Outage Performance Analysis and Optimization of Energy Harvesting Cognitive Multihop Relay Networks
-
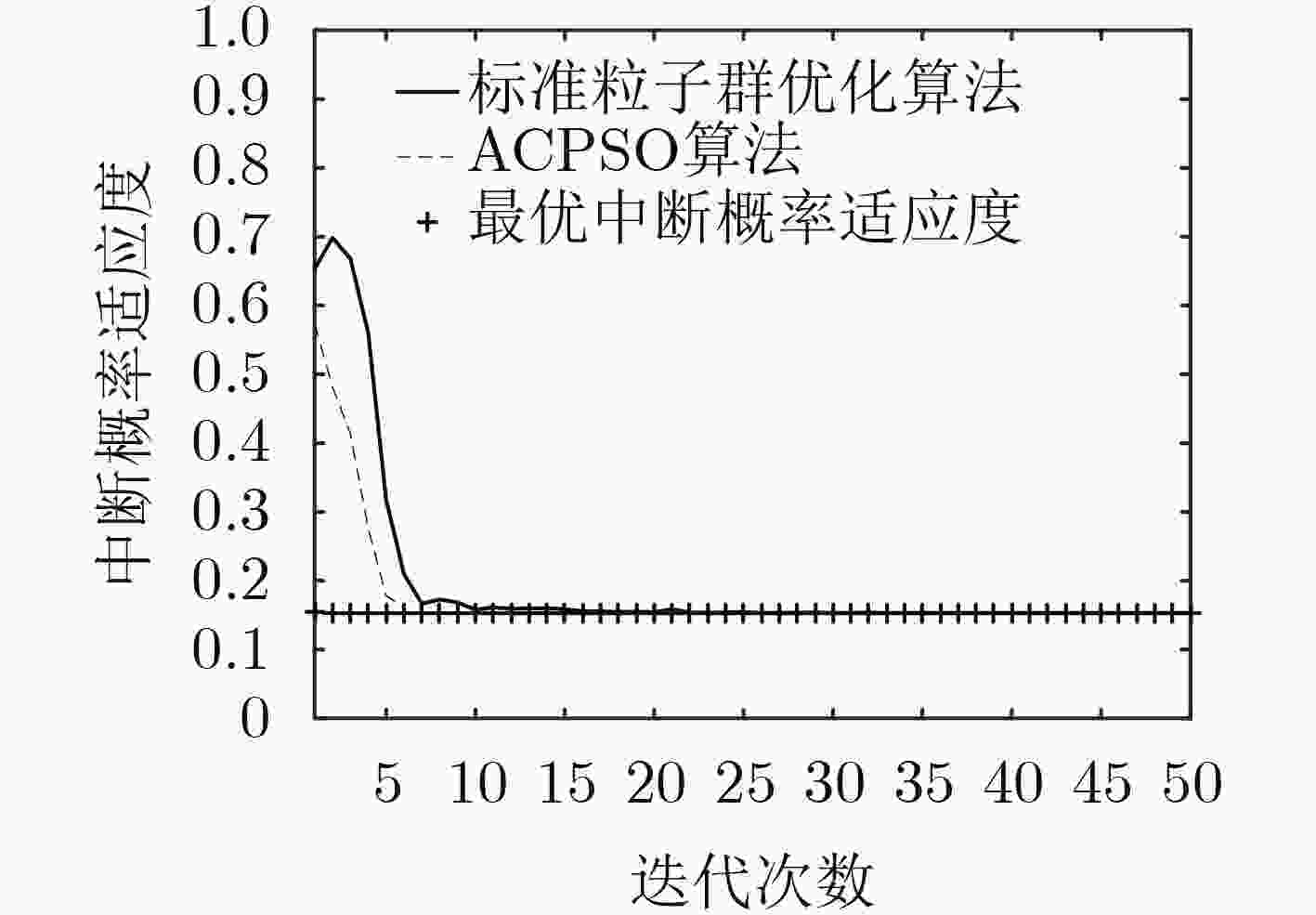
摘要: 针对能量收集认知无线网络中的多跳中继传输问题,该文构建了一种新的具有主网络干扰的功率信标(PB)辅助能量收集认知多跳中继网络模型,并提出单向传输方案。在干扰链路统计信道状态信息场景下,推导了次网络精确和渐近总中断概率闭合式。针对精确总中断概率表达式的复杂性和非凸性,采用自适应混沌粒子群优化(ACPSO)算法对次网络总中断性能进行优化。仿真结果表明,PB功率、干扰约束、次网络跳数、能量收集比率、主接收端数目和信道容量阈值等参数对中断性能影响显著,所提算法能快速和有效地对网络中断性能进行优化。Abstract: Considering the problems of multihop relay transmission in energy harvesting cognitive radio networks, a novel Power Beacon (PB) assisted energy harvesting cognitive multihop relay network model with primary network interference is proposed, and a one-way transmission scheme is proposed. In the scenario of interference link statistical channel state information, the closed-form formulas of exact and asymptotic total outage probability are derived. In view of the complexity and nonconvexity of the exact total outage probability expression, the Adaptive Chaos Particle Swarm Optimization (ACPSO) algorithm is used to optimize the total outage performance of the secondary network. Simulation results show that the parameters such as PB’s power, interference constraint, number of secondary network hops, energy harvesting ratio, the number of primary receivers and channel capacity threshold have significant impacts on outage performance, the proposed algorithm can quickly and effectively optimize the network outage performance.
-
Key words:
- Cognitive radio /
- Multihop relay networks /
- Energy harvesting /
- Outage probability
-
表 1 ACPSO算法
输入:${\lambda _k}$, ${\beta _k}$, ${\omega _k}$, ${\theta _k}$, ${P_{\rm{I}} }$, ${P_0}$, ${P_{\max }}$, $N$, $K$, ${R_{\rm{th}}}$, $\varepsilon $, $\eta $, $\zeta $, $S$, $l$和$L$; 输出:全局最优值$P_{\rm{t}}^ * $和${\alpha ^ * }$; (1)设置算法参数,采用式(29)分别对粒子s, $s = 1,2, \cdots ,S$的位置和速度进行初始化。其中,$t{\rm{ = }}1$, ${x_{s,1}}\left( t \right) \in \left[ {0,{P_{\max }}} \right]$, ${x_{s,2}}\left( t \right) \in \left( {0,1} \right]$, ${v_{s,1}}\left( t \right) \in \left[ { - \mu {P_{\max }},\mu {P_{\max }}} \right]$, ${v_{s,2}}\left( t \right) \in \left[ { - \mu ,\mu } \right]$, $\mu $为0~1之间均匀分布的随机数,也由式(29)产生; (2)将${x_{s,1}}\left( 1 \right)$和${x_{s,2}}\left( 1 \right)$代入式(23),计算${f_s}\left( 1 \right)$。令${p_{s,1}}{\rm{ = }}{x_{s,1}}\left( 1 \right)$, ${p_{s,2}}{\rm{ = }}{x_{s,2}}\left( 1 \right)$, ${p_{g,1}} = {x_{{s^*},1}}\left( 1 \right)$, ${p_{g,2}} = {x_{{s^*},2}}\left( 1 \right)$, ${s^*}$为${f_s}\left( 1 \right)$中最小值 所对应的粒子; (3)依据式(26)调整${\omega _s}\left( t \right)$;依据式(27)和式(28)分别调整${c_1}\left( t \right)$和${c_2}\left( t \right)$;依据式(29)调整${r_1}\left( t \right)$和${r_2}\left( t \right)$, $t \ge 1$; (4)依据式(24)和式(25)更新${v_{s,1}}\left( t \right){\rm{ = }}\min \left( {\max \left( { - \mu {P_{\max }},{v_{s,1}}\left( t \right)} \right),\mu {P_{\max }}} \right)$和${v_{s,2}}\left( t \right){\rm{ = }}\min \left( {\max \left( { - \mu ,{v_{s,2}}\left( t \right)} \right),\mu } \right)$以及 ${x_{s,1}}\left( t \right){\rm{ = }}\min \left( {\max \left( {0,{x_{s,1}}\left( t \right)} \right),{P_{\max }}} \right)$和${x_{s,2}}\left( t \right){\rm{ = }}\min \left( {\max \left( {0,{x_{s,2}}\left( t \right)} \right),1} \right)$, $t \ge2$;根据式(23)和式(30)分别计算${f_s}\left( t \right)$和$\varphi \left( t \right)$, $t \ge 2$, 计算更新${p_{s,1}}$, ${p_{s,2}}$, ${p_{g,1}}$和${p_{g,2}}$; (5)若满足$t > L$或$\varphi \left( t \right) < {10^{ - 6}}$,则停止迭代,输出$P_{\rm{t}}^ * = {p_{g,1}}$和${\alpha ^ * }{\rm{ = }}{p_{g,2}}$,否则返回步骤(3),继续迭代。 -
[1] LU Xiao, WANG Ping, NIYATO D, et al. Wireless networks with RF energy harvesting: A contemporary survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(2): 757–789. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2368999 [2] 欧静兰, 余欢欢, 吴皓威, 等. 基于携能通信的非信任双向中继网络安全传输方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 2908–2914. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200069OU Jinglan, YU Huanhuan, WU Haowei, et al. Security transmission scheme for two-way untrusted relay networks based on simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 2908–2914. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200069 [3] 赵太飞, 李永明, 许杉, 等. 军车隐秘编队的无线紫外光通信最优多跳中继研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2636–2642. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190172ZHAO Taifei, LI Yongming, XU Shan, et al. Research on optimum multi-hop relay of wireless ultraviolet communication in military vehicle secret formation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2636–2642. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190172 [4] FAN Rongfei, ATAPATTU S, CHEN Wen, et al. Throughput maximization for multi-hop decode-and-forward relay network with wireless energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 24582–24595. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2831253 [5] MONDAL S, ROY S D, KUNDU S, et al. Energy harvesting based multihop relaying in cognitive radio network[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 97(4): 6325–6342. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4840-9 [6] BANERJEE A, PAUL A, MAITY S P, et al. Joint power allocation and route selection for outage minimization in multihop cognitive radio networks with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(1): 82–92. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2017.2785769 [7] BHATT M, BODDAPATI H K, and PRAKRIYA S. Performance off cluster-based multi-hop underlay networks with energy harvesting nodes[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(9): 1476–1484. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2018.6271 [8] NGUYEN T V and AN B. Cognitive multihop wireless powered relaying networks over Nakagami-m fading channels[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 154600–154616. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2949081 [9] XU Chi, XIA Changqing, SONG Chunhe, et al. Multi-hop cognitive wireless powered networks: Outage analysis and optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 4338–4347. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2884916 [10] POORNIMA S and BABU A V. Performance analysis of energy harvesting cognitive relay networks with primary interference[J]. Telecommunication Systems, 2018, 68(3): 445–459. doi: 10.1007/s11235-017-0402-4 [11] 罗轶, 施荣华, 董健, 等. κ-μ衰落下能量采集认知中继网络性能分析[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2020, 47(1): 52–59. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2020.01.008LUO Yi, SHI Ronghua, DONG Jian, et al. Analysis of the performance of energy harvesting cognitive relay networks overκ-μ fading[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2020, 47(1): 52–59. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2020.01.008 [12] GE Lu, CHEN Gaojie, ZHANG Yue, et al. Performance analysis for multihop cognitive radio networks with energy harvesting by using stochastic geometry[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(2): 1154–1163. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2953130 [13] SMITH P J, DMOCHOWSKI P A, SURAWEERA H A, et al. The effects of limited channel knowledge on cognitive radio system capacity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2013, 62(2): 927–933. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2012.2227864 [14] GRADSHTEYN I S, RYZHIK I M, JEFFREY A, et al. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products[M]. 7th ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2007: 340–341. [15] CLERC M and KENNEDY J. The particle swarm - explosion, stability, and convergence in a multidimensional complex space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(1): 58–73. doi: 10.1109/4235.985692 [16] 周燕, 刘培玉, 赵静, 等. 基于自适应惯性权重的混沌粒子群算法[J]. 山东大学学报: 理学版, 2012, 47(3): 27–32. doi: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-9352.2012.03.006ZHOU Yan, LIU Peiyu, ZHAO Jing, et al. Chaos particle swarm optimization based on the adaptive inertia weight[J]. Journal of Shandong University:Natural Science, 2012, 47(3): 27–32. doi: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-9352.2012.03.006 [17] 曹艳阳, 冯云霞, 赵文涛. 基于logistic映射的自适应变尺度混沌粒子群算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2017, 29(10): 2241–2246. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201710002CAO Yanyang, FENG Yunxia, ZHAO Wentao, et al. Adaptive mutative scale chaos particles swarm optimization based on logistic mapping[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2017, 29(10): 2241–2246. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201710002 -





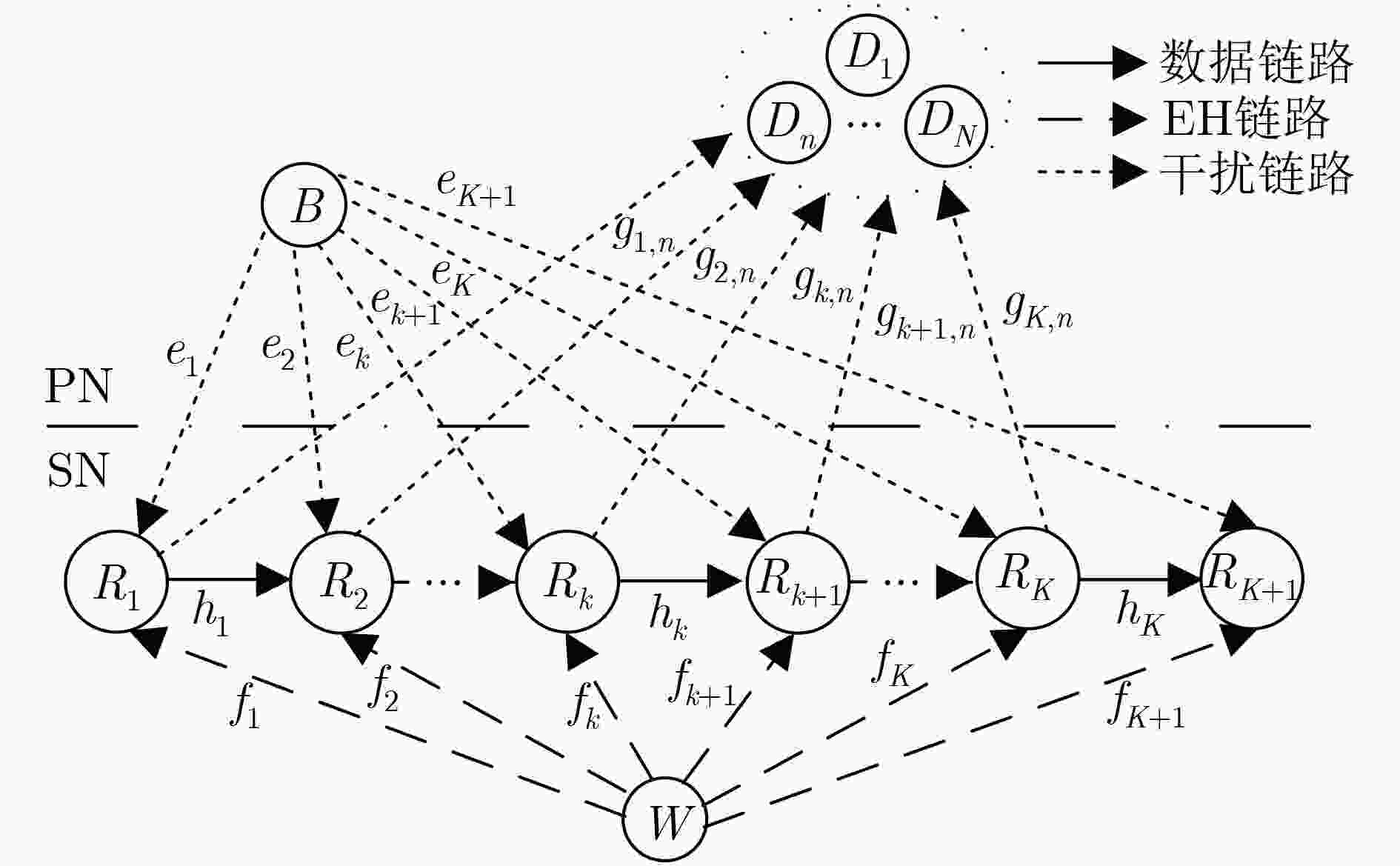
 下载:
下载:
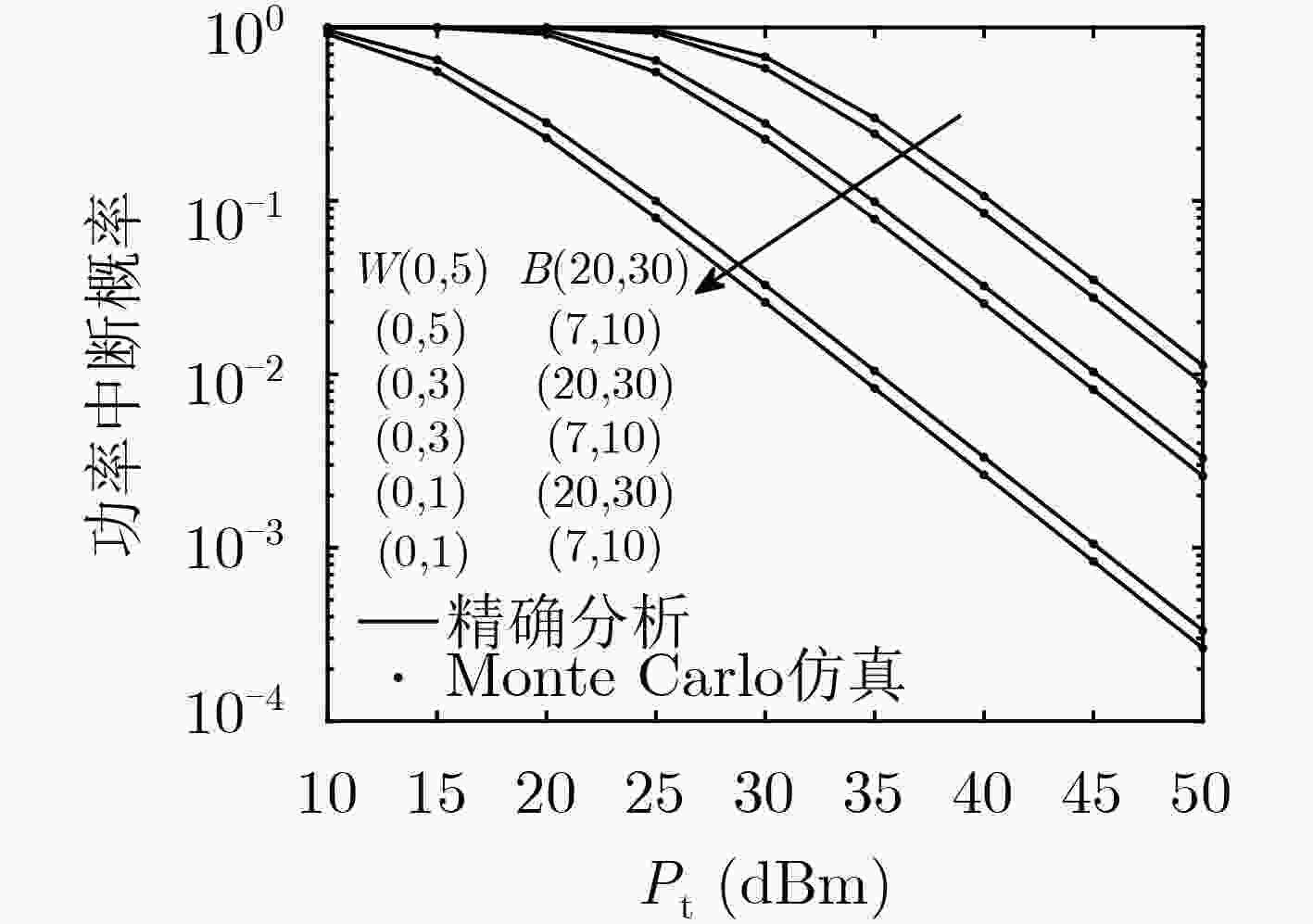

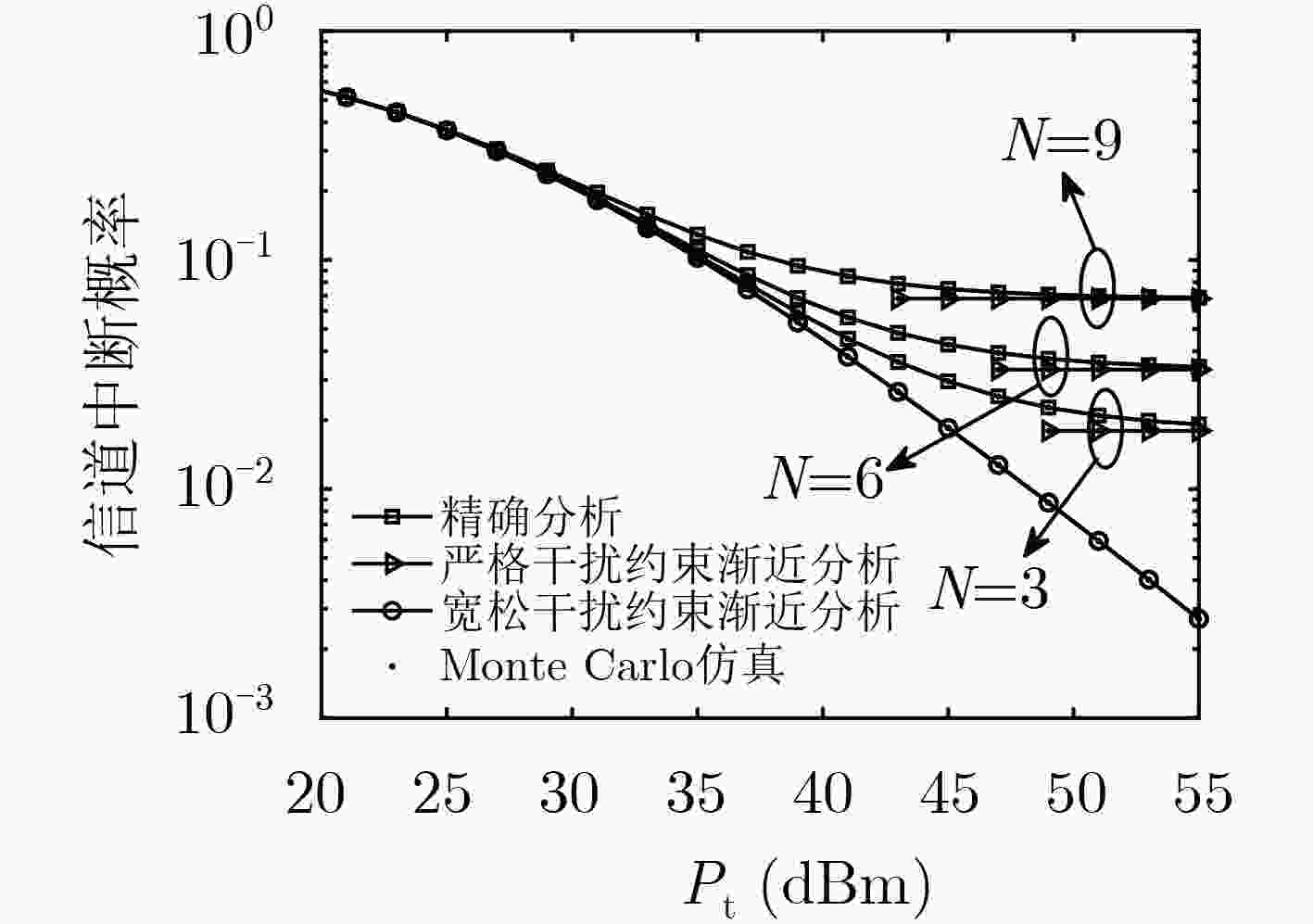

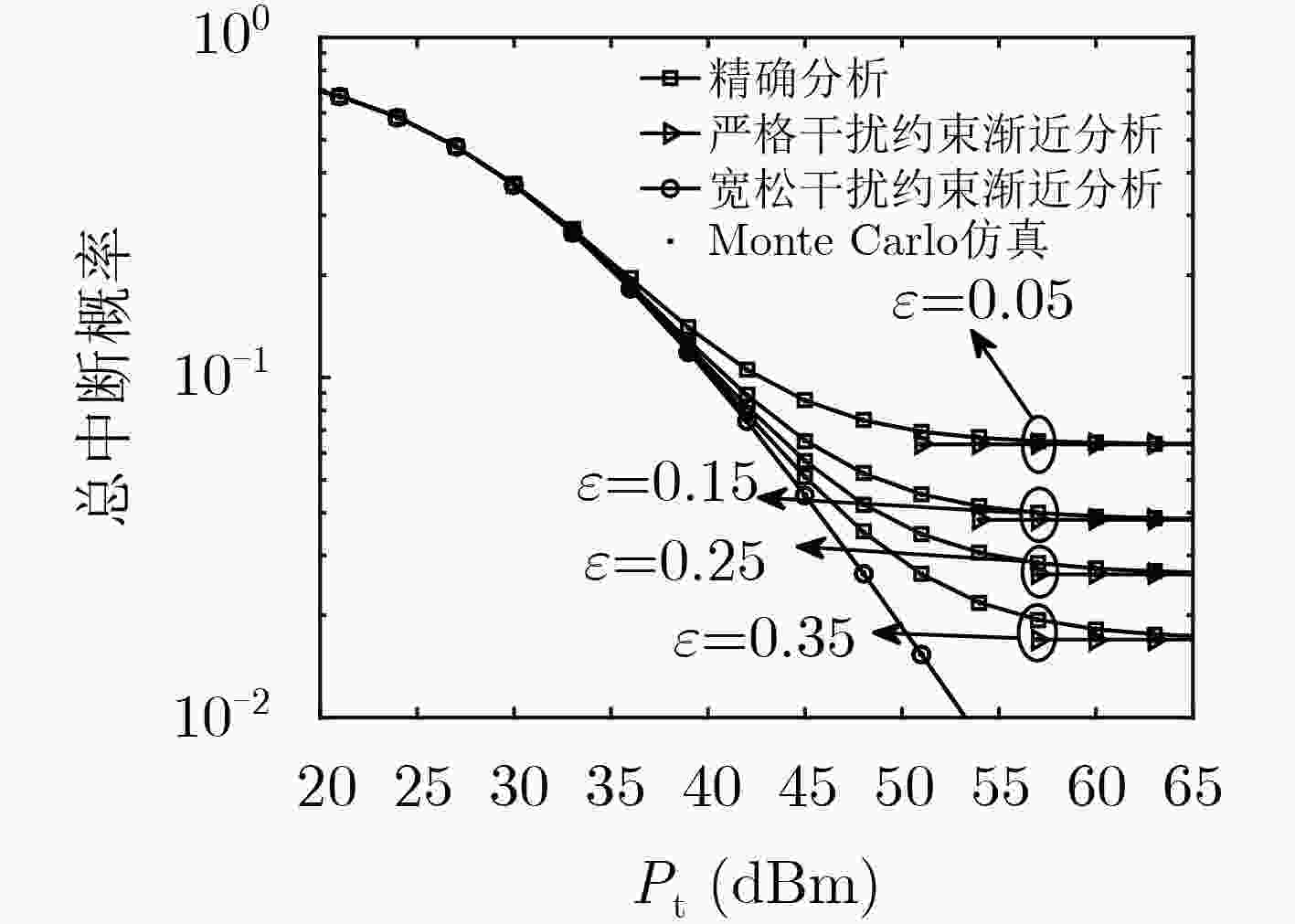

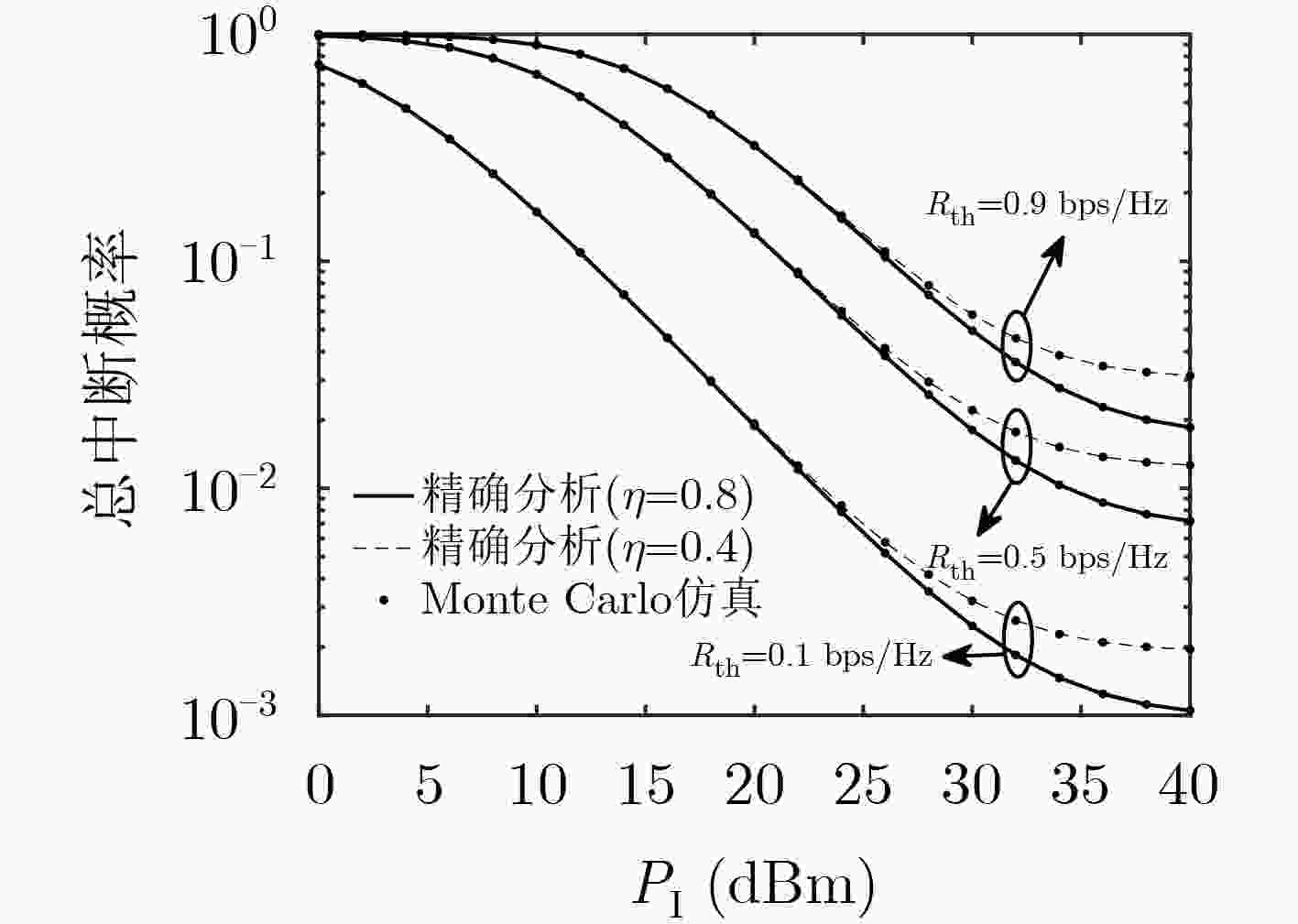

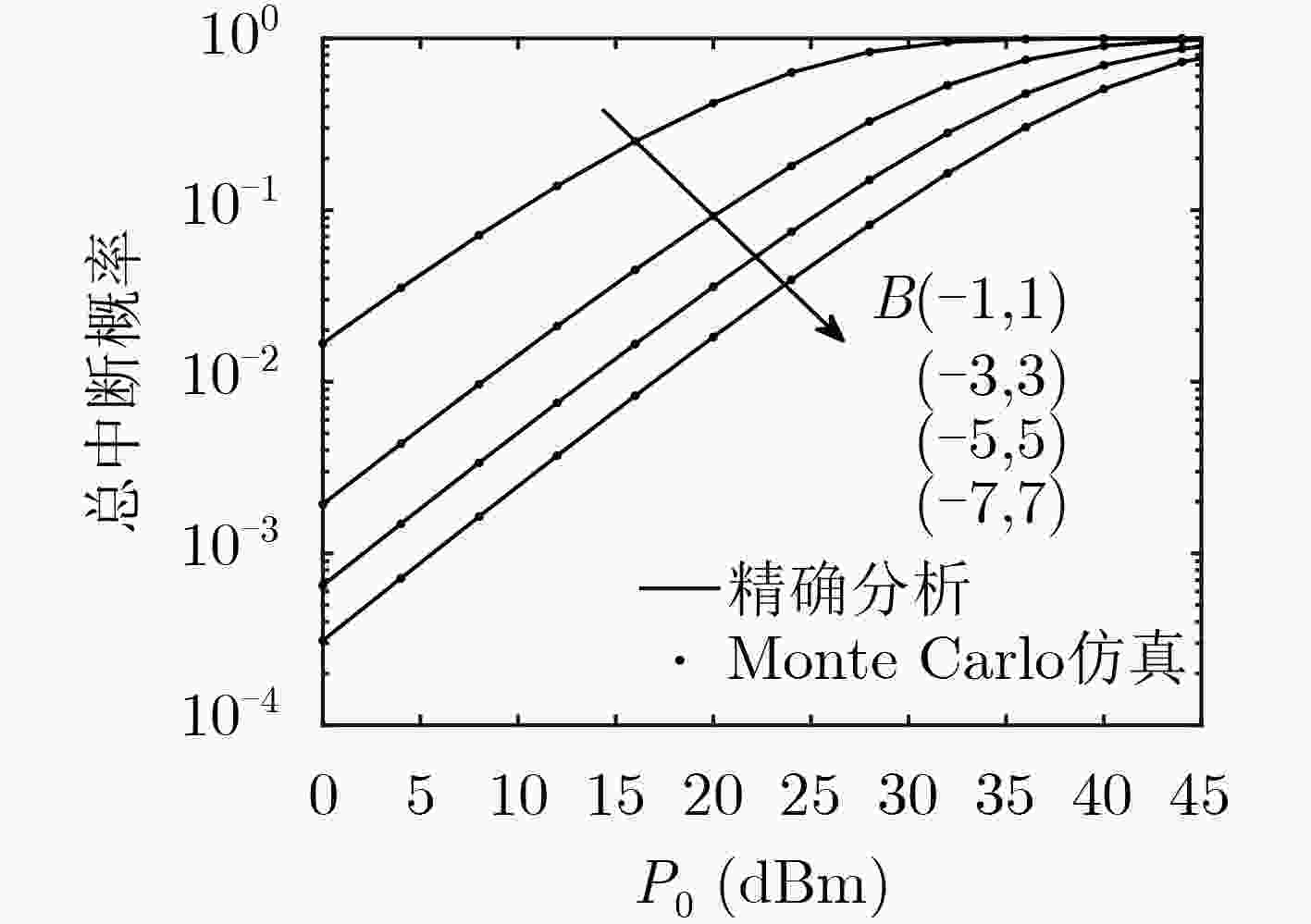

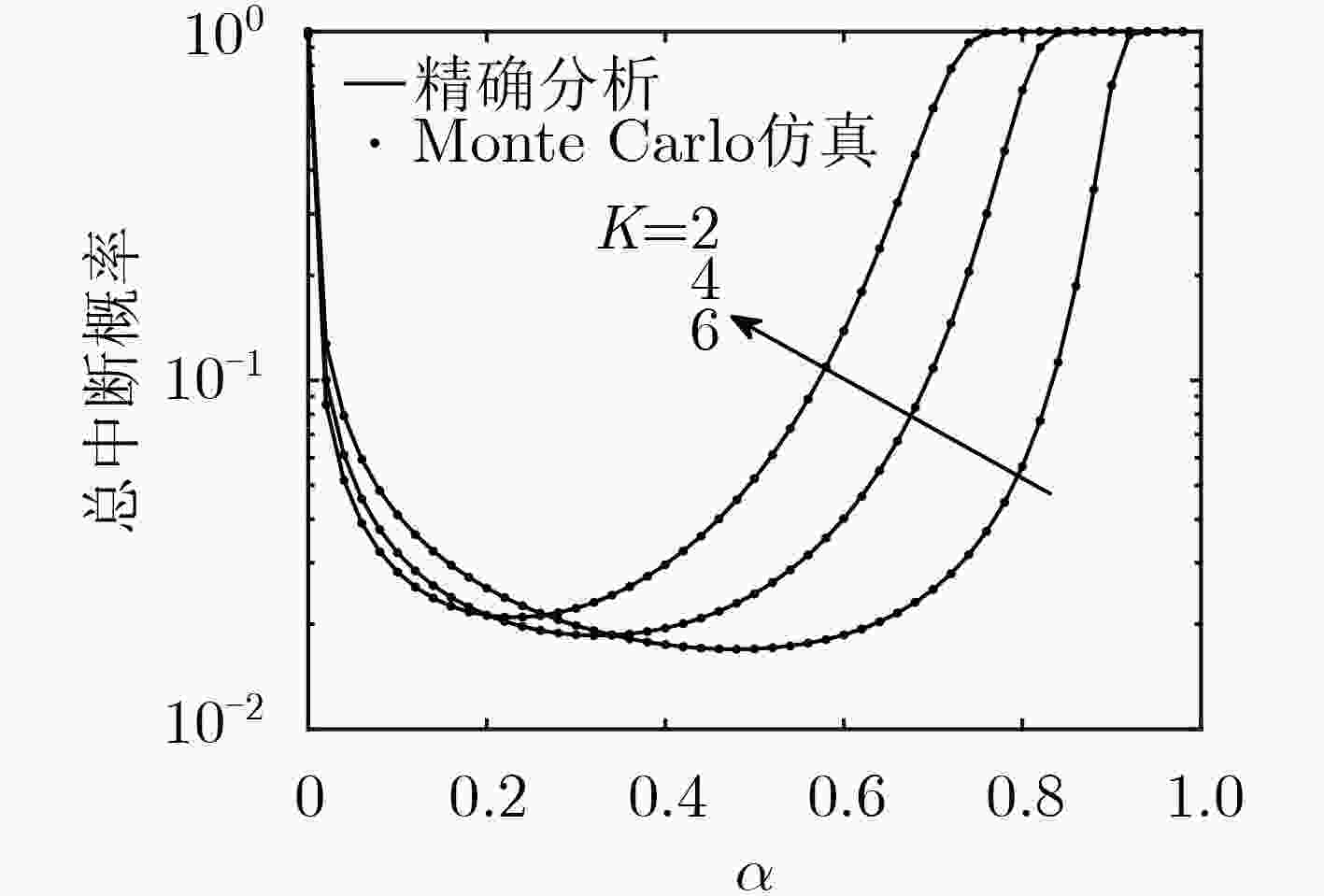

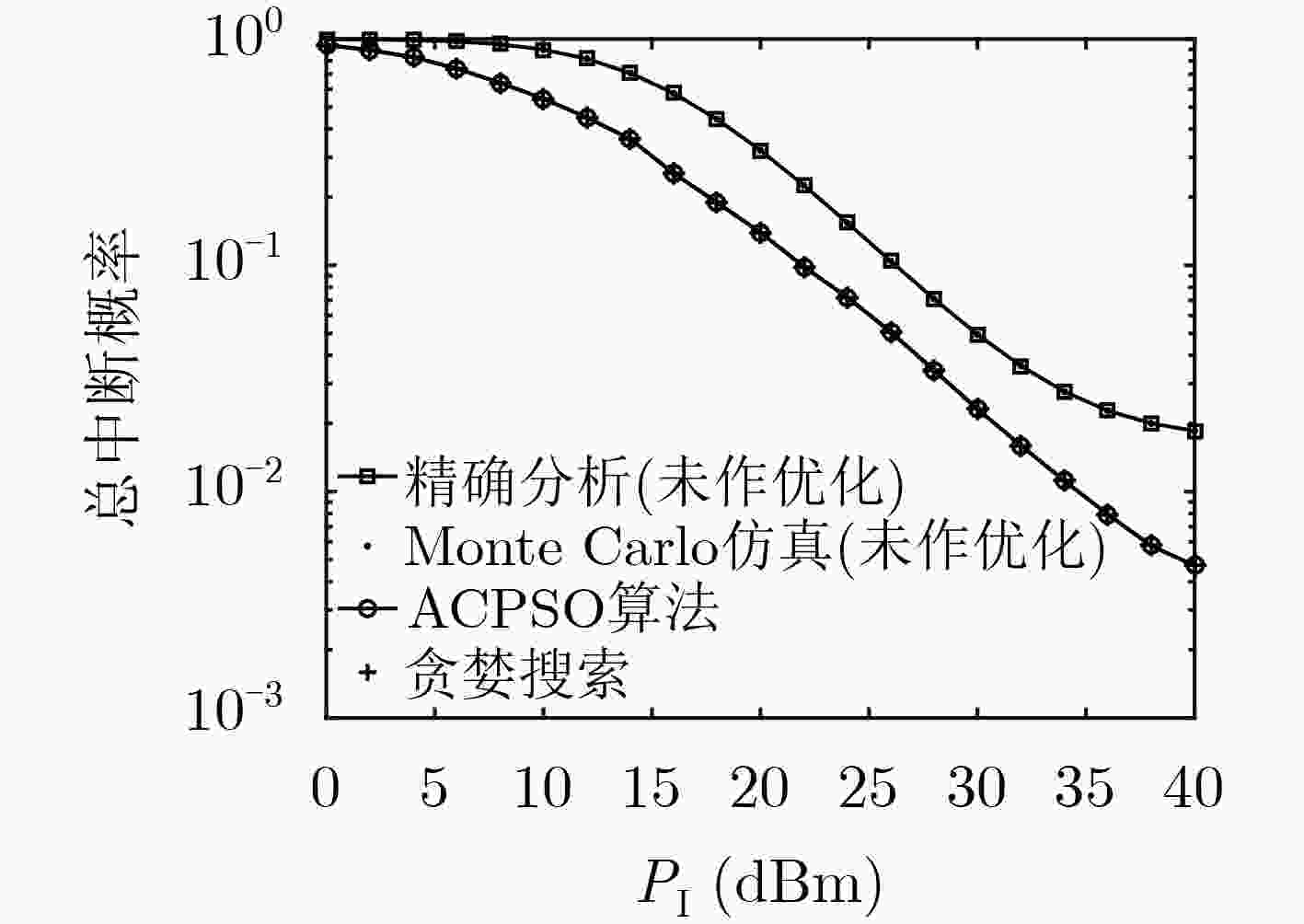


 下载:
下载:
