Spatial and Channel Attention Mechanism Method for Object Tracking
-
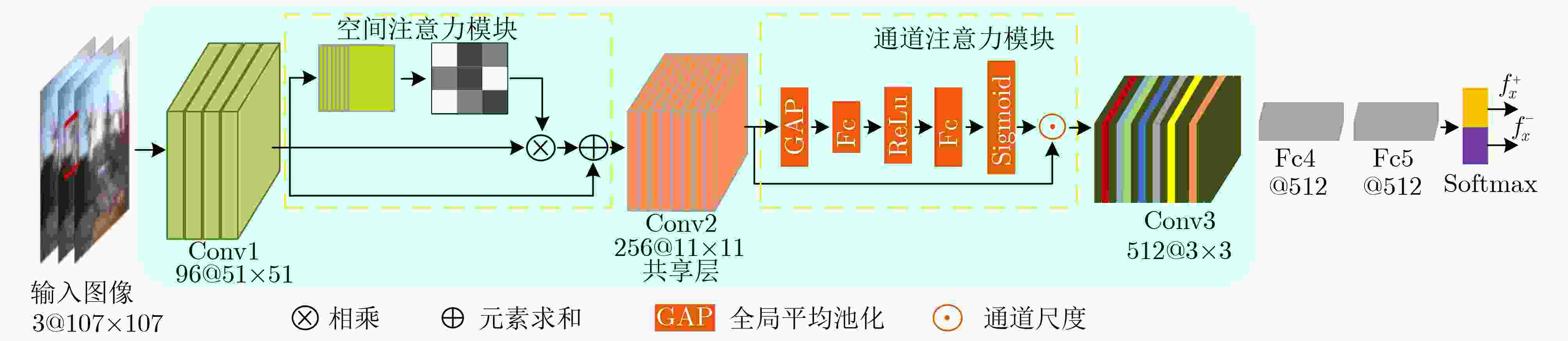
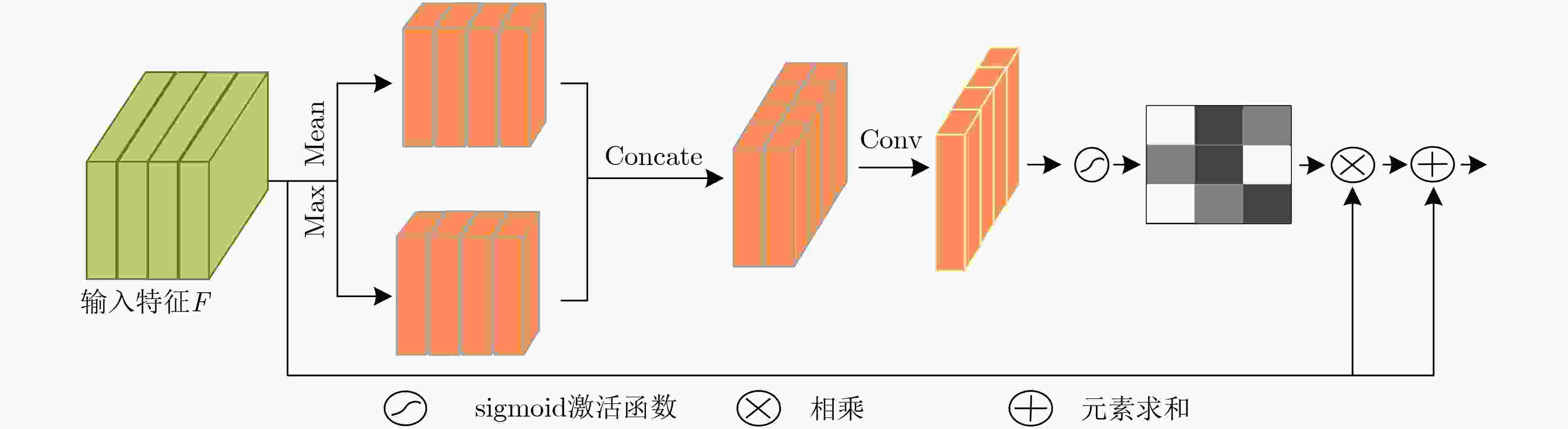
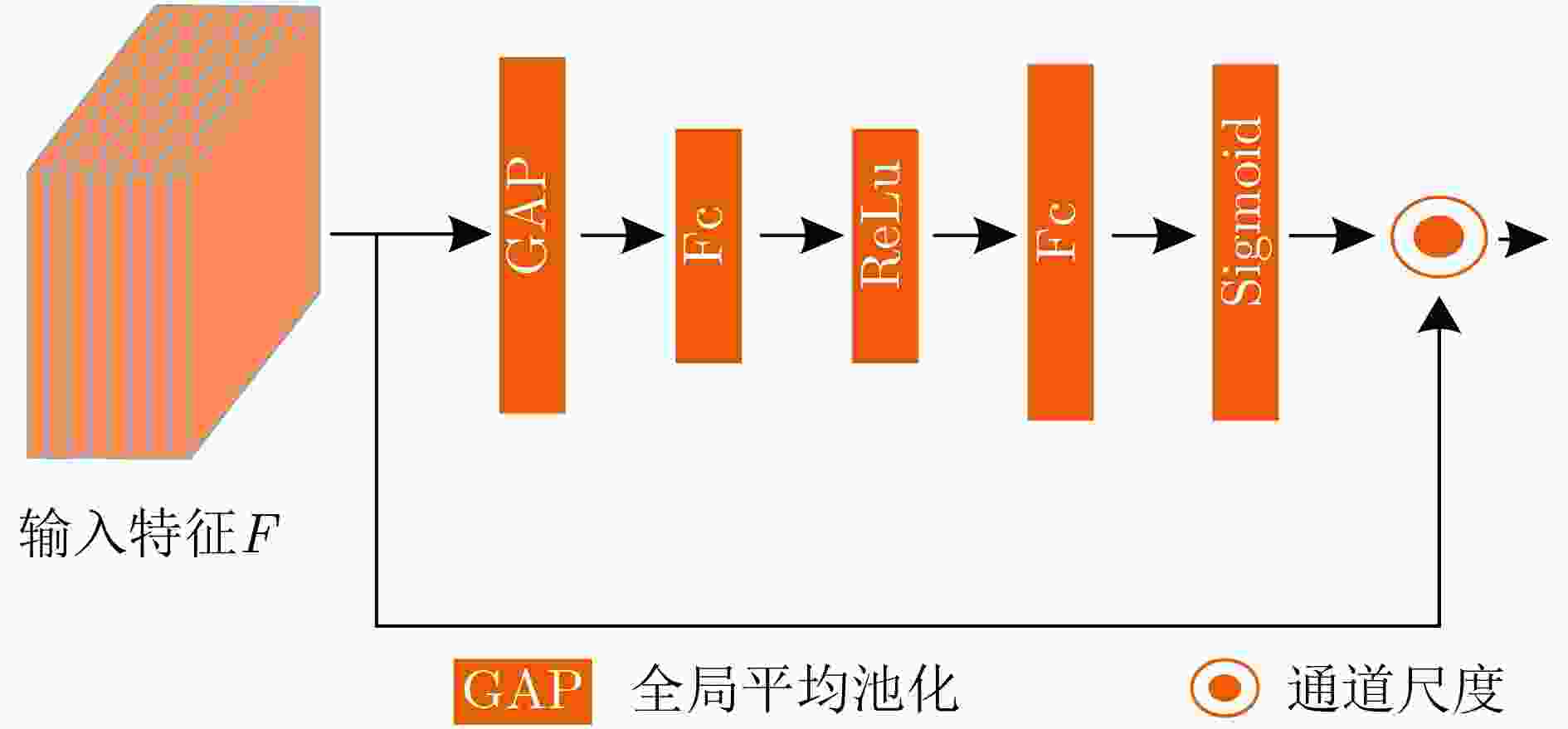
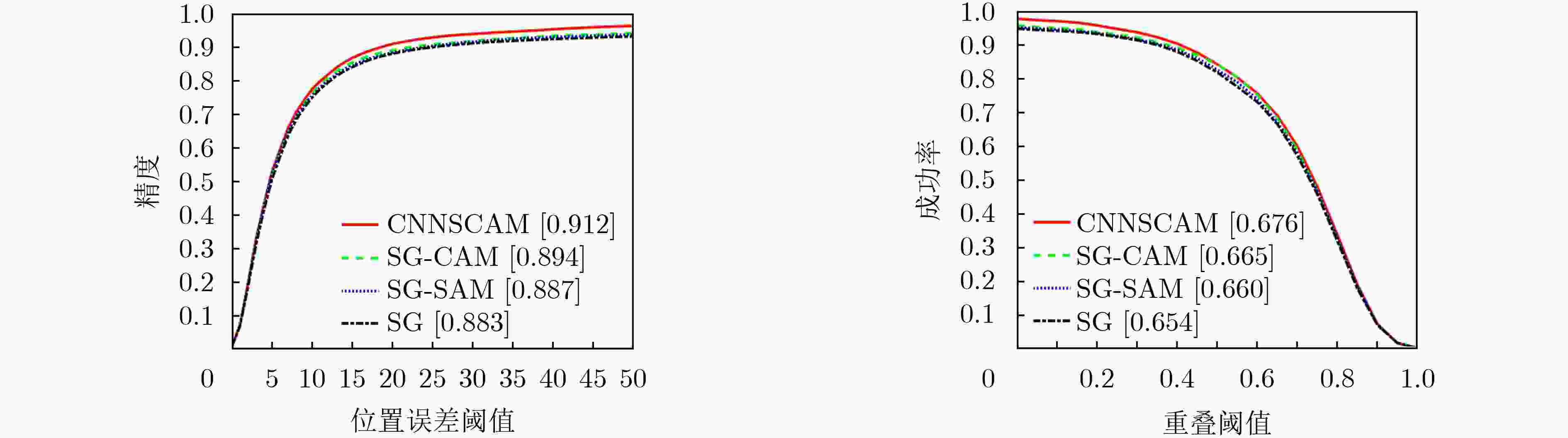
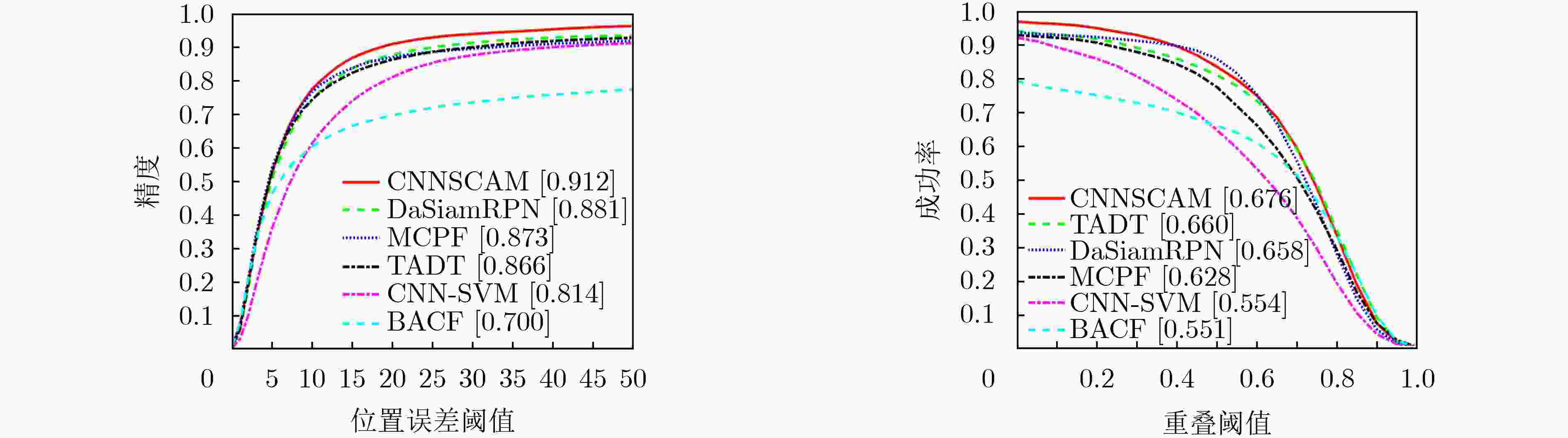
摘要: 目标跟踪是计算机视觉中重要的研究领域之一,大多跟踪算法不能有效学习适合于跟踪场景的特征限制了跟踪算法性能的提升。该文提出了一种基于空间和通道注意力机制的目标跟踪算法(CNNSCAM)。该方法包括离线训练的表观模型和自适应更新的分类器层。在离线训练时,引入空间和通道注意力机制模块对原始特征进行重新标定,分别获得空间和通道权重,通过将权重归一化后加权到对应的原始特征上,以此挑选关键特征。在线跟踪时,首先训练全连接层和分类器层的网络参数,以及边界框回归。其次根据设定的阈值采集样本,每次迭代都选择分类器得分最高的负样本来微调网络层参数。在OTB2015数据集上的实验结果表明:相比其他主流的跟踪算法,该文所提算法获得了更好的跟踪精度,重叠成功率和误差成功率分别为67.6%,91.2%。Abstract: Object tracking is one of the important research fields in computer vision. However, most tracking algorithm can not effectively learn the features suitable for tracking scene, which limits the performance improvement of tracking algorithm. To overcome this problem, this paper proposes a target tracking algorithm based on CNN Spatial and Channel Attention Mechanisms (CNNSCAM). The method consists of an off-line training apparent model and an adaptive updating classifier layer. In the offline training, the spatial and channel attention mechanism module is introduced to recalibrate the original features, and the space and channel weights are obtained respectively. The key features are selected by normalizing the weights to the corresponding original features. In online tracking, the network parameters of the full connection layer and classifier layer are trained, and the boundary box regression is used. Secondly, samples are collected according to the set threshold, and the negative sample with the highest classifier score is selected for each iteration to fine tune the network layer parameters. The experimental results on OTB2015 dataset show that compared with other mainstream tracking algorithms, the proposed method achieves better tracking accuracy. The overlap success rate and error success rate are 67.6% and 91.2% respectively.
-
Key words:
- Object tracking /
- Deep learning /
- Spatial attention /
- Channel attention /
- Online learning
-
表 1 在OTB2015数据集中的11个跟踪场景下算法的重叠成功率
IV OPR SV OCC MD FM IPR OV DEF BC LR CNNSCAM 0.680 0.657 0.663 0.644 0.671 0.658 0.660 0.651 0.631 0.675 0.622 DaSiamRPN 0.662 0.644 0.641 0.617 0.625 0.621 0.652 0.537 0.652 0.642 0.588 TADT 0.681 0.646 0.655 0.643 0.671 0.657 0.621 0.625 0.607 0.622 0.634 MCPF 0.629 0.619 0.604 0.620 0.599 0.597 0.620 0.553 0.569 0.601 0.581 CNN-SVM 0.537 0.548 0.489 0.514 0.578 0.546 0.548 0.488 0.547 0.548 0.403 BACF 0.547 0.506 0.532 0.475 0.541 0.511 0.497 0.483 0.499 0.552 0.502 表 2 在OTB2015数据集中的11个跟踪场景下算法的距离误差成功率
Attribute IV OPR SV OCC MD FM IPR OV DEF BC LR CNNSCAM 0.905 0.901 0.910 0.862 0.862 0.869 0.910 0.864 0.880 0.927 0.889 DaSiamRPN 0.878 0.878 0.858 0.818 0.820 0.819 0.889 0.720 0.887 0.856 0.814 TADT 0.865 0.872 0.863 0.842 0.833 0.834 0.832 0.816 0.822 0.805 0.881 MCPF 0.882 0.816 0.862 0.862 0.840 0.845 0.888 0.764 0.815 0.823 0.911 CNN-SVM 0.792 0.798 0.785 0.727 0.751 0.747 0.813 0.650 0.791 0.776 0.811 BACF 0.665 0.650 0.673 0.590 0.649 0.627 0.645 0.613 0.655 0.700 0.665 表 3 在OTB2015数据集中固定v=1.00时,不同A取值的距离误差成功率
A取值 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.00 Prec 0.686 0.770 0.834 0.850 0.877 0.912 0.876 0.886 0.875 0.858 表 4 在OTB2015数据集中固定A=0.6时,不同v取值的距离误差成功率
v取值 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Suc 0.599 0.621 0.641 0.651 0.661 0.676 0.671 0.666 0.657 0.643 0.622 -
[1] 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 等. 基于自适应背景选择和多检测区域的相关滤波算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 3061–3067. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190931PU Lei, FENG Xinxi, HOU Zhiqiang, et al. Correlation filter algorithm based on adaptive context selection and multiple detection areas[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 3061–3067. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190931 [2] 李康, 李亚敏, 胡学敏, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的鲁棒高精度目标跟踪算法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(9): 2087–2093. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.09.007LI Kang, LI Yamin, HU Xuemin, et al. A robust and accurate object tracking algorithm based on convolutional neural network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(9): 2087–2093. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.09.007 [3] 王鹏, 孙梦宇, 王海燕, 等. 一种目标响应自适应的通道可靠性跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1950–1958. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190569WANG Peng, SUN Mengyu, WANG Haiyan, et al. An object tracking algorithm with channel reliability and target response adaptation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1950–1958. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190569 [4] HONG S, YOU T, KWAK S, et al. Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 597–606. [5] ZHU Zheng, WANG Qiang, LI Bo, et al. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 104–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_7. [6] LI Xin, MA Chao, WU Baoyuan, et al. Target-aware deep tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1369–1378. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00146. [7] WANG Ning, SONG Yibing, MA Chao, et al. Unsupervised deep tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1308–1317. [8] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [9] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 1352–1368. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [10] WANG Qiang, TENG Zhu, XING Junliang, et al. Learning attentions: Residual attentional Siamese network for high performance online visual tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4854–4863. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00510. [11] CHEN Boyu, LI Peixia, CHONG Sun, et al. Multi attention module for visual tracking[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 87: 80–93. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.10.005 [12] 张文明, 姚振飞, 高雅昆, 等. 一种平衡准确性以及高效性的显著性目标检测深度卷积网络模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1201–1208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190229ZHANG Wenming, YAO Zhenfei, GAO Yakun, et al. A deep convolutional network for saliency object detection with balanced accuracy and high efficiency[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1201–1208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190229 [13] WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834–1848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 [14] ZHANG Tianzhu, XU Changsheng, and YANG M H. Multi-task correlation particle filter for robust object tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4819–4827. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.512. [15] GALOOGAHI H K, FAGG A, and LUCEY S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1144–1152. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.129. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
