8 IV型 GRU大小=16,隐藏层大小=8 VII型 GRU大小=8,隐藏层大小=4 II型 GRU大小=32,隐藏层大小=4 V型 GRU大小=16,隐藏层大小=4 VIII型 GRU大小=4,隐藏层大小=4 III型 GRU大小=16,隐藏层大小=16 VI型 GRU大小=8,隐藏层大小=8 VIIII型 GRU大小=4,隐藏层大小=8 -
[1] 杨国威, 徐泓, 李丹, 等. 未来互联网体系结构研究现状与趋势[J]. 中国基础科学, 2018, 20(3): 32–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2018.03.006YANG Guowei, XU Hong, LI Dan, et al. Research status and trends of future internet architecture[J]. China Basic Science, 2018, 20(3): 32–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2018.03.006 [2] 黄韬, 刘江, 霍如, 等. 未来网络体系架构研究综述[J]. 通信学报, 2014, 35(8): 184–197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.08.023HUANG Tao, LIU Jiang, HUO Ru, et al. Survey of research on future network architectures[J]. Journal on Communications, 2014, 35(8): 184–197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.08.023 [3] YAO Haipeng, LI Mengnan, DU Jun, et al. Artificial intelligence for information-centric networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(6): 47–53. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1800734 [4] ZHANG Lixia, AFANASYEV A, BURKE J, et al. Named data networking[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2014, 44(3): 66–73. doi: 10.1145/2656877.2656887 [5] 伊鹏, 李根, 张震. 内容中心网络中能耗优化的隐式协作缓存机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 770–777. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170635YI Peng, LI Gen, and ZHANG Zhen. Energy optimized implicit collaborative caching scheme for content centric networking[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 770–777. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170635 [6] GRITTER M and CHERITON D R. An architecture for content routing support in the Internet[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems, San Francisco, USA, 2001: 4. [7] BARI M F, CHOWDHURY S R, AHMED R, et al. A survey of naming and routing in information-centric networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2012, 50(12): 44–53. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2012.6384450 [8] 许志伟, 陈波, 张玉军. 针对层次化名字路由的聚合机制[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(2): 381–398. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005572XU Zhiwei, CHEN Bo, and ZHANG Yujun. Hierarchical name-based route aggregation scheme[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(2): 381–398. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005572 [9] FREDKIN E. Trie memory[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1960, 3(9): 490–499. doi: 10.1145/367390.367400 [10] DHARMAPURIKAR S, KRISHNAMURTHY P, and TAYLOR D E. Longest prefix matching using bloom filters[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2006, 14(2): 397–409. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2006.872576 [11] TAN Yun and ZHU Shuhua. Efficient name lookup scheme based on hash and character trie in named data networking[C]. Proceedings of the 12th Web Information System and Application Conference, Ji’nan, China, 2015: 130–135. doi: 10.1109/WISA.2015.72. [12] KRASKA T, BEUTEL A, CHI E H, et al. The case for learned index structures[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.01208, 2020. [13] MITZENMACHER M. Optimizing learned bloom filters by sandwiching[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.01474, 2018. [14] LI Fu, CHEN Fuyu, WU Jianming, et al. Fast longest prefix name lookup for content-centric network forwarding[C]. Proceedings of the 8th ACM/IEEE Symposium on Architectures for Networking and Communications Systems, Austin, USA, 2012: 73–74. doi: 10.1145/2396556.2396569. [15] LI Dagang, LI Junmao, and DU Zheng. An improved trie-based name lookup scheme for named data networking[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communication, Messina, Italy, 2016: 1294–1296. [16] LEE J, SHIM M, and LIM H. Name prefix matching using bloom filter pre-searching for content centric network[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Application, 2016, 65: 36–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2016.02.008 [17] GOVINDARAJAN P, SOUNDARAPANDIAN R K, GANDOMI A H, et al. Classification of stroke disease using machine learning algorithms[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(3): 817–828. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04041-y [18] SUTSKEVER I, VINYALS O, and LE Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 3104–3112. [19] CHO K, VAN MËRRIENBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]. Proceedings of 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1724–1734. doi: 10.3115/v1/D14-1179. [20] BLOOM B H. Space/time trade-offs in hash coding with allowable errors[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1970, 13(7): 422–426. doi: 10.1145/362686.362692 [21] BRODER A and MITZENMACHER M. Network applications of bloom filters: A survey[J]. Internet Mathematics, 2004, 1(4): 485–509. doi: 10.1080/15427951.2004.10129096 [22] Blacklist[DB/OL]. http://squidguard.mesd.k12.or.us/blacklists.tgz.2020.7.5. [23] WANG Qianyu, WU Qingtao, ZHANG Mingchuan, et al. Learned bloom-filter for an efficient name lookup in information-centric networking[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Marrakesh, Morocco, 2019: 1–6. -





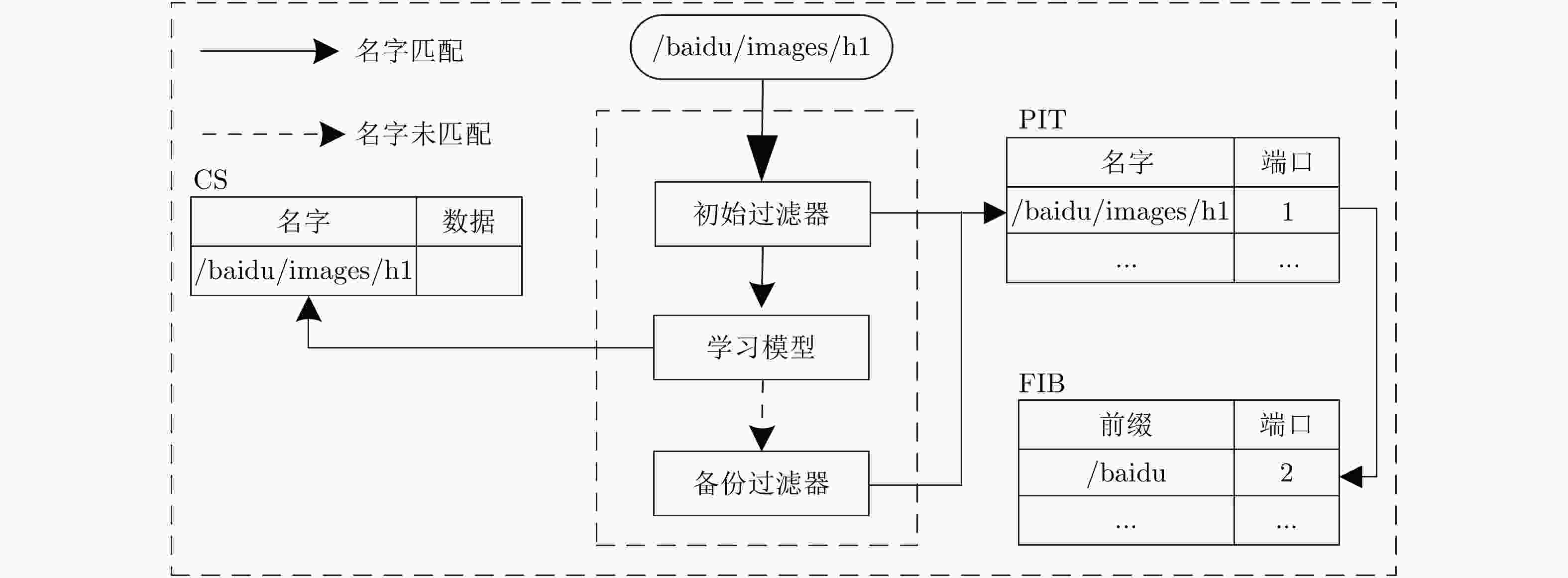
 下载:
下载:
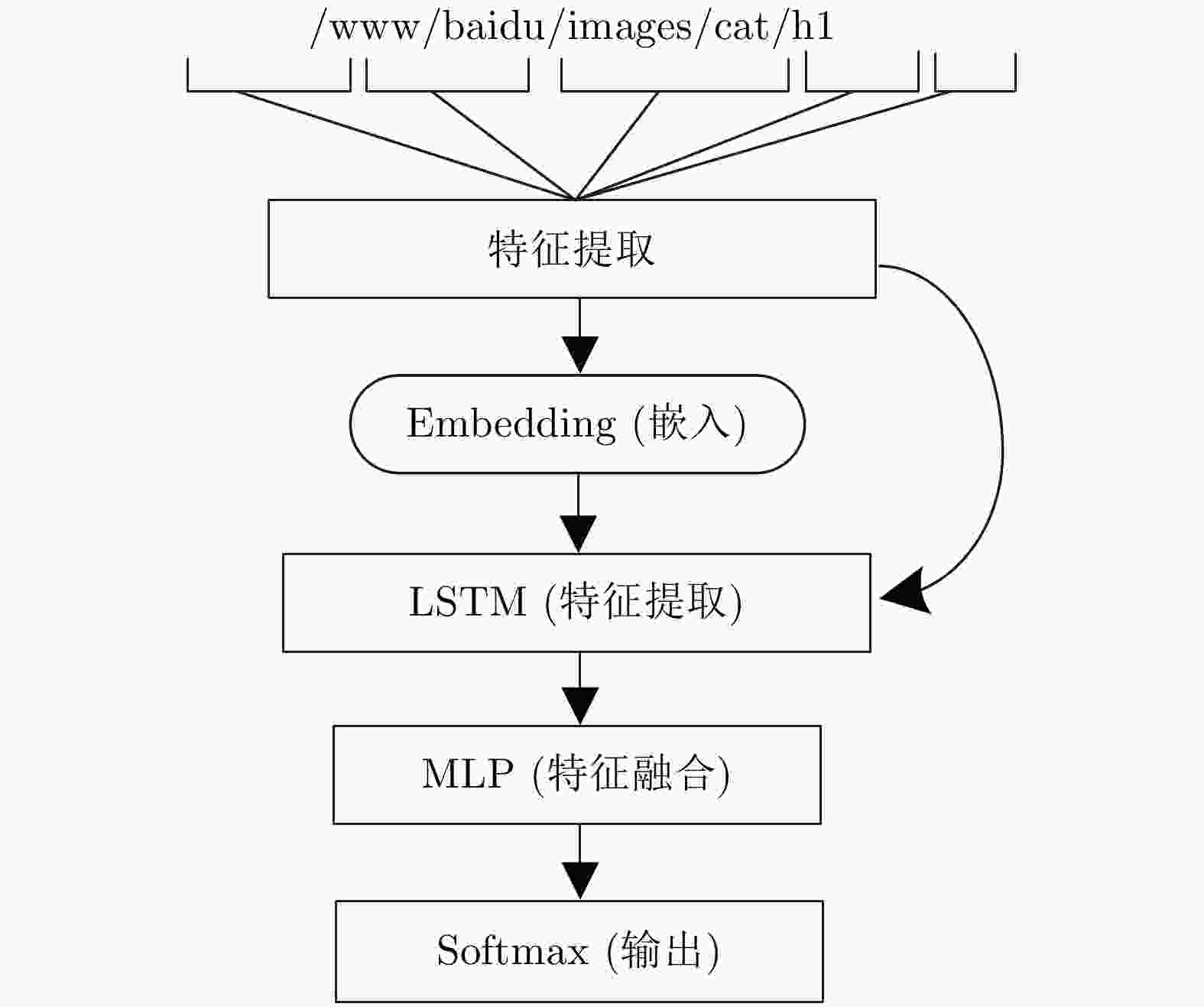
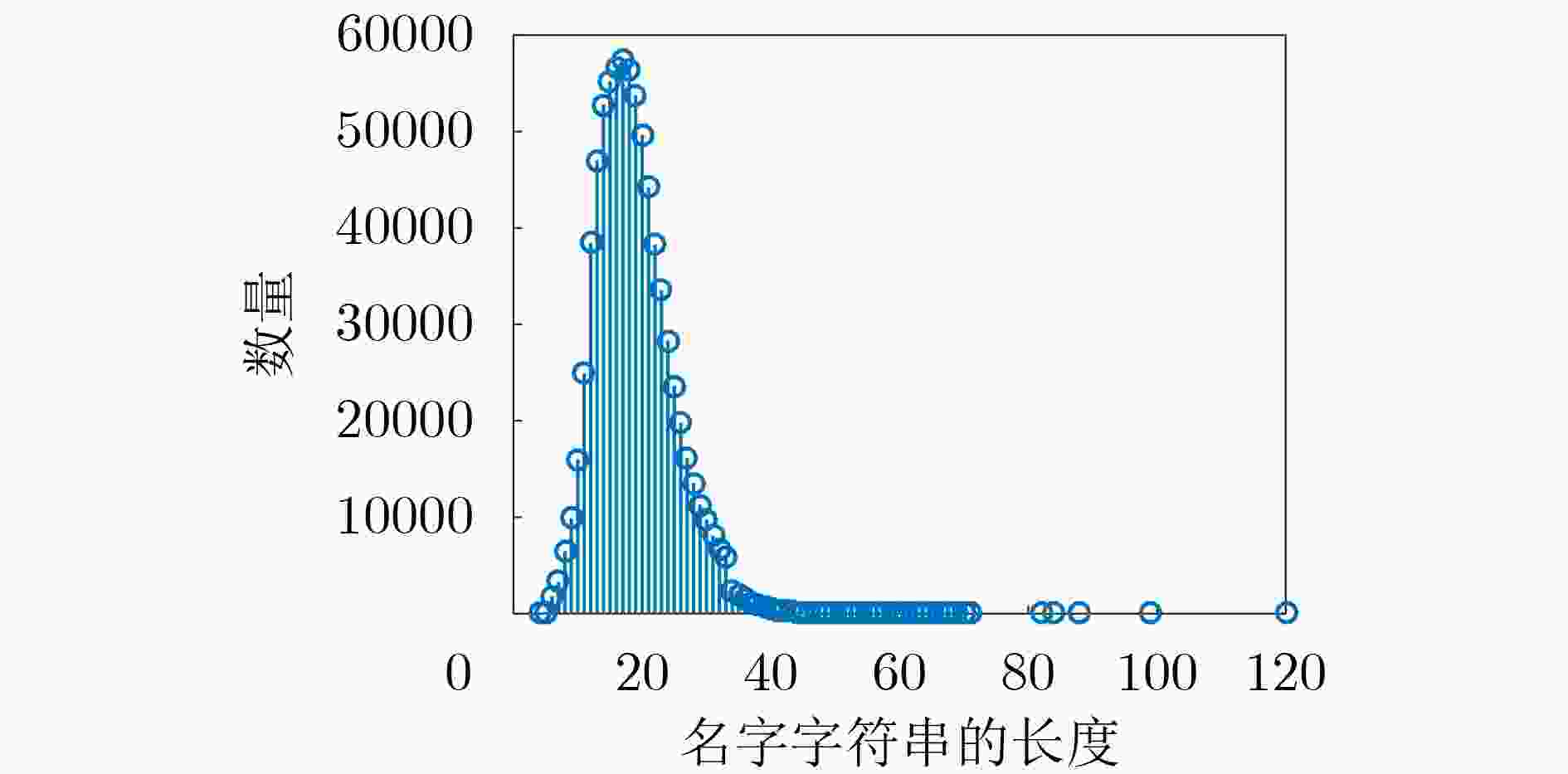

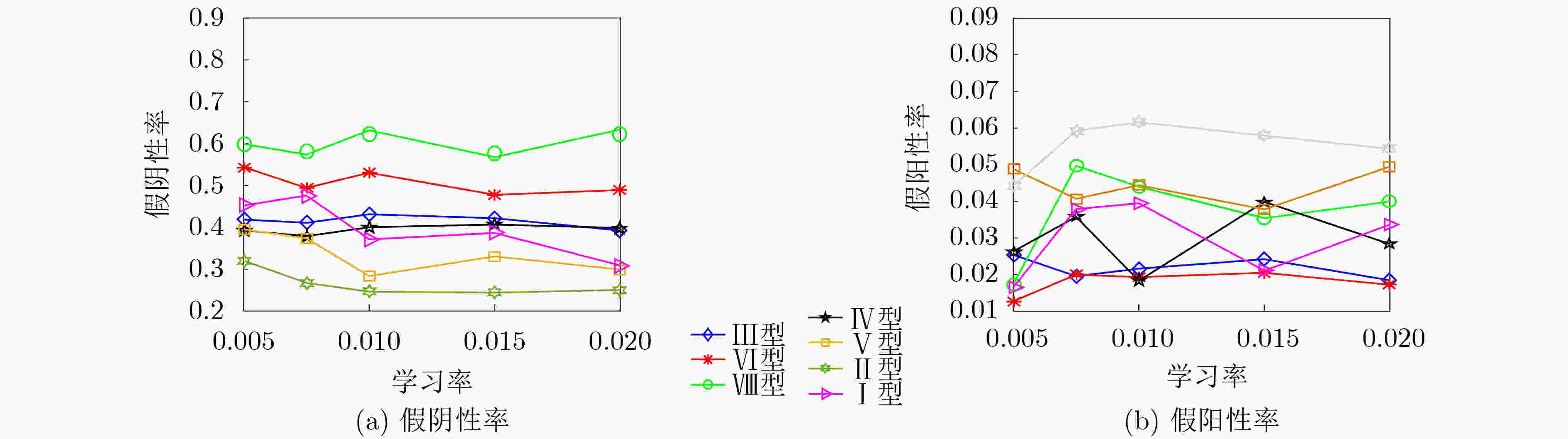



 下载:
下载:
