Analysis of RF Interference Characteristics of Broadcasting Satellite TV Receivers to SMAP Satellite L-Band Microwave Radiometer
-
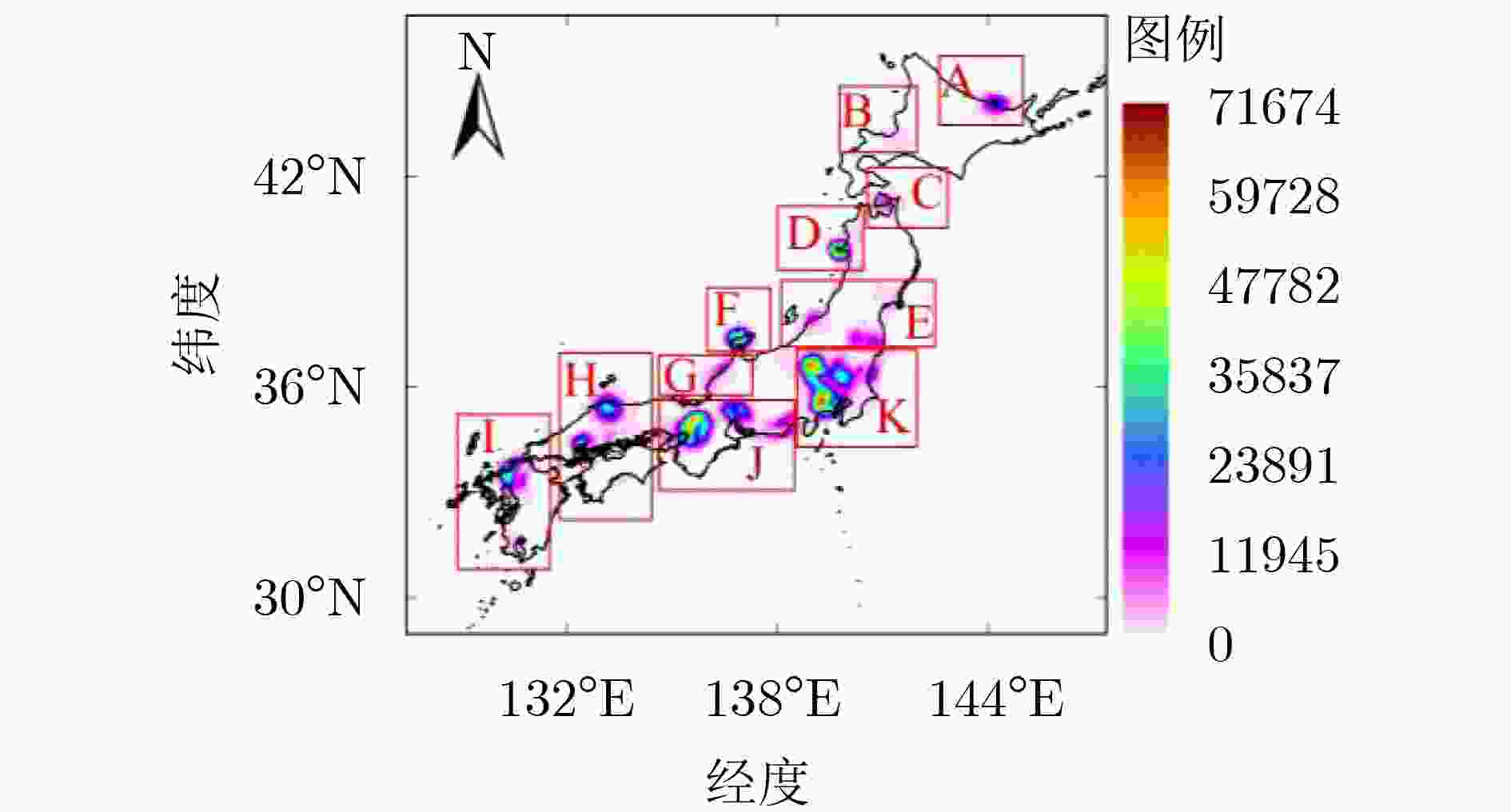
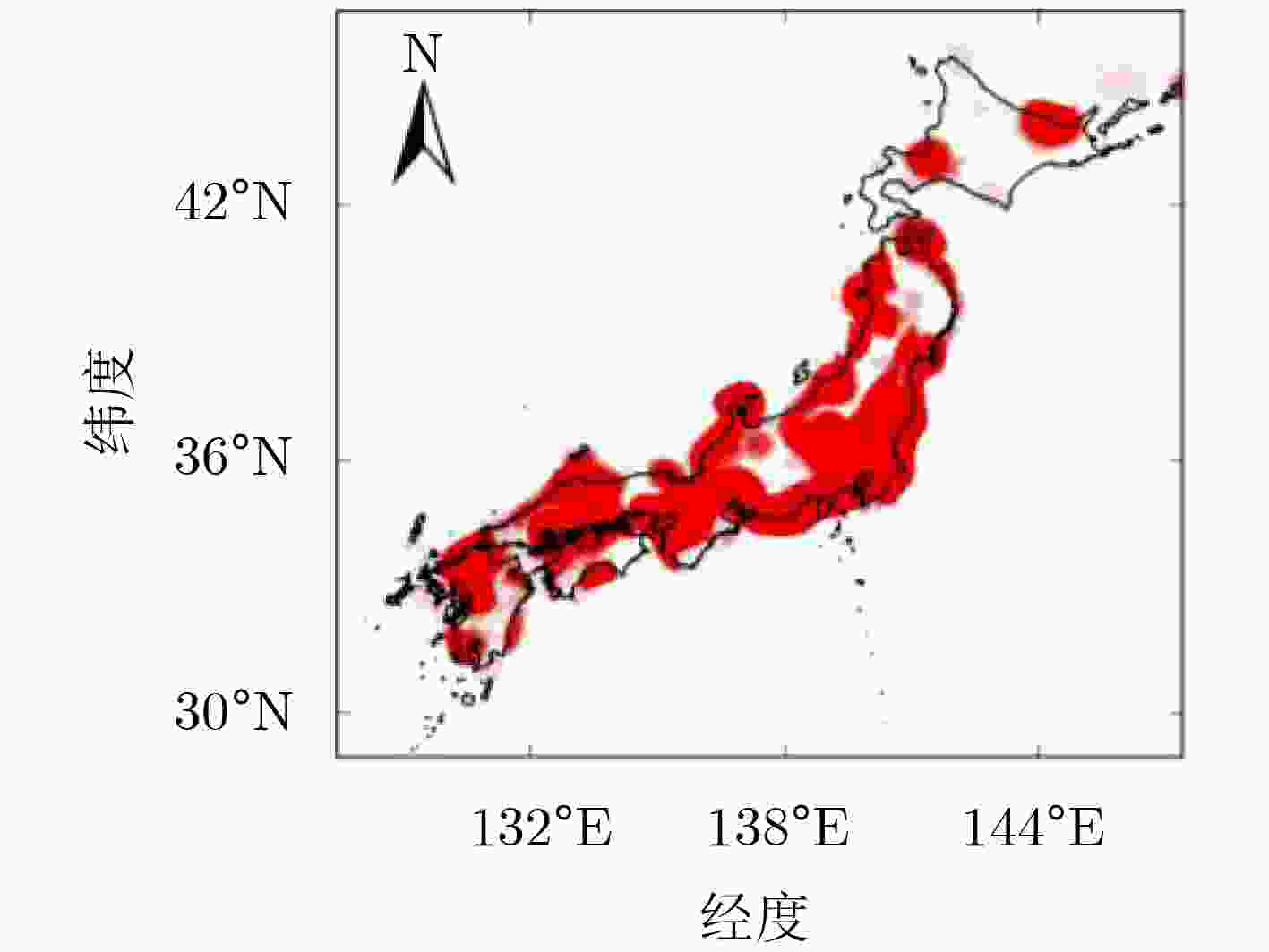
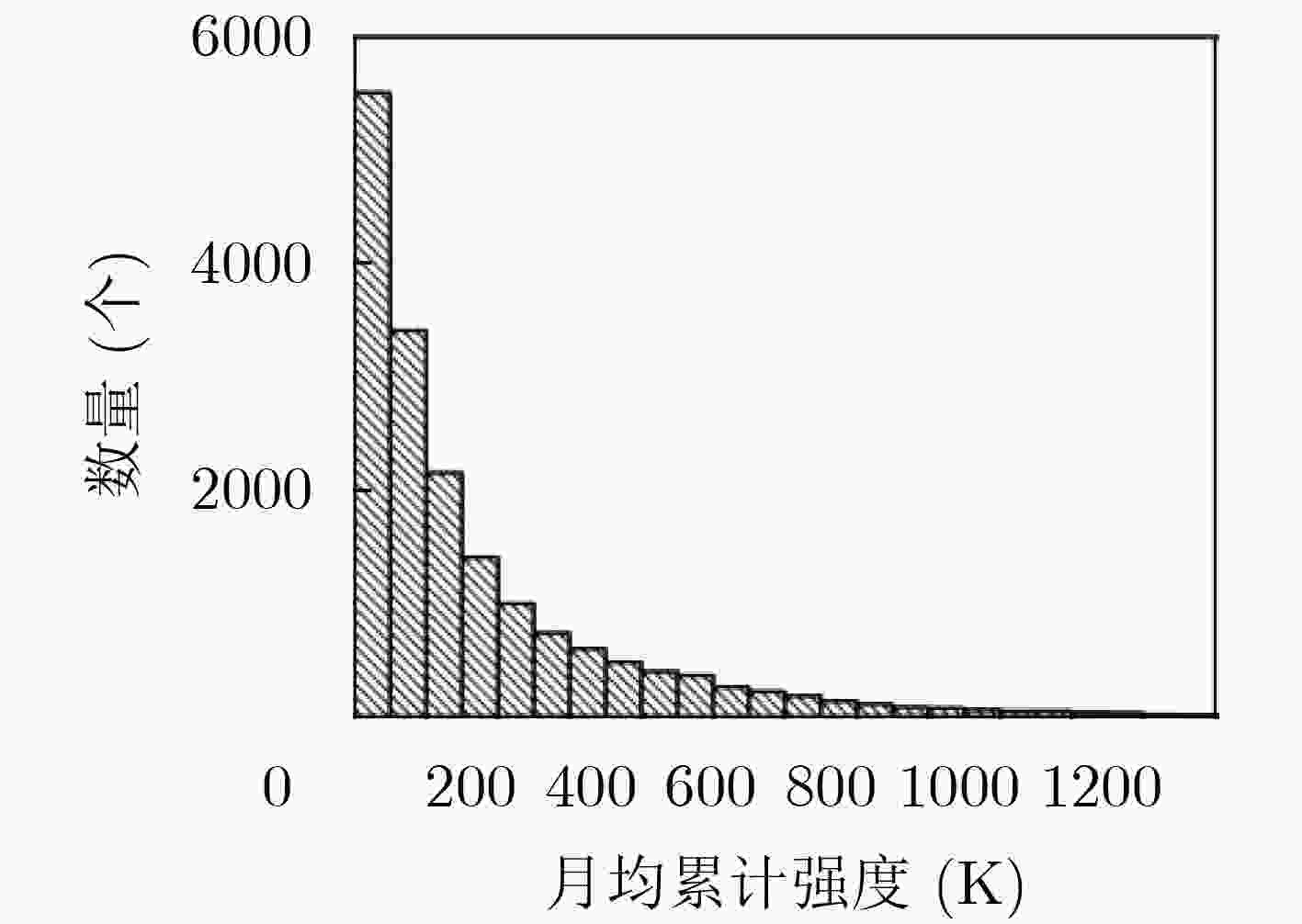
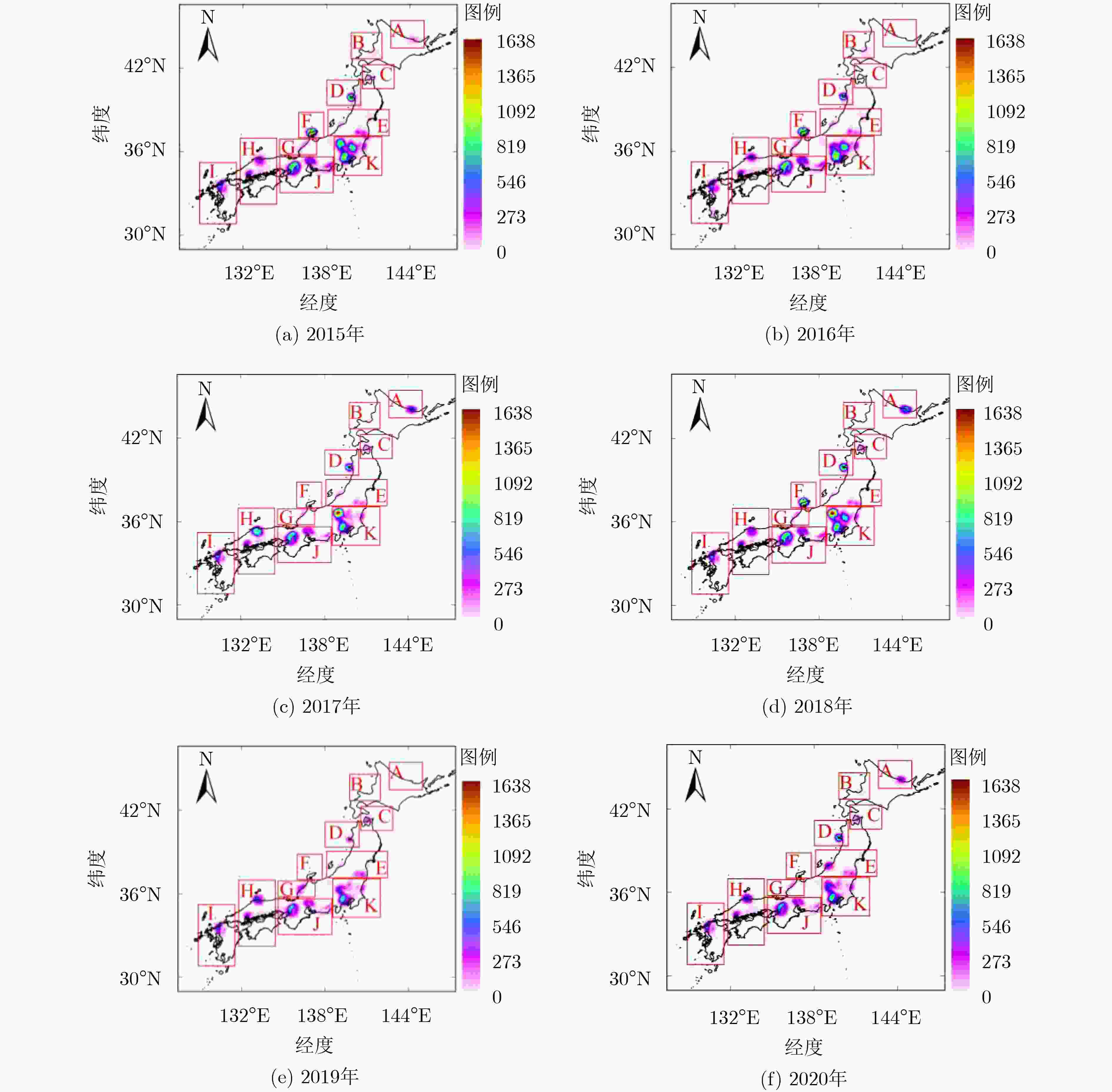
摘要: 该文通过融合SMAP卫星L波段交叉极化亮温,建立基于密度和强度空间分布特征的多重迭代聚类射频干扰(RFI)检测识别算法。分析并提取日本典型RFI源(广播卫星电视接收机)密度和累积强度的时空分布和变化特征。电视接收机作为典型的RFI源,主要分布在日本城市化水平和范围均相对较大的区域(条状或面状),局部区域内分布点圆状RFI(可能为微波辐射基站),导致局地化RFI累积强度具有很高的水平。同时,在日本其他区域也检测到独立分布的点圆状RFI,干扰强度和范围相对局限。2018年开始,日本RFI整体分布范围和强度能级呈下降趋势。典型RFI源特征分析对于我国建立RFI检测、识别及抑制模型具有重要意义。Abstract: Based on the fusion of SMAP satellite L-band cross-polarized brightness temperature, a multi-iteration clustering Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) detection and recognition algorithm based on its spatial distribution of density and intensity is established, and the spatial and temporal distribution and variation characteristics of the density and cumulative intensity of typical Japanese RFI sources (broadcast satellite TV receivers) are analyzed and extracted. As a typical RFI source, TV receivers are mainly distributed in areas with relatively large urbanization level and range (stripes or planes), with dotted RFI sources (possibly microwave radiation base stations) distributed in local areas, resulting in local areas with high RFI levels. In other areas where the urbanization level and scope are relatively small, the dot-round RFI sources are also detected, but the interference intensity and range are relatively limited. Beginning in 2018, the overall RFI distribution range and intensity level showed a downward trend. This work is of great significance to the establishment of RFI detection, identification and suppression models in China.
-
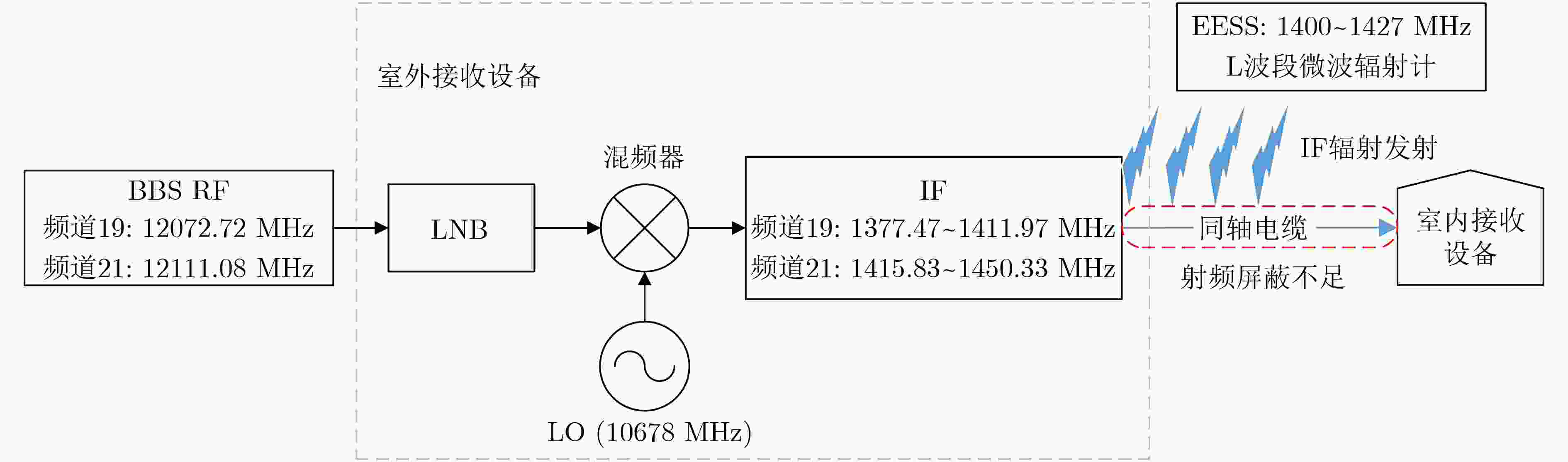
表 1 日本Ku波段BBS新增频道号与指派频率的对应关系及RF转换IF后对应的IF中心频率及频率范围[20]
BBS
频道号指派频率(MHz) 转换IF中心频率(MHz) 转换IF频率范围(MHz) 17 12034.36 1356.36 1339.11~1373.61 19 12072.72 1394.72 1377.47~1411.97 21 12111.08 1433.08 1415.83~1450.33 23 12149.44 1471.44 1454.19~1488.69 注:本振LO频率:10678 MHz;带宽BW:34.5 MHz 表 2 2015年4月至2020年6月RFI检测识别结果统计表
年份 2015年 2016年 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 合计 有效数据天数(天) 274 366 365 365 332 181 1883 有效数据轨道数(个) 669 900 913 905 817 457 4661 平均每月数据个数(个) 74 75 76 75 74 76 75 检测为RFI疑似样本数(个) 111294 144865 147848 134979 114354 56745 710085 识别为符合RFI特征样本数(个) 102072 133798 135805 123103 104097 51759 650634 未识别为符合RFI特征样本数(个) 9222 11067 12043 11876 10257 4986 59451 疑似样本识别率P(%) 91.71 92.36 91.85 91.20 91.03 91.21 91.63 -
[1] DINNAT E P, LE VINE D M, BOUTIN J, et al. Satellite sea surface salinity: Evaluation of products and impact of retrieval algorithms[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 7936–7939. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8899065. [2] FORE A, YUEH S, TANG Wenqing, et al. The JPL SMAP sea surface salinity algorithm[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 7920–7923. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898359. [3] OLIVA R, DAGANZO E, KERR Y H, et al. SMOS radio frequency interference scenario: Status and actions taken to improve the RFI environment in the 1400–1427-MHz passive band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(5): 1427–1439. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2182775 [4] LE VINE D M, DE MATTHAEIS P, RUF C S, et al. Aquarius RFI detection and mitigation algorithm: Assessment and examples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4574–4584. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282595 [5] MISRA S, JOHNSON J, AKSOY M, et al. SMAP RFI mitigation algorithm performance characterization using airborne high-rate direct-sampled SMAPVEX 2012 data[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 41–44. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2013.6721087. [6] MOHAMMED P N, AKSOY M, PIEPMEIER J R, et al. SMAP L-band microwave radiometer: RFI mitigation prelaunch analysis and first year on-orbit observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6035–6047. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2580459 [7] CAMPS A J, CORBELLA I, TORRES F, et al. RF interference analysis in aperture synthesis interferometric radiometers: Application to L-band MIRAS instrument[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 942–950. doi: 10.1109/36.841976 [8] CAMPS A, GOURRION J, TARONGI J M, et al. Radio-frequency interference detection and mitigation algorithms for synthetic aperture radiometers[J]. Algorithms, 2011, 4(3): 155–182. doi: 10.3390/a4030155 [9] PARK J, JOHNSON J T, MAJUREC N, et al. Airborne L-Band radio frequency interference observations from the SMAPVEX08 campaign and associated flights[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(9): 3359–3370. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2107560 [10] SOLDO Y, DE MATTHAEIS P, and LE VINE D M. L-band RFI in Japan[C].2016 Radio Frequency Interference (RFI), Socorro, USA, 2016: 111–114. doi: 10.1109/RFINT.2016.7833542. [11] LE VINE D M, JOHNSON J T, and PIEPMEIER J. RFI and remote sensing of the earth from space[C]. 2016 Radio Frequency Interference (RFI), Socorro, USA, 2016: 49–54. doi: 10.1109/RFINT.2016.7833530. [12] SOLDO Y, LE VINE D M, DE MATTHAEIS P, et al. L-Band RFI detected by SMOS and Aquarius[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 4220–4235. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2690406 [13] MIRANDA J J, VALL-LLOSSERA M, CAMPS A, et al. Sea state effect on the sea surface emissivity at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(10): 2307–2315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817190 [14] KERR Y H, WALDTEUFEL P, WIGNERON J P, et al. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(8): 1729–1735. doi: 10.1109/36.942551 [15] MISRA S and RUF C S. Detection of radio-frequency interference for the Aquarius radiometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3123–3128. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.920371 [16] PIEPMEIER J R, JOHNSON J T, MOHAMMED P N, et al. Radio-frequency interference mitigation for the soil moisture active passive microwave radiometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 761–775. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281266 [17] 王新新, 王祥, 韩震, 等. 基于L波段Stokes参数遥感数据射频干扰检测及特性分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(10): 2342–2348. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141577WANG Xinxin, WANG Xiang, HAN Zhen, et al. Radio frequency interference detection and characteristic analysis based on the L band Stokes parameters remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(10): 2342–2348. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141577 [18] PENG Jinzheng, MISRA S, CHAN S, et al. SMAP radiometer brightness temperature calibration for the L1B_TB, L1C_TB (Version 4), and L1C_TB_E (Version 2) data products[EB/OL]. https://nsidc.org/sites/nsidc.org/files/technical-references/SMAP_L1_Assessment%20Report%2020180601_v9.pdf.2020.2. [19] QUEROL J, PEREZ A, and CAMPS A. A review of RFI mitigation techniques in microwave radiometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 3042. doi: 10.3390/rs11243042 [20] DAGANZO E, OLIVA R, RICHAUME P, et al. SMOS RFI experience in the 1400–1427 MHz passive band: Case of extended interference caused by broadcasting satellite home-TV receivers[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 4455–4458. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8897873. [21] AKSOY M. Radio frequency interference characterization and detection in L-band microwave radiometry[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], The Ohio State University, 2015. [22] PIEPMEIER J R, FOCARDI P, HORGAN K A, et al. SMAP L-band microwave radiometer: Instrument design and first year on orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(4): 1954–1966. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2631978 [23] SOLDO Y, LE VINE D M, BRINGER A, et al. Recent advances in Smap RFI processing[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 313–315. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8518891. [24] SOLDO Y, LE VINE D M, BRINGER A, et al. Location of radio-frequency interference sources using the SMAP L-band radiometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6854–6866. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2844127 [25] 姜涛, 赵凯, 万祥坤. L波段微波辐射计周期脉冲式干扰时域检测方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(7): 1539–1545. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170954JIANG Tao, ZHAO Kai, and WAN Xiangkun. Research on detection methods to periodic pulsed interference for L band microwave radiometer in time domain[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(7): 1539–1545. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170954 [26] KRISTENSEN S S, BALLING J E, SKOU N, et al. RFI detection in SMOS data using 3rd and 4th Stokes parameters[C]. The 12th Specialist Meeting on Microwave Radiometry and Remote Sensing of the Environment (MicroRad), Rome, Italy, 2012: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/MicroRad.2012.6185254. [27] WANG Xinxin, WANG Xiang, FAN Jianchao, et al. Automatic detection and identification of RFI sources for SMAP satellite polarized data based on IDL[C]. The 10th International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), Marrakesh, Morocco, 2019: 76–80. doi: 10.1109/ICICIP47338.2019.9012190. [28] 马廷. 夜光遥感大数据视角下的中国城市化时空特征[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(1): 59–67. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2019.180361MA Ting. Spatiotemporal characteristics of urbanization in china from the perspective of remotely sensed big data of nighttime light[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2019, 21(1): 59–67. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2019.180361 [29] JIN Rong, LI Qingxia, and LIU Hang. A subspace algorithm to mitigate energy unknown RFI for synthetic aperture interferometric radiometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(1): 227–237. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2936005 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
