Maximum Power Point Tracking for Photovoltaic System Based on Improved Multi-Verse Optimization
-
摘要: 在局部遮蔽条件下,光伏阵列的功率输出曲线呈现多峰特性,传统控制算法无法持续准确地跟踪最大功率输出点,该文提出一种基于改进多元宇宙优化(MVO)算法跟踪全局最大功率点的方法(IMVO)。引入螺旋更新和自适应压缩因子,增强了算法的全局搜索能力;改变旅行距离率的更新方式,加快了算法的收敛速度,3方面改进有效提高了算法的寻优能力。仿真结果表明:在均匀光照、局部遮蔽和变光照强度3种条件下,改进多元宇宙优化算法均能持续稳定地跟踪最大功率点,在收敛时间和收敛精度上均有较大提高,由此验证了该算法在最大功率点跟踪控制中的可行性。Abstract: The power output curve of the photovoltaic array exhibits multi-peak characteristics under partial shading conditions, and the traditional control algorithm can not track the maximum power point continuously and accurately. A method for tracking the global maximum power point based on the Improved Multi-Verse Optimization (IMVO) algorithm is proposed. Spiral update and adaptive compression factor are introduced to enhance the algorithm's global search capability. Travelling distance rate update method is changed, and the convergence speed of algorithm is accelerated, so the optimization ability of the algorithm is improved. The simulation results show that the improved Multi-Verse Optimization (MVO) algorithm can track the maximum power point continuously and stably under the three conditions of uniform irradiance, partial shading and variable irradiance, and the convergence time and convergence accuracy are greatly improved, thus the feasibility of the algorithm is verified in the maximum power point tracking control.
-
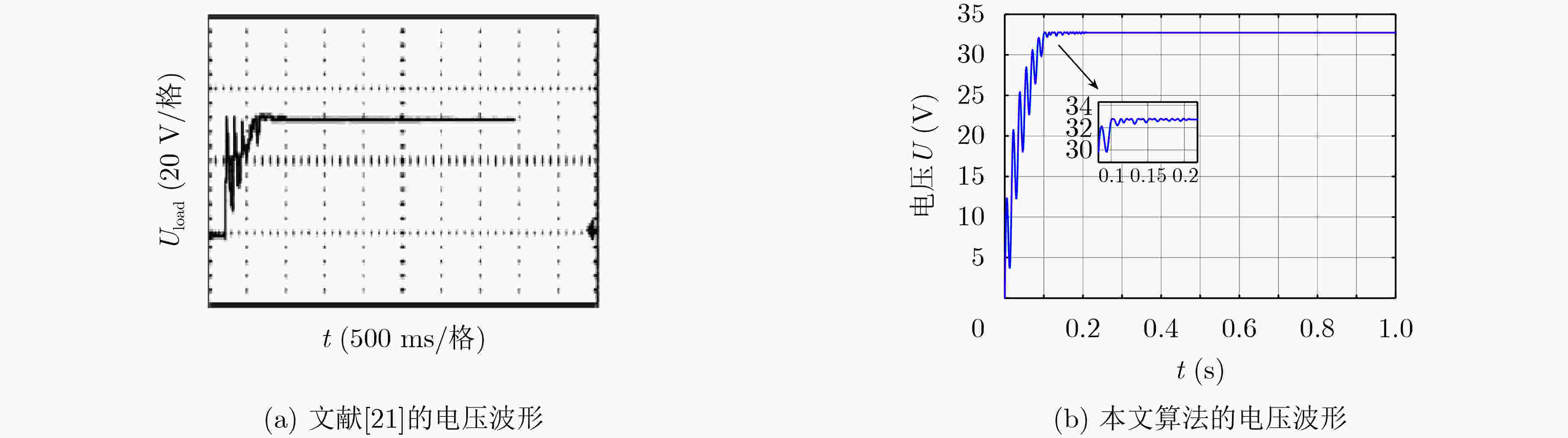
图 8 文献[21]和本文算法电压波形对比
表 1 系统参数设置
参数名称 参数值 短路电流 3.8 A 开路电压 21.1 V 最大功率点电流 3.5 A 最大功率点电压 17.1 V 标准辐照度 1000 W/m2 标准温度 25 °C 表 2 5种算法在各算例下的稳定值和收敛时间统计结果
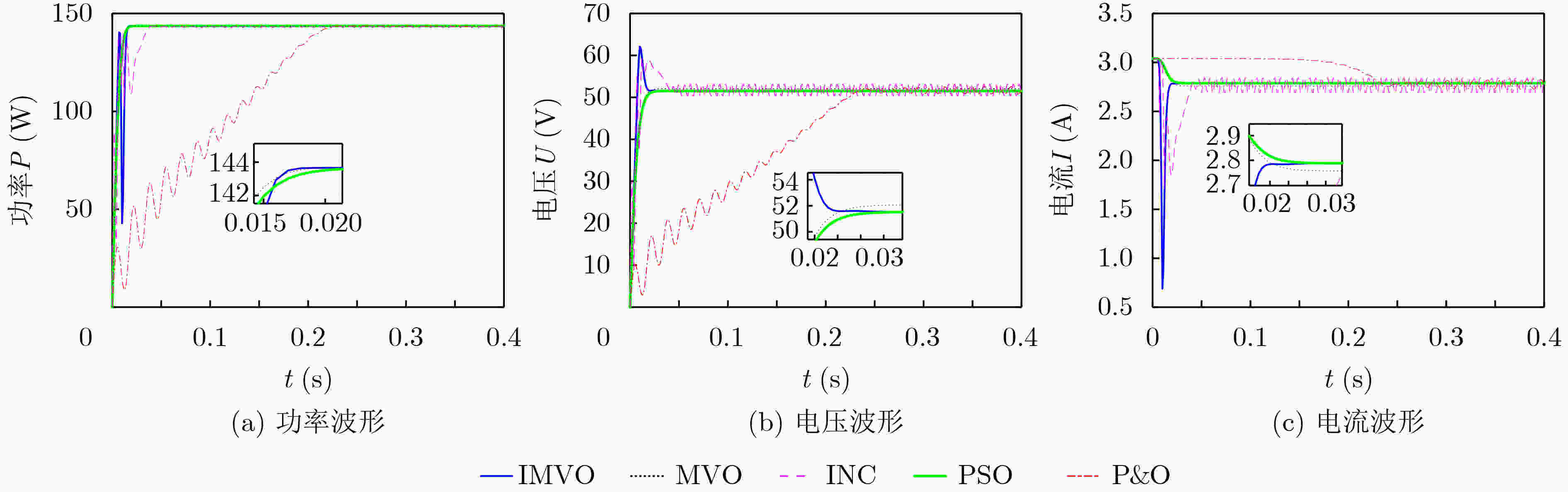
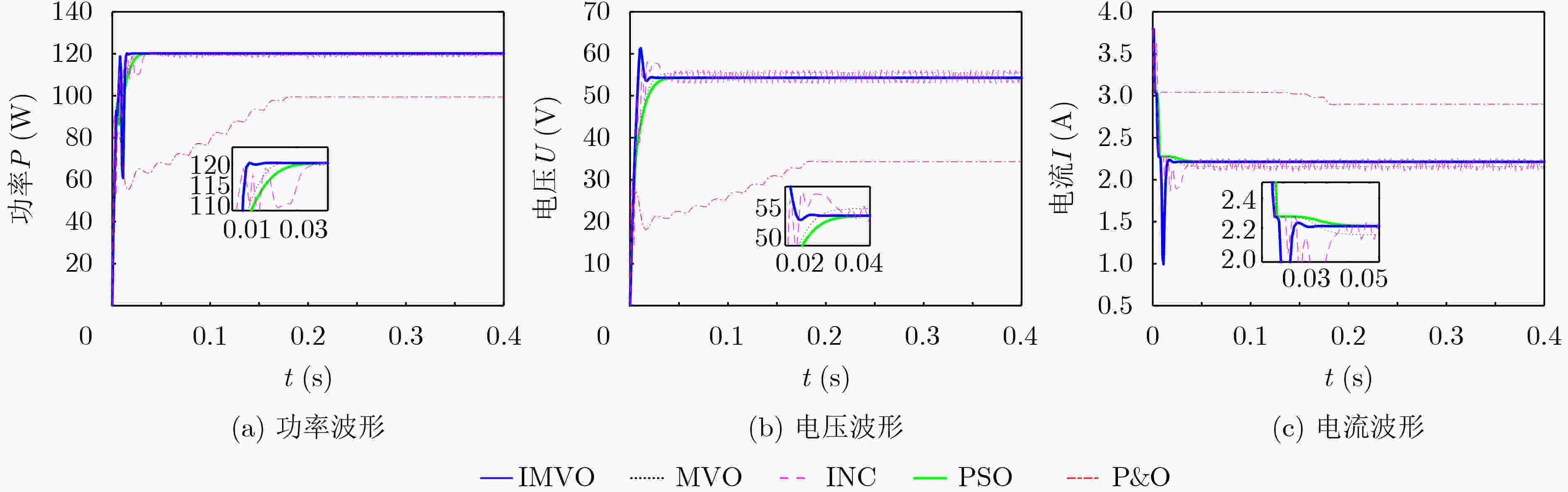
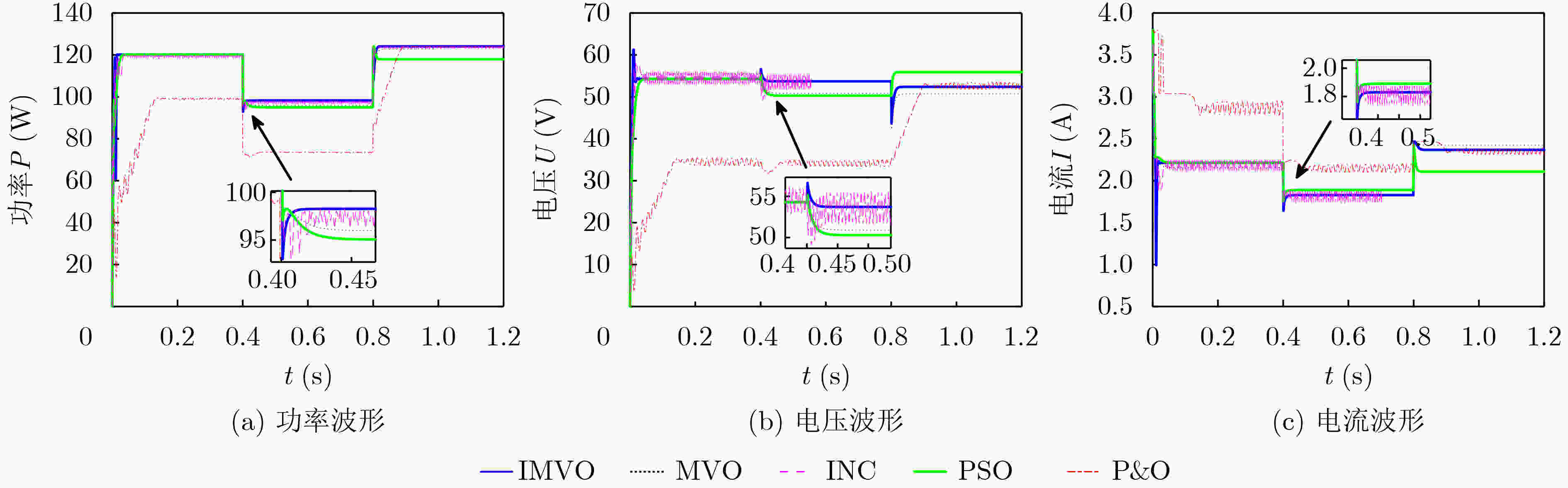
算例 统计量 IMVO MVO PSO INC P&O 均匀光照
(143.7)收敛时间(s) 0.016 0.017 0.021 0.048 0.231 稳定值(W) 143.7 143.5 143.6 143.5 143..5 恒定阴影条件
(120.02)收敛时间(s) 0.015 0.025 0.029 0.042 0.181 稳定值(W) 120.02 120.01 120.01 119.87 99.38 变光照(120.02/
98.27/124.12)收敛时间(s) 0.015/0.421/0.821 0.025/0.443/0.821 0.029/0.451/0.788 0.042/0.431/0.785 0.181/0.452/0.895 稳定值(W) 120.02/98.27/124.12 120.01/97.88/123.65 120.01/95.12/120.02 119.87/96.55/123.48 99.38/70.56/124.01 -
[1] 周孝信, 陈树勇, 鲁宗相, 等. 能源转型中我国新一代电力系统的技术特征[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(7): 1893–1904. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.180067ZHOU Xiaoxin, CHEN Shuyong, LU Zongxiang, et al. Technology features of the new generation power system in China[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(7): 1893–1904. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.180067 [2] SANGWONGWANICH A, YANG Yongheng, and BLAABJERG F. High-performance constant power generation in grid-connected PV systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 31(3): 1822–1825. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2015.2465151 [3] 王立舒, 蒋赛加, 王君, 等. 基于混合策略的光伏MPPT算法优化控制[J]. 太阳能学报, 2016, 37(6): 1396–1402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0096.2016.06.006WANG Lishu, JIANG Saijia, WANG Jun, et al. Optimization control of PV MPPT algorithm based on mixed strategy[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2016, 37(6): 1396–1402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0096.2016.06.006 [4] ZHANG Longlong, HURLEY W G, and WÖLFLE W H. A new approach to achieve maximum power point tracking for PV system with a variable inductor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2011, 26(4): 1031–1037. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2010.2089644 [5] 张商州, 楚冰清, 袁训锋, 等. 光伏阵列模型分析及最大功率点跟踪研究[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2019(10): 114–116. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.1001-9227.2019.10.114ZHANG Shangzhou, CHU Bingqing, YUAN Xunfeng, et al. Photovoltaic array model analysis and maximum power point tracking study[J]. Automation &Instrumentation, 2019(10): 114–116. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.1001-9227.2019.10.114 [6] 蔡小庆, 陈晓芳. 改进型扰动观察法在光伏发电MPPT中的应用[J]. 电子测试, 2019(1): 59–60, 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2019.01.024CAI Xiaoqing and CHEN Xiaofang. Application of improved perturbation observation method in MPPT of photovoltaic[J]. Electronic Test, 2019(1): 59–60, 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2019.01.024 [7] 苏有功, 王大成, 王毅, 等. 基于改进型变步长电导增量法的MPPT控制策略仿真[J]. 自动化技术与应用, 2019, 38(10): 11–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2019.10.003SU Yougong, WANG Dacheng, WANG Yi, et al. Simulation of MPPT control strategy based on improved variable step conductance increment method[J]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 2019, 38(10): 11–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2019.10.003 [8] 贾林壮, 陈侃, 李国杰, 等. 局部阴影条件下光伏阵列MPPT算法研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2014, 35(9): 1614–1621. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2020.04.020JIA Linzhuang, CHEN Kan, LI Guojie, et al. The MPPT method research for PV array under partially shaded conditions[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2014, 35(9): 1614–1621. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2020.04.020 [9] TESHOME D F, LEE C H, LIN Y W, et al. A modified firefly algorithm for photovoltaic maximum power point tracking control under partial shading[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2017, 5(2): 661–671. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2016.2581858 [10] 聂晓华, 王薇. 混沌改进猫群算法及其在光伏MPPT中的应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(22): 6103–6110. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.161022NIE Xiaohua and WANG Wei. Chaos improved cat swarm optimization and its application in the PV MPPT[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(22): 6103–6110. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.161022 [11] 王雨, 胡仁杰. 基于粒子群优化和爬山法的MPPT算法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2014, 35(1): 149–153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0096.2014.01.025WANG Yu and HU Renjie. MPPT algorithm based on particle swarm optimization with hill climbing method[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 149–153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0096.2014.01.025 [12] 胡克用, 胥芳, 艾青林, 等. 自适应遗传算法在光伏发电系统中的应用[J]. 光子学报, 2016, 45(1): 158–166. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20164501.0135001HU Keyong, XU Fang, AI Qinglin, et al. Adaptive genetic algorithm in the application of photovoltaic power generation system[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2016, 45(1): 158–166. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20164501.0135001 [13] MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, and HATAMLOU A. Multi-verse optimizer: A nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27(2): 495–513. doi: 10.1007/s00521-015-1870-7 [14] KUMAR P, GARG S, SINGH A, et al. MVO-based 2-D path planning scheme for providing quality of service in UAV environment[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 1698–1707. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2796243 [15] 刘小龙. 改进多元宇宙算法求解大规模实值优化问题[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1666–1673. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180751LIU Xiaolong. Application of improved multiverse algorithm to large scale optimization problems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1666–1673. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180751 [16] LAI Wenhao, ZHOU Mengran, HU Feng, et al. A new DBSCAN parameters determination method based on improved MVO[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 104085–104095. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931334 [17] MIRJALILI S and LEWIS A. The whale optimization algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 95: 51–67. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 [18] KIM K A, XU C Y, JIN L, et al. A dynamic photovoltaic model incorporating capacitive and reverse-bias characteristics[J]. IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 2013, 3(4): 1334–1341. doi: 10.1109/JPHOTOV.2013.2276483 [19] 邹德旋, 高立群, 段纳. 用修正的差分进化算法确定光电模型参数[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(10): 2521–2525.ZOU Dexuan, GAO Liqun, and DUAN Na. Determining the parameters of photovoltaic modules by a modified differential evolution algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(10): 2521–2525. [20] 刘宜罡, 邹应全, 张晓强, 等. 基于差分进化的光伏MPPT算法改进[J]. 太阳能学报, 2020, 41(6): 264–271.LIU Yigang, ZOU Yingquan, ZHANG Xiaoqiang, et al. An improved photovoltaic MPPT algorithm based on differential evolution algorithm[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 264–271. [21] 石季英, 张登雨, 薛飞, 等. 基于改进灰狼优化-黄金分割混合算法的光伏阵列MPPT方法[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2019, 31(5): 21–26. doi: 10.19635/j.cnki.csu-epsa.000020SHI Jiying, ZHANG Dengyu, XUE Fei, et al. Maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic array based on modified hybrid method of grey wolf optimization and golden-section optimization[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2019, 31(5): 21–26. doi: 10.19635/j.cnki.csu-epsa.000020 -





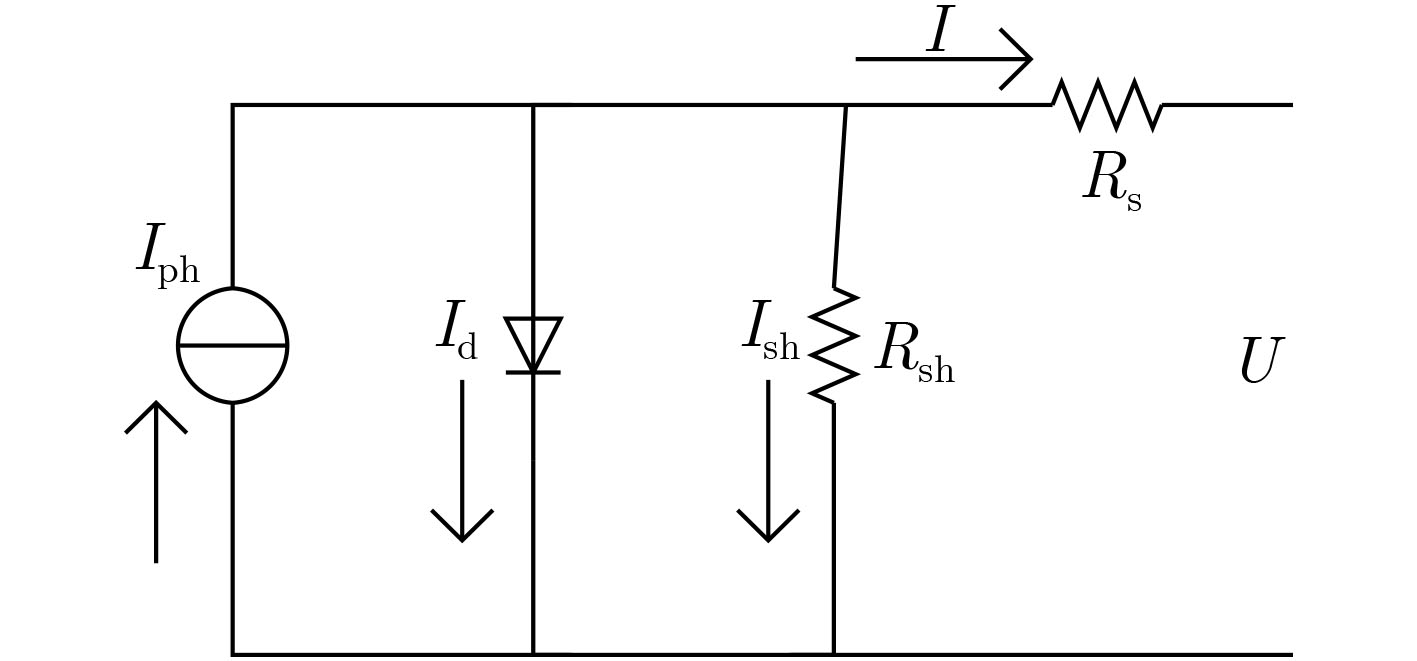
 下载:
下载:
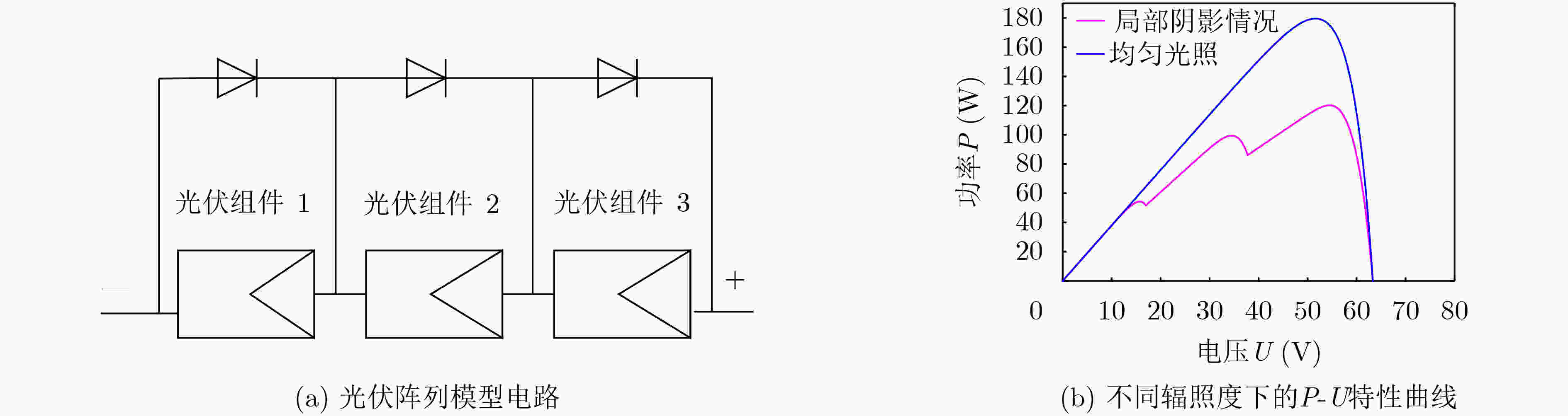
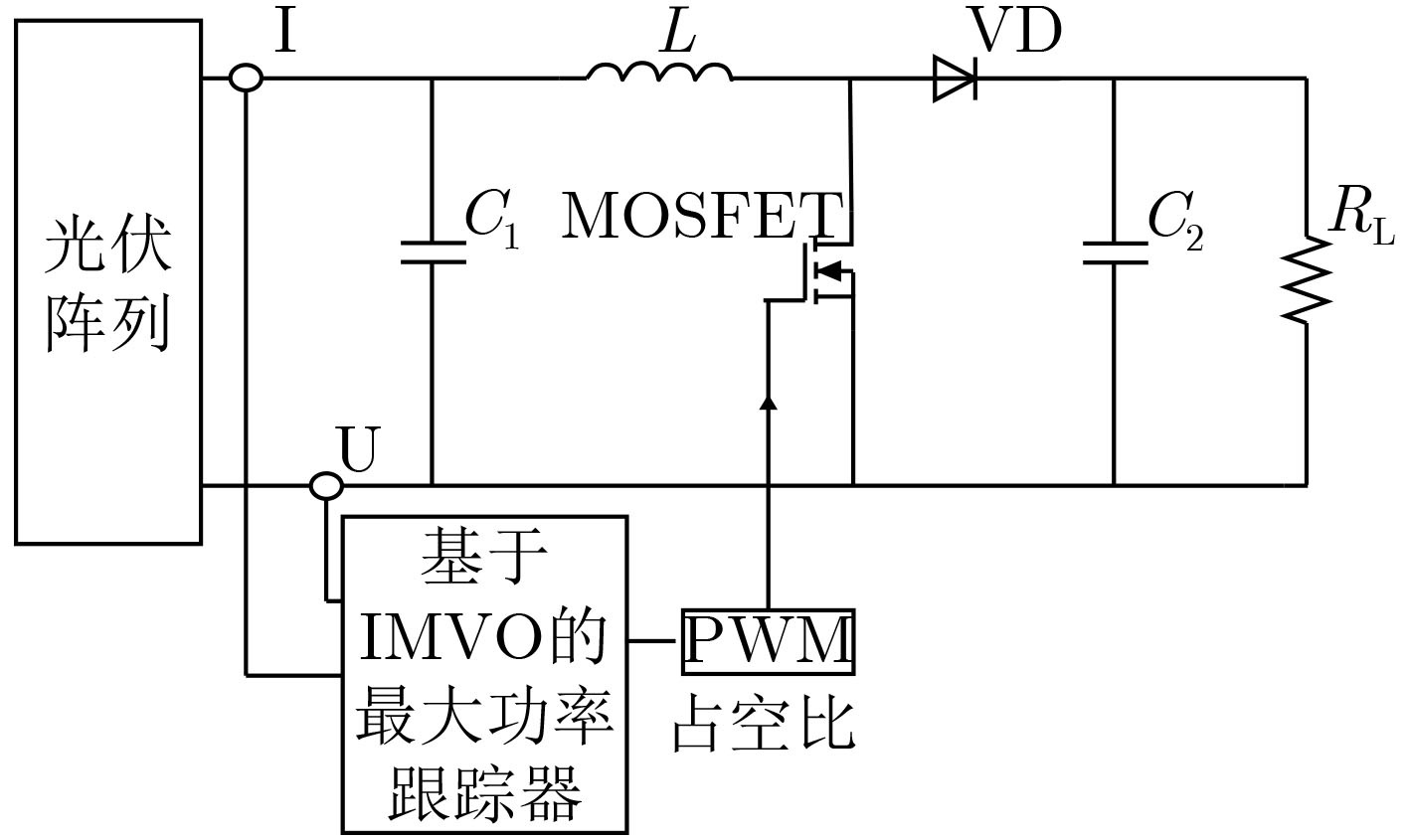



 下载:
下载:
