Malicious Domain Name Detection Model Based on CNN and LSTM
-
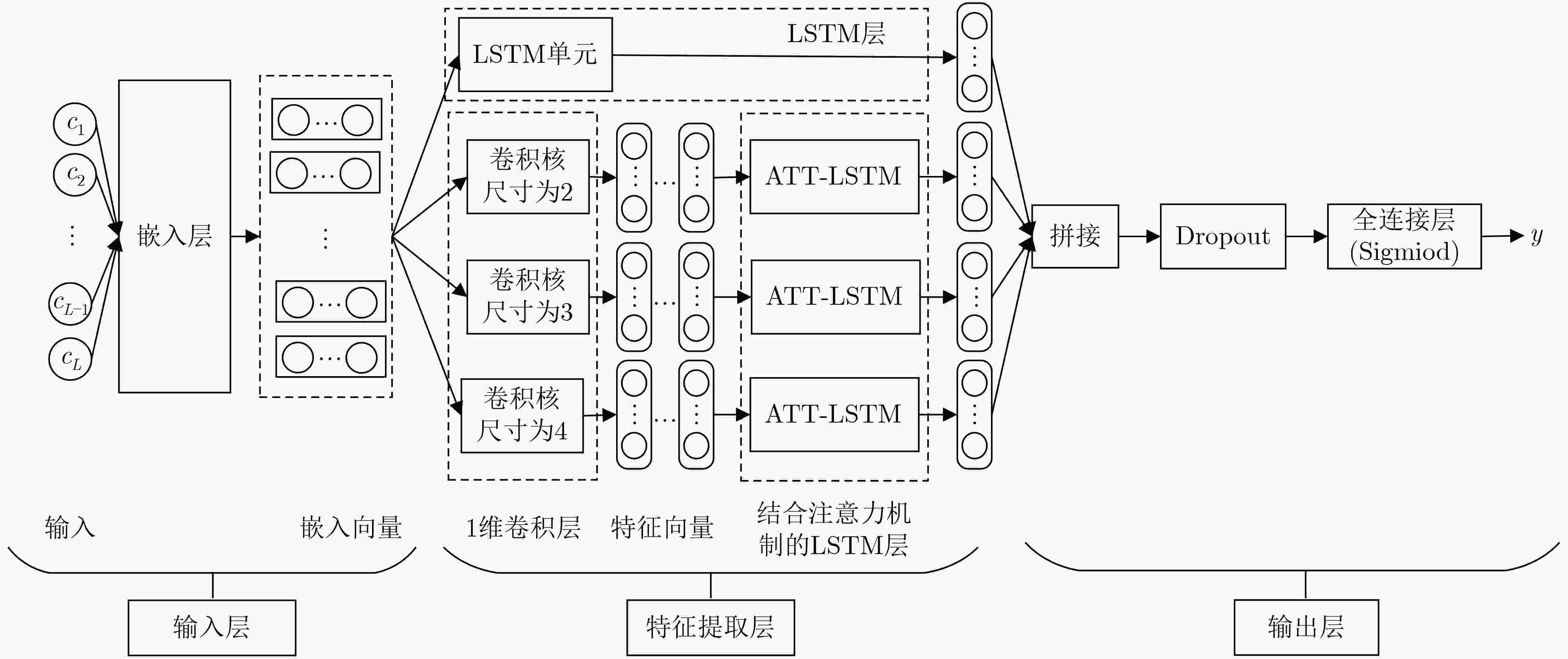
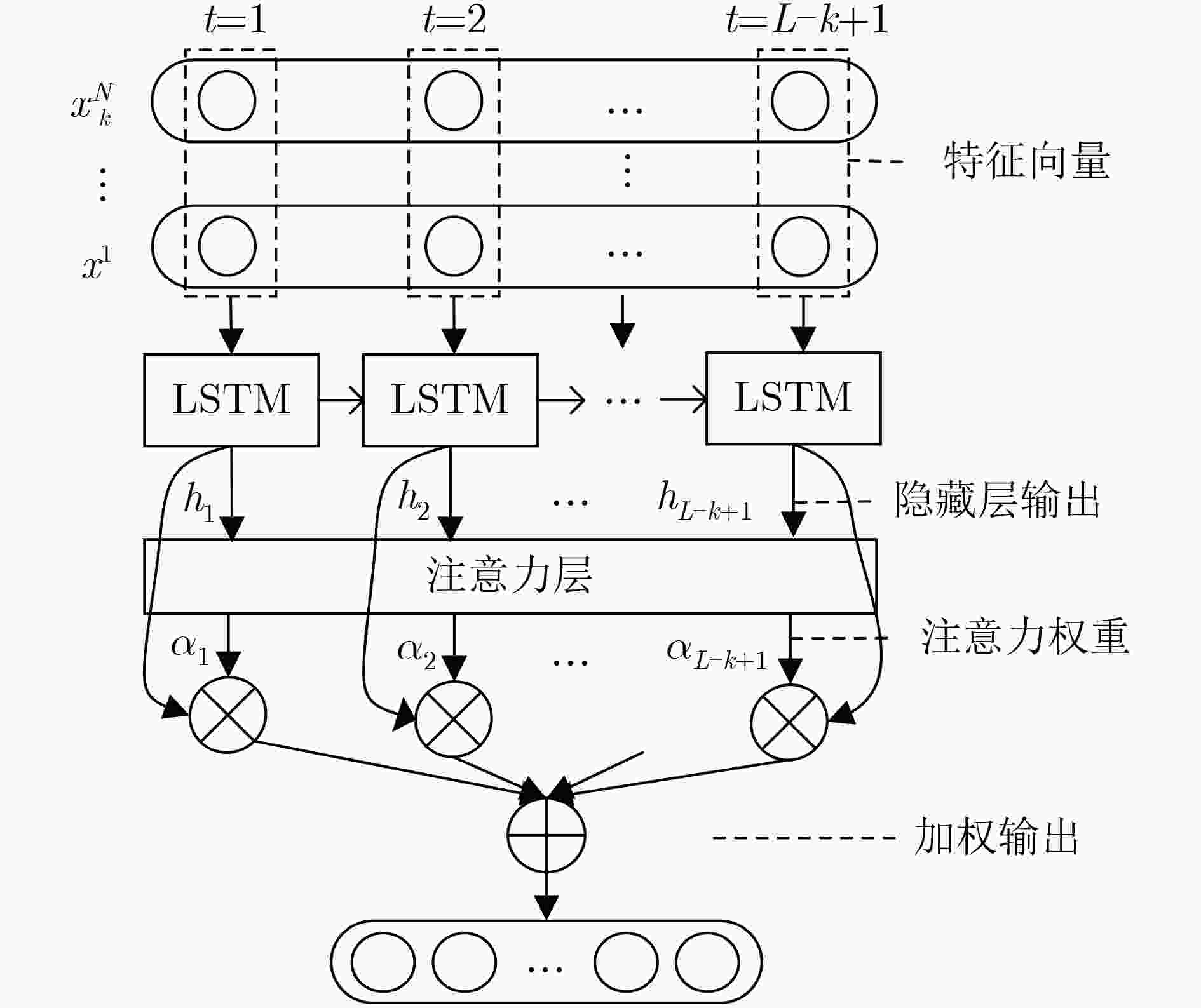
摘要: 为提高恶意域名检测准确率,该文提出一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)与长短期记忆网络(LSTM)相结合的域名检测模型。该模型通过提取域名字符串中不同长度字符组合的序列特征进行恶意域名检测:首先,为避免N-Gram特征稀疏分布的问题,采用CNN提取域名字符串中字符组合特征并转化为维度固定的稠密向量;其次,为充分挖掘域名字符串上下文信息,采用LSTM提取字符组合前后关联的深层次序列特征,同时引入注意力机制为填充字符所处位置的输出特征分配较小权重,降低填充字符对特征提取的干扰,增强对长距离序列特征的提取能力;最后,将CNN提取局部特征与LSTM提取序列特征的优势相结合,获得不同长度字符组合的序列特征进行域名检测。实验表明:该模型较单一采用CNN或LSTM的模型具有更高的召回率和F1分数,尤其对matsnu和suppobox两类恶意域名的检测准确率较单一采用LSTM的模型提高了24.8%和3.77%。Abstract: To improve the accuracy of malicious domain name detection, a new detection model based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) is proposed. The model extracts the sequence features from different length strings to classify the domain name. Firstly, in view of the sparseness of the N-Gram feature, the model utilizes CNN with different kernels to preserve the local association between the characters in the domain name strings and convert it to dense feature vectors. Secondly, in order to mine the context information of the domain name strings, LSTM is used to extract the deep-level sequence features of different character combinations. A sequence feature attention module is designed to assign little weight value to the sequence feature extracted from the padding characters, which decreases the interference by the padding characters and enhances the ability to capture distant sequence features. Finally, combining the advantages of CNN to extract local features and LSTM to extract sequence features, both partial and sequential information are put forward to improving the detection performance. Experimental results show that the recall rate and the F1-score of the proposed model are superior to other comparative models which are solely composed of CNN or LSTM. Particularly, when dealing with the matsnu and suppobox, the proposed model has increased by 24.8% and 3.77% in accuracy compared with the model based on LSTM, respectively.
-
表 1 模型检测性能对比表
模型 Recall (%) Precision (%) FPR (%) F1-Score Test Time(s) Bi-Gram DT 84.37 75.32 22.60 0.7959 1.05 LSTM 93.75 93.58 6.57 0.9367 4.46 Bi-LSTM 90.88 96.49 3.38 0.9360 7.34 Stack-CNN 86.31 94.01 5.62 0.9001 0.62 Parallel-CNN 88.39 94.54 5.22 0.9136 0.57 PCAL 92.66 95.96 3.98 0.9428 12.16 L-PCL 92.17 96.38 3.54 0.9423 13.26 CAL-PCAL 93.02 95.41 3.98 0.9420 11.94 本文L-PCAL 93.91 95.42 4.61 0.9466 12.67 表 2 不同模型TPR与AUC对比表
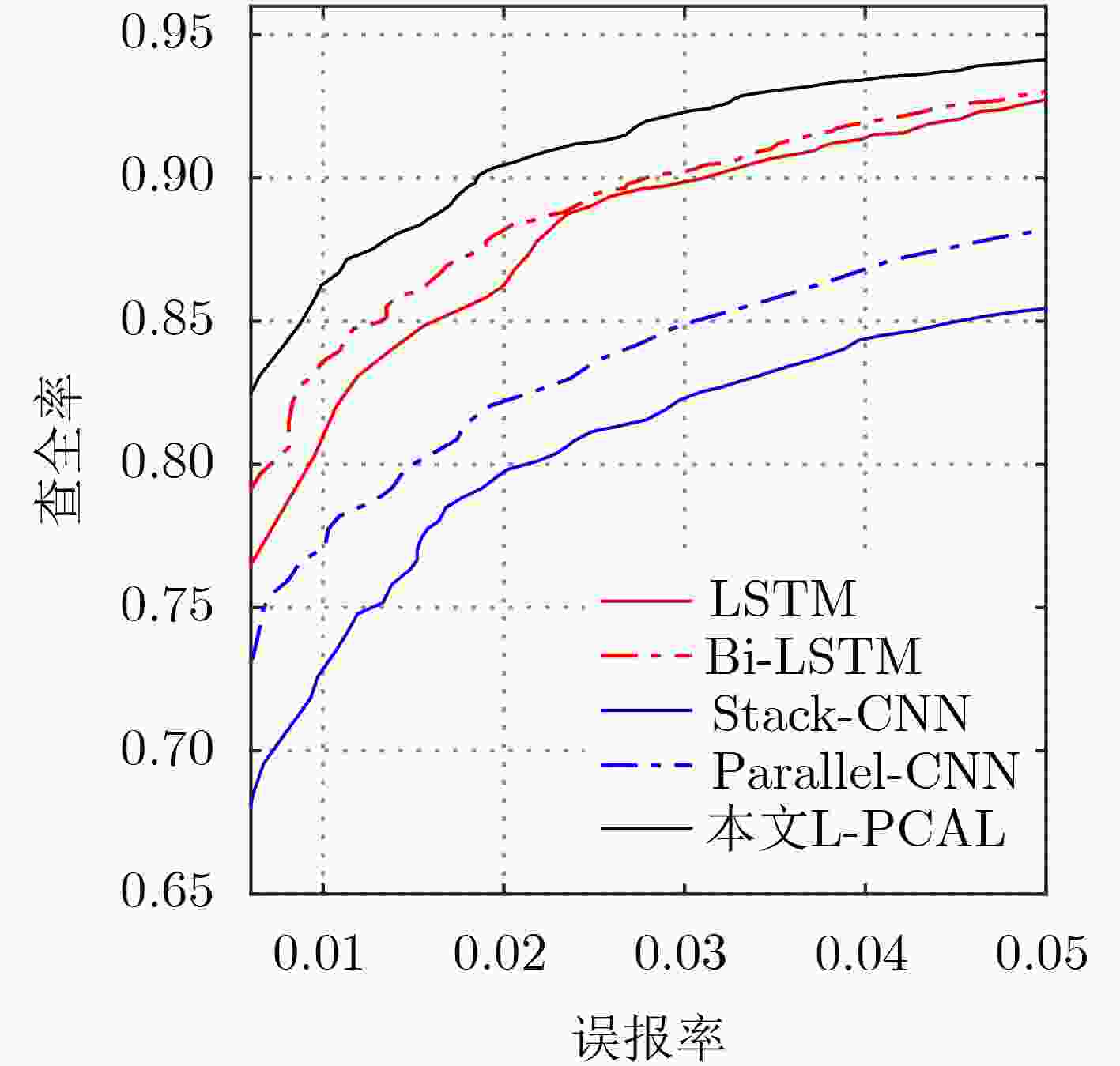
模型 TPR (%) AUC FPR: 1% FPR:2% FPR:3% LSTM 80.12 85.82 89.83 0.9846 Bi-LSTM 83.11 88.19 90.23 0.9840 Stack-CNN 72.58 79.82 82.24 0.9613 Parallel-CNN 77.13 82.04 84.85 0.9671 本文L-PCAL 85.74 90.40 92.17 0.9867 表 3 单词拼接类恶意域名检测准确率对比表
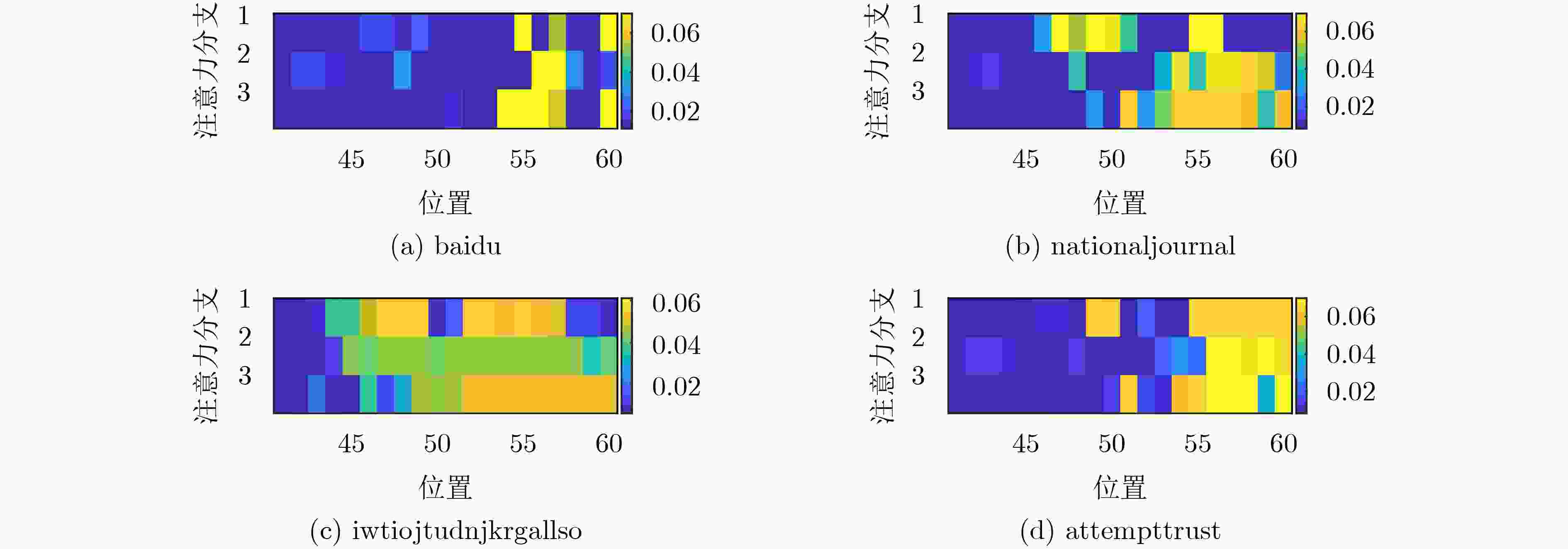
模型 Accuracy (%) matsnu suppobox LSTM 0.78 81.57 Bi-LSTM 0.78 74.59 Stack-CNN 0 18.39 Parallel-CNN 0.78 16.08 PCAL 0 66.86 L-PCL 37.98 74.59 CAL-PCAL 7.75 74.59 本文L-PCAL 25.58 85.34 -
[1] ZHAUNIAROVICH Y, KHALIL I, YU Ting, et al. A survey on malicious domains detection through DNS data analysis[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2018, 51(4): 67. doi: 10.1145/3191329 [2] 张维维, 龚俭, 刘茜, 等. 基于词素特征的轻量级域名检测算法[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(9): 2348–2364. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004913ZHANG Weiwei, GONG Jian, LIU Qian, et al. Lightweight domain name detection algorithm based on morpheme features[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(9): 2348–2364. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004913 [3] SCHIAVONI S, MAGGI F, CAVALLARO L, et al. Phoenix: DGA-based botnet tracking and intelligence[C]. The 11th International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment, Egham, UK, 2014: 192–211. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-08509-8_11. [4] YADAV S, REDDY A K K, REDDY A L N, et al. Detecting algorithmically generated domain-flux attacks with DNS traffic analysis[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2012, 20(5): 1663–1677. doi: 10.1109/tnet.2012.2184552 [5] YU Bin, PAN Jie, HU Jiaming, et al. Character level based detection of DGA domain names[C]. 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ijcnn.2018.8489147. [6] SAXE J and BERLIN K. eXpose: A character-level convolutional neural network with embeddings for detecting malicious URLs, file paths and registry keys[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.08568, 2017. [7] 杨路辉, 刘光杰, 翟江涛, 等. 一种改进的卷积神经网络恶意域名检测算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2020, 47(1): 37–43. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2020.01.006YANG Luhui, LIU Guangjie, ZHAI Jiangtao, et al. Improved algorithm for detection of the malicious domain name based on the convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2020, 47(1): 37–43. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2020.01.006 [8] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [9] WOODBRIDGE J, ANDERSON H S, AHUJA A, et al. Predicting domain generation algorithms with long short-term memory networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.00791, 2016. [10] TRAN D, MAC H, TONG V, et al. A LSTM based framework for handling multiclass imbalance in DGA botnet detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 2401–2413. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.11.018 [11] 杜鹏, 丁世飞. 基于混合词向量深度学习模型的DGA域名检测方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(2): 433–446. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190160DU Peng and DING Shifei. A DGA domain name detection method based on deep learning models with mixed word embedding[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(2): 433–446. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190160 [12] MIKOLOV T, CHEN Kai, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781, 2013. [13] RAFFEL C and ELLIS D P W. Feed-forward networks with attention can solve some long-term memory problems[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.08756, 2015. [14] 谢金宝, 侯永进, 康守强, 等. 基于语义理解注意力神经网络的多元特征融合中文文本分类[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1258–1265. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170815XIE Jinbao, HOU Yongjin, KANG Shouqiang, et al. Multi-feature fusion based on semantic understanding attention neural network for Chinese text categorization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1258–1265. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170815 [15] Alexa Internet, Inc. Alexa top-ranked websites[EB/OL]. http://s3.amazonaws.com/alexa-static/top-1m.csv.zip, 2020. [16] Qihoo 360 Technology Co, Ltd. 360 DGA feeds[EB/OL]. https://data.netlab.360.com/dga/, 2020. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
