A Second-order Squeezed Wavelet Transform Algorithm for Seismic Signal Analysis
-
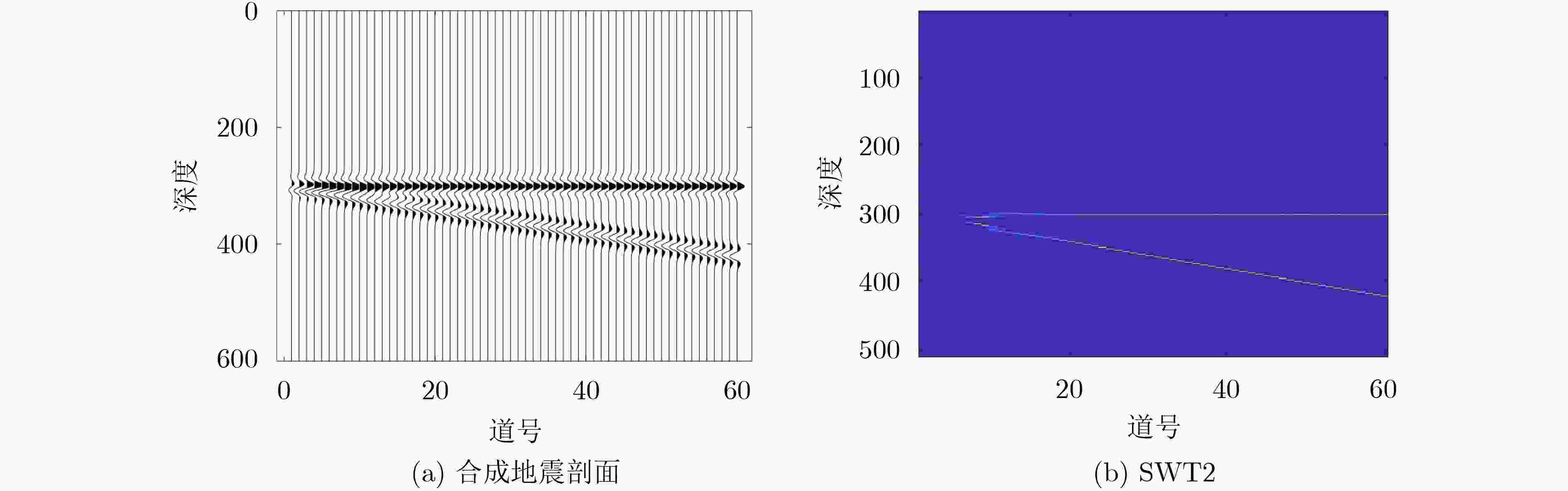
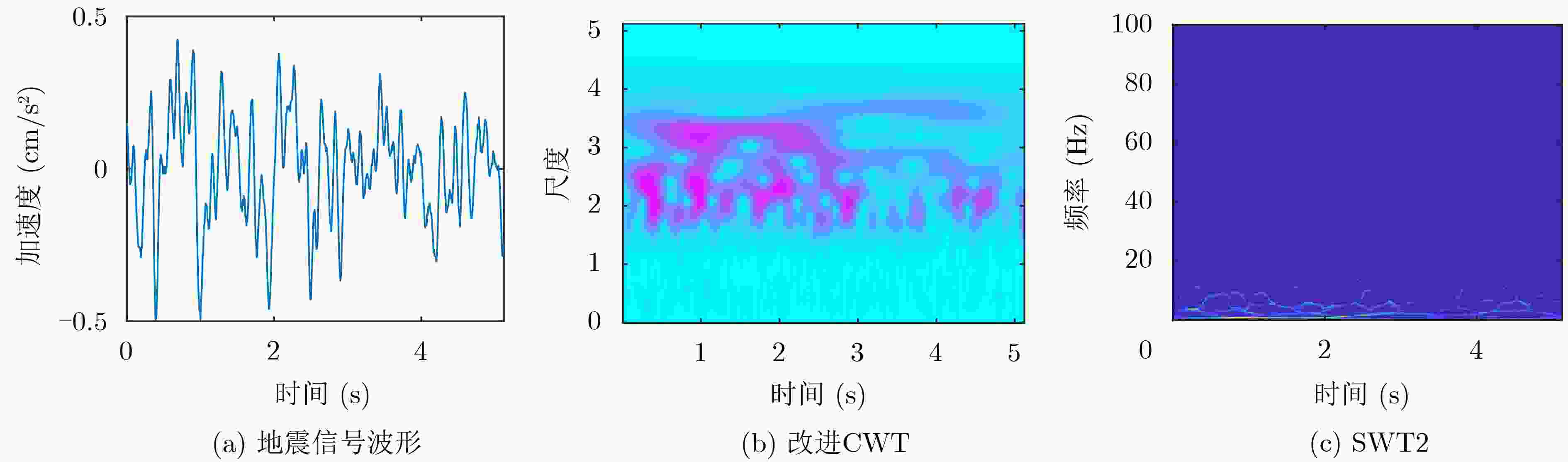
摘要: 地震信号分析在地质岩性、储层、流体、沉积相带的检测,以及地层界面识别与储层分析、地震资料处理和解释等方面具有重要研究意义。针对现有时频分析算法在处理地震信号时,存在时频分辨率低、能量聚集性差等问题,该文以Ricker子波为数学模型,提出了一种新的2阶挤压小波变换算法(SWT2)。考虑到传统时频同步压缩变换中的瞬时频率估计对地震信号失效,利用改进的母小波对地震信号进行匹配,进而通过谱峰对齐对参考频率进行修正,从而提升时频能量聚集性和时频分辨率。仿真实验结果表明,提出的2阶挤压小波变换算法可以极大地提升地震信号的时频聚集性,精确地反映信号的时延和主频,对地层结构的刻画更加精确。Abstract: Seismic signal is of great significance in the detection of geological lithology, reservoir, fluid and sedimentary facies, as well as the identification of stratigraphic interface, reservoir analysis, seismic data processing and interpretation. In view of the problems of low time-frequency resolution and poor energy aggregation when the traditional time-frequency analysis algorithms process seismic signals, a new 2nd-order Synchrosqueezing Wavelet Transform (SWT2) algorithm is proposed based on the model of Ricker wavelet. The proposed second-order squeezing algorithm uses the improved mother wavelet to match the seismic signals, and then corrects the reference frequency through spectral peak alignment, thus improving the time-frequency energy concentration and time-frequency resolution. Simulation results show that the proposed method can greatly improve the time-frequency aggregation, accurately reflect the time delay and dominant frequency of signals, and describe the stratigraphic structure more accurately.
-
Key words:
- Signal processing /
- Seismic signal /
- Synchrosqueezing transform /
- Spectral decomposition
-
表 1 各种时频分析方法的瑞利熵对比
时频分布 STFT WVD 伪WVD CWT SST SST2 改进CWT SWT SWT2 瑞利熵 24.7226 24.4484 24.0051 28.6346 17.6892 16.5572 28.5278 17.6841 16.0846 -
[1] 黄昱丞, 郑晓东, 栾奕, 等. 地震信号线性与非线性时频分析方法对比[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(5): 975–989. doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2018.05.011HUANG Yucheng, ZHENG Xiaodong, LUAN Yi, et al. Comparison of linear and nonlinear time-frequency analysis methods for seismic signals[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(5): 975–989. doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2018.05.011 [2] OKAYA D A, KARAGEORGI E, MCEVILLY T V, et al. Removing vibrator-induced correlation artifacts by filtering in frequency-uncorrelated time space[J]. Geophysics, 1992, 57(7): 916–926. doi: 10.1190/1.1443304 [3] SINHA S, ROUTH P S, ANNO P D, et al. Spectral decomposition of seismic data with continuous-wavelet transform[J]. Geophysics, 2005, 70(6): 29–25. doi: 10.1190/1.2127113 [4] 郝国成, 谈帆, 程卓, 等. 强鲁棒性和高锐化聚集度的BGabor-NSPWVD时频分析算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 566–576. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170530HAO Guocheng, TAN Fan, CHENG Zhuo, et al. Time-frequency analysis of BGabor-NSPWVD algorithm with strong robustness and high sharpening concentration[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 566–576. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170530 [5] 郑成龙, 王宝善. S变换在地震资料处理中的应用及展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(4): 1580–1591. doi: 10.6038/pg20150412ZHENG Chenlong and WANG Baoshan. Applications of stransform in seismic data processing[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(4): 1580–1591. doi: 10.6038/pg20150412 [6] 严海滔, 黄饶, 周怀来, 等. 同步挤压广义S变换在南海油气识别中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(3): 1229–1235. doi: 10.6038/pg2019CC0143YAN Haitao, HUANG Rao, ZHOU Huailai, et al. Application of Nanhai oil and gas identification based on synchrosqueezing generalized S transform[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(3): 1229–1235. doi: 10.6038/pg2019CC0143 [7] HERRERA R H, HAN Jiajun, and VAN DER BAAN M. Applications of the synchrosqueezing transform in seismic time-frequency analysis[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(3): V55–V64. doi: 10.1190/geo2013-0204.1 [8] 包乾宗, 许杰, 许明瑞. 高铁地震信号时频特征对比分析[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 55(5): 804–811. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2019.076BAO Qianzong, XU Jie, and XU Mingrui. Comparative analysis of time-frequency characteristics of seismic signal induced by high-speed train[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2019, 55(5): 804–811. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2019.076 [9] XUE Yajuan, CAO Junxing, WANG Daxing, et al. Application of the variational-mode decomposition for seismic time–frequency analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(8): 3821–3831. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2529702 [10] HAN Jiajun and VAN DER BAAN M. Empirical mode decomposition for seismic time-frequency analysis[J]. Geophysics, 2013, 78(2): O9–O19. doi: 10.1190/geo2012-0199.1 [11] DAUBECHIES I, LU Jianfeng, and WU H T. Synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms: An empirical mode decomposition-like tool[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2011, 30(2): 243–261. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2010.08.002 [12] 李林, 王林, 韩红霞, 等. 自适应时频同步压缩算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 438–444. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190146LI Lin, WANG Lin, HANG Hongxia, et al. Research on the adaptive synchrosqueezing algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 438–444. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190146 [13] LI Lin, CAI Haiyan, HAN Hongxia, et al. Adaptive short-time Fourier transform and synchrosqueezing transform for non-stationary signal separation[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 166: 107231. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.07.024 [14] 沈微, 陶新民, 高珊, 等. 基于同步挤压小波变换的振动信号自适应降噪方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(14): 239–247. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2018.14.034SHEN Wei, TAO Xinmin, GAO Shan, et al. Self-adaptive de-noising algorithm for vibration signals based on synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(14): 239–247. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2018.14.034 [15] 黄忠来, 张建中, 邹志辉. 二阶同步挤压S变换及其在地震谱分解中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(7): 2833–2844. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170728HUANG Zhonglai, ZHANG Jianzhong, and ZOU Zhihui. A second-order synchrosqueezing S-transform and its application in seismic spectral decomposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(7): 2833–2844. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170728 [16] STANKOVIĆ L. A measure of some time–frequency distributions concentration[J]. Signal Processing, 2001, 81(3): 621–631. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(00)00236-X -





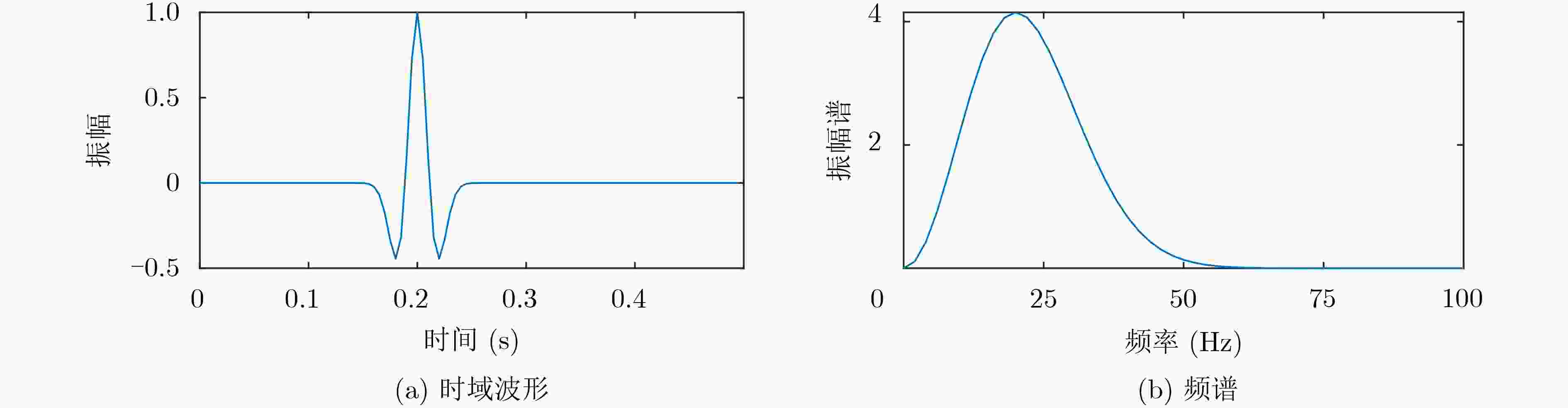
 下载:
下载:
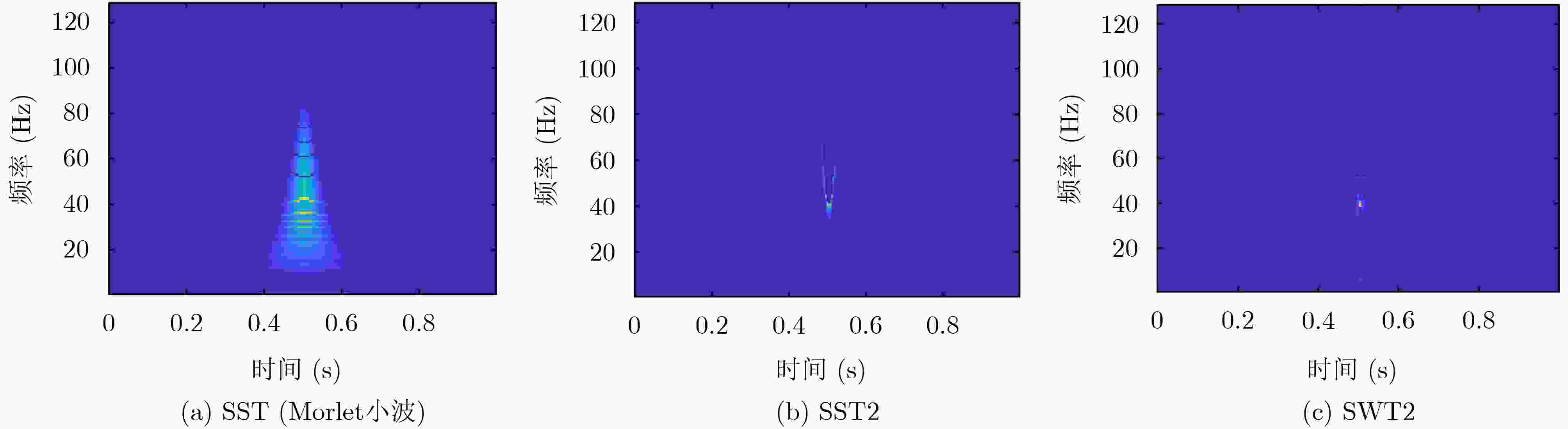
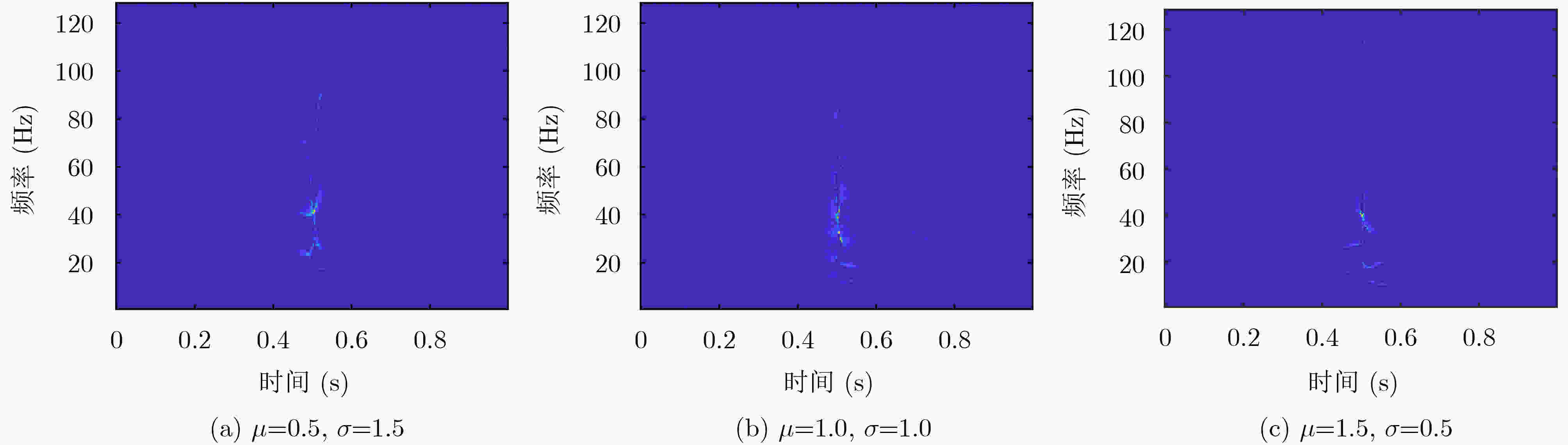
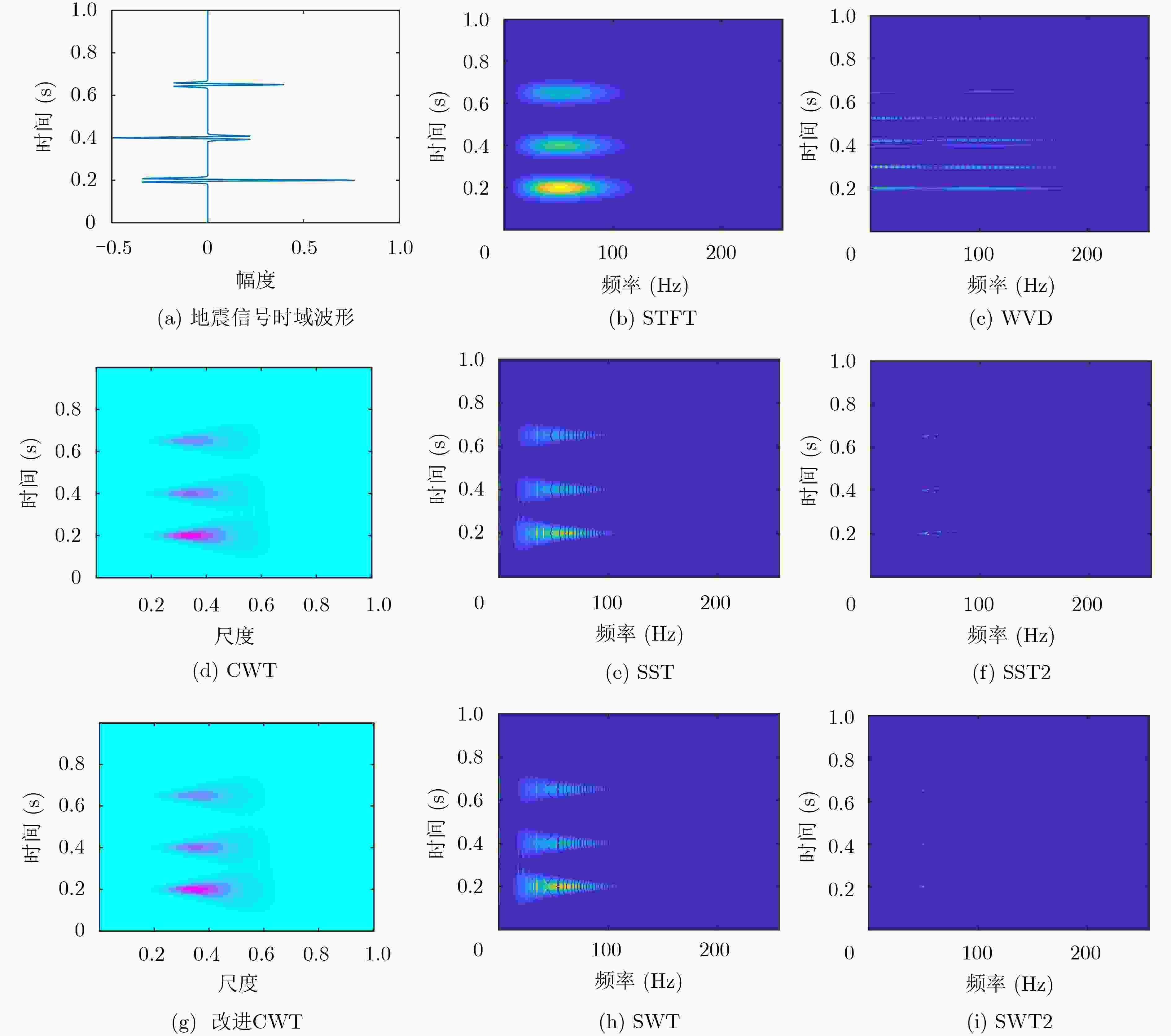


 下载:
下载:
