Multi-level Feature Fusion SAR Automatic Target Recognition Based on Deep Forest
-
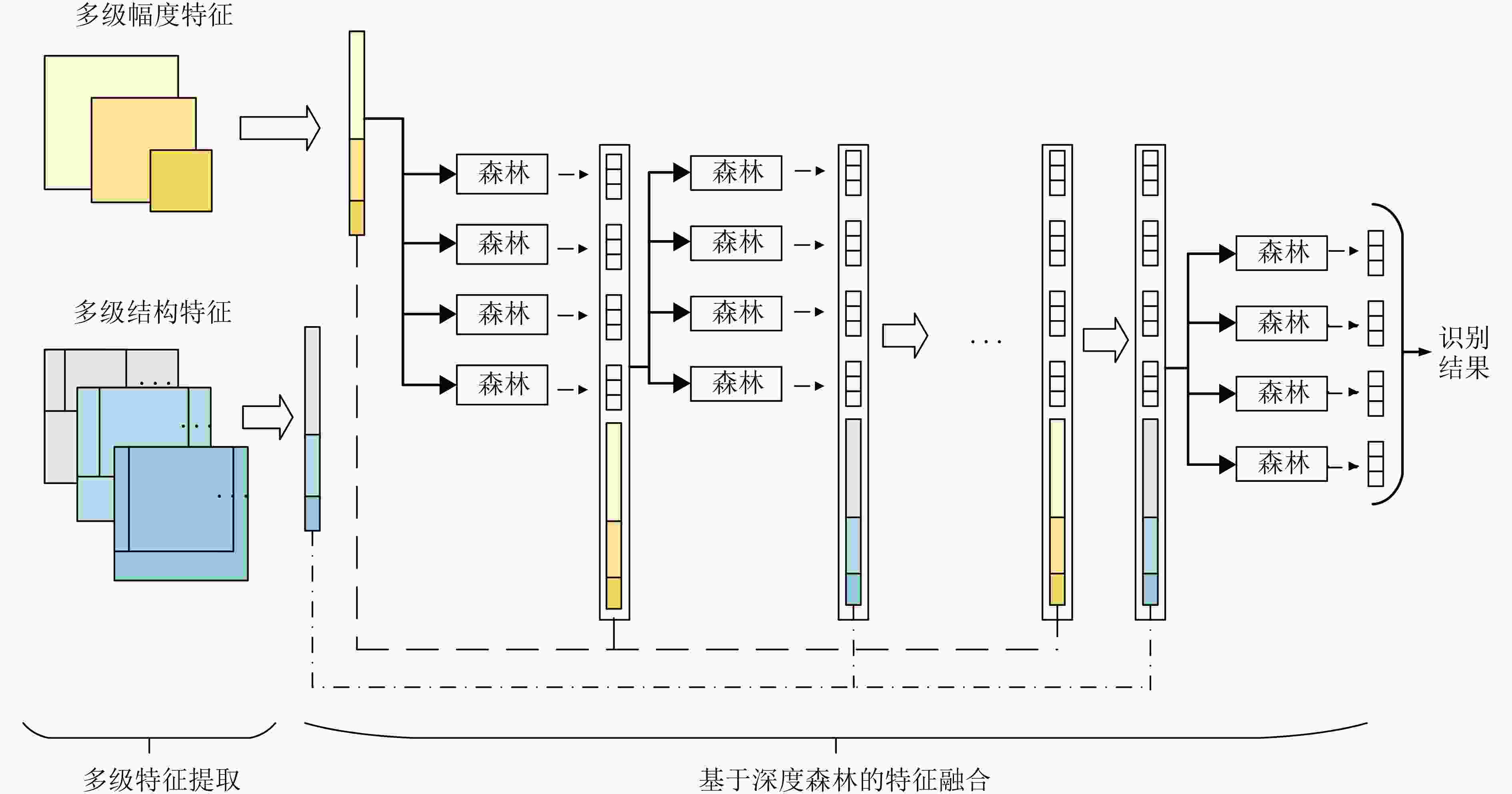
摘要: 大多数传统的合成孔径雷达(SAR)目标识别方法仅仅使用了单一的幅度特征,但是由于斑点噪声的存在,仅仅使用幅度特征会限制识别的性能。为了进一步提高SAR目标识别的性能,该文提出了一个基于深度森林的多级特征融合SAR目标识别方法。首先,在特征提取阶段,提取了多级幅度特征和多级密集尺度不变特征变换(Dense-SIFT)特征。幅度特征反映了目标反射强度,Dense-SIFT特征描述了目标的结构特征。而多级特征可以从局部到全局表征目标。随后,为了更完整、充分地反映SAR目标信息,借鉴深度森林的思想对多级幅度特征和多级Dense-SIFT特征进行联合利用。一方面通过堆叠的方式不断将多级幅度特征和多级Dense-SIFT特征进行融合,另一方面通过逐层的特征变换挖掘深层信息。最后利用得到的深层融合特征对目标进行识别任务。该文在MSTAR数据集上进行对比实验,实验结果表明所提算法在性能方面取得了提升,且其性能对超参数设置具有一定的鲁棒性。Abstract: In most of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) target recognition methods, only the amplitude feature, i.e., intensity of pixels, is used to recognize targets. Nevertheless, due to the speckle noise, only using the amplitude feature will affect the recognition performance. For further improving the recognition performance, in this paper, a novel multi-level feature fusion target recognition method based on deep forest for SAR images is proposed. At First, in the feature extraction step, two kinds of features, i.e., the multi-level amplitude feature and the multi-level Dense Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (Dense-SIFT) feature are extracted. The amplitude feature describes intensity information and the Dense-SIFT feature describes structure information. Furthermore, for each feature, its corresponding multi-level features are extracted to represent target information from local to global. Then, for reflecting target information more comprehensive and sufficient, the multi-level amplitude feature and the multi-level Dense-SIFT feature are jointly utilized profiting from the idea of deep forest. On the one hand, the cascade structure can fusion multi-level amplitude feature and the multi-level Dense-SIFT feature steadily. On the other hand, the deep feature representation can be mined by layer-by-layer feature transformation. Finally, the fusion feature is used to recognize targets. Experiments on the moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition data show that the proposed method is an effective target recognition method, and the recognition performance is robust to the hyper-parameters.
-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Target recognition /
- Feature fusion /
- Deep model
-
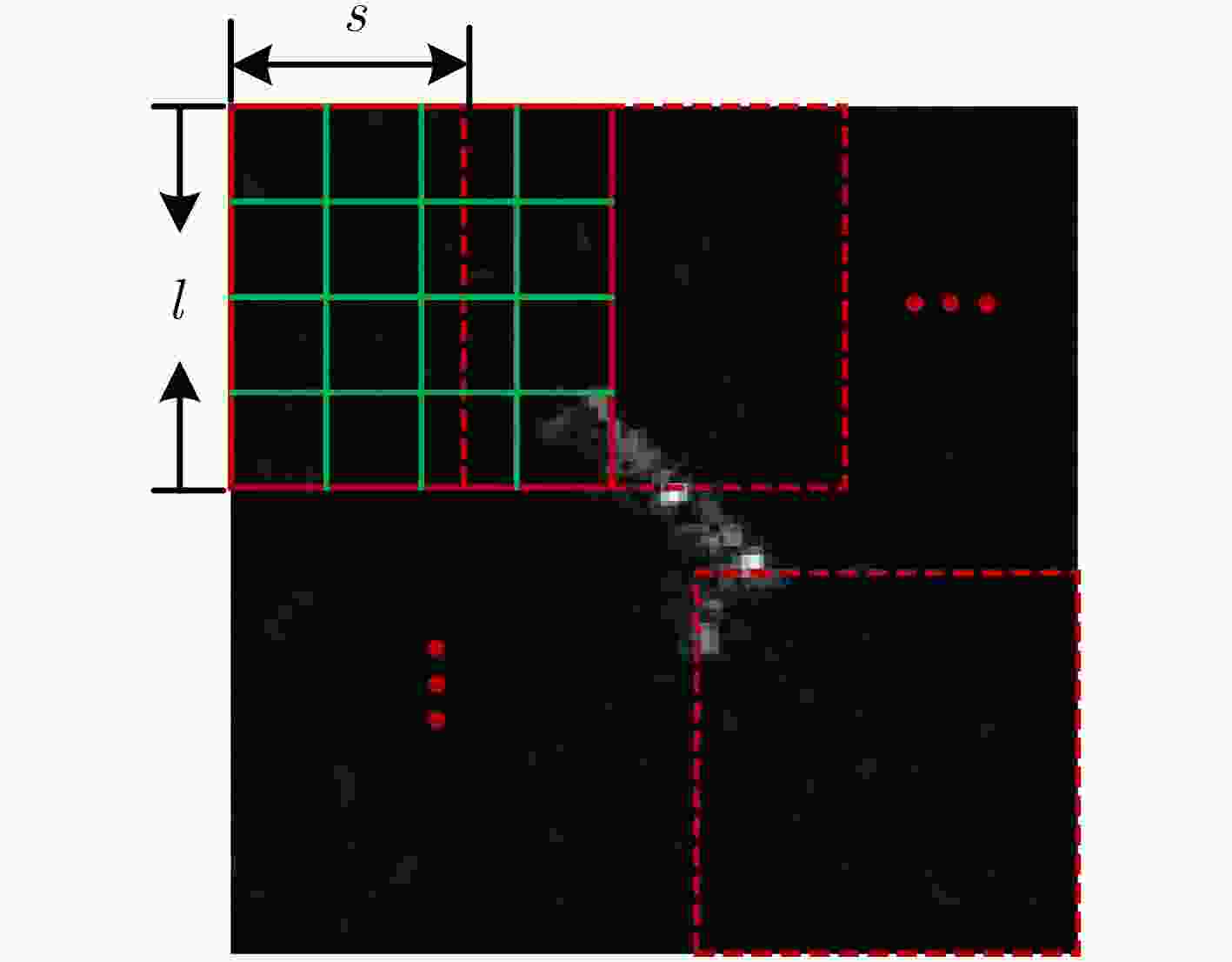
表 1 提取Dense-SIFT特征的流程
输入:SAR图像${{I}}$,切片窗口尺寸$l \times l$,滑窗步长$s$ 输出:Dense-SIFT特征${{F}}$ (1) 对SAR图像${{I}}$分别用水平梯度模板${{A}} = \left[ {{\rm{ - }}0.5,0,0.5} \right]$和垂直梯度模板${{{A}}^{\rm{T}}}$进行卷积,得到每一个像素点对应的梯度 (2) 根据切片窗口尺寸在SAR图像上得到第1个$l \times l$的SAR子图 重复: (3) 将子图无重叠地划分成$4 \times 4$个小区域 (4) 计算得到每一个小区域在$\left[ {0,{\pi / 4},{\pi / 2},{{3\pi } / 4},\pi ,{{5\pi } / 4},{{3\pi } / 2},{{7\pi } / 4}} \right]$共8个方向上的梯度直方图 (5) 将所有小区域得到的梯度直方图按照小区域位置的顺序首尾拼接,得到当前子图128维的特征向量 (6) 根据切片窗口尺寸和滑窗步长$s$在SAR图像上滑窗得到下一个SAR子图 直到:所有子图处理完毕 (7) 将所有子图的128维特征向量首尾拼接得到Dense-SIFT特征$F$ 表 2 基于深度森林的特征融合算法的流程
输入:多级幅度特征${{{F}}_{\rm{m}}}$,多级Dense-SIFT特征${{{F}}_{\rm{s}}}$,迭代停止阈值$T$ 输出:识别结果$P$ (1) 将两个随机森林和两个完全随机森林组成深度森林的第1层;将训练样本的多级幅度特征作为特征输入深度森林的当前层,根据训练样
本特征和标签训练当前层中的随机森林和完全随机森林,得到每个森林对训练样本的预测输出,将每个森林得到的预测输出拼成类别向量;(2) 将两个随机森林和两个完全随机森林组成深度森林的第2层;将训练样本的多级结构特征与前一层生成的类别向量拼接起来作为新的特
征,输入深度森林的当前层,根据训练样本特征和标签训练当前层中的随机森林和完全随机森林,得到每个森林对训练样本的预测输
出,将每个森林得到的预测输出拼成类别向量,并得到深度森林当前层对训练样本的预测正确率$A{c_2}$;(3) 设迭代次数$k = 1$ 重复: (4) 将两个随机森林和两个完全随机森林组成深度森林的第$2k{\rm{ + }}1$层;将训练样本的多级幅度特征与前一层生成的类别向量拼接起来作为新
的特征,输入深度森林的当前层,根据训练样本特征和标签训练当前层中的随机森林和完全随机森林,得到每个森林对训练样本的预
测输出,将每个森林得到的预测输出拼成类别向量,并得到深度森林当前层对训练样本的预测正确率$A{c_{2k + 1}}$;(5) 比较深度森林相邻的两个层对训练样本的预测正确率$A{c_{2k}}$和$A{c_{2k + 1}}$,当$\left| {A{c_{2k + 1}} - A{c_{2k}}} \right|$小于阈值$T$则停止,否则继续执行; (6) 将两个随机森林和两个完全随机森林组成深度森林的第$2k{\rm{ + 2}}$层;将训练样本的多级结构特征与前一层生成的类别向量拼接起来作为新
的特征,输入深度森林的当前层,根据训练样本特征和标签训练当前层中的随机森林和完全随机森林,得到每个森林对训练样本的预
测输出,将每个森林得到的预测输出拼成类别向量,并得到深度森林当前层对训练样本的预测正确率$A{c_{2k + 2}}$;(7) 比较深度森林相邻的两个层对训练样本的预测正确率$A{c_{2k{\rm{ + }}1}}$和$A{c_{2k + 2}}$,当$\left| {A{c_{2k + 2}} - A{c_{2k{\rm{ + }}1}}} \right|$小于阈值$T$则停止,否则$k = k{\rm{ + }}1$并重
复步骤(4)—步骤(7);直到:满足终止条件 (8) 得到最优的深度森林模型,对测试数据进行预测,得到识别结果$P$ 表 3 MSTAR数据集3类目标识别场景训练集、测试集划分
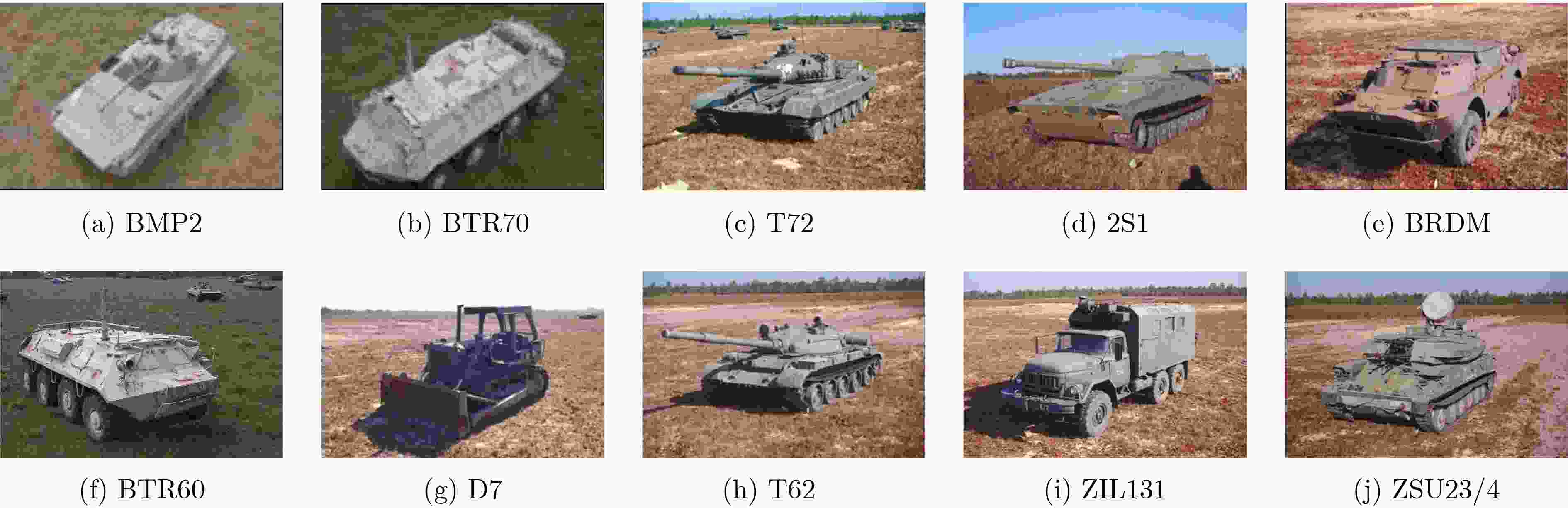
类型 BMP2 BTR70 T72 SN9563 SN9566 SNC21 SNC71 SN132 SNS7 SN812 训练(17°) 0 0 233 233 232 0 0 测试(15°) 195 196 196 196 196 191 195 表 4 MSTAR数据集10类目标识别场景训练集、测试集划分
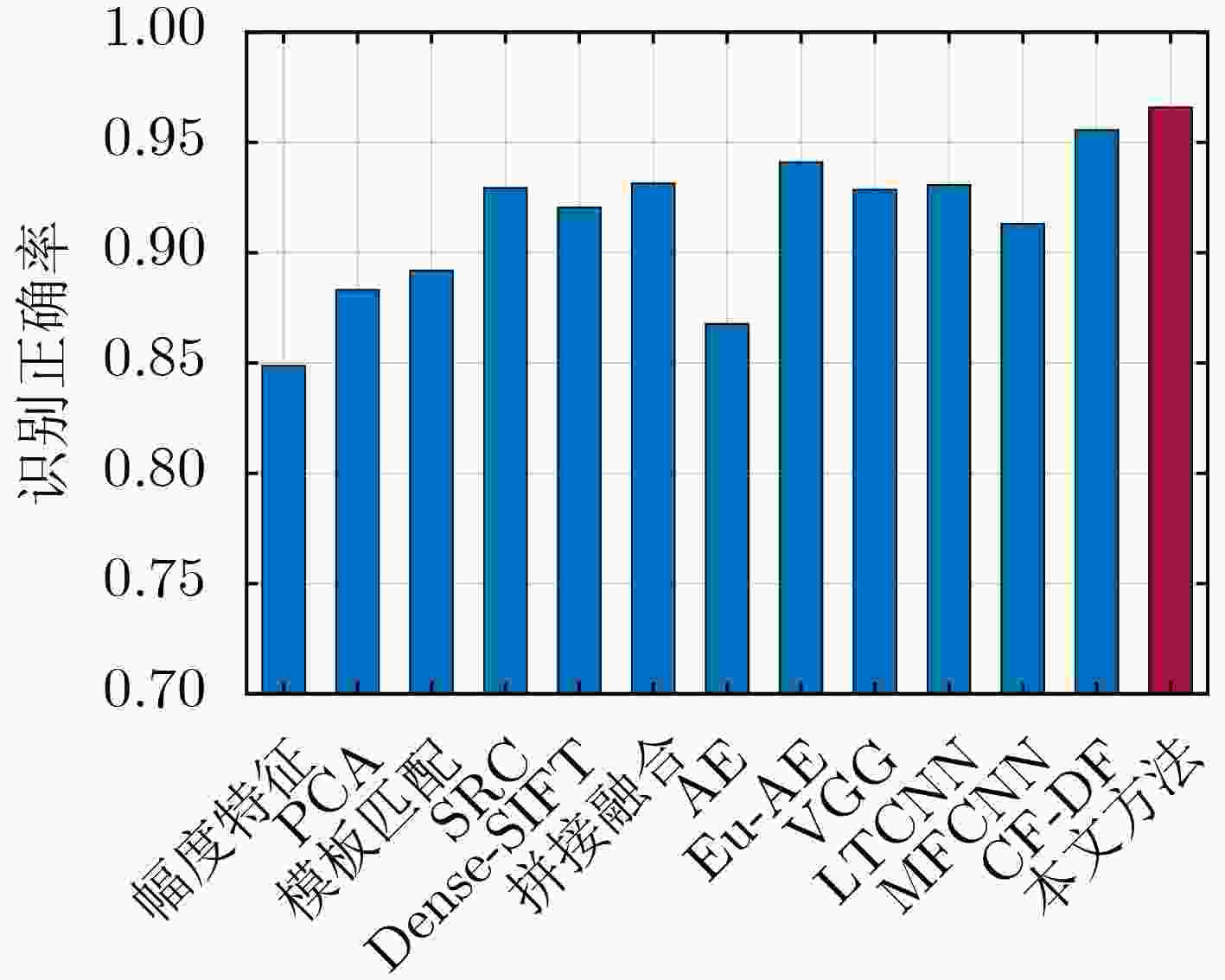
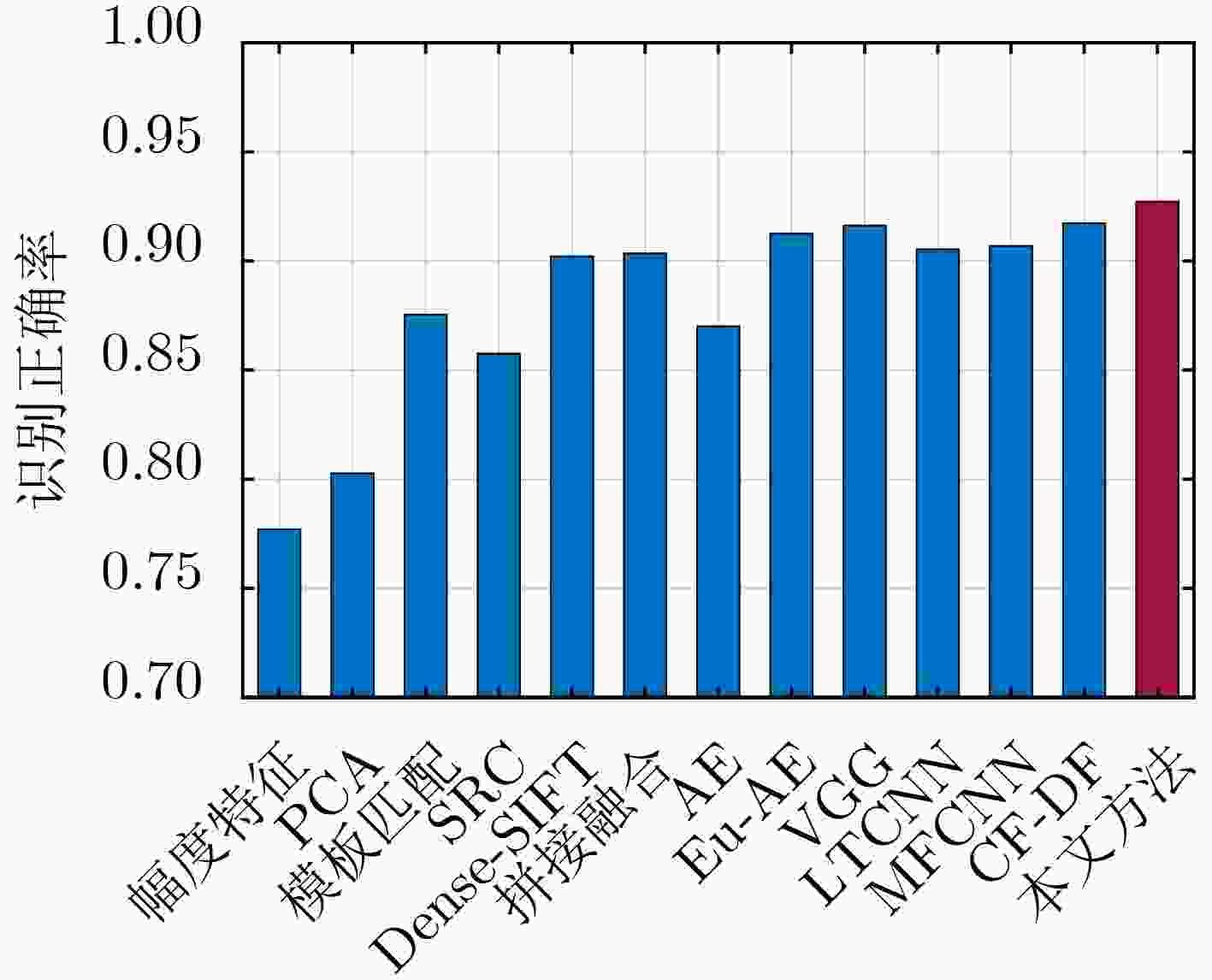
类型 BMP2 BTR70 T72 2S1 BRDM BTR60 D7 T62 ZIL131 ZSU23/4 训练集 (17°) 233(C21) 233 232(132) 299 298 255 299 299 299 299 测试集 (15°) 587(C21,9566,9563) 196 582(132,S7,812) 274 274 195 274 273 274 274 表 5 不同识别方法对应的3类7型MSTAR数据测试样本识别正确率
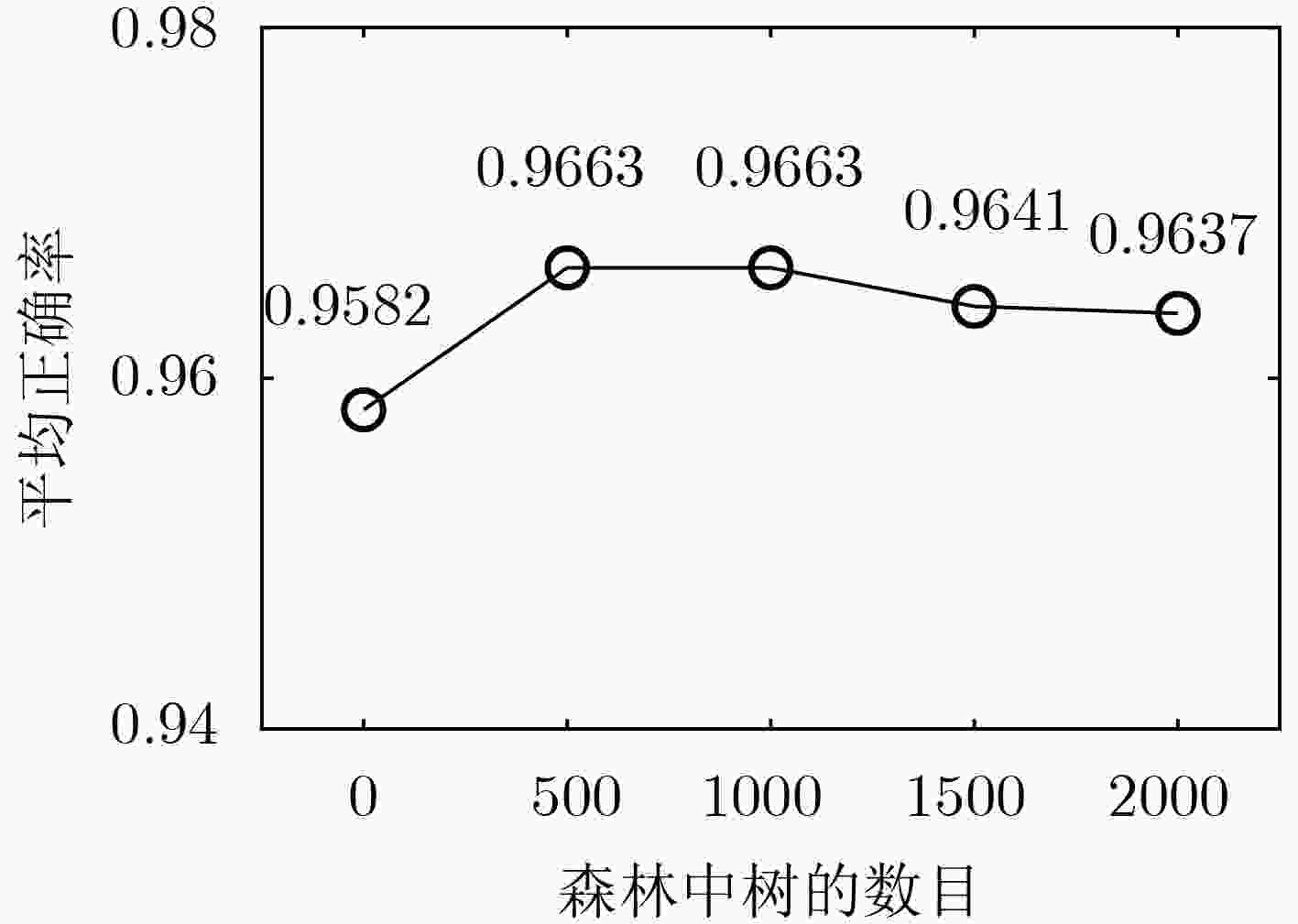
实验方法 幅度特征 PCA 模板匹配 SRC Dense-SIFT 拼接融合 AE Eu-AE[11] VGG LTCNN MFCNN CF-DF 本文方法 正确率 0.8491 0.8835 0.8923 0.9297 0.9209 0.9318 0.8681 0.9414 0.9289 0.9311 0.9135 0.9560 0.9663 表 6 不同识别方法对应的10类14型MSTAR数据测试样本识别正确率
实验方法 幅度特征 PCA 模板匹配 SRC Dense-SIFT 拼接融合 AE Eu-AE[11] VGG LTCNN MFCNN CF-DF 本文方法 正确率 0.7774 0.8030 0.8758 0.8579 0.9025 0.9038 0.8704 0.9129 0.9166 0.9057 0.9072 0.9176 0.9276 -
姜文, 牛杰, 吴一荣, 等. 机载多通道SAR运动目标方位向速度和法向速度联合估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1542–1548. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190672JIANG Wen, NIU Jie, WU Yirong, et al. Joint estimation algorithm for azimuth velocity and normal velocity of moving targets in airborne multi-channel SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1542–1548. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190672 杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104 金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083 DU Lan, LI Lu, WEI Di, et al. Saliency-guided single shot multibox detector for target detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(5): 3366–3376. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2953936 LI Lu, DU Lan, and WANG Zhaocheng. Target detection based on dual-domain sparse reconstruction saliency in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(11): 4230–4243. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2874128 杜兰, 魏迪, 李璐, 等. 基于半监督学习的SAR目标检测网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783DU Lan, WEI Di, LI Lu, et al. SAR target detection network via semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783 WANG Yan, DU Lan, and DAI Hui. Target discrimination method for SAR images based on semisupervised co-training[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 015004. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.12.015004 WANG Zhaocheng, DU Lan, and SU Hongtao. Superpixel-level target discrimination for high-resolution SAR images in complex scenes[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(9): 3127–3143. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2850043 WANG Ying, HAN Ping, LU Xiaoguang, et al. The performance comparison of adaboost and SVM applied to SAR ATR[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006. doi: 10.1109/ICR.2006.343515. BRYANT M L, WORRELL S W, and DIXON A C. MSE template size analysis for MSTAR data[J]. SPIE, 1998, 3370: 396–405. doi: 10.1117/12.321844. DENG Sheng, DU Lan, LI Chen, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on Euclidean distance restricted autoencoder[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(7): 3323–3333. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2670083 TAO Lei, JIANG Xue, LIU Xingzhao, et al. Multiscale supervised kernel dictionary learning for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6281–6297. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2976203 LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. SUN Yongguang, DU Lan, WANG Yan, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on dictionary learning and joint dynamic sparse representation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1777–1781. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2608578 HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2947634 GAO Fei, LIU Qiuyang, SUN Jinping, et al. Integrated GANs: Semi-supervised SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 113999–114013. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935167 贺丰收, 何友, 刘准钆, 等. 卷积神经网络在雷达自动目标识别中的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899HE Fengshou, HE You, LIU Zhunga, et al. Research and development on applications of convolutional neural networks of radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899 ZHOU Zhihua and FENG Ji. Deep forest[J/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.08835.pdf, 2020. NI Jiacheng and XU Yuelei. SAR automatic target recognition based on a visual cortical system[C]. The 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2013. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2013.6745270. HUANG Xiayuan, YANG Qiao, and QIAO Hong. Lightweight two-stream convolutional neural network for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, , To be published. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2983718 CHO J H and PARK C G. Multiple feature aggregation using convolutional neural networks for SAR image-based automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(12): 1882–1886. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2865608 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
