Blind Stereo Image Quality Evaluation Based on Spatial Domain and Transform Domain Feature Extraction
-
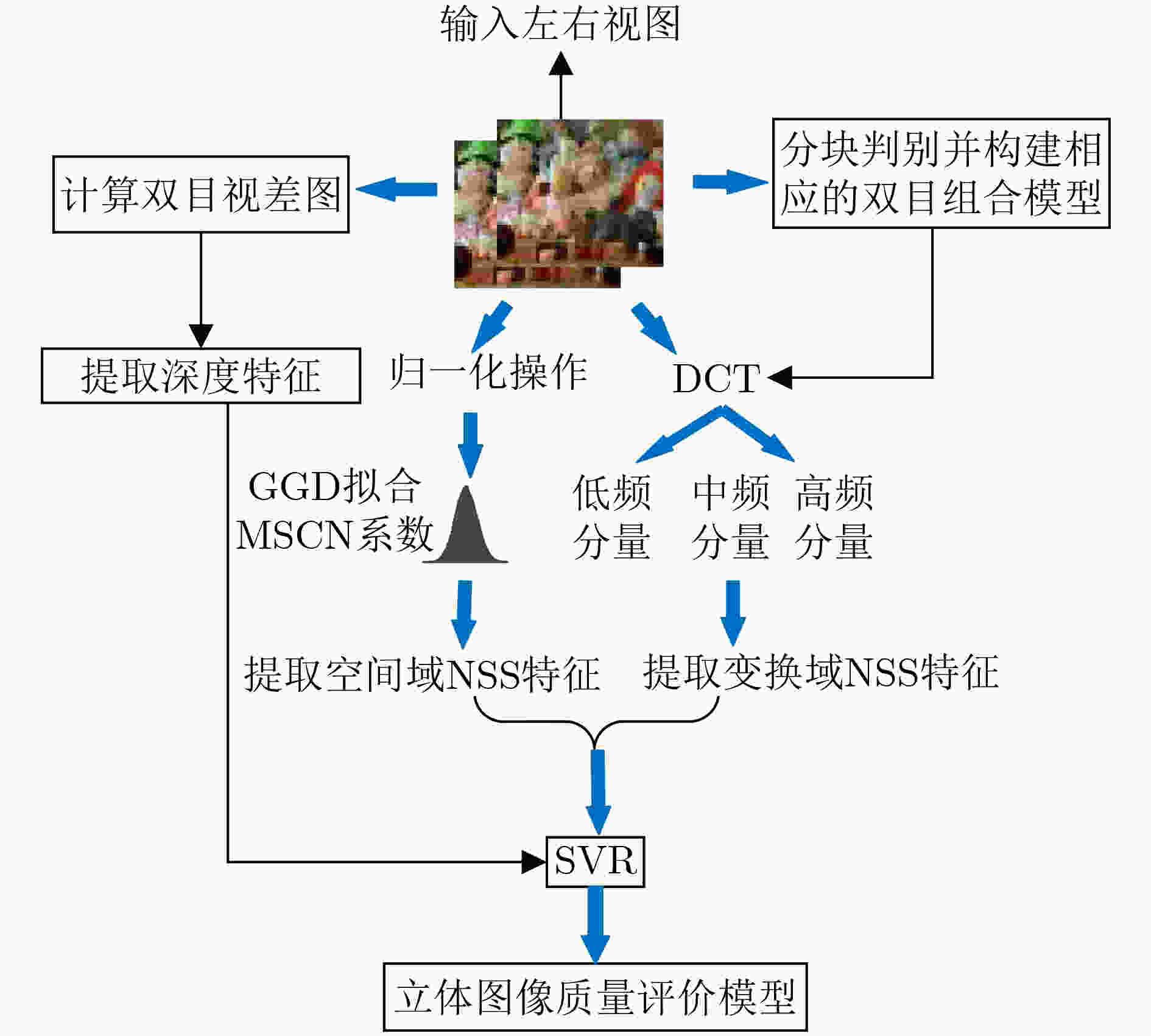
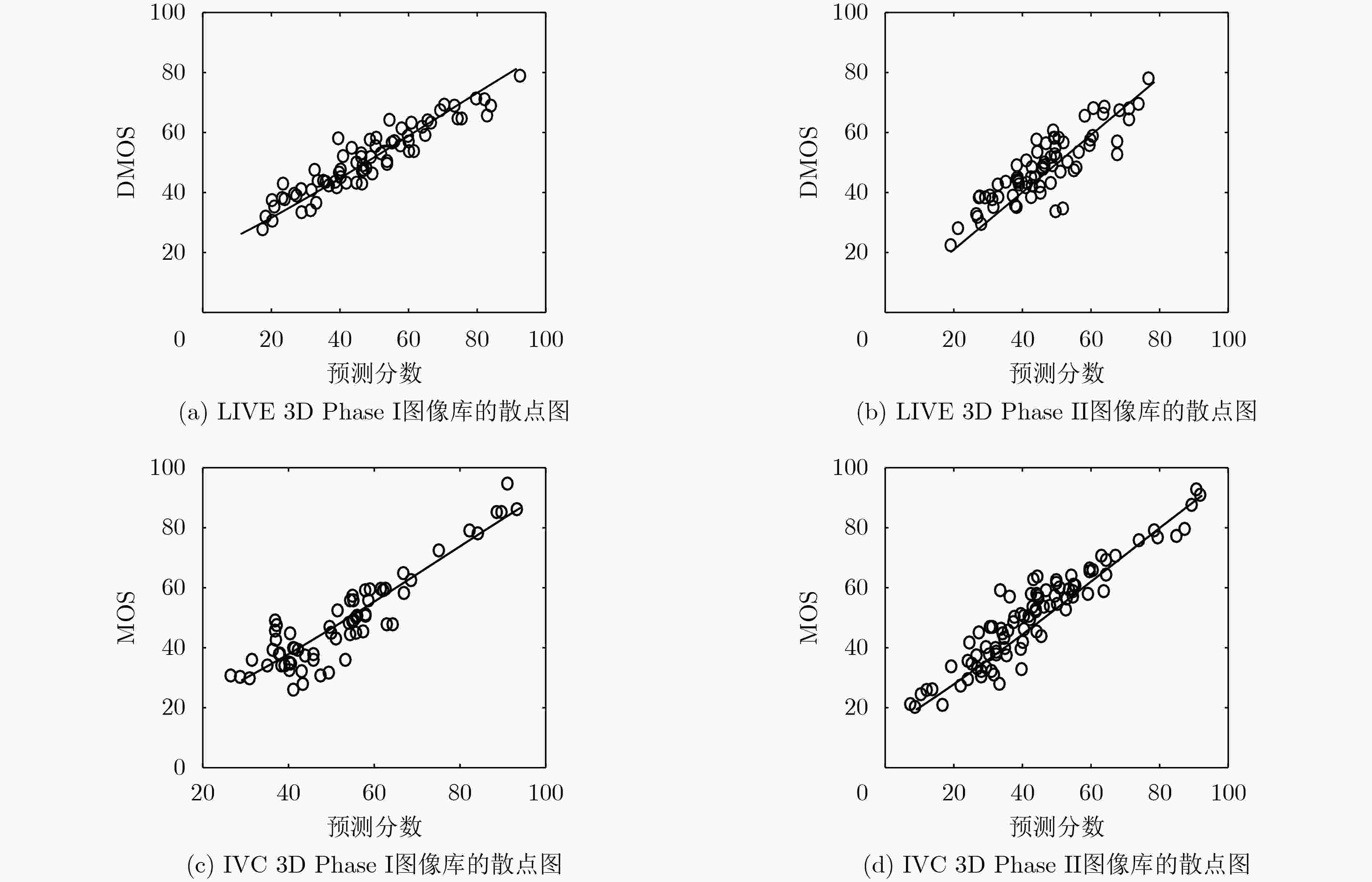
摘要: 针对立体图像质量预测准确性不足的问题,该文提出了一种结合空间域和变换域提取质量感知特征的无参考立体图像质量评价模型。在空间域和变换域分别提取输入的左、右视图的自然场景统计特征,并在变换域提取合成独眼图的自然场景统计特征,然后将其输入到支持向量回归(SVR)中,训练从特征域到质量分数域的预测模型,并以此建立SIQA客观质量评价模型。在4个公开的立体图像数据库上与一些主流的立体图像质量评价算法进行对比,以在LIVE 3D Phase I图像库中的性能测试为例,Spearman秩相关系数、皮尔逊线性相关系数和均方根误差分别达到0.967,0.946和5.603,验证了所提算法的有效性。Abstract: For the problem of insufficient accuracy of stereo image quality prediction, a blind stereoscopic image quality assessment model combining spatial domain and transform domain to extract quality-aware features is proposed. Firstly, the statistical features of the natural scenes in the left and right views are extracted respectively in space domain and transformation domain, and statistical features of natural scenes from synthetic monocular images is extracted in transformation domain. Finally, Support Vector Regression (SVR) is used to train a stereoscopic image quality evaluation model from the feature domain to the quality score domain, so as to establish SIQA objective quality evaluation model. The performance of the proposed method is compared with some state-of-the-art full-reference, reduced-reference and no-reference stereoscopic image quality evaluation algorithms on the four public stereo image databases, taking the performance test in live 3D phase I image library as an example. SROCC of 0.967, PLCC of 0.946 and RMSE of 5.603 are achieved, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 LIVE 3D Phase I和II图像库中的性能测试
失真类型 PLCC SROCC RMSE WN 0.964(0.988) 0.958(0.964) 6.004(4.954) JP2K 0.924 (0.927) 0.907(0.915) 6.518(5.361) JPEG 0.730 (0.903) 0.785(0.900) 7.010(5.337) Gblur 0.972 (0.979) 0.937(0.962) 5.412(3.478) FF 0.943 (0.945) 0.913(0.921) 5.433(3.679) All 0.967 (0.949) 0.946(0.935) 5.603(3.501) 表 2 LIVE 3D Phase I和II图像库中整体性能比较
对比算法 LIVE 3D Phase I LIVE 3D Phase II PLCC SROCC RMSE PLCCS ROCCR MSE Lin[29] FR 0.936 0.931 5.744 0.911 0.893 4.647 Khan[23] FR 0.927 0.916 – 0.932 0.922 – Chen FR[14] FR 0.833 0.915 6.268 0.770 0.888 4.892 Jiang[24] FR 0.945 0.933 5.276 0.916 0.903 4.523 Ma[25] RR 0.930 0.929 6.024 0.921 0.917 4.390 SINQ[8] NR 0.955 0.935 4.781 0.936 0.931 3.959 Zhou[8] NR 0.941 0.921 5.540 0.923 0.919 4.262 Karimi[26] NR 0.956 0.940 4.998 0.923 0.913 4.436 Yang-SAE[27] NR 0.961 0.949 – 0.938 0.928 – Fezza[13] NR – – – 0.925 0.908 3.018 BRISQUE[28] NR 0.910 0.901 6.793 0.782 0.770 7.038 本文算法 NR 0.967 0.946 5.603 0.949 0.935 3.501 -
[1] 高新波, 路文, 查林, 等. 超高清视频画质提升技术及其芯片化方案[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 32(5): 681–697. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2020.05.001GAO Xinbo, LU Wen, ZHA Lin, et al. Quality elevation technique for UHD video and its VLSI solution[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 32(5): 681–697. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2020.05.001 [2] 张敏辉, 杨剑. 评价SAR图像去噪效果的无参考图像质量指标[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 30(4): 530–536. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.04.014ZHANG Minhui and YANG Jian. A new referenceless image quality index to evaluate denoising performance of SAR images[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 30(4): 530–536. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.04.014 [3] 徐弦秋, 刘宏清, 黎勇, 等. 基于RGB通道下模糊核估计的图像去模糊[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 30(2): 216–221. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.02.009XU Xianqiu, LIU Hongqing, LI Yong, et al. Image deblurring with blur kernel estimation in RGB channels[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 30(2): 216–221. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.02.009 [4] CHEN Yong, ZHU Kaixin, and LIU Huanlin. Blind stereo image quality assessment based on binocular visual characteristics and depth perception[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 85760–85771. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992746 [5] DING Jian and SPERLING G. A gain-control theory of binocular combination[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(4): 1141–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509629103 [6] DING Yong and ZHAO Yang. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment guided by visual hierarchical structure and binocular effects[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(10): 2610–2621. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.002610 [7] HACHICHA W, KAANICHE M, BEGHDADI A, et al. No-reference stereo image quality assessment based on joint wavelet decomposition and statistical models[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2017, 54: 107–117. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2017.03.005 [8] LIU Lixiong, LIU Bao, SU Chechun, et al. Binocular spatial activity and reverse saliency driven no-reference stereopair quality assessment[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2017, 58: 287–299. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2017.08.011 [9] DAKIN S C and BEX P J. Natural image statistics mediate brightness ‘filling in’[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences, 2003, 270(1531): 2341–2348. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2003.2528 [10] 陈勇, 帅锋, 樊强. 基于自然统计特征分布的无参考图像质量评价[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(7): 1645–1653. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151058CHEN Yong, SHUAI Feng, and FAN Qiang. A no-reference image quality assessment based on distribution characteristics of natural statistics[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(7): 1645–1653. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151058 [11] MOORTHY A K, SU Chechun, MITTAL A, et al. Subjective evaluation of stereoscopic image quality[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2013, 28(8): 870–883. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2012.08.004 [12] RYU S and SOHN K. No-reference quality assessment for stereoscopic images based on binocular quality perception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2014, 24(4): 591–602. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2013.2279971 [13] ZHOU Jun, WANG Ling, YIN Haibing, et al. Eye movements and visual discomfort when viewing stereoscopic 3D content[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 91: 41–53. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2018.12.008 [14] CHEN Mingjun, SU Chechun, KWON D K, et al. Full-reference quality assessment of stereopairs accounting for rivalry[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2013, 28(9): 1143–1155. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2013.05.006 [15] MEEGAN D V, STELMACH L B, and TAM W J. Unequal weighting of monocular inputs in binocular combination: Implications for the compression of stereoscopic imagery[J]. Journal of Experimental Psychology:Applied, 2001, 7(2): 143–153. doi: 10.1037/1076-898X.7.2.143 [16] SMITH III E L, FERN K, MANNY R, et al. Interocular suppression produced by rivalry stimuli: A comparison of normal and abnormal binocular vision[J]. Optometry and Vision Science:Official Publication of the American Academy of Optometry, 1994, 71(8): 479–491. doi: 10.1097/00006324-199408000-00001 [17] FEZZA S A, CHETOUANI A, and LARABI M C. Using distortion and asymmetry determination for blind stereoscopic image quality assessment strategy[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2017, 49: 115–128. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2017.08.009 [18] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [19] LAGO-FERNÁNDEZ L F and DECO G. A model of binocular rivalry based on competition in IT[J]. Neurocomputing, 2002, 44/46: 503–507. doi: 10.1016/S0925-2312(02)00408-3 [20] SHEIKH H R and BOVIK A C. Image information and visual quality[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(2): 430–444. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.859378 [21] GEISLER W S. Visual perception and the statistical properties of natural scenes[J]. Annual Review of Psychology, 2008, 59: 167–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085632 [22] WANG Jiheng, ZENG Kai, and WANG Zhou. Quality prediction of asymmetrically distorted stereoscopic images from single views[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Chengdu, China, 2014: 1–6. [23] KHAN S and CHANNAPPAYYA S S. Estimating depth-salient edges and its application to stereoscopic image quality assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(12): 5892–5903. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2860279 [24] JIANG Gangyi, XU Haiyong, YU Mei, et al. Stereoscopic image quality assessment by learning non-negative matrix factorization-based color visual characteristics and considering binocular interactions[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2017, 46: 269–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2017.04.010 [25] MA Jian, AN Ping, and SHEN Liquan. Reduced-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment using natural scene statistics and structural degradation[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 2768–2780. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2785282 [26] KARIMI M, SOLTANIAN N, SAMAVI S, et al. Blind stereo image quality assessment inspired by brain sensory-motor fusion[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 91: 91–104. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.03.004 [27] YANG Jiache, SIM K, LU Wen, et al. Predicting stereoscopic image quality via stacked auto-encoders based on stereopsis formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(7): 1750–1761. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2889562 [28] MITTAL A, MOORTHY A K, and BOVIK A C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(12): 4695–4708. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050 [29] LIN Yancong, YANG Jiachen, LU Wen, et al. Quality index for stereoscopic images by jointly evaluating cyclopean amplitude and cyclopean phase[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(1): 89–101. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2632422 [30] ZHANG Wei, QU Chenfei, MA Lin, et al. Learning structure of stereoscopic image for no-reference quality assessment with convolutional neural network[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 59: 176–187. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.01.034 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
