An Optimal Plot-to-Track Association Method Based on JVC Algorithm for Maritime Target with Compact HFSWR
-
摘要: 紧凑型地波雷达由于接收天线阵列孔径减小导致对海上目标的定位精度低,在多目标跟踪算法中采用序贯式的点迹-航迹关联方式易发生误关联导致航迹断裂、误跟踪等问题。对此,该文将多目标点迹-航迹关联转化为最优分配问题,提出一种基于JVC算法的多目标点迹-航迹最优关联方法。对于关联波门重叠区域内存在公共候选点迹的多条航迹,首先以雷达获取的目标多普勒速度、距离与方位角作为目标特征参数,利用最小代价函数确定公共候选点迹与所有航迹之间的相似度,得到关联代价矩阵;然后以总关联代价最小化作为优化准则,采用JVC算法求解得到最优的点迹-航迹关联结果。利用仿真与实测目标数据开展了点迹-航迹关联实验,并与序贯最近邻关联方法的关联结果进行了对比。实验结果表明:采用该文所提方法跟踪得到的航迹时长明显优于序贯最近邻关联方法的结果,解决了序贯式关联因关联错误导致的航迹断裂、误跟踪等问题,提高了航迹跟踪的连续性。Abstract: The compact High-Frequency Surface Wave Radar (HFSWR) has low spatial resolution for target detection due to its reduced aperture size of the receiving antenna array. The sequential plot-to-track association method used in multi-target tracking algorithms is prone to erroneous association, which easily leads to track fragmentation and false tracking. In order to solve this problem, regarding the multi-target plot-to-track association as an optimal allocation problem, an optimal multi-target plot-to-track association method based on JVC (Jonker-Volgenant-Castanon) algorithm is proposed. For multiple tracks with common candidate plots in their overlapped association gate, firstly, the similarity between their candidate plots and all tracks is calculated using the minimal cost function with target Doppler velocity, range and azimuth as parameters and an association cost matrix is formed. Then, the optimal association result is achieved by minimizing the total association cost using the JVC algorithm. Both simulation and field target data are used to carry out the plot-to-track association experiment, and the association results are compared with those of the sequential nearest neighbor association method. The experimental results show that the track length obtained by the proposed method is superior to that of the sequential nearest neighbor method, thus the track continuity is improved.
-
Key words:
- Compact HFSWR /
- Multitarget tracking /
- Plot-to-track association /
- Optimal association
-
表 1 仿真目标的参数
初始距离(km) 初始方位角(°) 初始多普勒速$({\rm{km/h}})$ 帧数 目标1 147.2 8.4 20.8 180 目标2 151.6 8.7 19.7 180 目标3 157.4 11.1 19.4 180 目标4 138.1 –19.5 30.6 180 目标5 138.8 –19.0 19.1 180 表 2 不同跟踪时长的航迹数量对比
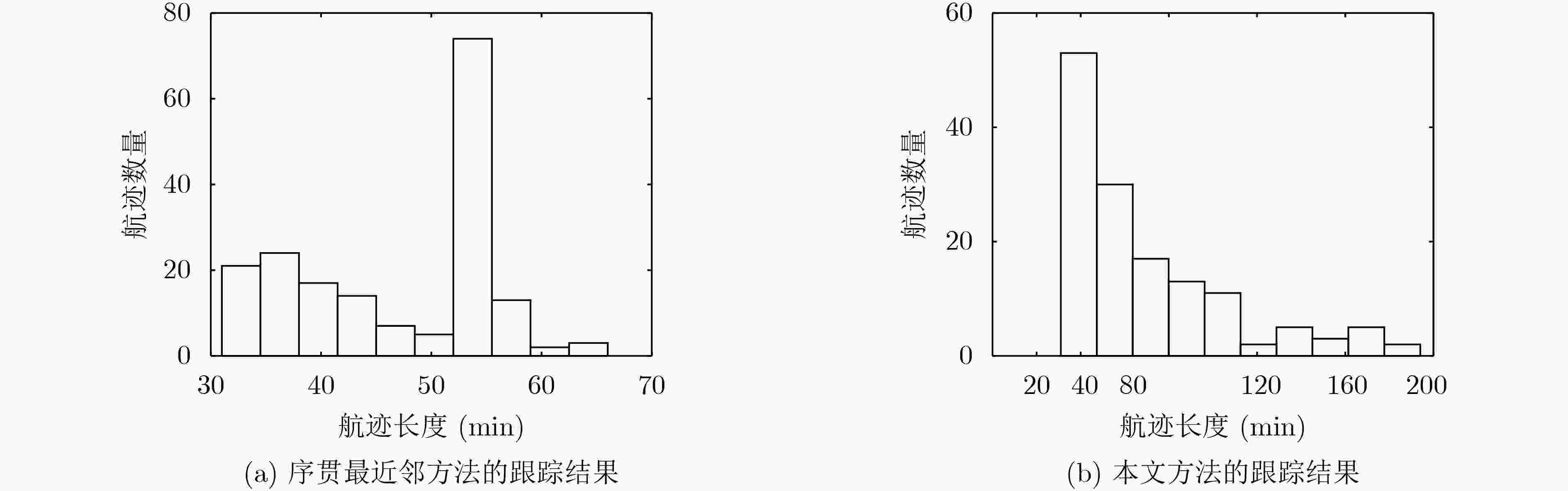
方法 跟踪时长>30 min 跟踪时长>40 min 跟踪时长>50 min 航迹总数 平均跟踪时长(min) 航迹总数 平均跟踪时长(min) 航迹总数 平均跟踪时长(min) 序贯最近邻关联方法 181 46.9 123 52.4 92 54.8 本文方法 145 69.1 109 80.7 81 93.7 表 3 目标个例详细信息
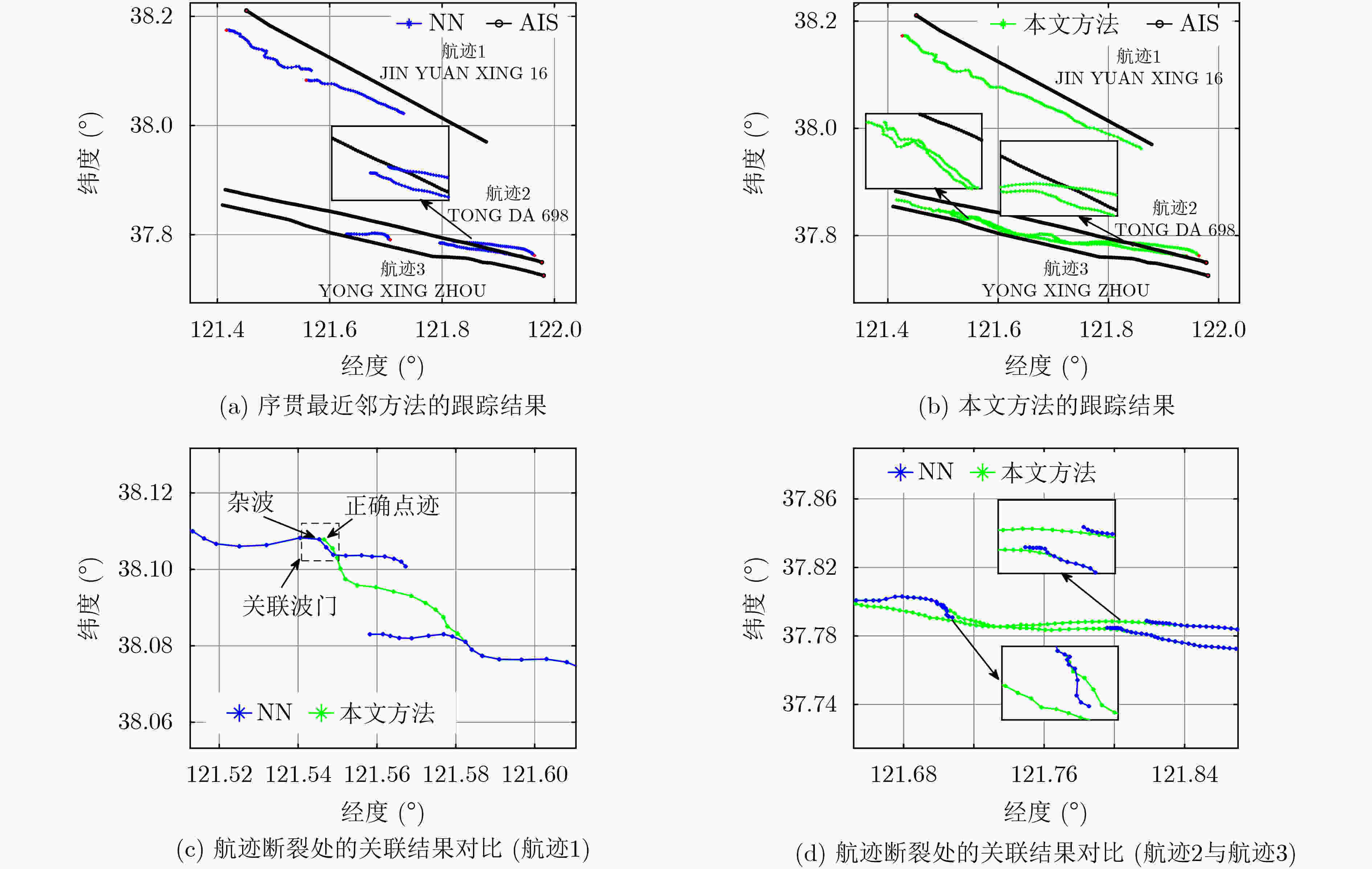
船名 MMSI 船长(m) 船宽(m) 吃水深度(m) 初始距离${\rm{(km)}}$ 初始方位角${(^ \circ })$ 多普勒速度$({\rm{km/h}})$ 跟踪时长(m) JIN YUAN XING 16 413271210 224 32 12.4 91.7 10.4 20.1 124 TONG DA 698 412454070 103 16 3.5 26.6 28.8 –10.2 180 YONG XING ZHOU 413203000 228 32 11.4 27.1 26.4 –12.2 150 表 4 采用两种方法时的跟踪结果比较
关联方法 正确关联航迹数目 关联正确率(%) 平均运行时间(s) NNDA 29 53.7 49.61 本文方法 44 81.5 54.7 -
[1] 纪永刚, 张杰, 王祎鸣, 等. 紧凑型高频地波雷达目标探测研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(2): 1–7. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20160285JI Yonggang, ZHANG Jie, WANG Yiming, et al. An overview of target monitoring with compact HFSWR[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(2): 1–7. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20160285 [2] 叶磊, 王勇, 杨强, 等. 基于对数行列式散度与对称对数行列式散度的高频地波雷达目标检测器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1931–1938. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181078YE Lei, WANG Yong, YANG Qiang, et al. High frequency surface wave radar detector based on log-determinant divergence and symmetrized log-determinant divergence[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1931–1938. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181078 [3] PARK S, CHO C J, KU B, et al. Compact HF surface wave radar data generating simulator for ship detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(6): 969–973. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2691741 [4] SMITH M, ROARTY H, GLENN S, et al. Methods of associating CODAR seasonde vessel detection data into unique tracks[C]. 2013 IEEE OCEANS, San Diego, USA, 2013: 1–5. doi: 10.23919/OCEANS.2013.6741197. [5] LU Bo, WEN Biyang, TIAN Yingwei, et al. A vessel detection method using compact-array HF radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(11): 2017–2021. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2748142 [6] HELZEL T, HANSEN B, KNIEPHOFF M, et al. Introduction of the compact HF radar WERA-S[C]. 2012 IEEE/OES Baltic International Symposium (BALTIC), Klaipeda, Lithuania, 2012: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/BALTIC.2012.6249215. [7] JI Yonggang, ZHANG Jie, WANG Yiming, et al. Target monitoring using small-aperture compact high-frequency surface wave radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2018, 33(3): 22–31. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2018.170023 [8] SUN Weifeng, HUANG Weimin, JI Yonggang, et al. A vessel azimuth and course joint re-estimation method for compact HFSWR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(2): 1041–1051. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2943065 [9] SUN Weifeng, HUANG Weimin, JI Yonggang, et al. Vessel tracking with small-aperture compact high-frequency surface wave radar[C]. OCEANS 2019- Marseille, Marseille, France, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/OCEANSE.2019.8867267. [10] 辛云宏, 杨万海. 被动多站多目标的测量数据关联算法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2005, 26(6): 748–752, 797. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.06.015XIN Yunhong and YANG Wanhai. A method of the passive multi-sensor multi-target measurement data association[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2005, 26(6): 748–752, 797. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.06.015 [11] CHEN Qinxin, YAN Yude, and DAI Yuewei. Joint nearest neighbor data association based on interacting multiple model Kalman filtering[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2016: 75–79. doi: 10.1109/CompComm.2016.7924668. [12] 李保珠, 关键, 董云龙. 基于航迹矢量检测的雷达与电子支援设施抗差关联算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 123–129. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180303LI Baozhu, GUAN Jian, and DONG Yunlong. Anti-bias track association algorithm of radar and electronic support measurements based on track vectors detection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 123–129. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180303 [13] HUANG Yuan, SONG T L, and KIM D S. Linear multitarget integrated probabilistic data association for multiple detection target tracking[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(9): 945–953. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0481 [14] ZHANG Hui, LIU Yongxin, JI Yonggang, et al. Vessel fusion tracking with a dual-frequency high-frequency surface wave radar and calibrated by an automatic identification system[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 37(7): 131–140. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1250-0 [15] 李文超, 邹焕新, 雷琳, 等. 目标数据关联技术综述[J]. 计算机仿真, 2014, 31(3): 1–5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2014.03.001LI Wenchao, ZOU Huanxin, LEI Lin, et al. A survey of target data association[J]. Computer Simulation, 2014, 31(3): 1–5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2014.03.001 [16] 康旭超, 何广军, 陈峰, 等. 密集杂波下的模糊数据关联多目标跟踪算法[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2019, 41(4): 56–61, 65.KANG Xuchao, HE Guangjun, CHEN Feng, et al. Fuzzy data associated with multi-target tracking algorithm under dense clutter[J]. Journal of Detection &Control, 2019, 41(4): 56–61, 65. [17] WINTER M, SCHMIDLIN V, and FAVIER G. Classical and neural solutions for plot-to-track association[C]. SPIE 3163, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets, San Diego, USA, 1997: 546–557. doi: 10.1117/12.279537. [18] BORDONARO S, WILLETT P, and BAR-SHALOM Y. Decorrelated unbiased converted measurement Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1431–1444. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120563 [19] 盛卫东, 林两魁, 安玮, 等. 基于全局最优的被动多传感器多目标轨迹关联算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(7): 1621–1625. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01091SHENG Weidong, LIN Liangkui, AN Wei, et al. A passive multisensor multitarget track association algorithm based on global optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(7): 1621–1625. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01091 [20] NIKOLIC D, STOJKOVIC N, and LEKIC N. Maritime over the horizon sensor integration: High frequency surface-wave- radar and automatic identification system data integration algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(4): 1147. doi: 10.3390/s18041147 -





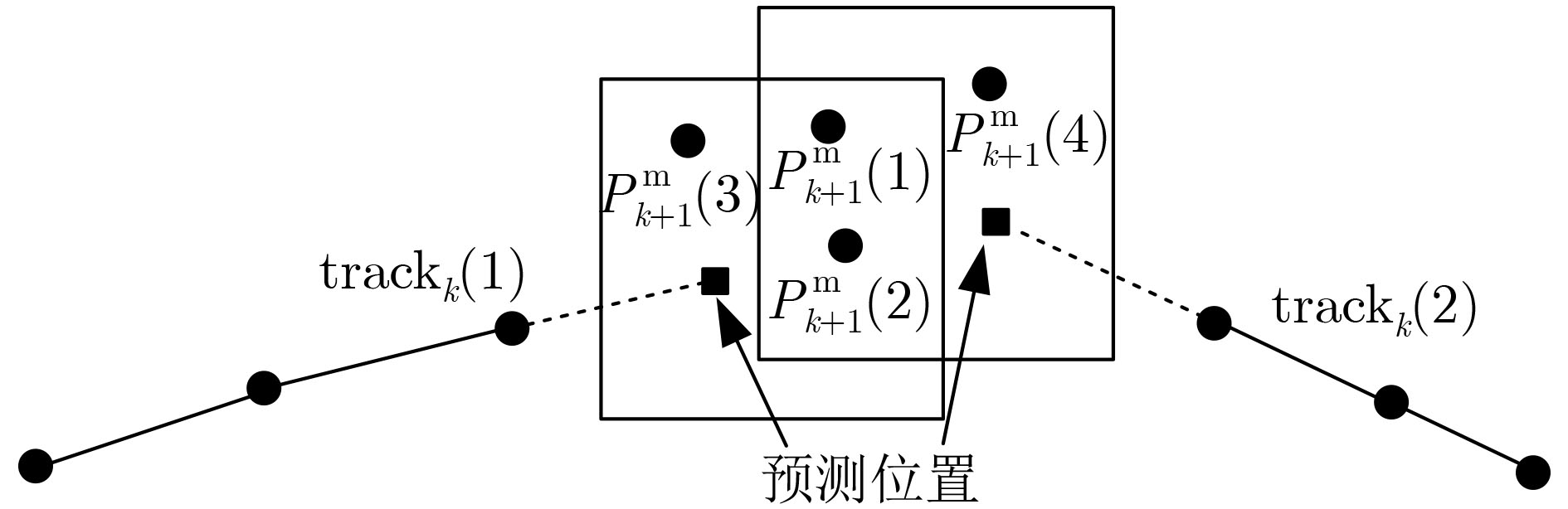
 下载:
下载:
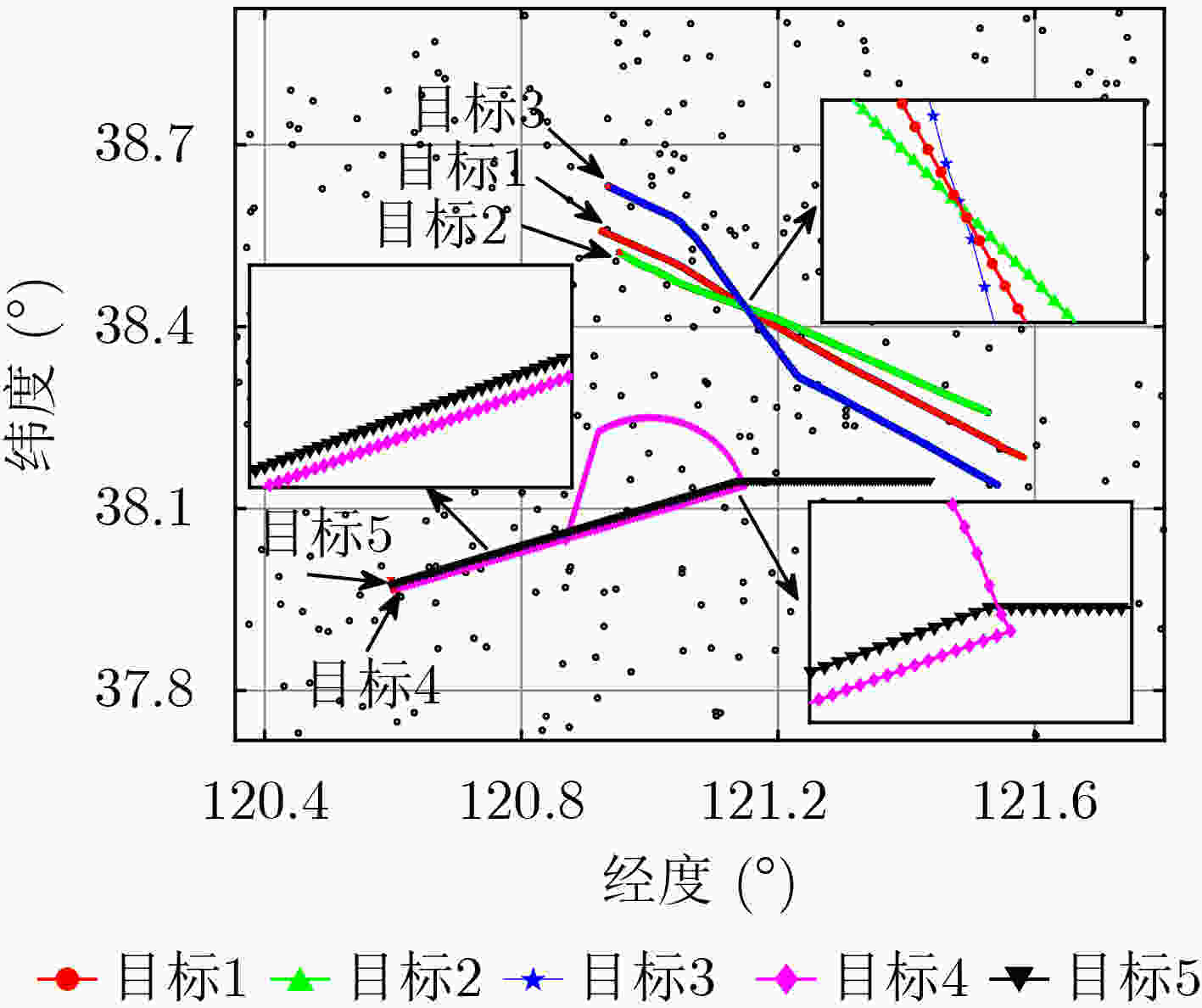
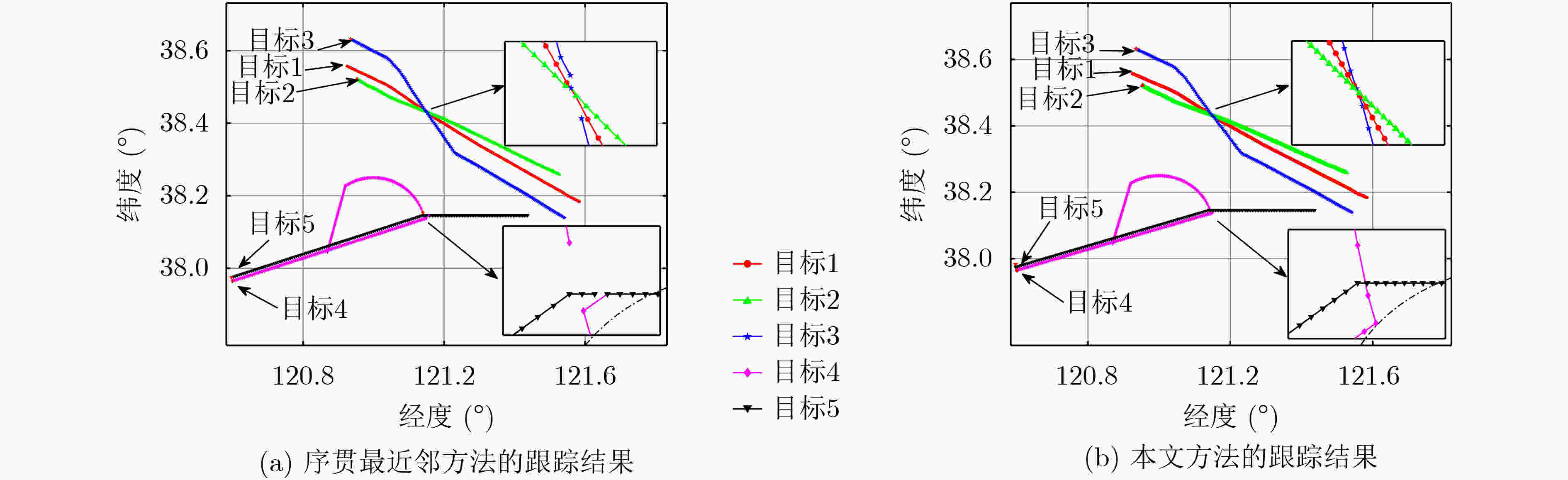
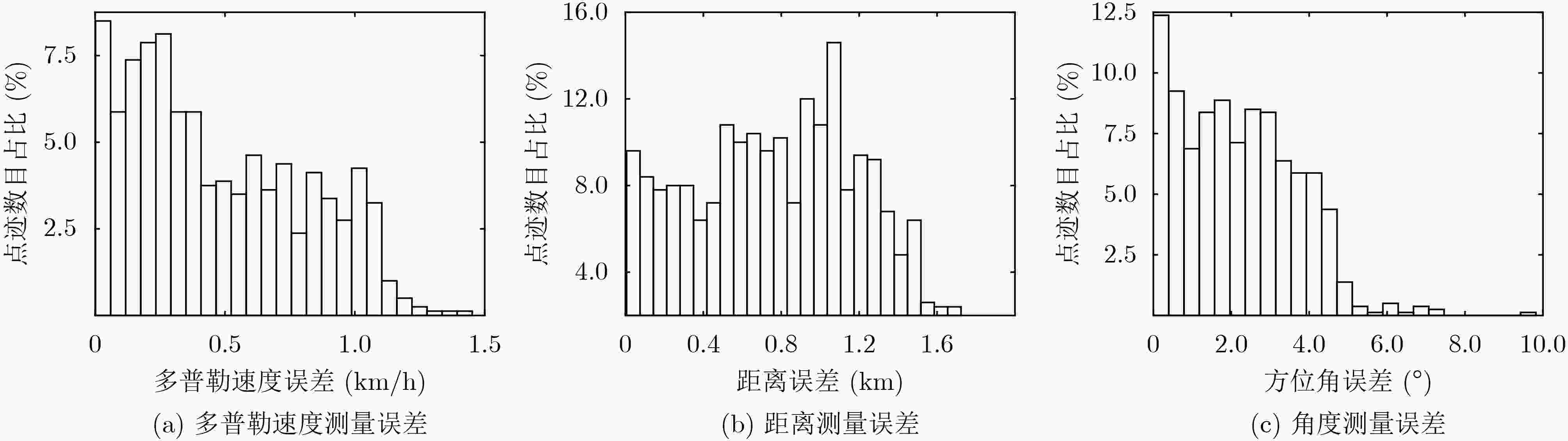


 下载:
下载:
