Speech Enhancement Algorithm Based on Robust Principal Component Analysis with Whitened Spectrogram Rearrangement in Colored Noise
-
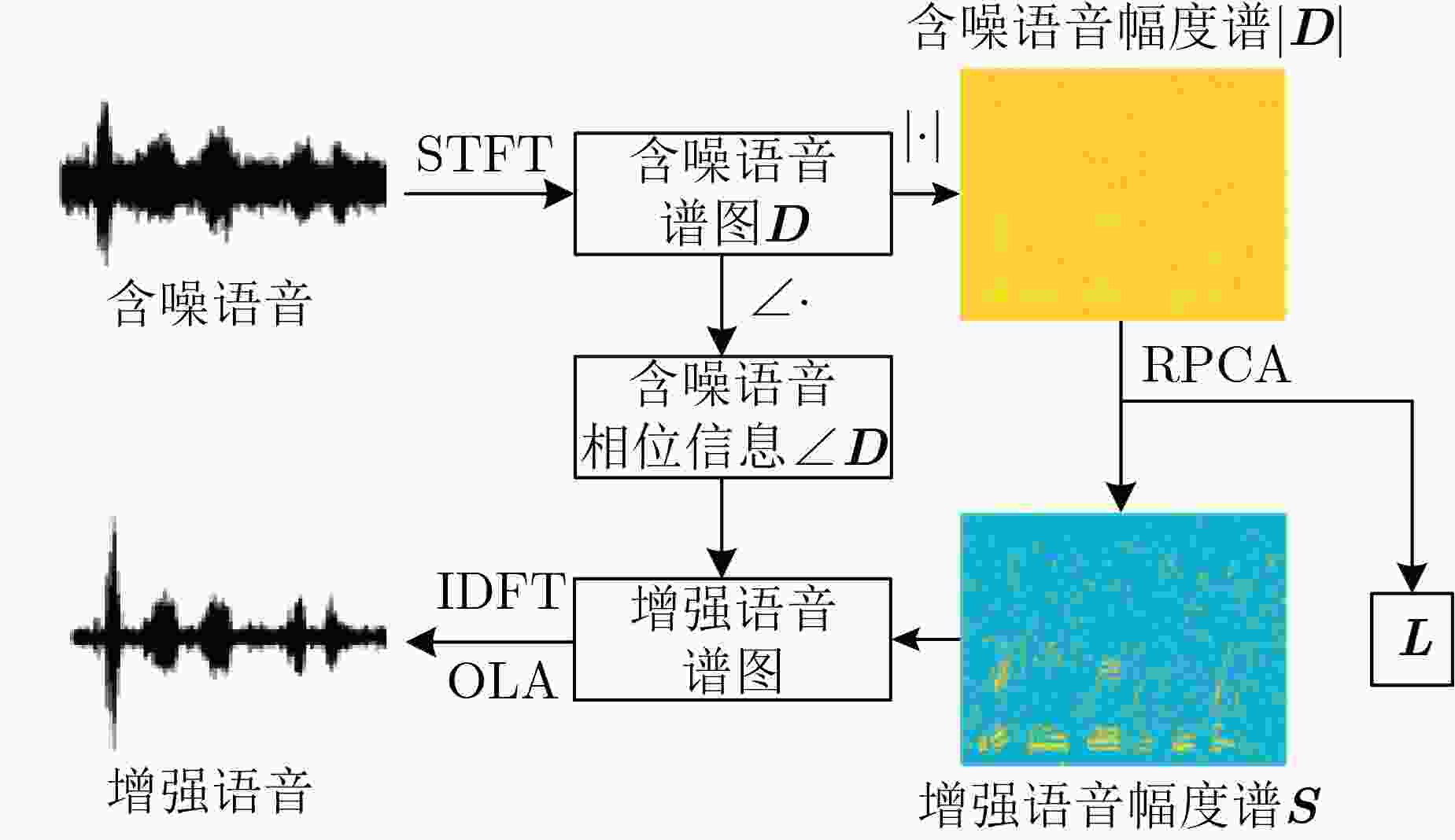
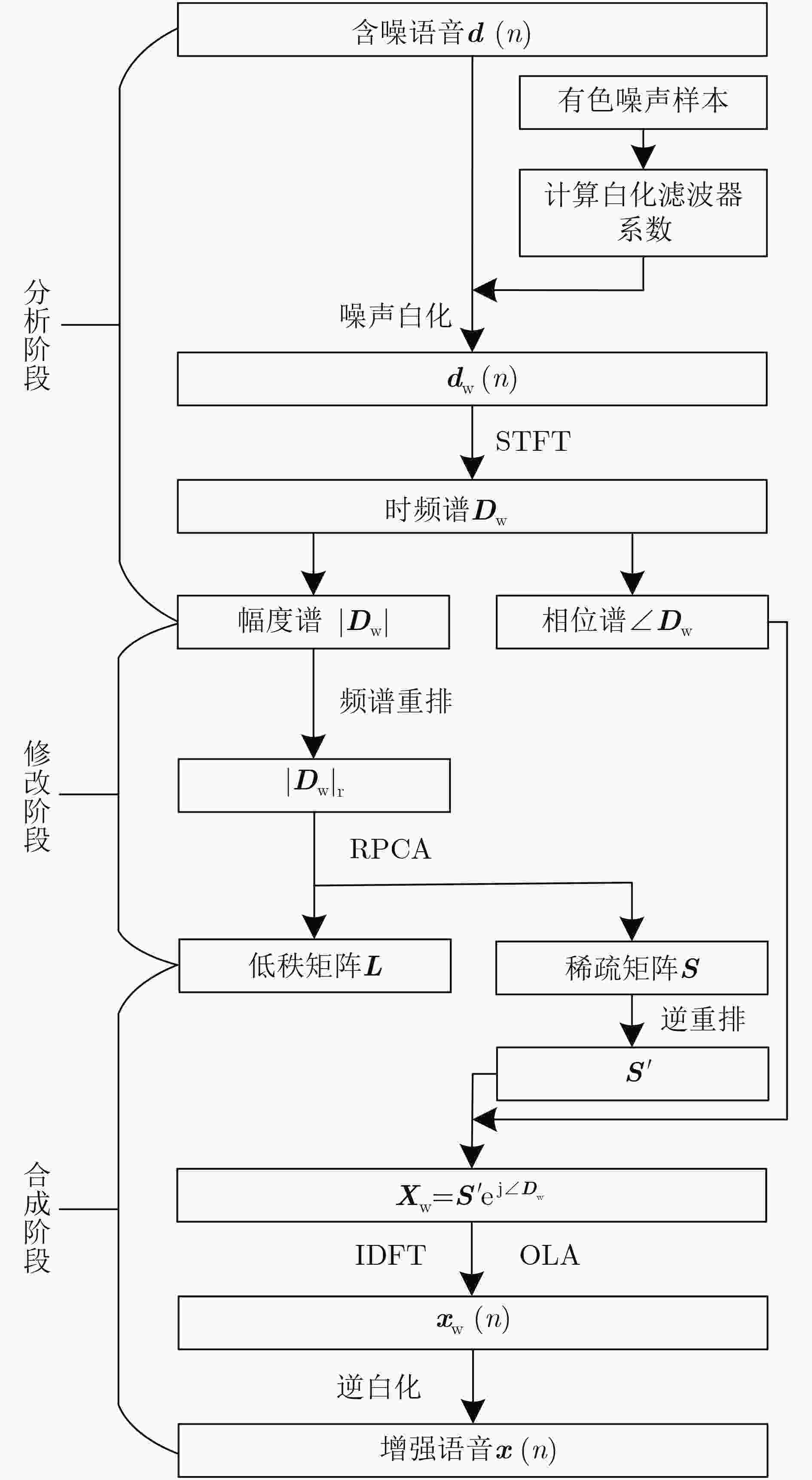
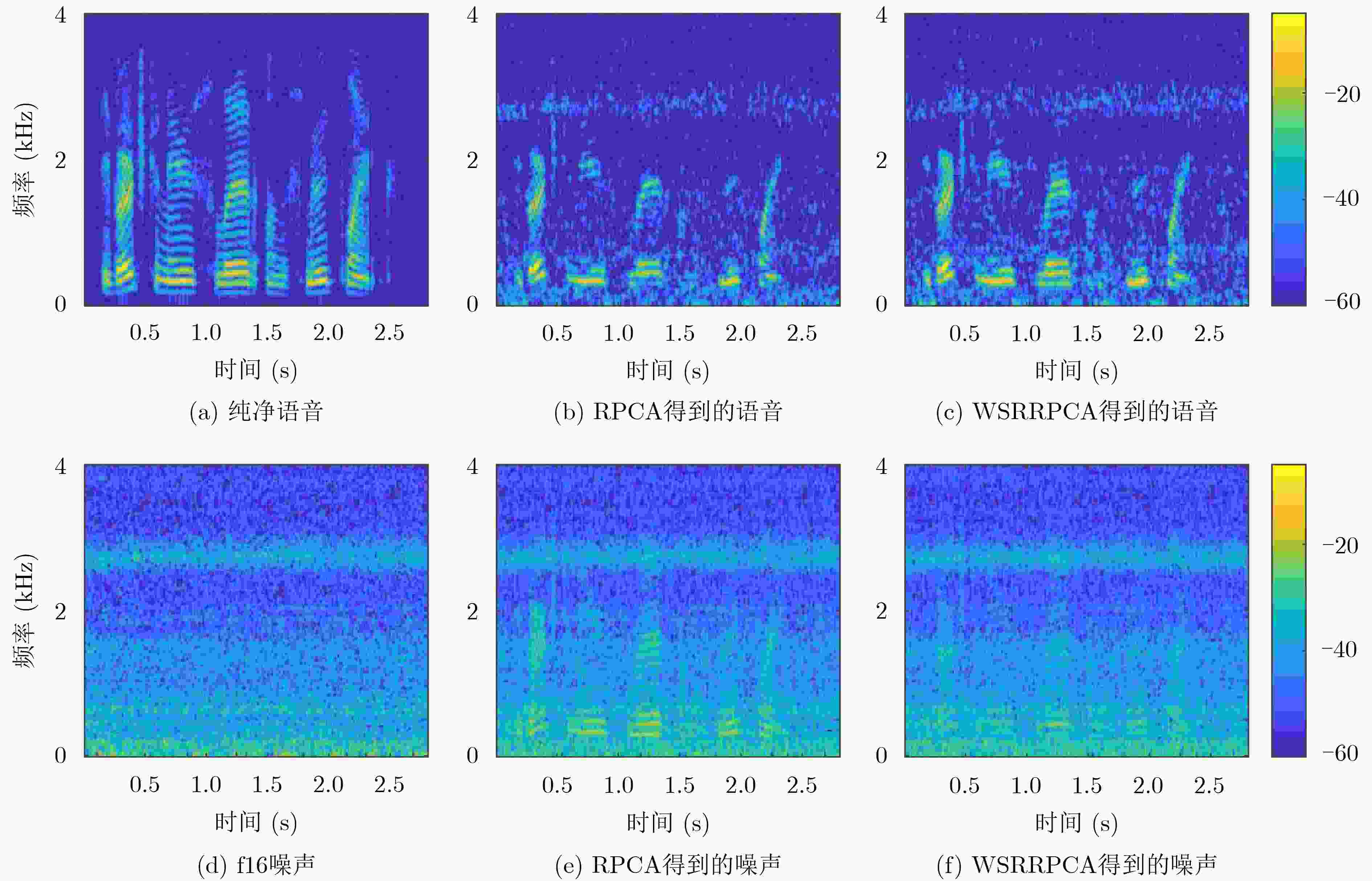
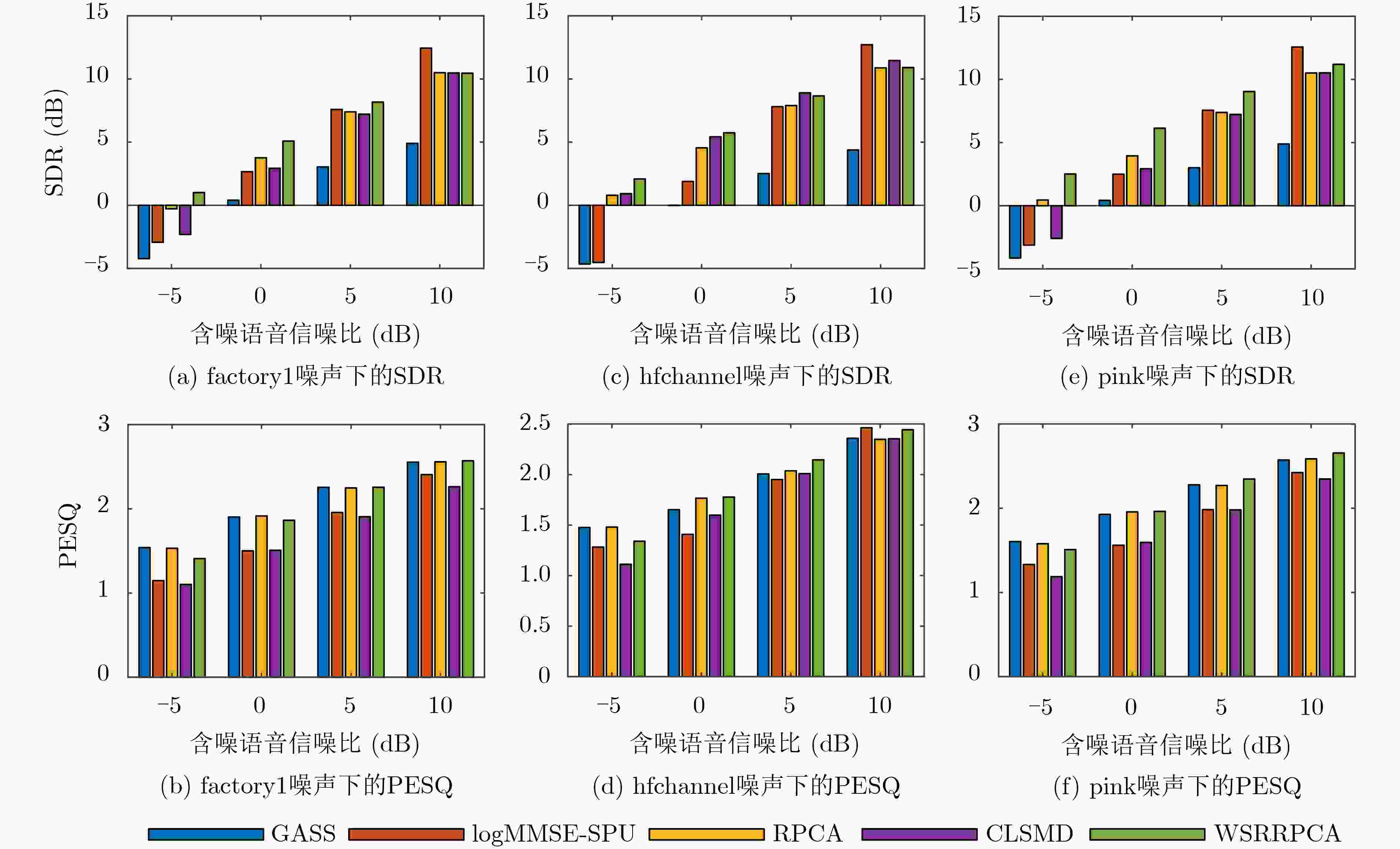
摘要: 基于鲁棒主成分分析(RPCA)的单通道语音增强算法是高斯白噪声环境下语音增强的一种重要处理手段,但其对低秩语音分量处理效果欠佳且无法较好地抑制色噪声。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于白化频谱重排RPCA的改进语音增强算法(WSRRPCA),通过优化噪声白化模型,将色噪声语音增强转换成白噪声语音信号处理,利用频谱重排改进RPCA语音增强处理算法,从而获得色噪声环境下语音信号处理性能的整体提升。仿真实验表明,该算法能够较好地实现色噪声环境下的语音增强,且相对于其他算法具有更佳的噪声抑制和语音质量提升能力。Abstract: The Robust Principal Component Analysis (RPCA) based speech enhancement algorithm plays an important role for single channel speech processing in white Gaussian noise environment, but it has a poor processing effect on low-rank speech components and can not well suppress color noise. In view of this problem, an improved speech algorithm based on Whitening Spectrum Rearrangement RPCA (WSRRPCA) is proposed in this paper, which by optimizing the noise whitening model, color noise speech enhancement is converted into white noise speech signal processing, and spectrum rearrangement is used to improve RPCA speech enhancement processing algorithm to obtain an overall improvement in speech signal processing performance in a colored noise environment. Simulation experiments show that this algorithm can better achieve speech enhancement in a colored noise environment, and has better noise suppression and speech quality improvement capabilities than other algorithms.
-
表 1 不同噪声下多种算法的性能对比
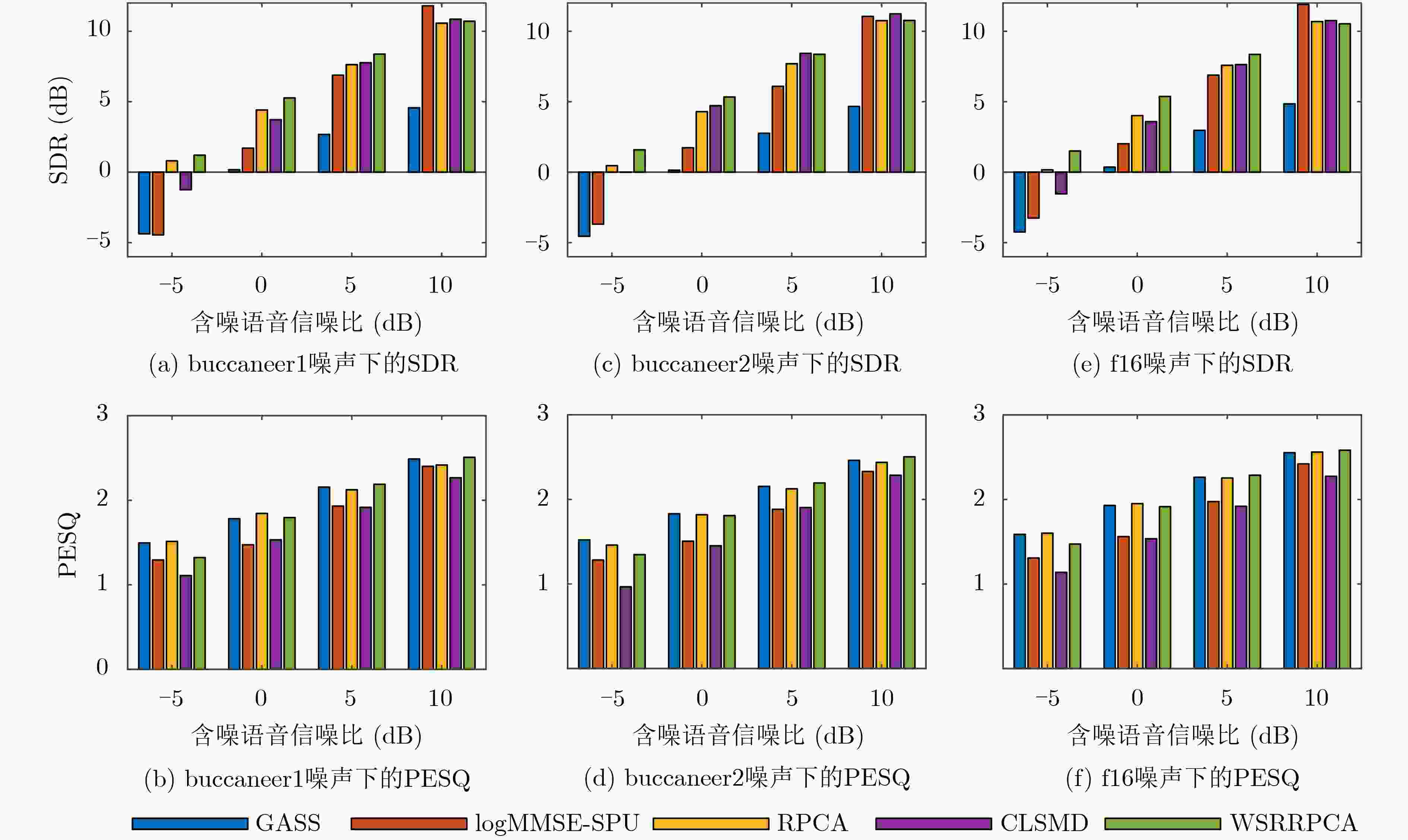
噪声类型 语音增强算法 SDR (dB) PESQ GASS 1.1148 1.5057 logMMSE-SPU –2.9566 0.9222 buccaneer1 RPCA 4.8432 1.6275 CLSMD 5.3583 1.0624 WSRRPCA 6.2530 1.6106 GASS –0.4980 1.5690 logMMSE-SPU –3.0210 1.1192 buccaneer2 RPCA 3.8481 1.7261 CLSMD 4.6147 0.9079 WSRRPCA 4.9989 1.6944 GASS 1.4805 1.7816 logMMSE-SPU –2.3210 1.1926 f16 RPCA 4.3886 1.8461 CLSMD 5.4681 1.1948 WSRRPCA 6.2030 1.8751 GASS 0.3133 1.4930 logMMSE-SPU –2.7692 1.1512 factory1 RPCA 4.0886 1.8264 CLSMD 4.2691 1.2895 WSRRPCA 5.1138 1.7905 GASS 1.4168 1.3519 logMMSE-SPU –3.0150 1.0336 hfchannel RPCA 5.1769 1.6378 CLSMD 6.7771 1.1689 WSRRPCA 6.1418 1.6441 GASS 1.0008 1.6570 logMMSE-SPU –1.4077 1.2425 pink RPCA 4.0835 1.8472 CLSMD 3.9805 1.4122 WSRRPCA 7.0699 1.9045 -
[1] LOIZOU P C. Speech Enhancement: Theory and Practice[M]. 2nd ed. London: CRC Press, 2013: 1–2. [2] BOLL S. Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1979, 27(2): 113–120. doi: 10.1109/tassp.1979.1163209 [3] EPHRAIM Y and MALAH D. Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1985, 33(2): 443–445. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164550 [4] SCALART P and FILHO J V. Speech enhancement based on a priori signal to noise estimation[C]. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Atlanta, 1996: 629–632. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1996.543199. [5] EPHRAIM Y and VAN TREES G L. A signal subspace approach for speech enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 1995, 3(4): 251–266. doi: 10.1109/89.397090 [6] YI Hu and LOIZOU P C. A generalized subspace approach for enhancing speech corrupted by colored noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 2003, 11(4): 334–341. doi: 10.1109/TSA.2003.814458 [7] SUN Chengli, ZHANG Qin, WANG Jian, et al. Noise reduction based on robust principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 2014, 10(10): 4403–4410. doi: 10.12733/jcis10408 [8] HUANG Jianjun, ZHANG Xiongwei, ZHANG Yafei, et al. Speech denoising via low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition[J]. ETRI Journal, 2014, 36(1): 167–170. doi: 10.4218/etrij.14.0213.0033 [9] MAVADDATY S, AHADI S M, and SEYEDIN S. A novel speech enhancement method by learnable sparse and low-rank decomposition and domain adaptation[J]. Speech Communication, 2016, 76: 42–60. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2015.11.003 [10] SUN Pengfei and QIN Jun. Low-rank and sparsity analysis applied to speech enhancement via online estimated dictionary[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1862–1866. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2016.2627029 [11] LUO Yongjiang and MAO Yu. Single-channel speech enhancement based on multi-band spectrogram-rearranged RPCA[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(7): 415–417. doi: 10.1049/el.2018.8131 [12] CANDÈS E J, LI Xiaodong, MA Yi, et al. Robust principal component analysis?[J]. Journal of the ACM, 2011, 58(3): 11. doi: 10.1145/1970392.1970395 [13] NAZIH M, MINAOUI K, and COMON P. Using the proximal gradient and the accelerated proximal gradient as a canonical polyadic tensor decomposition algorithms in difficult situations[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 171: 107472. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107472 [14] FENG Peihua, LING B W K, LEI Ruisheng, et al. Singular spectral analysis-based denoising without computing singular values via augmented Lagrange multiplier algorithm[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2019, 13(2): 149–156. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2018.5086 [15] LEI Yunwen and ZHOU Dingxuan. Analysis of singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2019, 25(6): 2957–2972. doi: 10.1007/s00041-019-09688-8 [16] JARAMILLO A E, NIELSEN J K, CHRISTENSEN M G, et al. A study on how pre-whitening influences fundamental frequency estimation[C]. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, England, 2019: 6495–6499. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683653. [17] VASEGHI S V. Advanced Digital Signal Processing and Noise Reduction[M]. 4th ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008: 229–230. [18] SMITH III J O. Spectral Audio Signal Processing[M]. W3K Publishing, USA, 2011: 298–301. [19] 张明, 刘祥楼, 姜峥嵘. 基于LPC的语音信号预测仿真分析[J]. 光学仪器, 2015, 37(1): 71–74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5630.2015.01.015ZHANG Ming, LIU Xianglou, and JIANG Zhengrong. Simulation analysis of speech signal prediction based on LPC[J]. Optical Instruments, 2015, 37(1): 71–74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5630.2015.01.015 [20] KAPRALOV M. Sparse Fourier transform in any constant dimension with nearly-optimal sample complexity in sublinear time[C]. The Forty-eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Virtual Event, Italy, 2016: 264–277. doi: 10.1145/2897518.2897650. [21] WANG D L and LIM J S. The unimportance of phase in speech enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1982, 30(4): 679–681. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1982.1163920 [22] VINCENT E, GRIBONVAL R, and FEVOTTE C. Performance measurement in blind audio source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2006, 14(4): 1462–1469. doi: 10.1109/TSA.2005.858005 [23] RAM R and MOHANTY M N. Use of radial basis function network with discrete wavelet transform for speech enhancement[J]. International Journal of Computational Vision and Robotics, 2019, 9(2): 207–223. doi: 10.1504/IJCVR.2019.10019996 [24] SUN Chengli, ZHU Qi, and WAN Minghua. A novel speech enhancement method based on constrained low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition[J]. Speech Communication, 2014, 60: 44–55. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2014.03.002 [25] LU Yang and LOIZOU P C. A geometric approach to spectral subtraction[J]. Speech Communication, 2008, 50(6): 453–466. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2008.01.003 [26] COHEN I. Optimal speech enhancement under signal presence uncertainty using log-spectral amplitude estimator[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2002, 9(4): 113–116. doi: 10.1109/97.1001645 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
