Analysis of Wave Field Composition and Characteristics in Shallow Sea
-
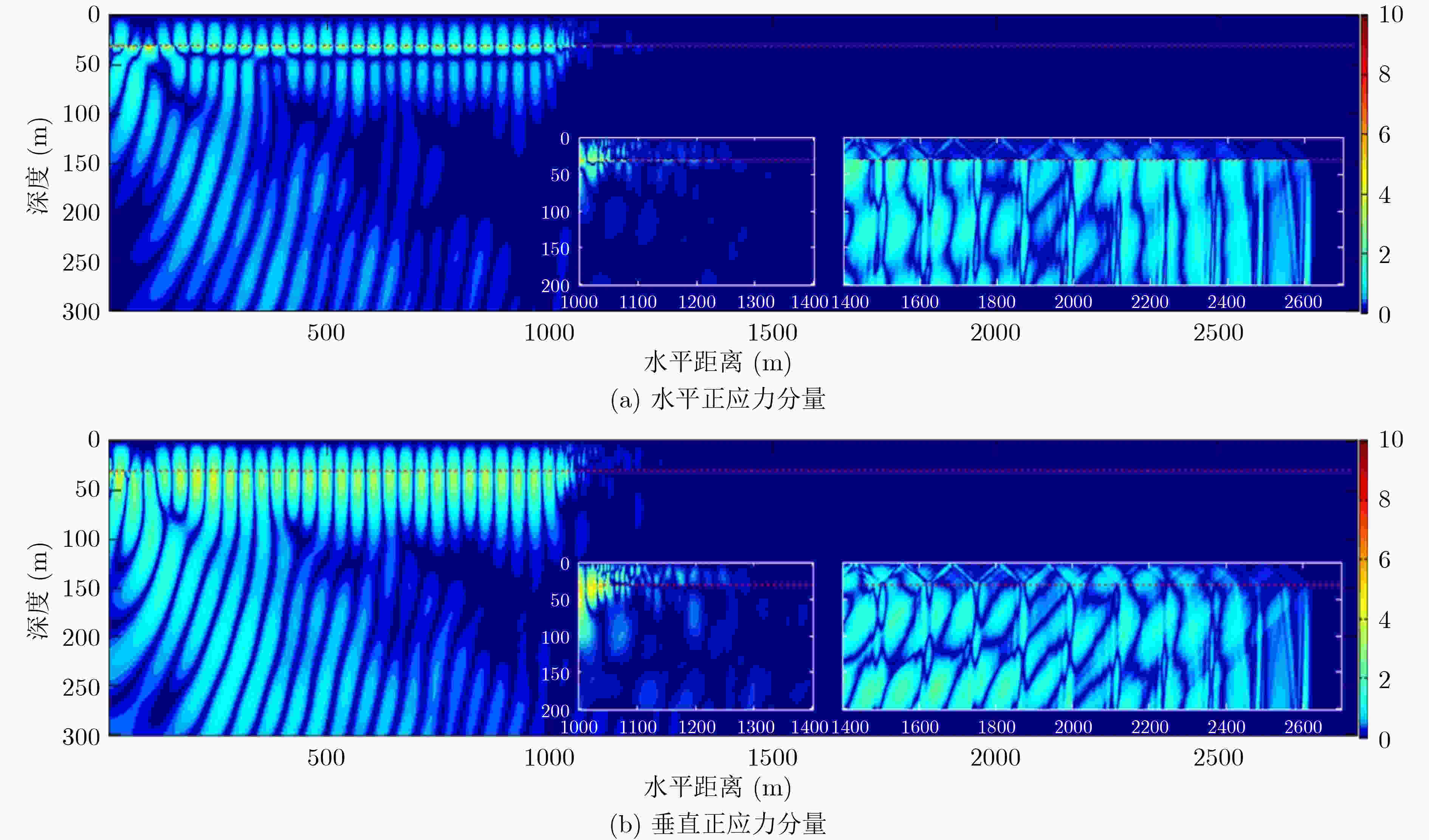
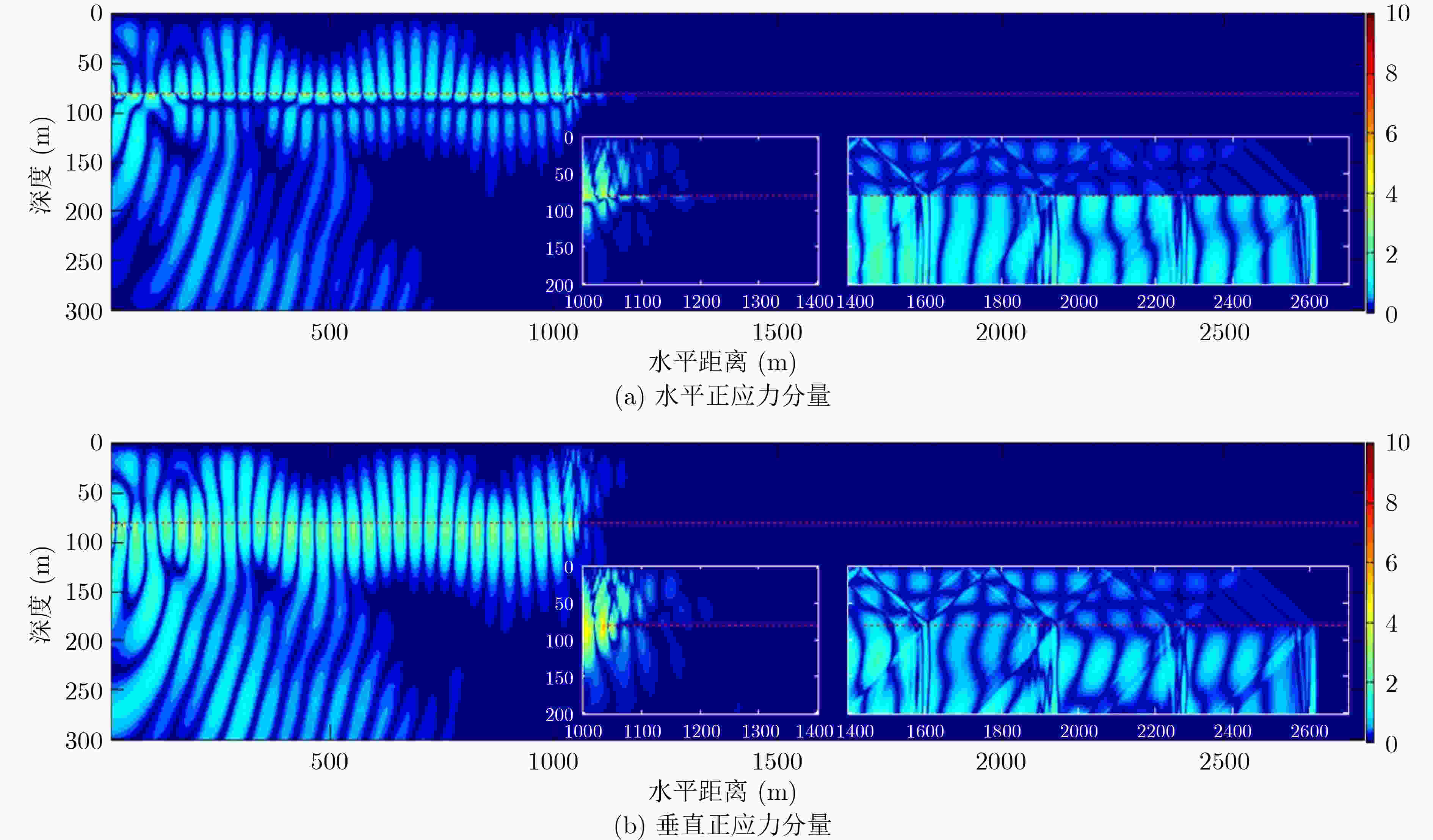
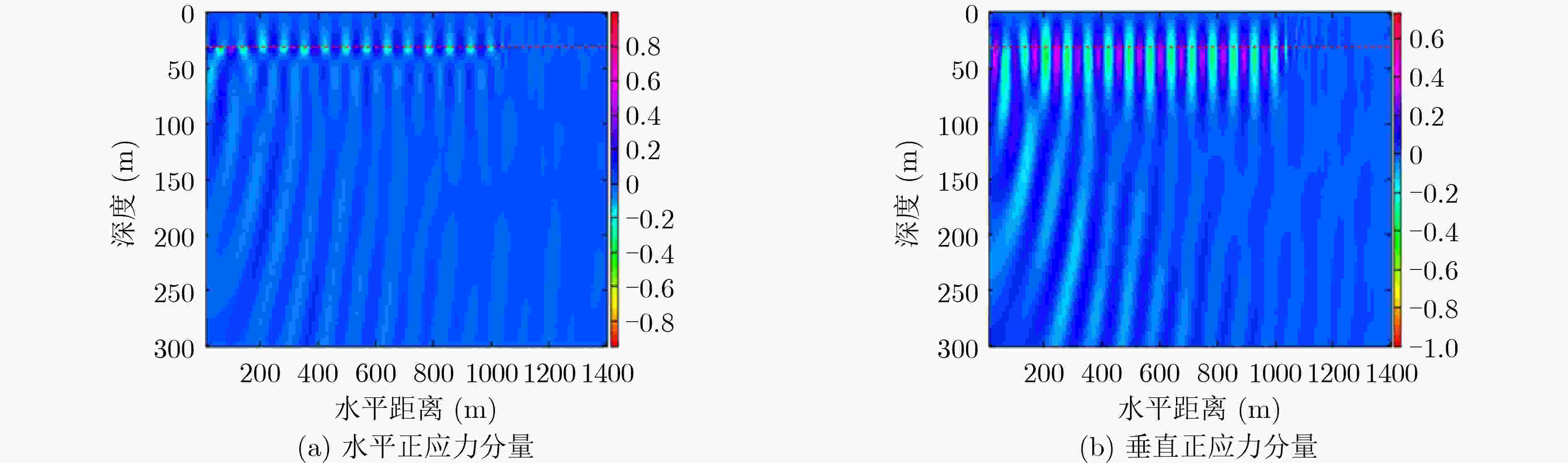
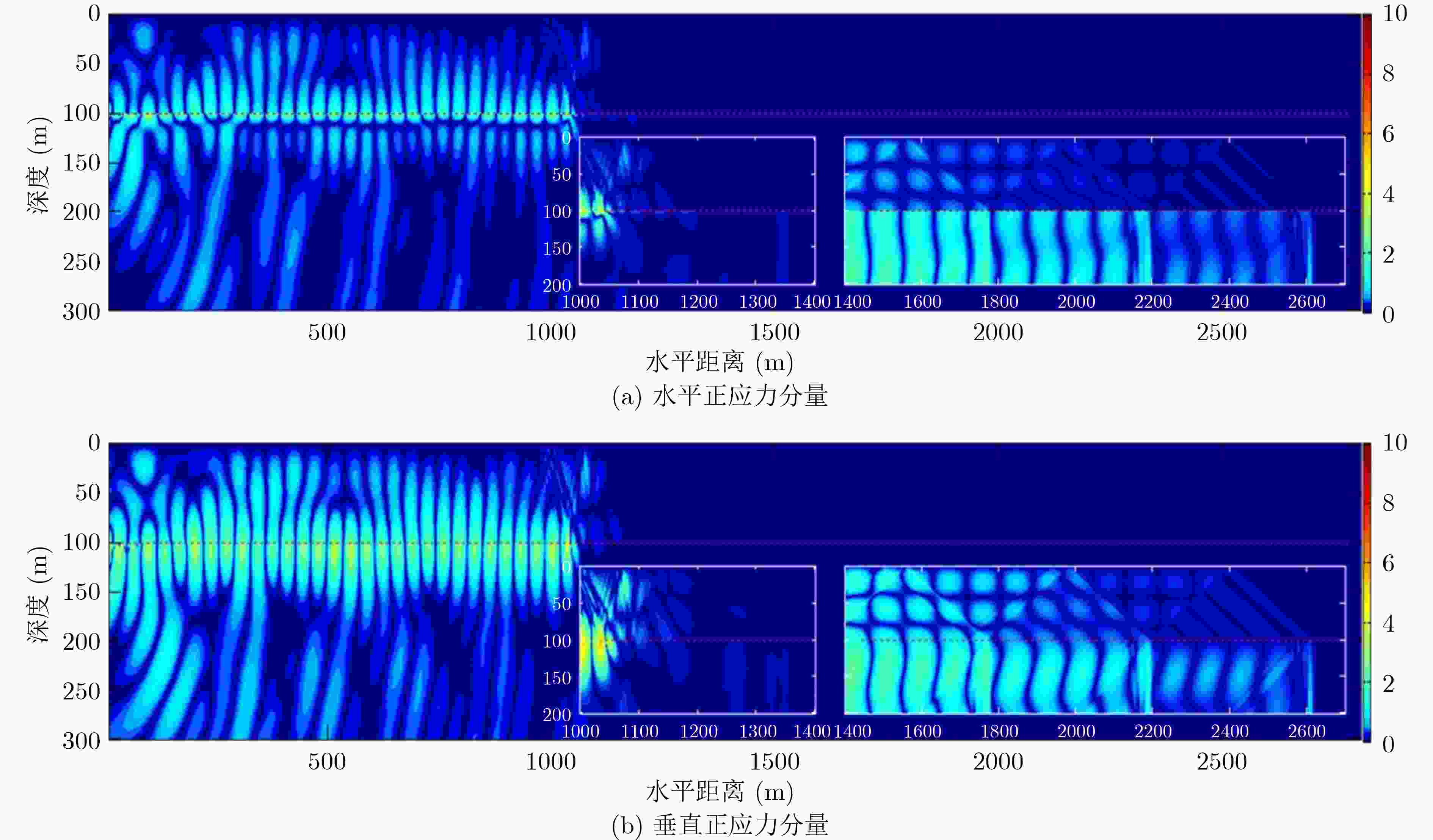
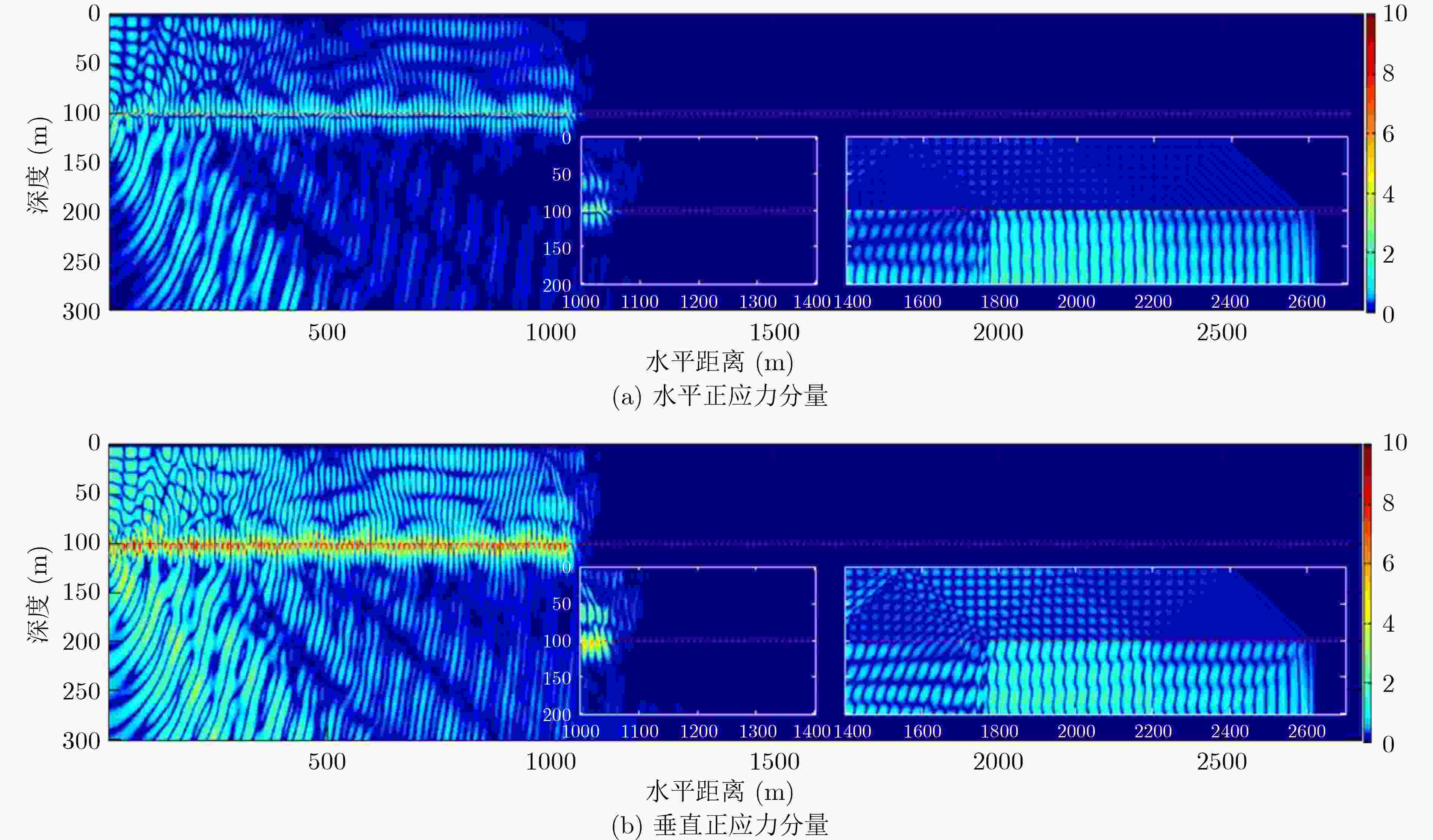
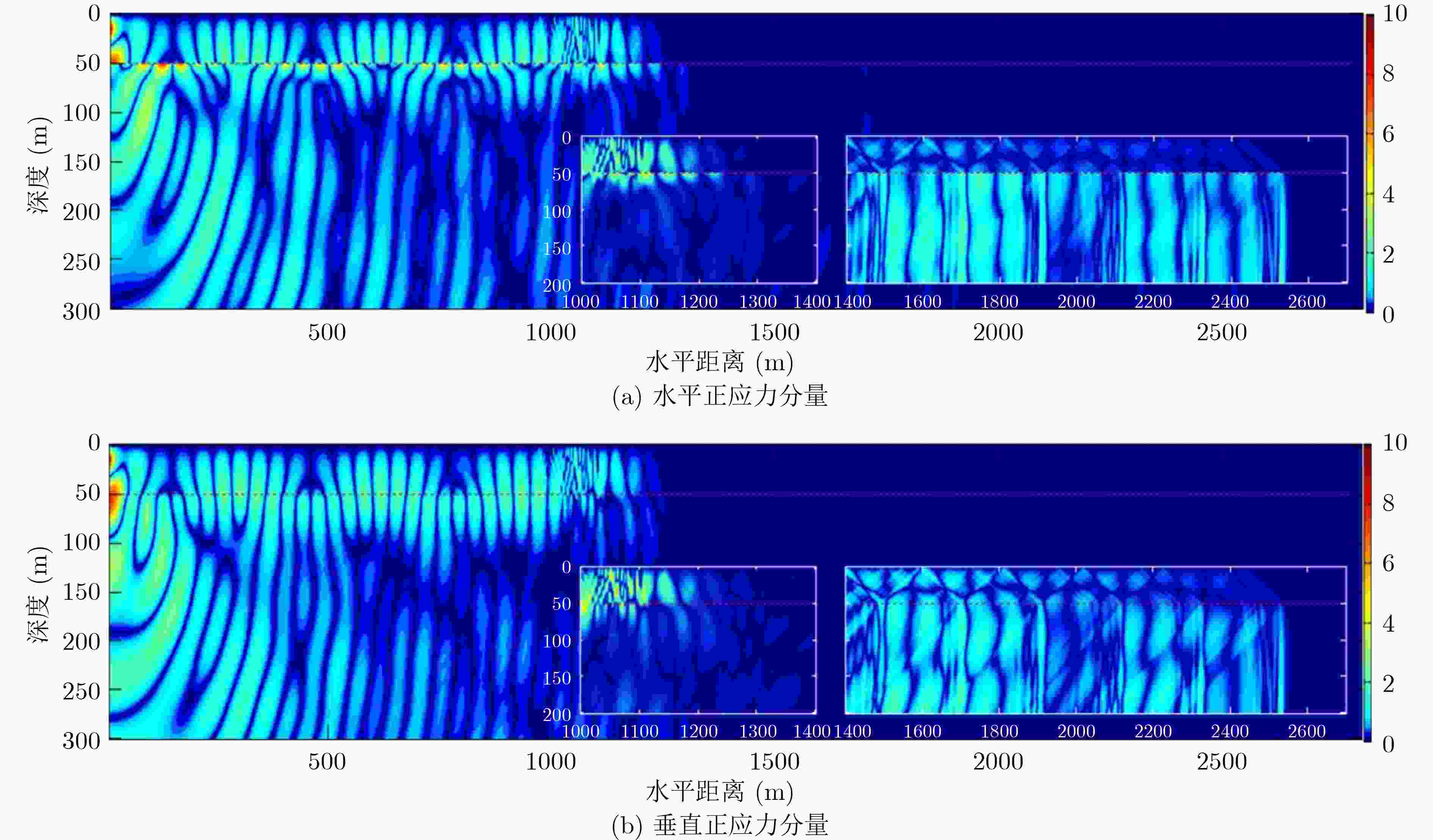
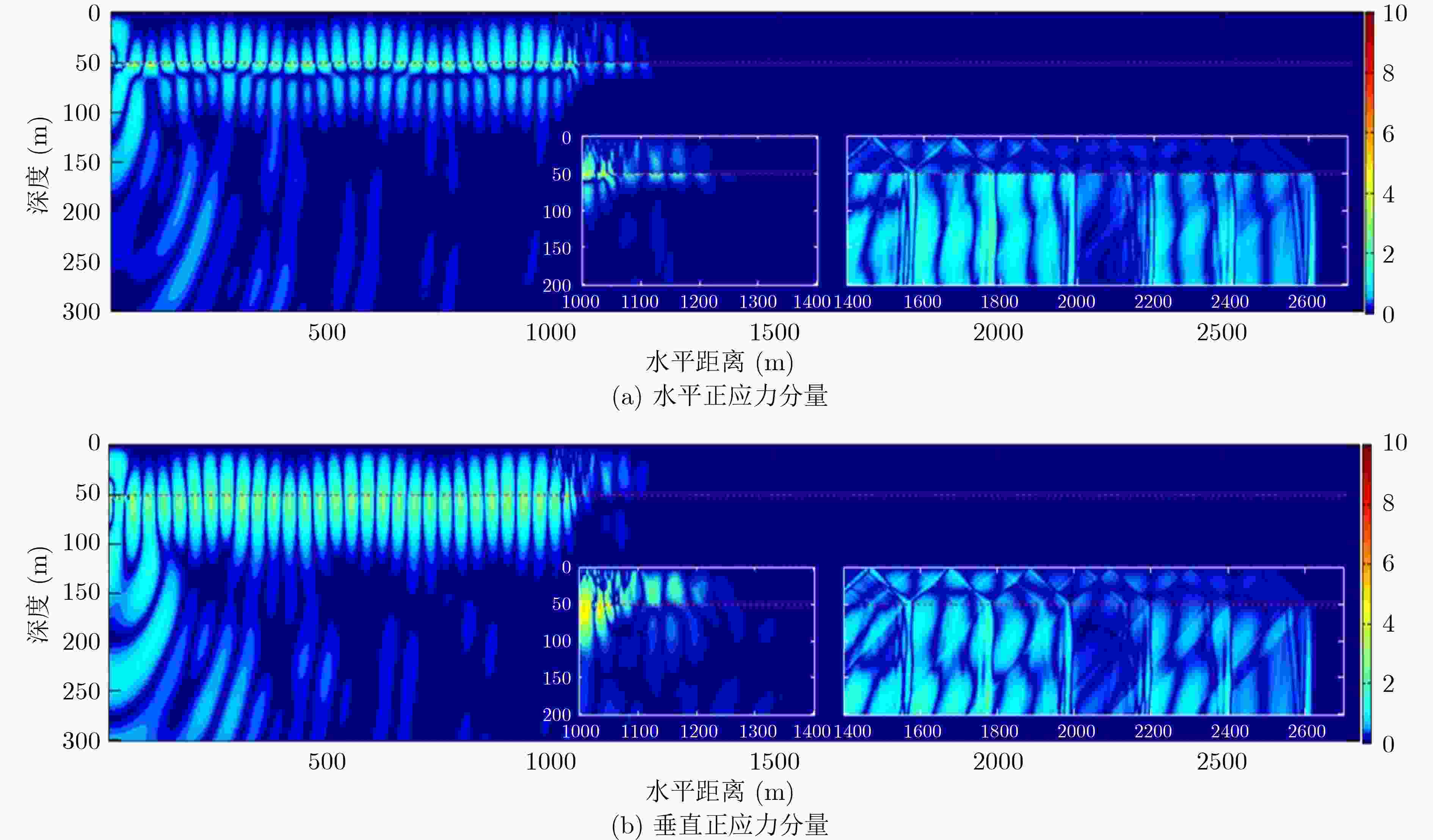
摘要: 为更好地认识和利用浅海波导中的声场,该文对浅海中声源激发的波场成分及特性进行了研究。提出了能给出浅海中声场全波解的理论研究方法,给出了声场的复积分表达式,并在复平面上利用围道积分对声场复积分式进行求解,得出了浅海中声源激发出的声场组成部分;同时应用高阶交错网格有限差分法对浅海中声场进行数值模拟,呈现出了不同海水深度、声源频率和声源深度下浅海波导中的波场结构和空间能量分布。研究表明:浅海中声场由离散谱部分和连续谱部分组成;其中离散谱部分包括各阶简正波和Scholte波,连续谱部分包括侧面波;简正波和Scholte波的振幅与水平传播距离的开方成反比,而侧面波的振幅与水平传播距离的平方成反比;海水越浅、声源频率越小、声源深度越大,都会导致海水中的能量越少,越有利于Scholte波的激发,此时声源辐射的能量主要以Scholte波的形式传播出去,能量更多地集中在海底界面处。Abstract: To better understand and utilize the acoustic field in shallow sea, a theoretical method that can give the full-wave solution is proposed, then the complex integral expression of the acoustic field is given. The complex integral fraction is solved in the complex plane, and the components of the acoustic field in shallow sea are obtained. The high-order staggered grid finite difference method is also used to numerically simulate the acoustic field in shallow sea, showing the wave field structure and spatial energy distribution. Results show that the acoustic field in shallow sea includes discrete spectrum and continuous spectrum; The discrete spectrum includes normal waves and Scholte wave, and the continuous wave includes lateral waves; The amplitudes of normal waves and Scholte wave are inversely proportional to the root of horizontal propagation distance, and the amplitude of lateral wave is inversely proportional to the power of horizontal propagation distance; The shallower the sea water, the lower the frequency and the greater the depth of the sound source, the less energy in the sea water will be. The energy radiated by the acoustic source is mainly propagated in the form of Scholte wave, and the energy is mostly concentrated at the seabed interface.
-
Key words:
- Shallow sea acoustic field /
- Full-wave solution /
- Discrete spectrum /
- Continuous spectrum
-
表 1 浅海波导模型中的介质类型及其声学参数
介质类型 纵波速度cp(m/s) 横波速度cs(m/s) 密度ρ(kg/m3) 海水 1500 0 1000 砂岩海底 3500 1800 2300 -
KOZACZKA E and GRELOWSKA G. Shipping low frequency noise and its propagation in shallow water[J]. Acta Physica Polonica A, 2011, 119(6A): 1009–1012. doi: 10.12693/APhysPolA.119.1009 LUNKOV A A and KATSNELSON B G. Using discrete low-frequency components of shipping noise for gassy sediment characterization in shallow water[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147(5): EL428–EL433. doi: 10.1121/10.0001277 DUNCAN A J, GAVRILOV A N, MCCAULEY R D, et al. Characteristics of sound propagation in shallow water over an elastic seabed with a thin cap-rock layer[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2013, 134(1): 207–215. doi: 10.1121/1.4809723 TOLLEFSEN D. Thin-sediment shear-induced effects on low-frequency broadband acoustic propagation in a shallow continental sea[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 104(5): 2718–2726. doi: 10.1121/1.423855 KOZACZKA E and GRELOWSKA G. Propagation of ship-generated noise in shallow sea[J]. Polish Maritime Research, 2018, 25(2): 37–46. doi: 10.2478/pomr-2018-0052 朱子尧, 韩树平, 郭正东, 等. 乘性噪声背景下基于非线性渐消滤波的单信标测距定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 165–171. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180239ZHU Ziyao, HAN Shuping, GUO Zhengdong, et al. Single beacon location algorithm based on nonlinear fading filter under multiplicative noise background[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 165–171. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180239 AKAL T and BERKSON J M. Ocean Seismo-Acoustics: Low-Frequency Underwater Acoustics[M]. Boston: Springer, 1986: 1–20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2201-6. KATSNELSON B, PETNIKOV V, and LYNCH J. Fundamentals of Shallow Water Acoustics[M]. Boston: Springer, 2012: 1–11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9777-7. 莫亚枭. 基于耦合简正波理论的水平变化波导声场建模与特性分析[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2015.MO Yaxiao. Acoustic field modeling and analysis based on coupled-mode in range-development waveguide[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2015. SABATINI R and CRISTINI P. A multi-domain collocation method for the accurate computation of normal modes in open oceanic and atmospheric waveguides[J]. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 2019, 105(3): 464–474. doi: 10.3813/AAA.919328 KOESSLER M W, DUNCAN A J, GAVRILOV A N. Low-frequency acoustic propagation modelling for Australian range-independent environments[J]. Acoustics Australia, 2017, 45(2): 331–341. doi: 10.1007/s40857-017-0108-5 王逸林, 马世龙, 邹男, 等. 时空域联合的水下未知线谱目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1682–1689. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180796WANG Yilin, MA Shilong, ZOU Nan, et al. Detection of unknown line-spectrum underwater target using space-time processing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1682–1689. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180796 孟路稳, 罗夏云, 程广利, 等. 海底地震波波动成分及传播特性分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(12): 1627–1633. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.12.012MENG Luwen, LUO Xiayun, CHENG Guangli, et al. Components and propagation characteristics of seabed seismic waves[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(12): 1627–1633. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.12.012 罗夏云, 孟路稳, 程广利, 等. 浅海地震波波动成分及传播规律分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 47(1): 120–126. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.190122LUO Xiayun, MENG Luwen, CHENG Guangli, et al. Analysis of wave component and propagation rule of seismic wave in shallow sea[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 47(1): 120–126. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.190122 LU Zaihua, ZHANG Zhihong, and GU Jiannong. Analysis on the frequency dispersion characteristics of seismic wave caused by low frequency sound source in shallow sea[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 106: 354–359. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.07.019 LI Li, PIAO Shengchun, ZHANG Haigang, et al. Broadband modeling of sound propagation in shallow water with an irregular elastic bottom[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2014, 135(4): 2302. doi: 10.1121/1.4877578 JENSEN F B, KUPERMAN W A, PORTER M B, et al. Computational Ocean Acoustics[M]. New York: Springer, 2011: 457–530. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-8678-8. O’REILLY O, LUNDQUIST T, DUNHAM E M, et al. Energy stable and high-order-accurate finite difference methods on staggered grids[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 346: 572–589. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2017.06.030 -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
