Adaptive Multi-scale Information Fusion Based on Dynamic Receptive Field for Image-to-image Translation
-
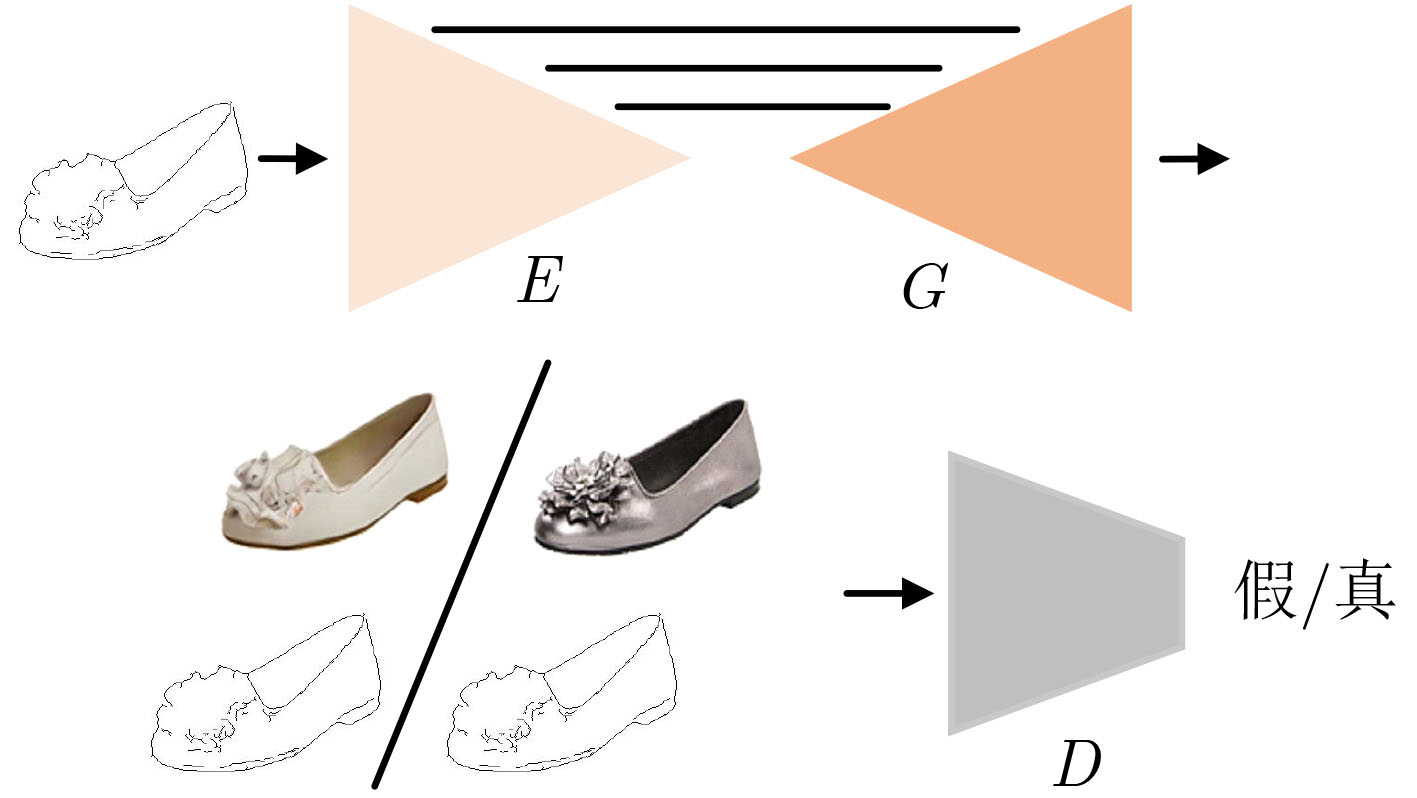
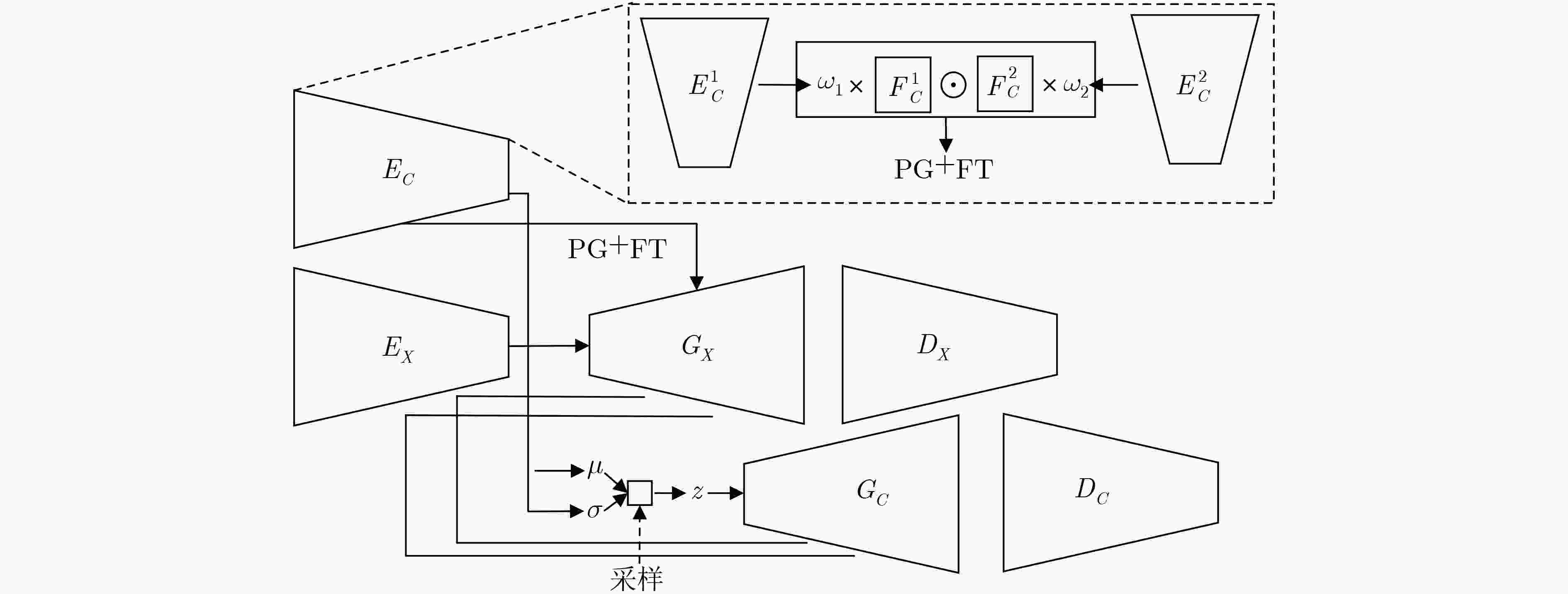
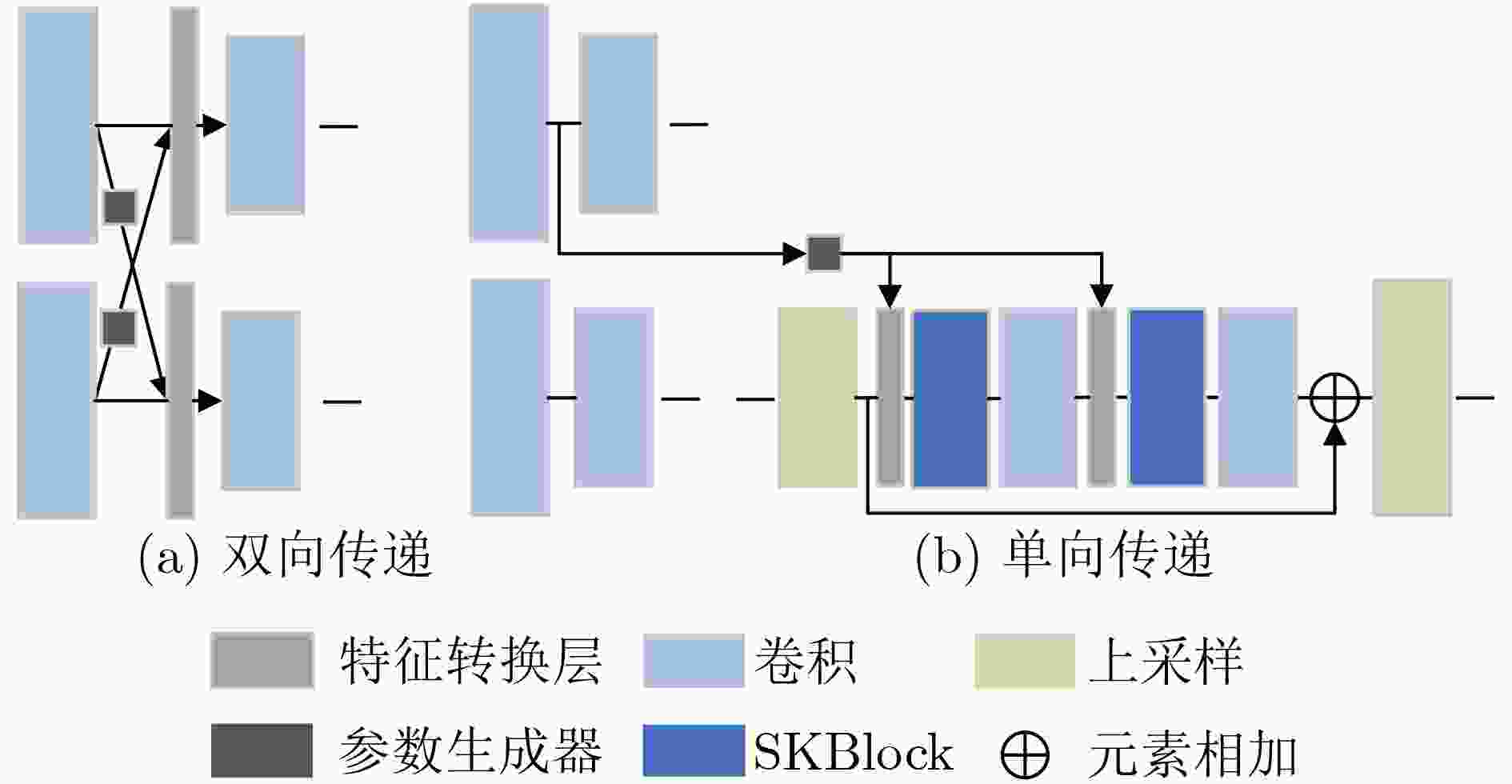
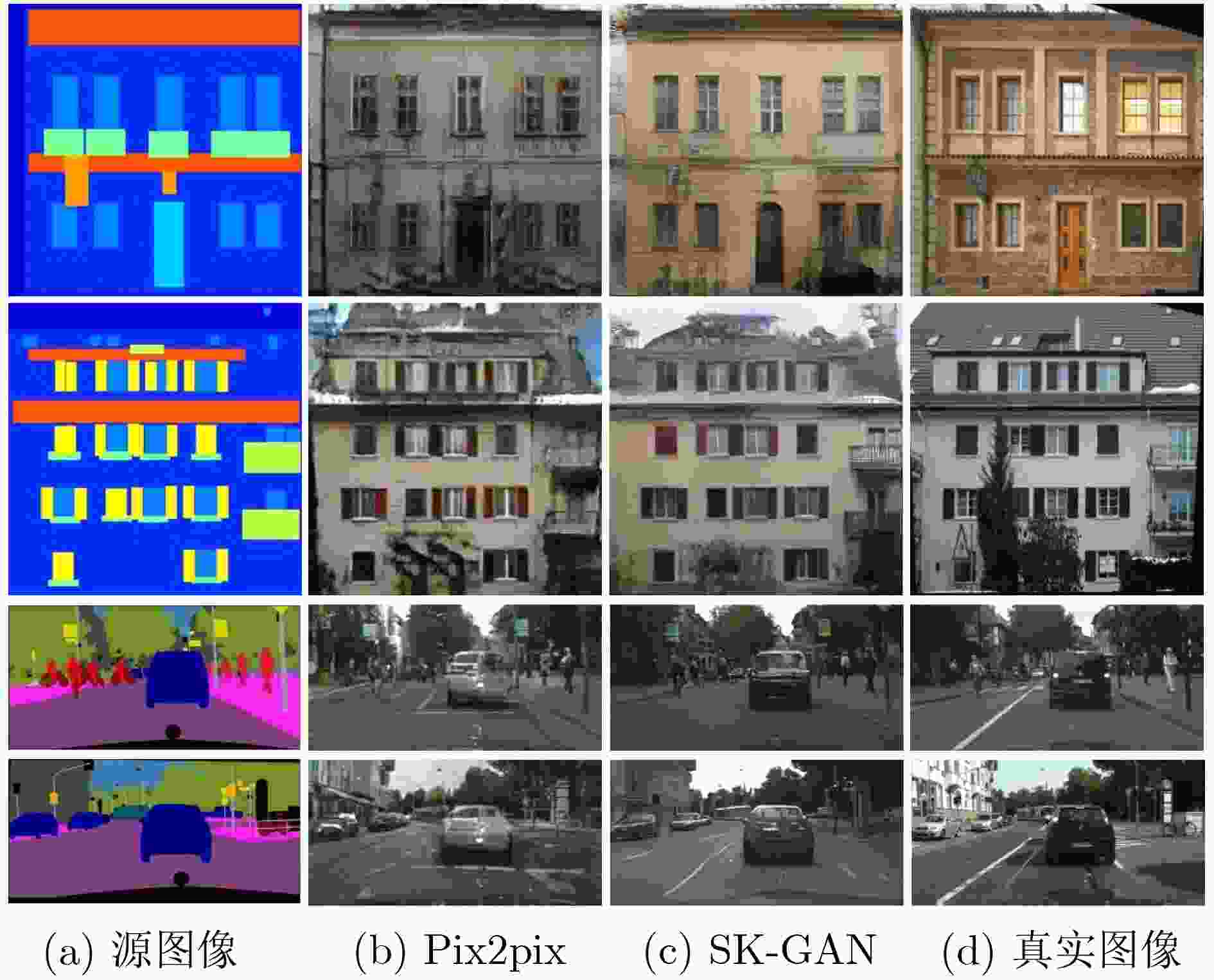
摘要: 为提高图像转换模型生成图像的质量,该文针对转换模型中的生成器进行改进,同时探究多样化的图像转换,拓展转换模型的生成能力。在生成器的改进方面,利用选择性(卷积)核模块(SKBlock)的动态感受野机制获取和融合生成器中每个上采样特征的多尺度信息,借助特征的多尺度信息和动态感受野构造选择性(卷积)核的生成式对抗网络(SK-GAN)。与传统生成器相比,SK-GAN以动态感受野获取多尺度信息的生成结构提高了生成图像的质量。在多样化图像转换方面,基于SK-GAN在草图合成真实图像任务提出带引导图像的选择性(卷积)核的生成式对抗网络(GSK-GAN)。该模型利用引导图像指导源图像的转换,通过引导图像编码器提取引导图像特征,然后由参数生成器(PG)和特征转换层(FT)将引导图像特征的信息传递至生成器。此外,该文还提出双分支引导图像编码器以提高转换模型的编辑能力,以及利用引导图像的隐变量分布实现随机样式的图像生成。实验表明,改进后的生成器有助于提高生成图像质量,SK-GAN在多个数据集中获得合理的生成结果。GSK-GAN不仅保证了生成图像的质量,还能生成更多样式的图像。Abstract: In order to improve the quality of the generated images by the image translation model, the generator in the translation model to obtain high-quality generated images is improved, the diversified image translation is explored and the generation ability of the translation model is expanded. In terms of generator improvement, the dynamic receptive field mechanism of Selective Kernel Block (SKBlock) is used to obtain and fuse the multi-scale information of each up sampling feature in the generator. With the help of multi-scale information of features and dynamic receptive field, the Selective Kernel Generative Adversarial Network (SK-GAN) is constructed. Compared with the traditional generator, SK-GAN improves the quality of the generated image by using dynamic receptive field to obtain multi-scale information. In terms of diversified image translation, the Selective Kernel Generative Adversarial Network with Guide (GSK-GAN) is proposed based on SK-GAN in sketch synthesis realistic image task. GSK-GAN uses the guided image to guide the source image translation and extracts the guide image features through the guided image encoder. Then transmits information of the guided image features to the generator by Parameter Generator (PG) and Feature Transformation (FT). In addition, a dual branch guided image encoder is proposed to improve the editing ability of the translation model. The random style image generation is realized by using the latent variable distribution of the guide image. The experimental results show that the improved generator is helpful to improve the quality of the generated images, and SK-GAN can obtain reasonable results in multiple datasets. GSK-GAN no only ensures the quality of the generated images, but also generates more styles of images
-
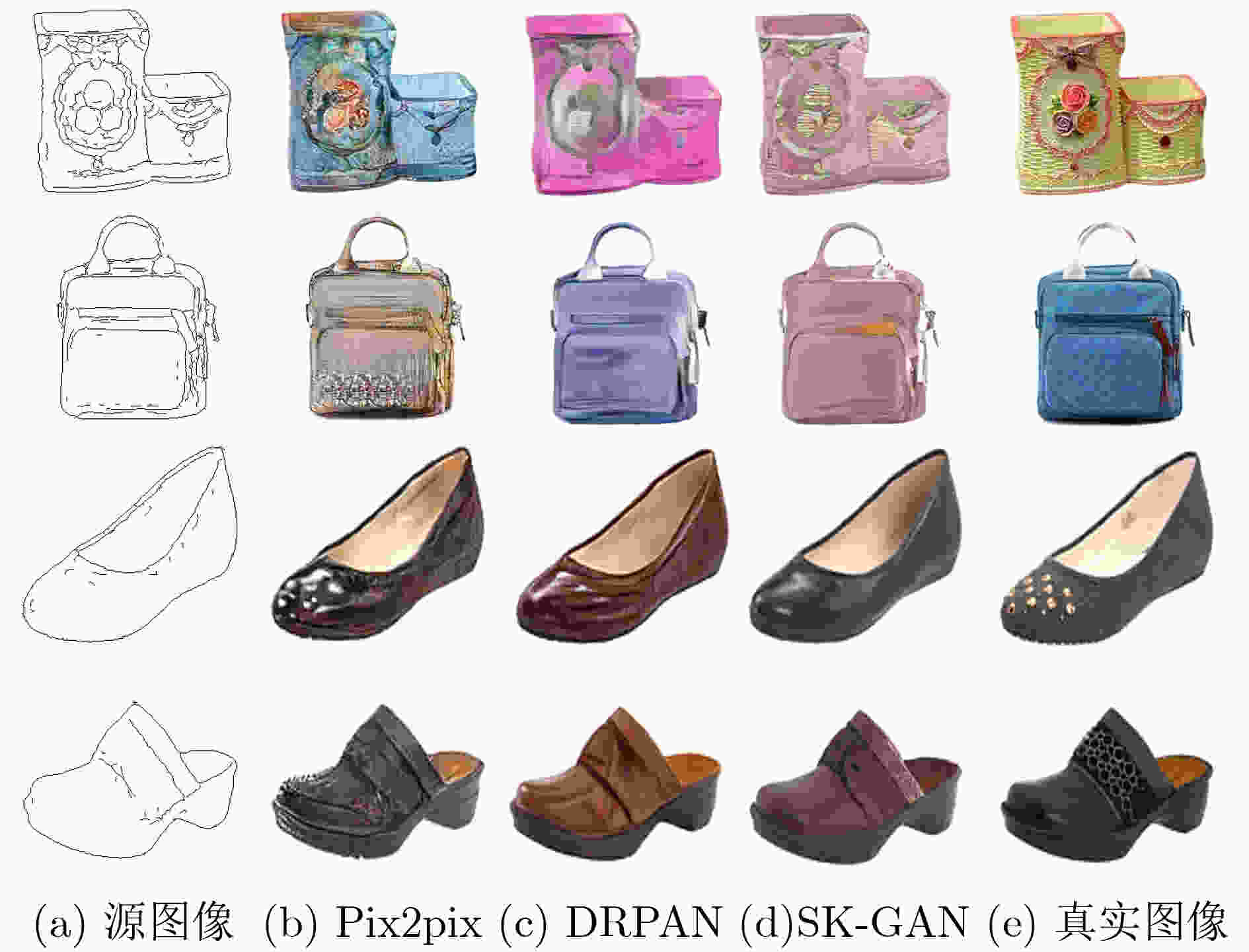
表 1 Edges2shoes和Edges2handbags数据集中定量对比结果
表 2 Cityscapes数据集中定量对比结果
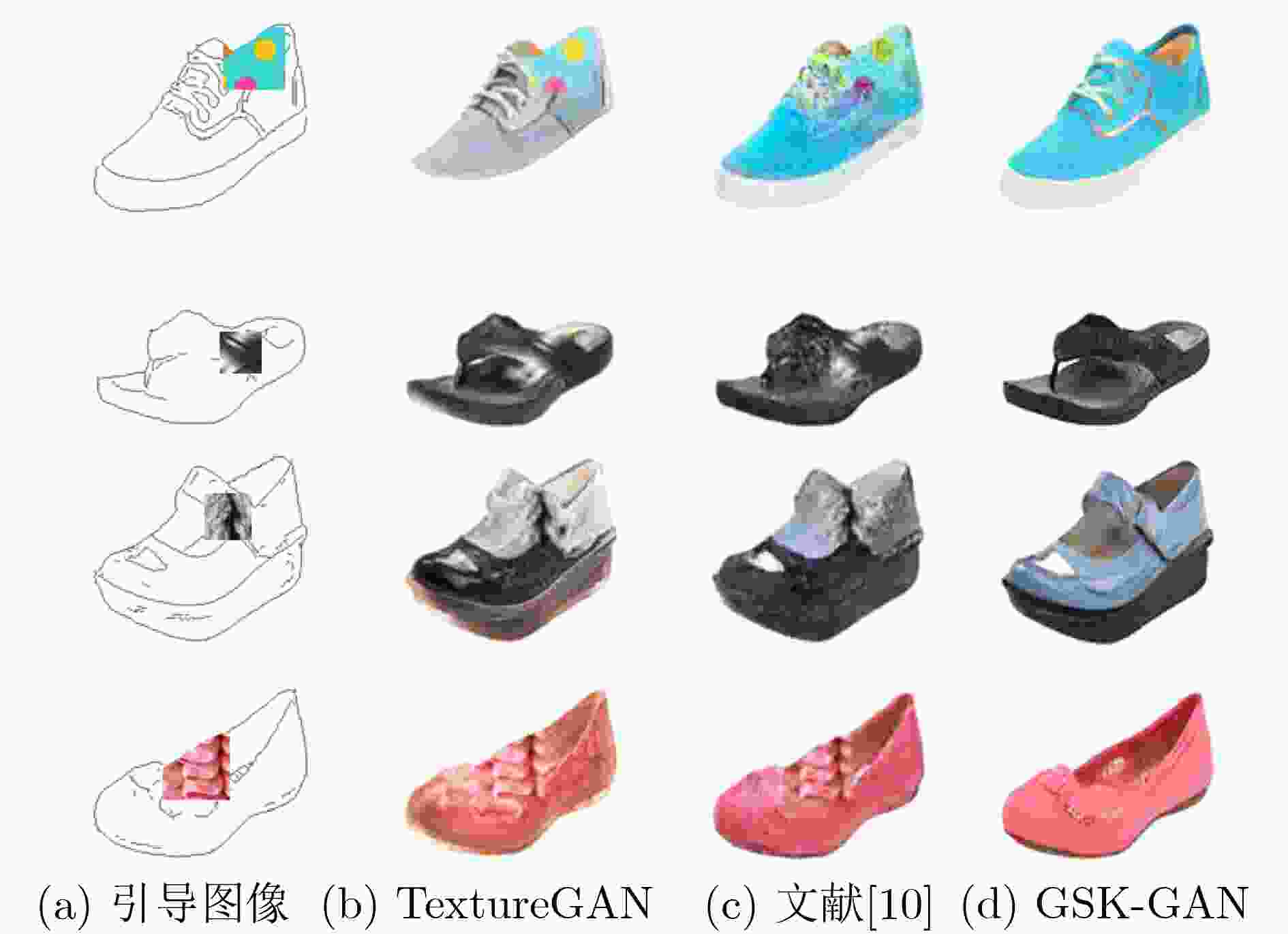
表 3 多模态图像转换Edges2shoes和Edges2handbags数据集中定量对比结果
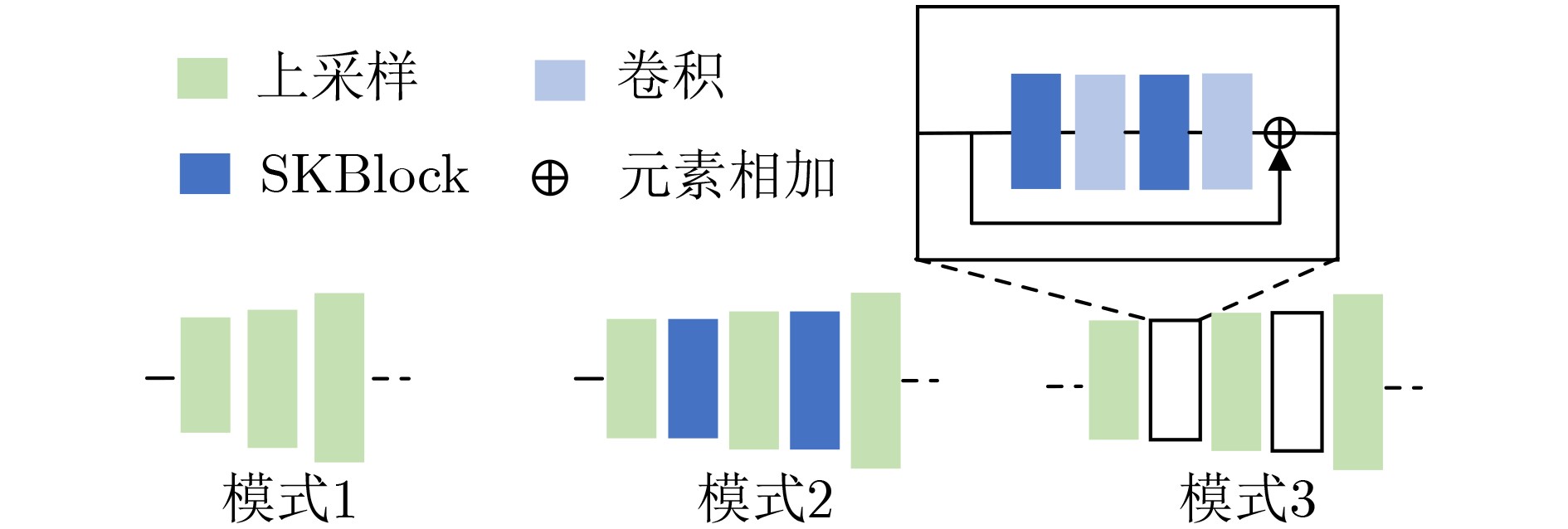
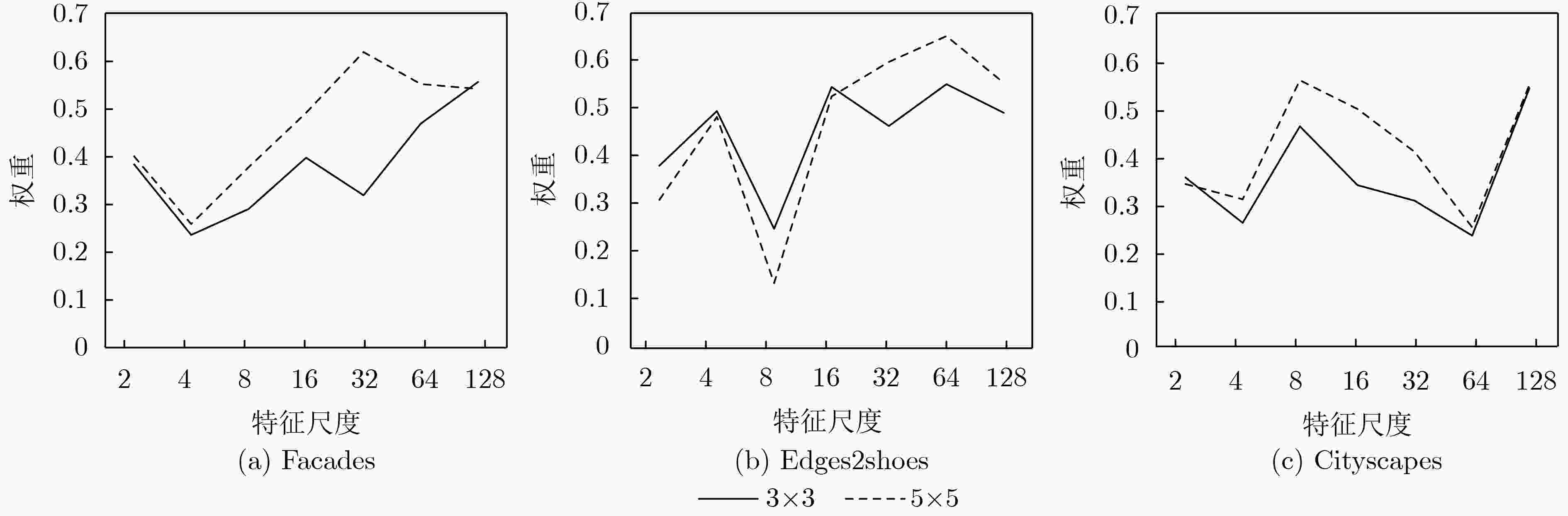
表 4 生成器中不同的上采样过程生成的图像质量对比结果
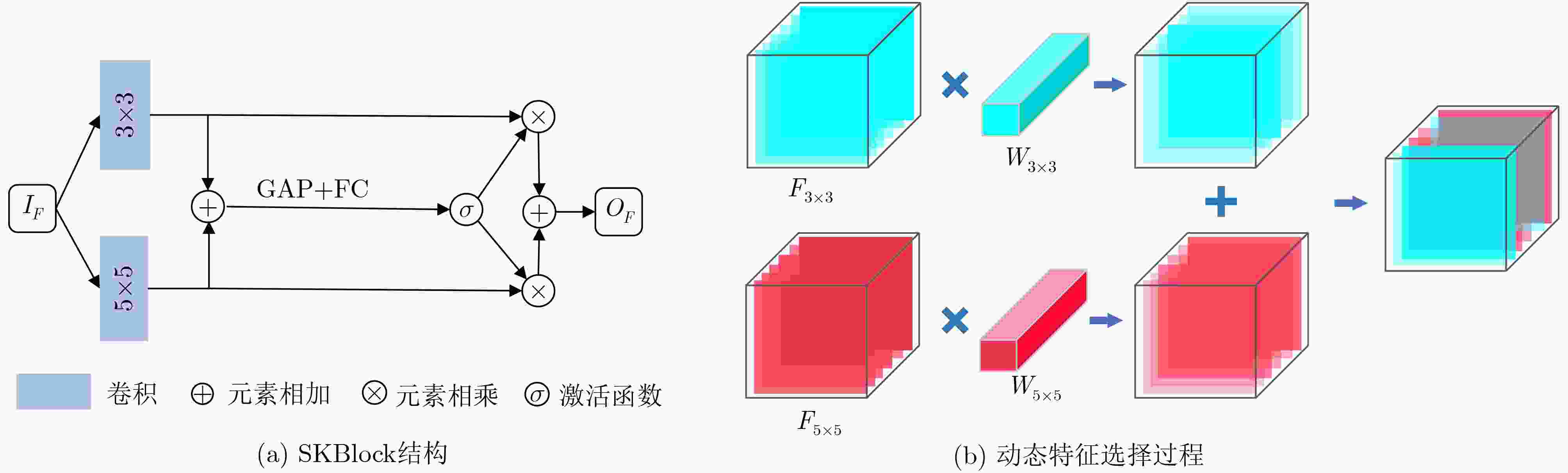
SSIM PSNR FID LPIPS 模式1 0.267 12.821 102.771 0.415 模式2 0.267 12.853 92.608 0.404 模式3 0.284 12.981 89.718 0.405 模式3 (GAN) 0.262 12.568 97.828 0.399 表 5 SKBlock中不同感受野分支组合对应的图像质量对比结果
SSIM PSNR FID LPIPS K13 0.276 12.961 100.532 0.398 K35 0.284 12.981 89.718 0.405 K57 0.268 13.007 98.132 0.400 -
[1] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.632. [2] CHEN Wengling and HAYS J. SketchyGAN: Towards diverse and realistic sketch to image synthesis[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9416–9425. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00981. [3] KINGMA D P and WELLING M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114, 2013. [4] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [5] RADFORD A, METZ L, and CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434, 2015. [6] SUNG T L and LEE H J. Image-to-image translation using identical-pair adversarial networks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(13): 2668. doi: 10.3390/app9132668 [7] WANG Chao, ZHENG Haiyong, YU Zhibin, et al. Discriminative region proposal adversarial networks for high-quality image-to-image translation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 796–812. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_47. [8] ZHU Junyan, ZHANG R, PATHAK D, et al. Toward multimodal image-to-image translation[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 465–476. [9] XIAN Wenqi, SANGKLOY P, AGRAWAL V, et al. TextureGAN: Controlling deep image synthesis with texture patches[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8456–8465. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00882. [10] ALBAHAR B and HUANG Jiabin. Guided image-to-image translation with bi-directional feature transformation[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9015–9024. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00911. [11] SUN Wei and WU Tianfu. Learning spatial pyramid attentive pooling in image synthesis and image-to-image translation[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.06322, 2019. [12] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.244. [13] LI Xiang, WANG Wenhai, HU Xiaolin, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 510–519. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00060. [14] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07261, 2016. [15] 柳长源, 王琪, 毕晓君. 基于多通道多尺度卷积神经网络的单幅图像去雨方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2285–2292. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190755LIU Changyuan, WANG Qi, and BI Xiaojun. Research on Rain Removal Method for Single Image Based on Multi-channel and Multi-scale CNN[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2285–2292. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190755 [16] LI Juncheng, FANG Faming, MEI Kangfu, et al. Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 527–542. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_32. [17] MAO Xudong, LI Qing, XIE Haoran, et al. Least squares generative adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2813–2821. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.304. [18] HEUSEL M, RAMSAUER H, UNTERTHINER T, et al. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6629–6640. [19] ZHANG R, ISOLA P, EFROS A A, et al. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 586–595. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00068. [20] CORDTS M, OMRAN M, RAMOS S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3213–3223. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.350. [21] TYLEČEK R and ŠÁRA R. Spatial pattern templates for recognition of objects with regular structure[C]. The 35th German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Saarbrücken, Germany, 2013: 364–374. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-40602-7_39. [22] CHEN Qifeng and KOLTUN V. Photographic image synthesis with cascaded refinement networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 1520–1529. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.168. -





 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:
