Information-Centric Networking Caching Scheme for Data Characteristics of Internet of Things
-
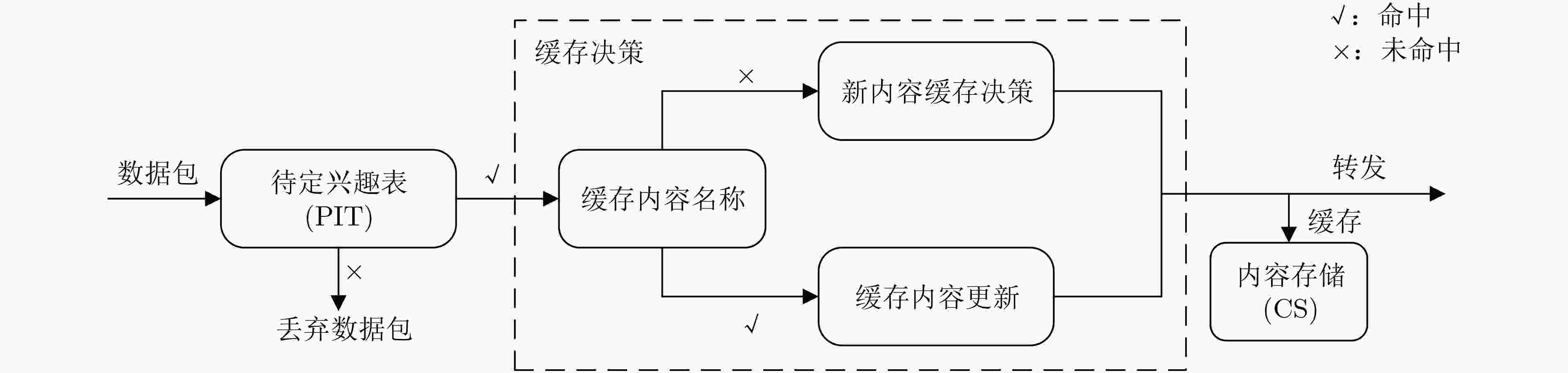
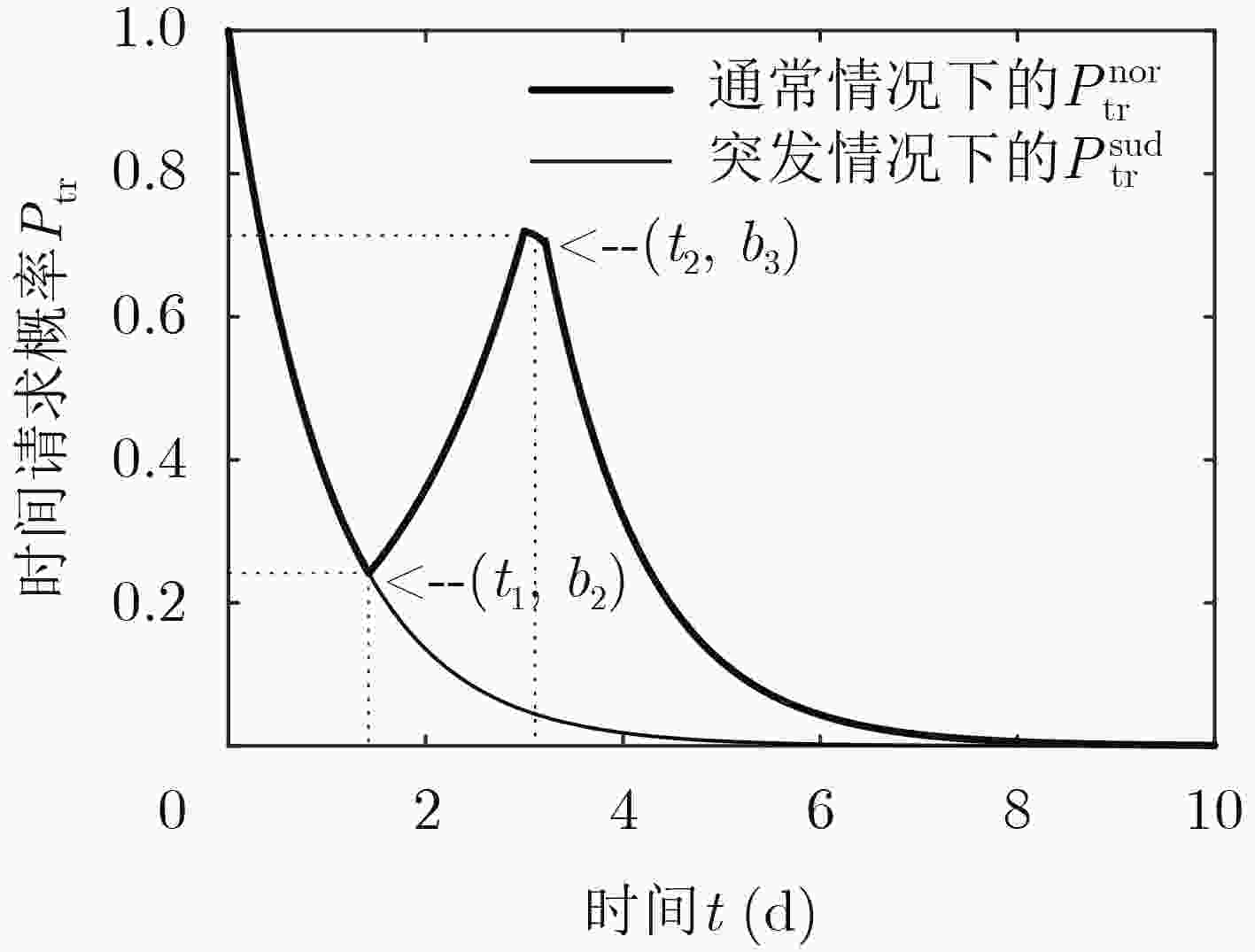
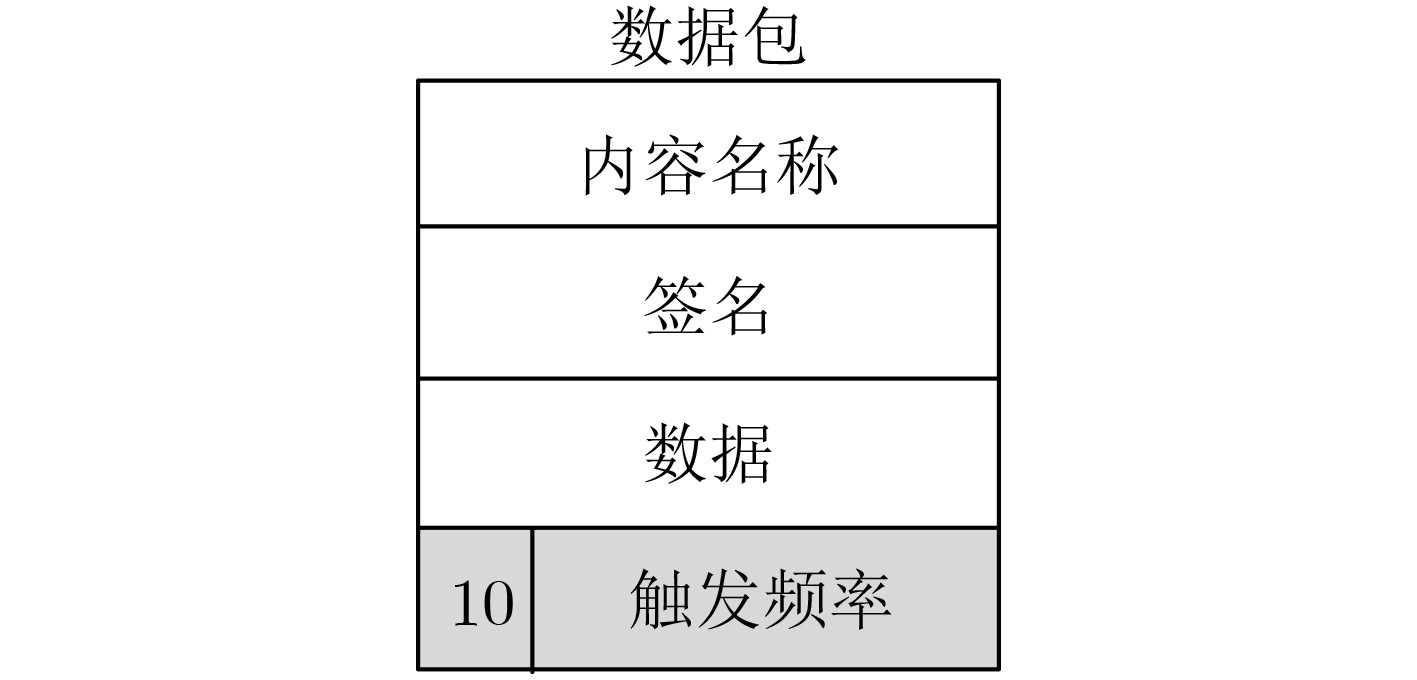
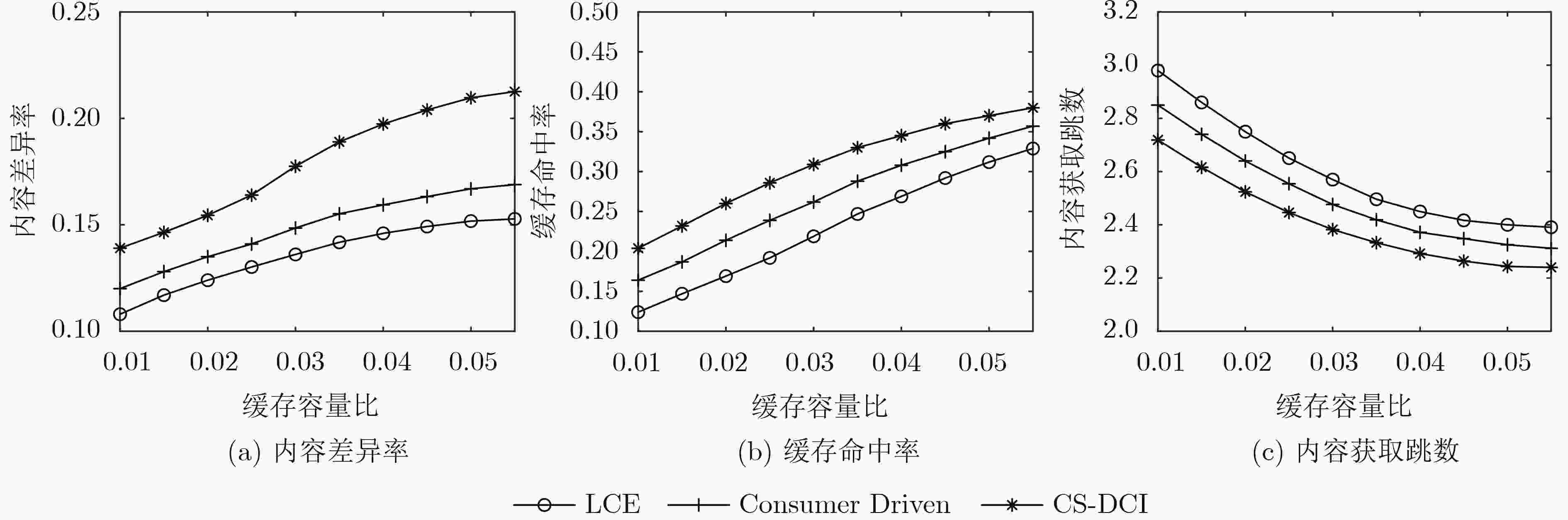
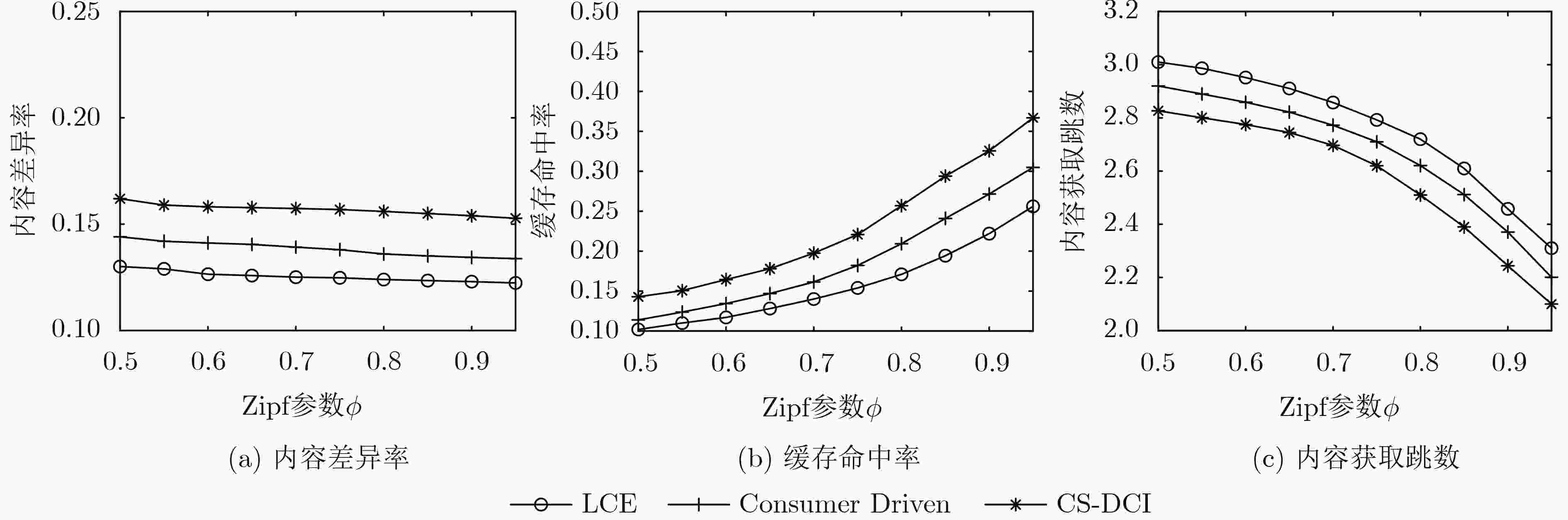
摘要: 将信息中心网络(ICN)应用到物联网(IoT)架构(ICN-IoT),可以有效地解决数据分发问题,提高数据的传输效率。但在ICN-IoT中,现有的缓存研究主要是在内容流行度或新鲜度等单一维度上实现缓存配置,无法适应海量和多态的物联网数据特征,导致缓存效率低。针对上述问题,该文首先分析了物联网数据特征,将数据分为周期性数据和事件触发性数据。然后,综合考虑物联网的这两种数据特征,提出一种具有不同缓存决策的ICN-IoT缓存方案(CS-DCI),路由器根据到达数据的特征类型执行相应的缓存决策。最后详细介绍两种数据类型的缓存策略,对于周期性数据,考虑内容流行度和时间请求概率缓存用户请求最多的数据;对于事件触发性数据,考虑内容流行度和事件触发频率缓存有意义的数据。仿真表明,该方案能够提高内容差异率,增加缓存内容的多样性,从而满足ICN-IoT不同应用的请求,获得较优的缓存命中率以及减少内容获取跳数。Abstract: Applying the Information-Centric Networking (ICN) to the Internet of Things (IoT) architecture(ICN-IoT)can solve the data distribution problem and improve the efficiency of data transmission. However, existing cache policies in ICN-IoT mainly realize cache configuration in a single dimension, such as content popularity or freshness, which can not adapt to the massive and polymorphic characteristics of IoT data, and result in low cache efficiency. To address the above problems, the characteristics of IoT data are firstly analyzed in this paper and the data are divided into periodic data and event-triggered data. Then, an ICN-IoT Caching Scheme for Data Characteristics of IoT (CS-DCI) with different cache decisions is proposed, combining with the characteristics of the IoT data. The cache routers differentiate the type of arriving data to call corresponding caching decisions. Finally, the caching strategies for IoT data characteristics are introduced in detail. For periodic data, based on content popularity and time request probability to cache the most requested data; For event-triggered data, based on content popularity and event trigger frequency to cache meaningful data. The simulation results show that the scheme can increase diversity of cache content, thereby satisfying the requests of different applications of ICN-IoT, obtaining better cache hit ratio and reducing content acquisition hops.
-
表 1 物联网流量特征
物联网流量 定义 例子 服务要求 特征 分类 连续性流量 数据持续性产生 视频监控 准确性低、优先级低 时间关联性强、短周期性 周期性数据 周期性流量 数据周期性产生 温度传感器 准确性低、优先级低 时间关联性强、周期性 事件触发性流量 事件触发数据产生 紧急报警 准确性高、优先级高 时间关联性弱 事件触发性数据 请求响应性流量 用户行为触发数据产生 移动支付 准确性高、优先级低 时间关联性弱 -
[1] DIN I U, HASSAN S, KHAN M K, et al. Caching in information-centric networking: Strategies, challenges, and future research directions[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 1443–1474. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2787609 [2] FANG Chao, YAO Haipeng, WANG Zhuwei, et al. A survey of mobile information-centric networking: Research issues and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(3): 2353–2371. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2809670 [3] MORELLI A, TORTONESI M, STEFANELLI C, et al. Information-Centric Networking in next-generation communications scenarios[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2017, 80: 232–250. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2016.12.026 [4] AWAIS M and SHAH M A. Information-centric networking: A review on futuristic networks[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Automation and Computing, Huddersfield, UK, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.23919/IConAC.2017.8082033. [5] 芮兰兰, 彭昊, 黄豪球, 等. 基于内容流行度和节点中心度匹配的信息中心网络缓存策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 325–331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150626RUI Lanlan, PENG Hao, HUANG Haoqiu, et al. Popularity and centrality based selective caching scheme for information-centric networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 325–331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150626 [6] ALBERTI A M, SANTOS M A S, SOUZA R, et al. Platforms for smart environments and future internet design: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 165748–165778. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2950656 [7] 程一凡, 曲至诚, 张更新. 低轨卫星星座物联网业务量建模[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1050–1056. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200091CHENG Yifan, QU Zhicheng, and ZHANG Gengxin. Traffic modeling for low earth orbit satellite constellation internet of things[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1050–1056. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200091 [8] ULLAH R, AHMED S H, and KIM B S. Information-centric networking with edge computing for IoT: Research challenges and future directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 73465–73488. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2884536 [9] NOUR B, IBN-KHEDHER H, MOUNGLA H, et al. Internet of things mobility over information-centric/named-data networking[J]. IEEE Internet Computing, 2020, 24(1): 14–24. doi: 10.1109/MIC.2019.2963187 [10] AMADEO M, CAMPOLO C, IERA A, et al. Named data networking for IoT: An architectural perspective[C]. 2014 European Conference on Networks and Communications, Bologna, Italy, 2014: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/EuCNC.2014.6882665. [11] SAADEH H, ALMOBAIDEEN W, SABRI K E, et al. Hybrid SDN-ICN architecture design for the internet of things[C]. The 6th International Conference on Software Defined Systems, Rome, Italy, 2019: 96–101. doi: 10.1109/SDS.2019.8768582. [12] ARSHAD S, AZAM M A, REHMANI M H, et al. Recent advances in information-centric networking-based internet of things (ICN-IoT)[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2128–2158. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2873343 [13] MEDDEB M, DHRAIEF A, BELGHITH A, et al. How to cache in ICN-based IoT environments?[C]. The 14th IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, Hammamet, Algeria, 2017: 1117–1124. doi: 10.1109/AICCSA.2017.37. [14] QUEVEDO J, CORUJO D, and AGUIAR R. Consumer driven information freshness approach for content centric networking[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Toronto, Canada, 2014: 482–487. doi: 10.1109/INFCOMW.2014.6849279. [15] 赵国锋, 林欢, 段洁, 等. 面向数据新鲜度的ICN-IoT缓存方案[J]. 计算机工程, 2020, 46(11): 223–230. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0056463ZHAO Guofeng, LIN Huan, DUAN Jie, et al. ICN-IoT caching scheme for data freshness[J]. Computer Engineering, 2020, 46(11): 223–230. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0056463 [16] HAIL M A, AMADEO M, MOLINARO A, et al. Caching in named data networking for the wireless internet of things[C]. 2015 International Conference on Recent Advances in Internet of Things, Singapore, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RIOT.2015.7104902. [17] CHEN Bo, LIU Liang, SUN Mingxin, et al. IoTCache: Toward data-driven network caching for internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10064–10076. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2935442 [18] LIU Rongduo, WU Wei, ZHU Hao, et al. M2M-oriented QoS categorization in cellular network[C]. The 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Wuhan, China, 2011: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/wicom.2011.6040143. [19] FAYAZBAKHSH S K, LIN Yin, TOOTOONCHIAN A, et al. Less pain, most of the gain: Incrementally deployable ICN[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2013, 43(4): 147–158. doi: 10.1145/2534169.2486023 [20] 樊占东. 面向信息中心网络的协作缓存策略研究[D]. [硕士论文], 河南科技大学, 2017.FAN Zhandong. Research on cooperative caching strategy oriented to information-centric networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Henan University of Science and Technology, 2017. -





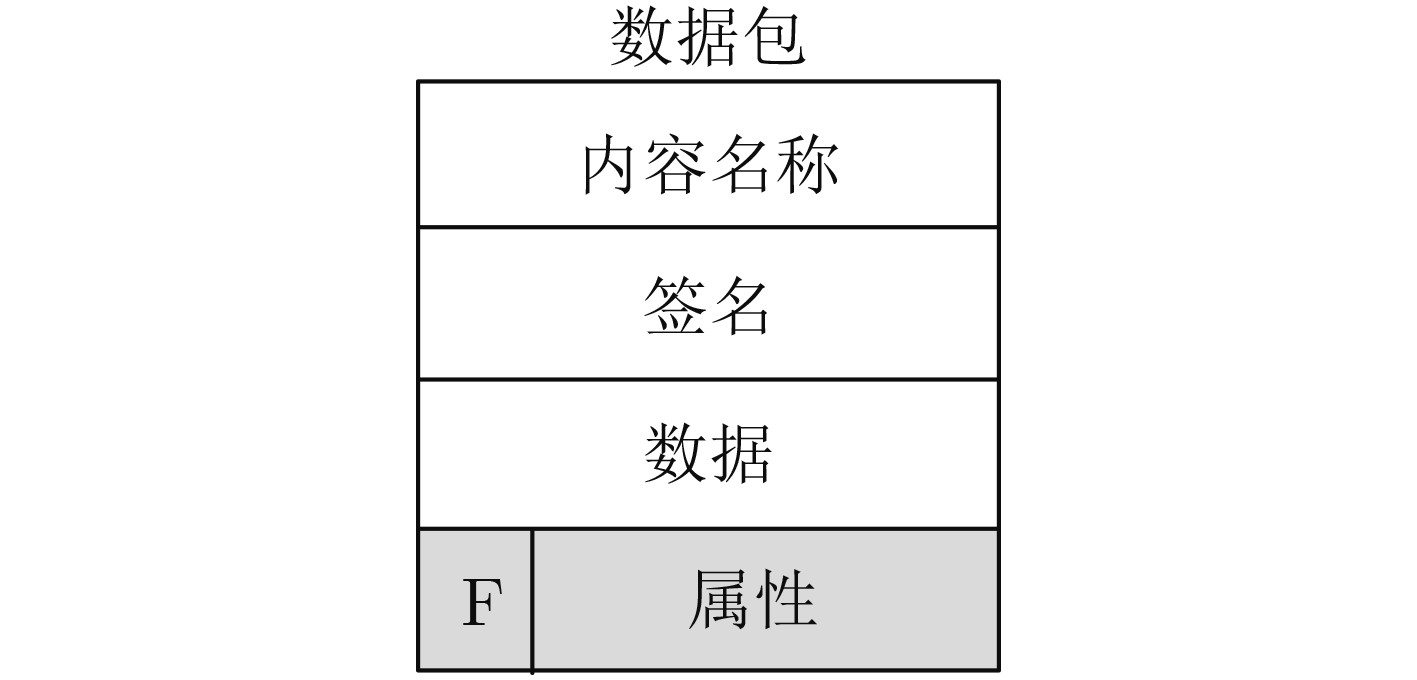
 下载:
下载:
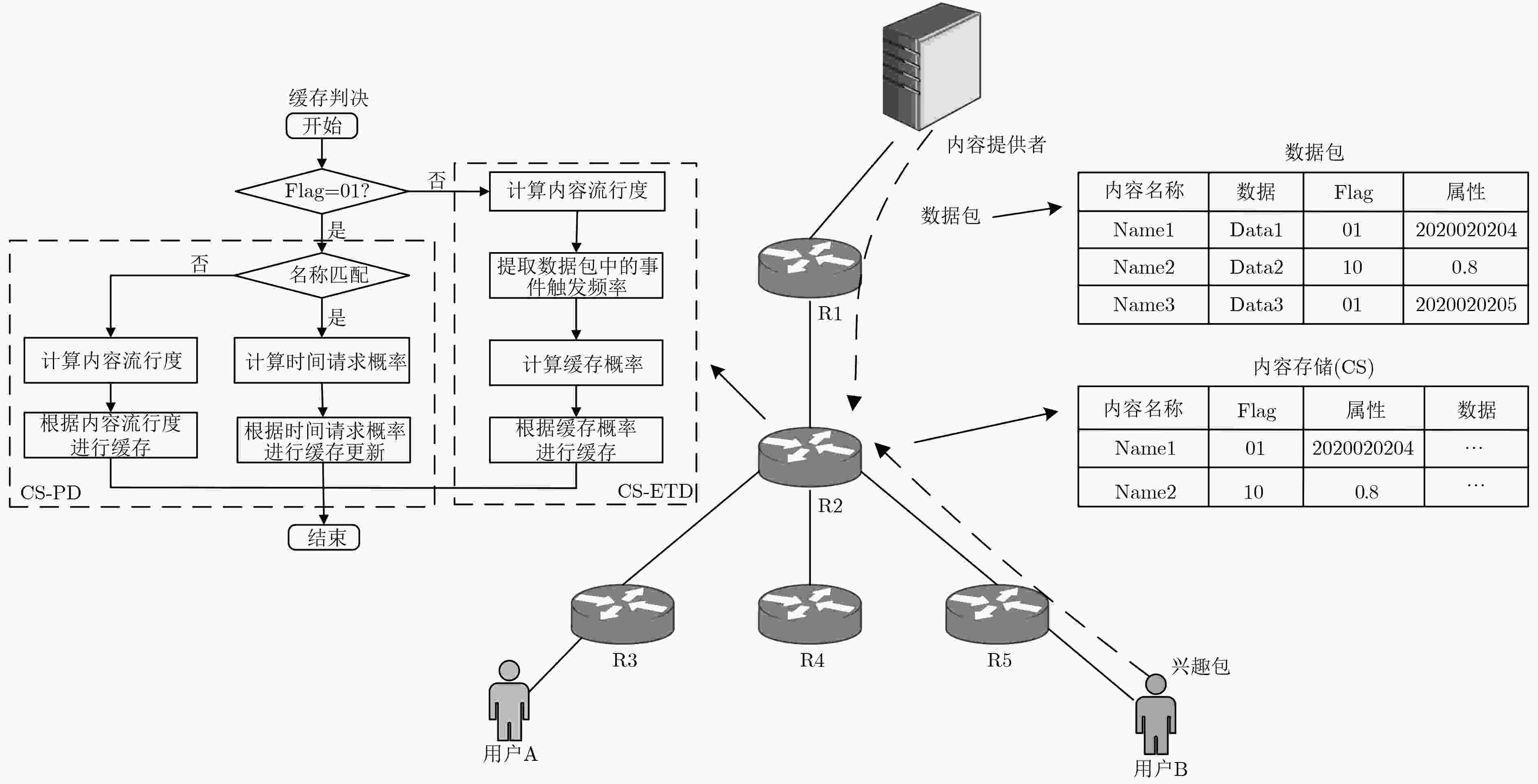
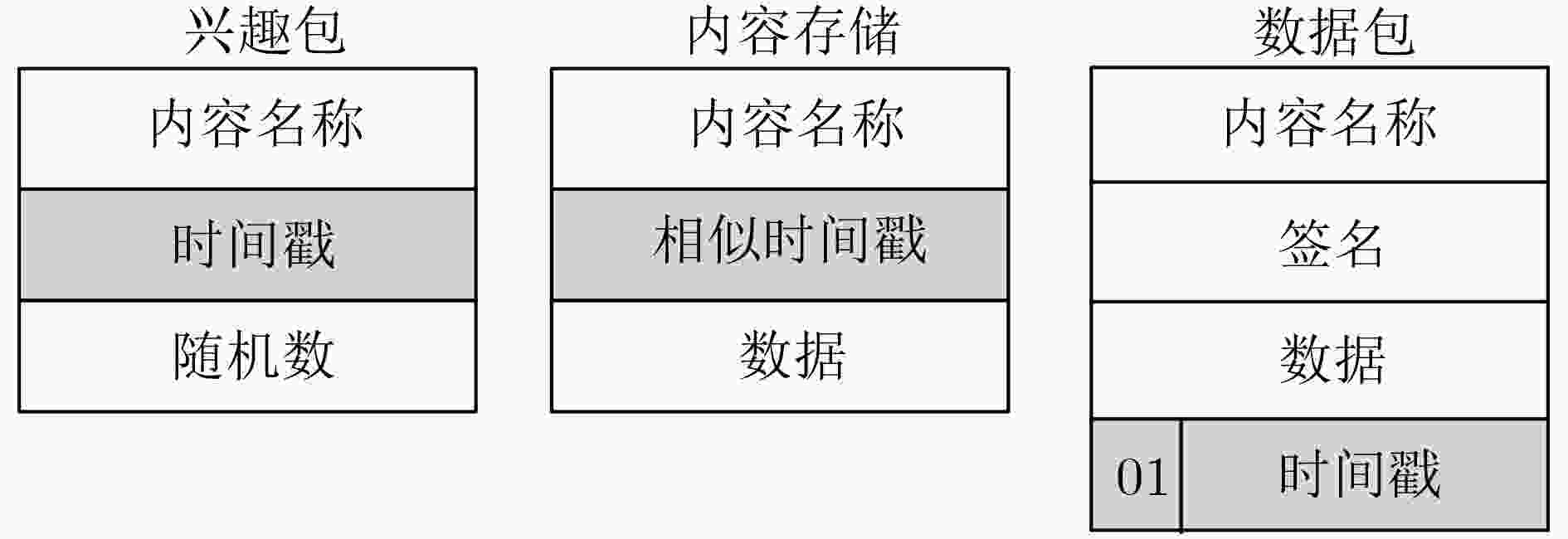
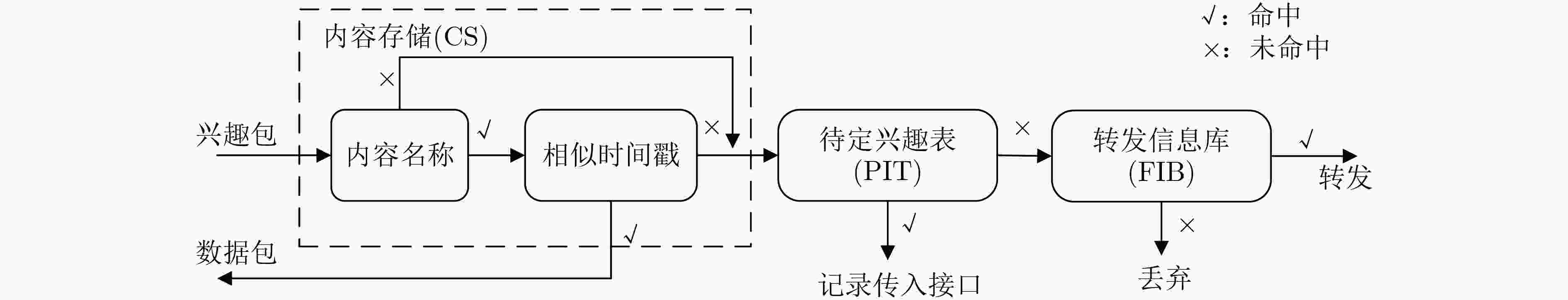


 下载:
下载:
