Off-grid DOA Estimation Method Based on Covariance Matrix Reconstruction
-
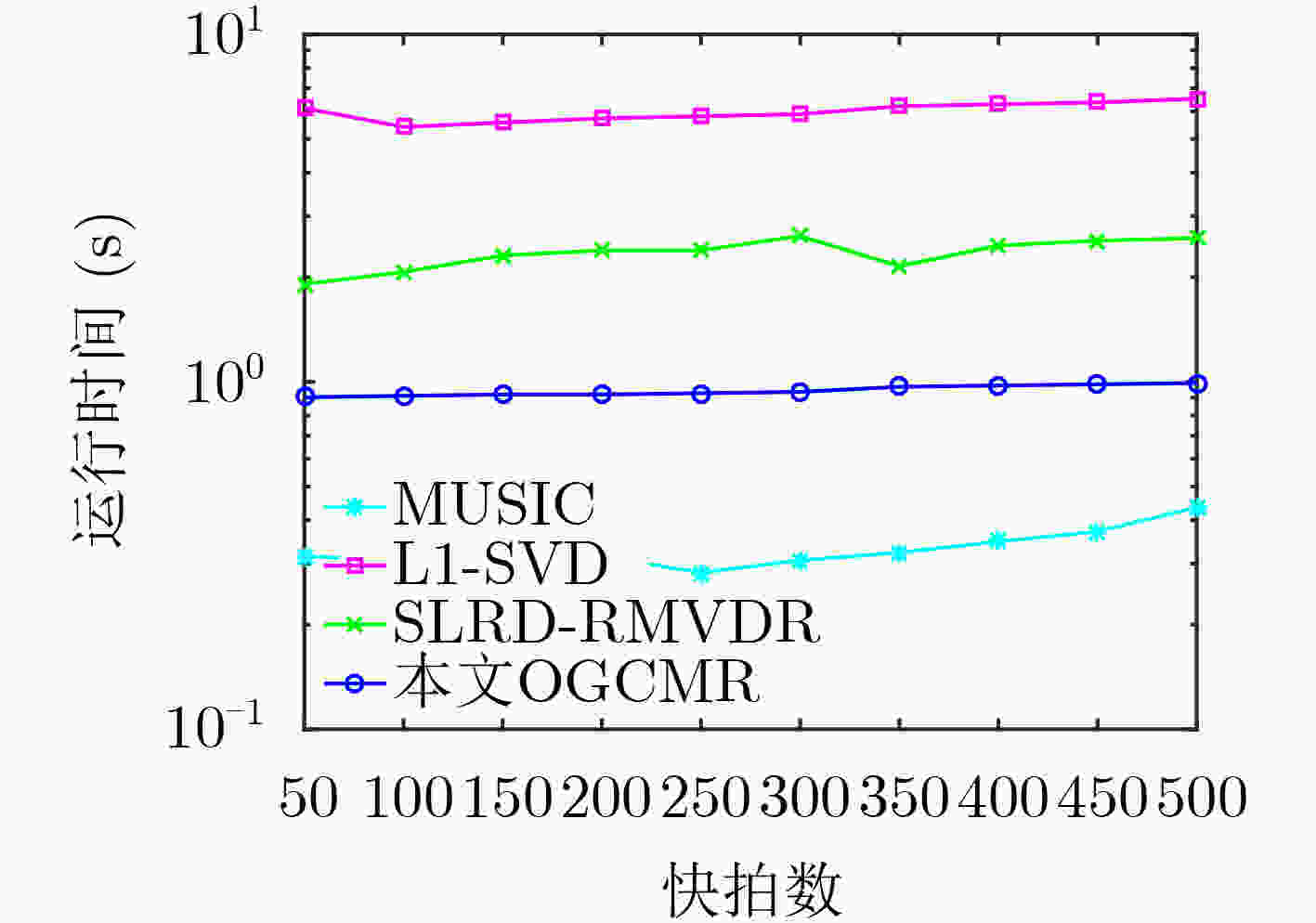
摘要: 针对稀疏表示模型中网格失配导致波达方向角(DOA)估计存在较大估计误差的问题,该文提出一种基于协方差矩阵重构的离网格(Off-Grid)DOA估计方法(OGCMR)。首先,将DOA与网格点之间偏移量包含进所构建接收数据空域离散稀疏表示模型;而后基于重构信号协方差矩阵建立关于DOA估计的稀疏表示凸优化问题;再构建采样协方差矩阵估计误差凸模型,并将此凸集显式包含进稀疏表示模型以改善稀疏信号重构性能;最后采用交替迭代方法求解所得联合优化问题以获得网格偏移参数及离网格DOA估计。数值仿真表明,与传统多重信号分类(MUSIC)、L1-SVD及基于稀疏和低秩恢复的稳健MVDR (SLRD-RMVDR)等估计算法相比,所提算法具有较好的角度分辨力以及较高的DOA估计精度。Abstract: Focusing on the problem of rather large estimation error in Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation caused by grid mismatch in the sparse representation model, an Off-Grid DOA estimation method based on Covariance Matrix Reconstruction (OGCMR) is proposed. Firstly, the offset between the DOA and the grid points is incorporated into the constructed spatial discrete sparse representation model of the received data; After that, based on the reconstructed signal covariance matrix, a sparse representation convex optimization problem associated with DOA estimation can be established; Subsequently, a sampling covariance matrix estimation error convex model is constructed, and then this convex set can be explicitly included into the sparse representation model to improve the performance of sparse signal reconstruction; Finally, an alternating optimization method can be exploited to solve the resultant joint optimization problem to acquire the grid offset parameters as well as the off-grid DOA estimation. Numerical simulations show that, compared with the traditional conventional MUltiple SIgnal Classification(MUSIC), L1-SVD, Sparse and Low-Rank Decomposition based Robust MVDR (SLRD-RMVDR) algorithms and so on, the proposed algorithm has rather better angular resolution and higher DOA estimation accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Direction Of Arrival (DOA) /
- Off-grid /
- Sparse representation /
- Convex optimization
-
表 1 误差参数对算法重构性能影响
误差参数$\eta $ 0.1 1 4 8 12 16 重构信号峰值功率${{\bar{\boldsymbol P}}_1}$ –0.0718 –0.1063 –0.2673 –1.3476 –2.4351 –3.0976 重构信号峰值功率${{\bar{\boldsymbol P}}_2}$ –0.0524 –0.0973 –0.1279 –0.4623 –1.3523 –1.7915 -
[1] XU Haiyun, WANG Daming, BA Bin, et al. Direction-of-arrival estimation for both uncorrelated and coherent signals in coprime array[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 18590–18600. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2896979 [2] 蒋莹, 王冰切, 韩俊, 等. 基于分布式压缩感知的宽带欠定信号DOA估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1690–1697. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180723JIANG Ying, WANG Bingqie, HAN Jun, et al. Underdetermined wideband DOA estimation based on distributed compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1690–1697. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180723 [3] 林云, 胡强. 多测量向量模型下的修正MUSIC算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2584–2589. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180001LIN Yun and HU Qiang. Modified MUSIC algorithm for multiple measurement vector models[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2584–2589. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180001 [4] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276 [5] SHIKAGAWAI Y and ICHIGE K. High-resolution and low-cost direction-of-arrival estimation by 2q-root-MUSIC method[C]. 2013 IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SiPS), Taipei City, China, 2013. [6] PESAVENTO M and GERSHMAN A B. Maximum-likelihood direction-of-arrival estimation in the presence of unknown nonuniform noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2001, 49(7): 1310–1324. doi: 10.1109/78.928686 [7] LIU Yuan, LIU Hongwei, XIA Xianggen, et al. Target localization in multipath propagation environment using dictionary-based sparse representation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 150583–150597. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947497 [8] WANG Xianpeng, MENG Dandan, HUANG Mengxing, et al. Reweighted regularized sparse recovery for DOA estimation with unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(2): 290–293. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2884457 [9] HU Bin, WU Xiaochuan, ZHANG Xin, et al. DOA estimation based on compressed sensing with gain/phase uncertainties[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(11): 1346–1352. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5087 [10] CUI Wei, SHEN Qing, LIU Wei, et al. Low complexity DOA estimation for wideband off-grid sources based on re-focused compressive sensing with dynamic dictionary[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(5): 918–930. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2932973 [11] MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, and WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010–3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882 [12] 韦娟, 计永祥, 牛俊儒. 一种新的稀疏重构的DOA估计算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 45(5): 13–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.05.003WEI Juan, JI Yongxiang, and NIU Junru. Novel algorithm for DOA estimation based on the sparse reconstruction[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2018, 45(5): 13–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.05.003 [13] YANG Jie, YANG Yixin, LIAO Guisheng, et al. A super-resolution direction of arrival estimation algorithm for coprime array via sparse Bayesian learning inference[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2018, 37(5): 1907–1934. doi: 10.1007/s00034-017-0637-z [14] 王洪雁, 于若男. 基于稀疏和低秩恢复的稳健DOA估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 589–596. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190263WANG Hongyan and YU Ruonan. Sparse and low rank recovery based robust DOA estimation method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 589–596. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190263 [15] WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. Direction of arrival estimation for off-grid signals based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(7): 2004–2016. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2508059 [16] DAI Jisheng, BAO Xu, XU Weichao, et al. Root sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(1): 46–50. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2636319 [17] TIAN Ye, SUN Xiaoying, and ZHAO Shishun. DOA and power estimation using a sparse representation of second-order statistics vector and -norm approximation[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 105: 98–108. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.05.014 [18] HE Zhenqing, SHI Zhiping, and HUANG Lei. Covariance sparsity-aware DOA estimation for nonuniform noise[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 28: 75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2014.02.013 [19] ZHANG Xiaowei, JIANG Tao, LI Yingsong, et al. An off-grid DOA estimation method using proximal splitting and successive nonconvex sparsity approximation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 66764–66773. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917309 [20] OTTERSTEN B, STOICA P, and ROY R. Covariance matching estimation techniques for array signal processing applications[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 1998, 8(3): 185–210. doi: 10.1006/dspr.1998.0316 [21] HORN R A and JOHNSON C R. Matrix Analysis[M]. Cambridge, U.K: Cambridge University Press, 1985: 1–162. [22] ARLOT S and CELISSE A. A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection[J]. Statistics Surveys, 2010, 4: 40–79. doi: 10.1214/09-SS054 [23] ZHOU Qing, ZHENG Hong, WU Xiongbin, et al. Fractional Fourier transform-based radio frequency interference suppression for high-frequency surface wave radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(1): 75. doi: 10.3390/rs12010075 [24] DAS A. A Bayesian sparse-plus-low-rank matrix decomposition method for direction-of-arrival tracking[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(15): 4894–4902. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2715347 -





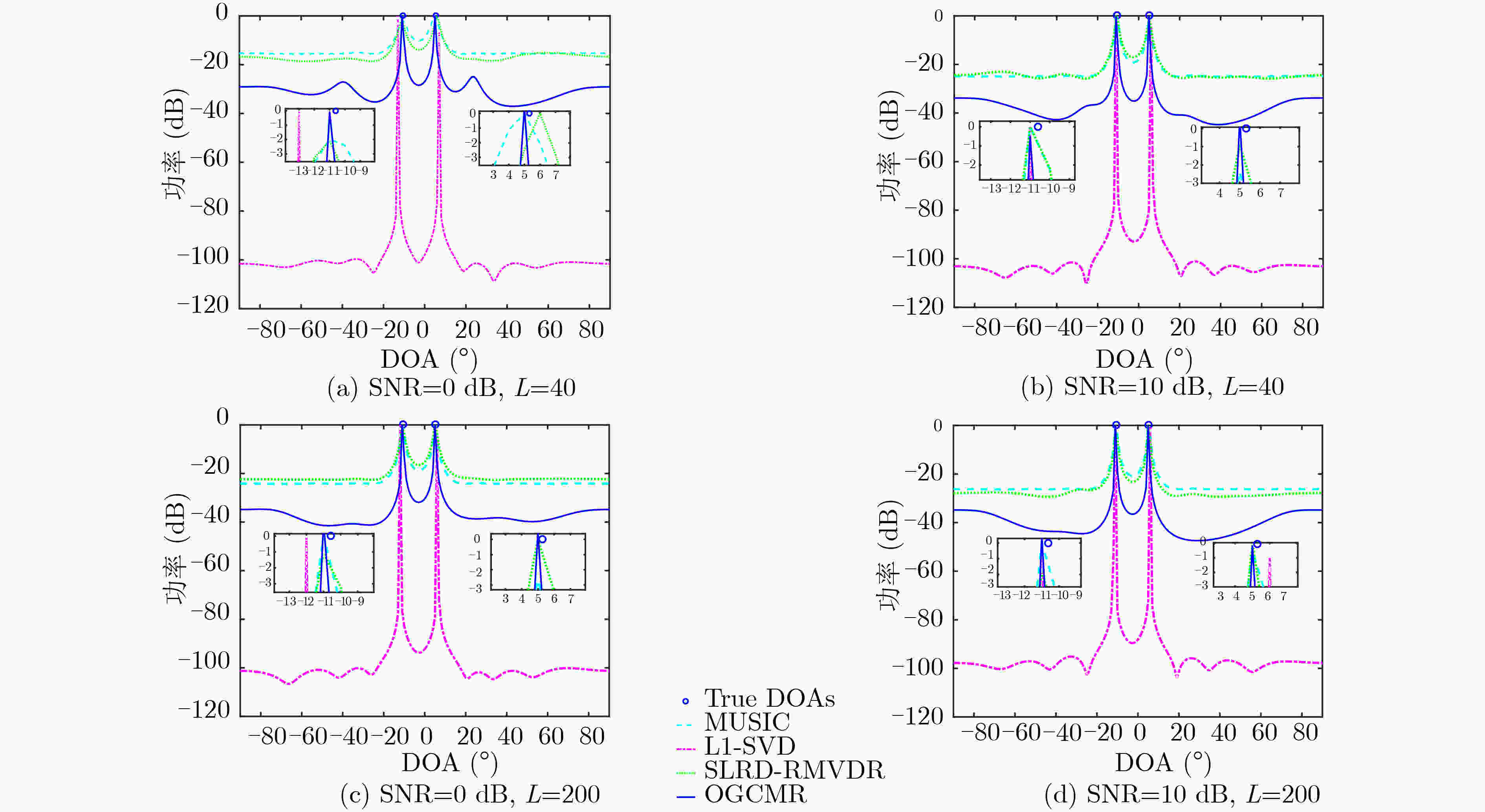
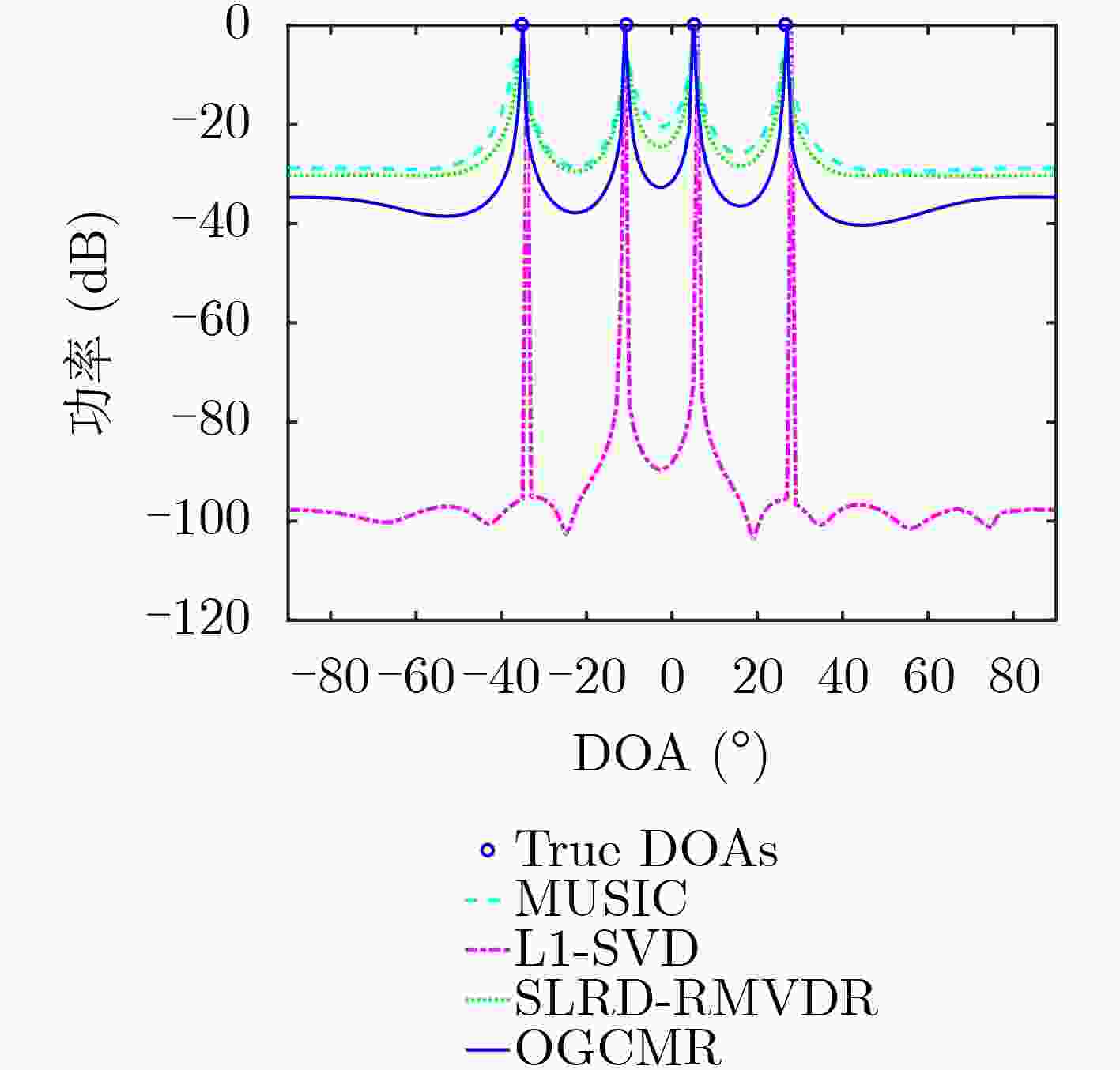
 下载:
下载:
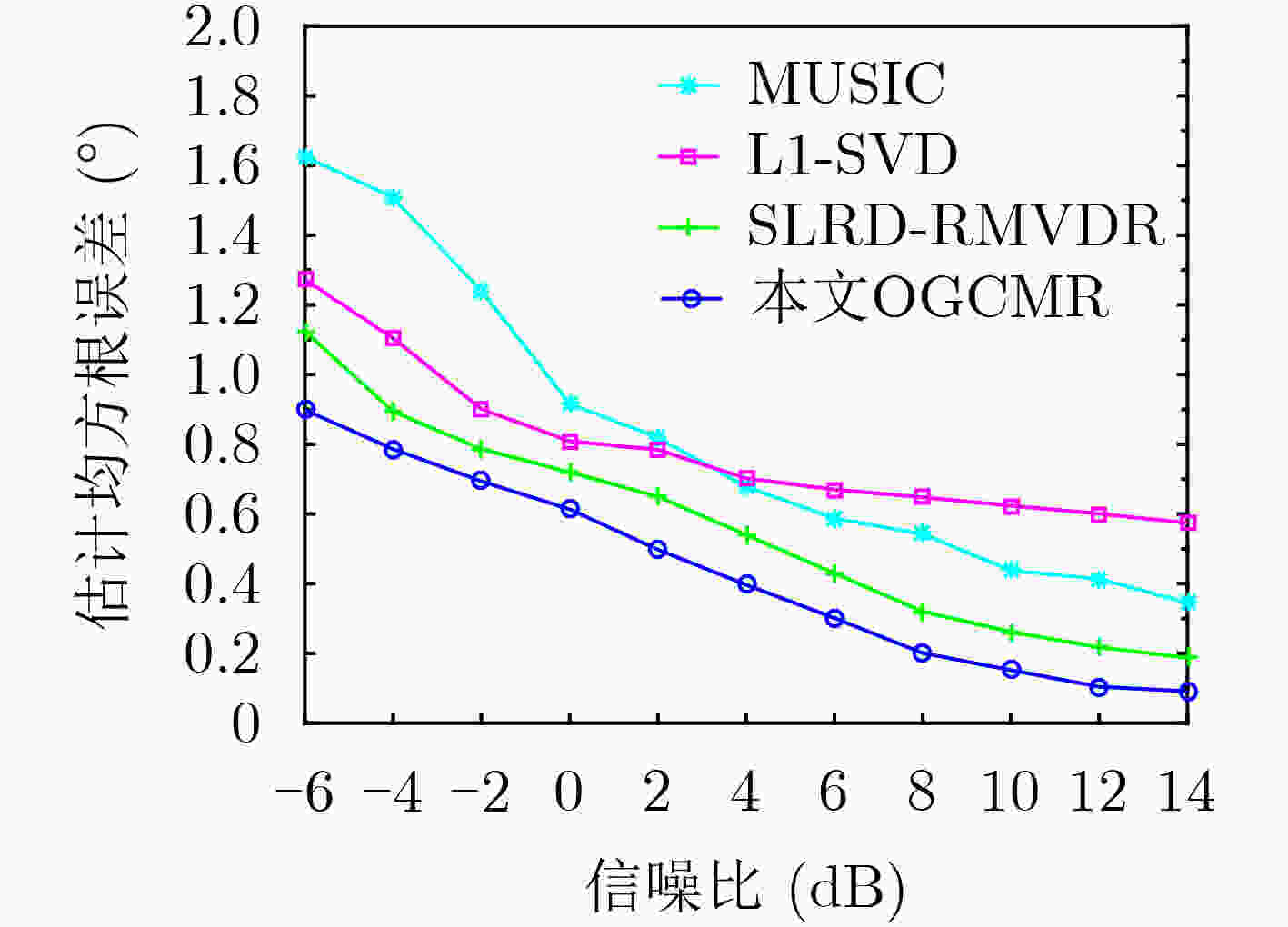
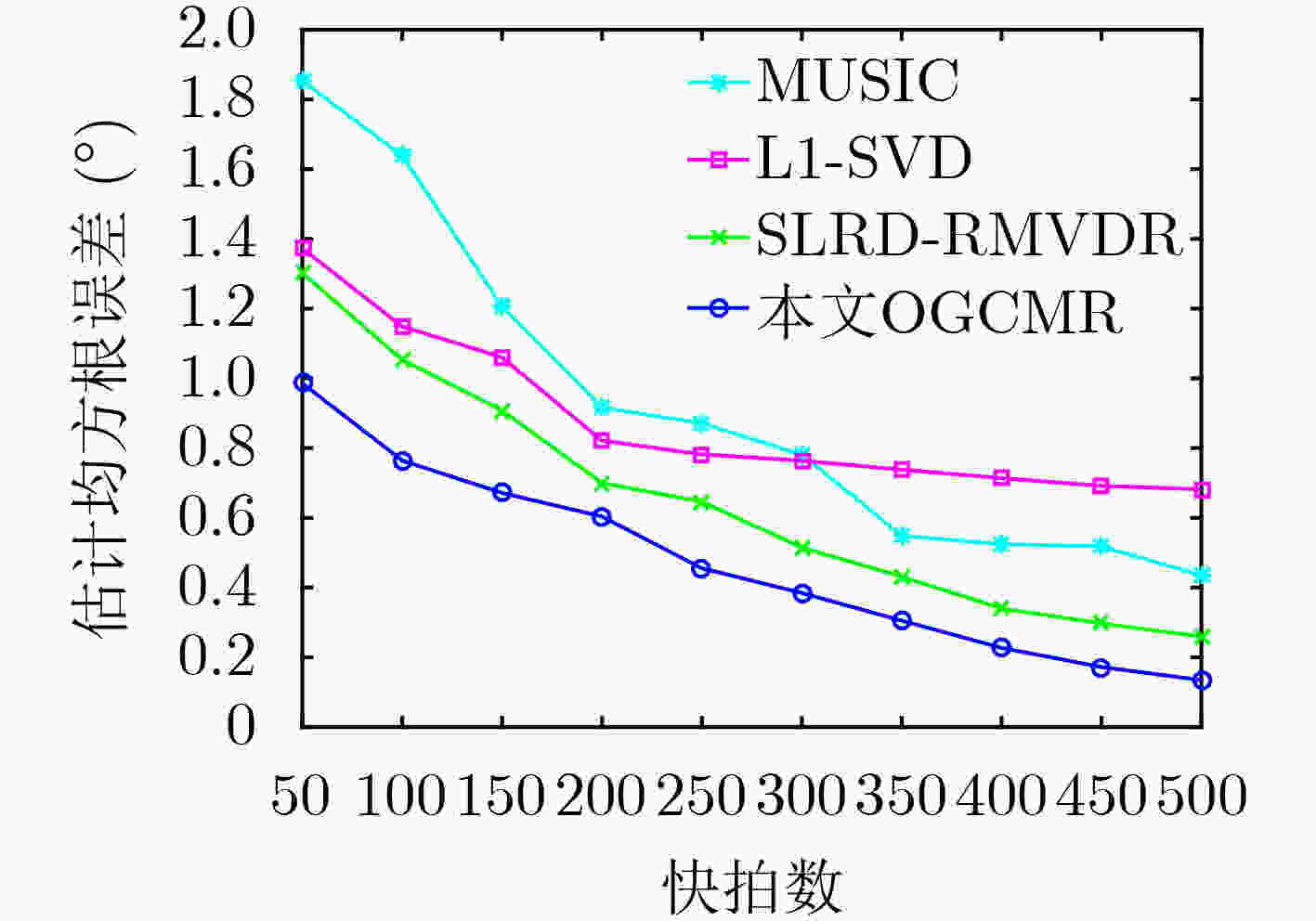


 下载:
下载:
