Cutset-type Possibilistic C-means Clustering Algorithms Based on Semi-supervised Information
-
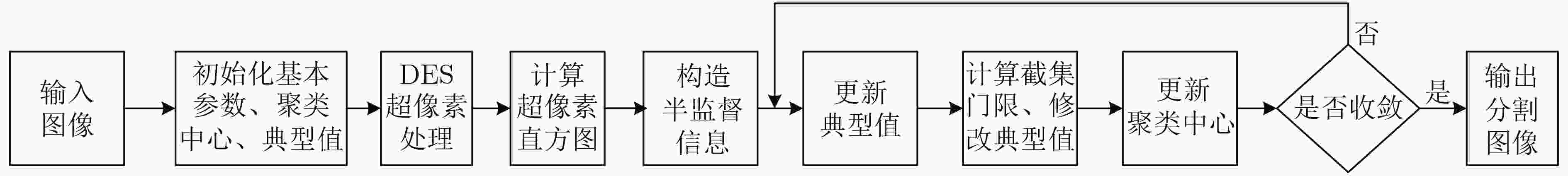
摘要: 截集式可能性C-均值(C-PCM)聚类算法将截集概念引入可能性C-均值(PCM)聚类算法中,明显改善了PCM的聚类中心重合问题,并能够对噪声和奇异点的数据进行有效聚类,但该聚类算法对小目标数据聚类时仍然存在聚类中心偏移的问题。针对此问题,该文将半监督学习机制引入C-PCM的目标函数中,通过部分先验信息来指导聚类过程,提出半监督截集式可能性C-均值(SS-C-PCM)聚类算法。为了提高彩色图像的分割效率和分割准确率,将差分进化超像素(DES)算法获得的图像空间邻域信息融入SS-C-PCM目标函数中,并利用彩色直方图重构目标函数,以降低算法的计算复杂度,进而提出基于差分进化超像素的半监督截集式可能性C-均值(desSS-C-PCM)聚类算法。通过人造数据和彩色图像分割的仿真并与多种相关算法进行对比,表明该文算法能够有效改善小目标数据的聚类效果,提高算法的执行效率。
-
关键词:
- 截集式可能性C-均值聚类 /
- 半监督 /
- 超像素 /
- 彩色直方图
Abstract: Cutset-type Possibilistic C-Means clustering (C-PCM) algorithm can significantly reduce the coincident clustering phenomenon of the Possibilistic C-Means clustering (PCM) algorithm by introducing the cut-set concept into the PCM. The C-PCM also has strong robustness to noise and outliers. However, the C-PCM still suffers from the center migration problem for datasets with small targets. In order to solve this problem, a Semi-Supervised Cutset-type Possibility C-Means (SS-C-PCM) clustering algorithm is proposed by introducing the semi-supervised learning mechanism into the objective function of the C-PCM and utilizing some prior information to guide the clustering process. Meanwhile, in order to improve the segmentation efficiency and accuracy of color images, a differential evolutionary superpixel-based Semi-Supervised Cutset-type Possibilistic C-Means (desSS-C-PCM) clustering algorithm is proposed. In the desSS-C-PCM, the Differential Evolutionary Superpixel(DES) algorithm is used to obtain the spatial neighborhood information of an image, which is integrated into the objective function of the semi-supervised C-PCM to improve the segmentation quality. Simultaneously, the color histogram is used to reconstruct the new objective function to reduce the computational complexity of the algorithm. Several experiments of artificial data clustering and color image segmentation show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the clustering effect of datasets with small targets and the execution efficiency compared with several related algorithms. -
表 1 针对数据集
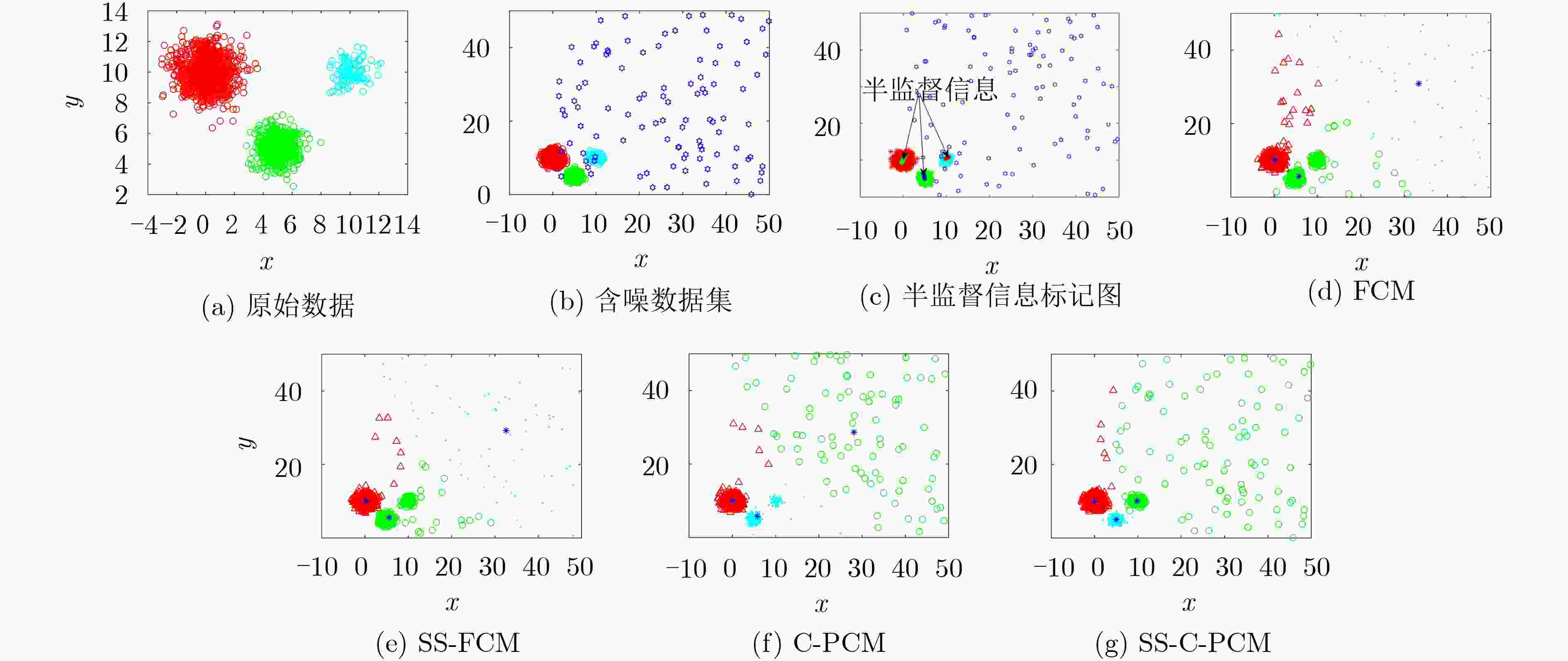
${X_{1600}}$ 各个算法的中心偏移量以及迭代次数算法 FCM SS-FCM C-PCM SS-C-PCM 中心偏移量 31.9391 29.8891 23.4551 0.1165 迭代次数 85 60 70 38 表 2 各个算法的分割准确率对比
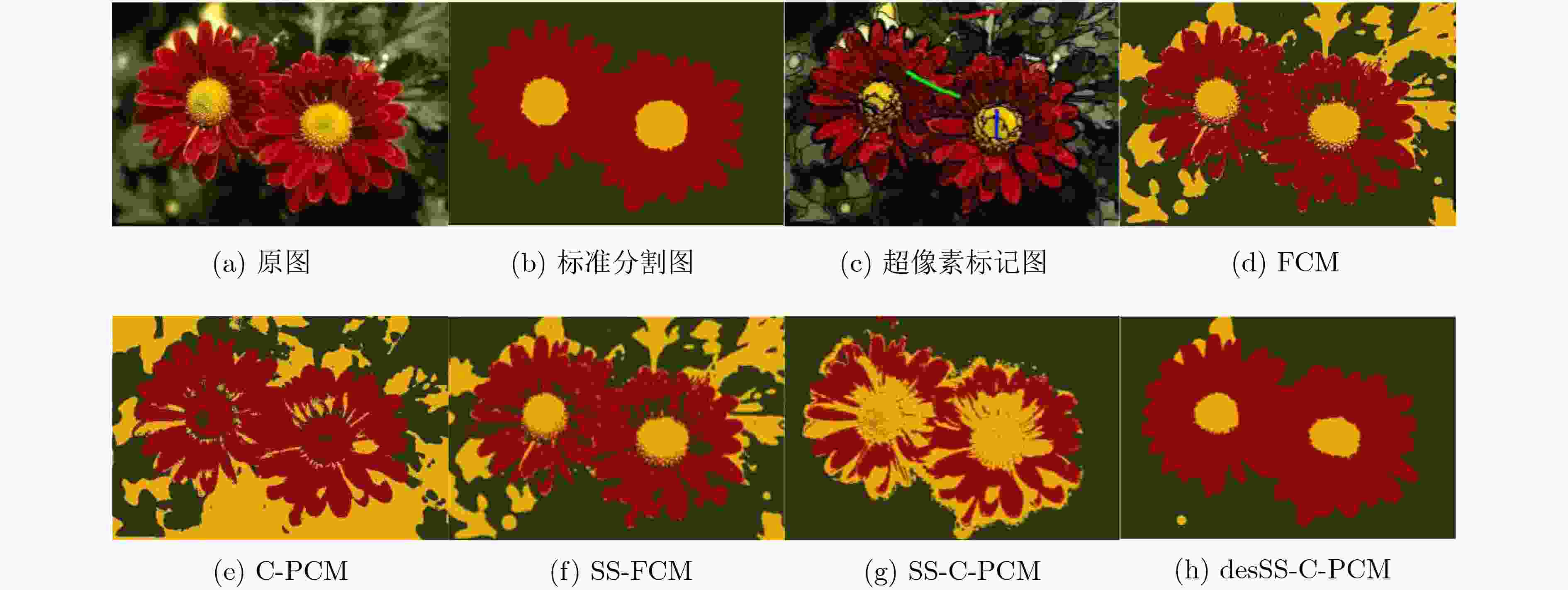
图像 FCM C-PCM SS-FCM SS-C-PCM desSS-C-PCM #3063 0.7292 0.6540 0.9924 0.9931 0.9939 #3096 0.9859 0.6324 0.9860 0.9921 0.9932 #135069 0.7358 0.5624 0.9919 0.9895 0.9905 #118035 0.9342 0.6970 0.9342 0.9457 0.9754 #124084 0.7486 0.6127 0.7487 0.8049 0.9658 #86016 0.8393 0.6126 0.8396 0.9676 0.9931 #161062 0.8846 0.9285 0.8847 0.9452 0.9885 #113044 0.8352 0.6243 0.8354 0.9521 0.9782 #12003 0.7738 0.5811 0.7740 0.9483 0.9740 #238011 0.8123 0.8090 0.9560 0.9282 0.9637 #101027 0.8840 0.6330 0.8846 0.9212 0.9418 #28075 0.4473 0.3987 0.4456 0.5922 0.9842 #24063 0.8919 0.5965 0.8919 0.8976 0.8920 #253036 0.6192 0.5360 0.6195 0.8966 0.9849 #42044 0.7525 0.8181 0.7526 0.8067 0.8884 #299091 0.6960 0.7950 0.6964 0.9941 0.9945 #113016 0.8168 0.5897 0.8185 0.7376 0.9806 #147091 0.9316 0.6690 0.9317 0.9253 0.9413 #67079 0.8274 0.8312 0.8276 0.8936 0.9918 -
[1] 章毓晋. 图像分割[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1–5.ZHANG Yujin. Image Segmentation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 1–5. [2] 范九伦. 灰度图像阈值分割法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 1–7.FAN Jiulun. Gray Image Thresholding Segmentation Methods[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 1–7. [3] ZHANG Yingchun, GUO He, CHEN Feng, et al. Weighted kernel mapping model with spring simulation based watershed transformation for level set image segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 249: 1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.044 [4] 胡炎, 单子力, 高峰. 基于增强指数加权均值比的SAR图像边缘检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1166–1172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170806HU Yan, SHAN Zili, and GAO Feng. Edge detection algorithm for SAR image based on enhanced ROEWA[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1166–1172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170806 [5] 赵凤, 孙文静, 刘汉强, 等. 基于近邻搜索花授粉优化的直觉模糊聚类图像分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1005–1012. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190428ZHAO Feng, SUN Wenjing, LIU Hanqiang, et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy clustering image segmentation based on flower pollination optimization with nearest neighbor searching[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1005–1012. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190428 [6] BEZDEK J C. Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms[J]. Advanced Applications in Pattern Recognition, 1981, 22(1171): 203–239. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0450-1 [7] KRISHNAPURAM R and KELLER J M. A possibilistic approach to clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 1993, 1(2): 98–110. doi: 10.1109/91.227387 [8] BARNI M, CAPPELLINI V, and MECOCCI A. Comments on "A possibilistic approach to clustering"[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 1996, 4(3): 393–396. doi: 10.1109/91.531780 [9] KRISHNAPURAM R and KELLER J M. The possibilistic C-means algorithm: Insights and recommendations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 1996, 4(3): 385–392. doi: 10.1109/91.531779 [10] PAL N R, PAL K, KELLER J M, et al. A possibilistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2005, 13(4): 517–530. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2004.840099 [11] MEMON K H, MEMON S, QURESHI M A, et al. Kernel possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering with local information for image segmentation[J]. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 21(1): 321–332. doi: 10.1007/s40815-018-0537-9 [12] YU Haiyan and FAN Jiulun. Cutset-type possibilistic C-means clustering algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 64: 401–422. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.12.024 [13] YASUNORI E, YUKIHIRO H, MAKITO Y, et al. On semi-supervised fuzzy c-means clustering[C]. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Jeju Island, South Korea, 2009: 1119–1124. doi: 10.1109/FUZZY.2009.5277177. [14] YIN Xuesong, SHU Ting, and HUANG Qi. Semi-supervised fuzzy clustering with metric learning and entropy regularization[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2012, 35: 304–311. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2012.05.016 [15] 赵凤, 张咪咪, 刘汉强. 区域信息驱动的多目标进化半监督模糊聚类图像分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1106–1113. doi: 10.12000/JEIT180605ZHAO Feng, ZHANG Mimi, and LIU Hanqiang. Multi-objective evolutionary semi-supervised fuzzy clustering image segmentation motivated by region information[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1106–1113. doi: 10.12000/JEIT180605 [16] REN Xiaofeng and MALIK J. Learning a classification model for segmentation[C]. The Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 2003: 10–17. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2003.1238308. [17] SHI Jianbo and MALIK J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(8): 888–905. doi: 10.1109/34.868688 [18] COMANICIU D and MEER P. Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(5): 603–619. doi: 10.1109/34.1000236 [19] GONG Yuejiao and ZHOU Yicong. Differential evolutionary superpixel segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3): 1390–1404. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2778569 [20] ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 [21] LEI Tao, JIA Xiaohong, ZHANG Yanning, et al. Superpixel-based fast fuzzy c-means clustering for color image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(9): 1753–1766. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2889018 [22] PEDRYCZ W. Shadowed sets: Representing and processing fuzzy sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) , 1998, 28(1): 103–109. doi: 10.1109/3477.658584 [23] 雒僖, 范九伦, 于海燕, 等. 基于阴影集的截集式可能性C-均值聚类截集门限的选取[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(8): 249–254. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.08.041LUO Xi, FAN Jiulun, YU Haiyan, et al. Selection of cutset threshold for cutset-type possibilistic C-means clustering based on shadowed set[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(8): 249–254. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.08.041 [24] ARBELÁEZ P, MAIRE M, FOWLKES C, et al. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(5): 898–916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.161 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
