A Low-Dose CT Image Denoising Method Based on Generative Adversarial Network and Noise Level Estimation
-
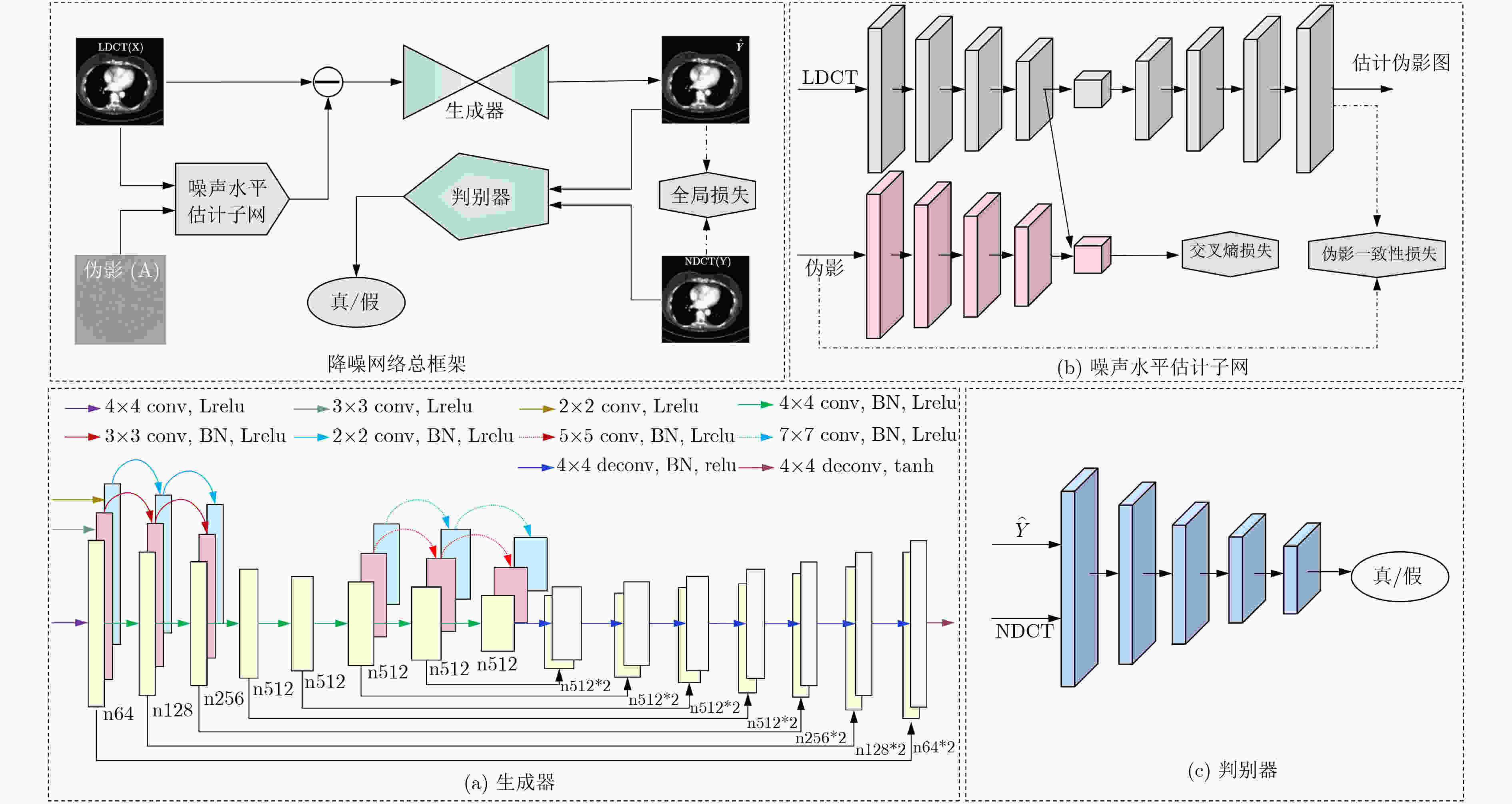
摘要: 生成对抗网络(GAN)用于低剂量CT(LDCT)图像降噪具有一定的性能优势,成为近年CT图像降噪领域新的研究热点。不同剂量的LDCT图像中噪声和伪影分布的强度发生变化时,GAN网络降噪性能不稳定,网络泛化能力较差。为了克服这一缺陷,该文首先设计了一个编解码结构的噪声水平估计子网,用于生成不同剂量LDCT图像对应的噪声图,并用原始输入图像与之相减来初步抑制噪声;其次,在主干降噪网络中,采用GAN框架,并将生成器设计为多路编码的U-Net结构,通过博弈对抗实现网络结构优化,进一步抑制CT图像噪声;最后,设计了多种损失函数来约束不同功能模块的参数优化,进一步保障了LDCT图像降噪网络的性能。实验结果表明,与目前流行算法相比,所提出的降噪网络能够在保留LDCT图像原有重要信息的基础上,取得较好的降噪效果。Abstract: Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for Low-Dose CT (LDCT) image noise reduction has certain performance advantages, and has become a new research hot field of CT image noise reduction in recent years. When the intensity of noise and artifact distribution changes in LDCT images of different doses, the noise reduction performance of GAN network is unstable, and the generalization ability of the network is low. In order to overcome these shortcomings, this paper first designs a noise level estimation subnet with a encoder-decoder structure to generate the noise maps corresponding to LDCT images with different doses, which is subtracted from the original input image to initially suppress the noise; Secondly, the backbone of the noise reduction network is designed as a multi-coded U-Net structure that is optimized through game confrontation to suppress further CT image noise; Finally, a variety of loss functions are designed to constrain the parameter optimization of each function modules, thus to guarantee further the performance of the LDCT image noise reduction network. Experimental results show that compared with current popular algorithms, the noise reduction network proposed in this paper can achieve a better noise reduction on the basis of retaining the original important information of LDCT images.
-
Key words:
- Image denoising /
- Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) /
- Low-Dose CT (LDCT) /
- U-Net /
- Noise level
-
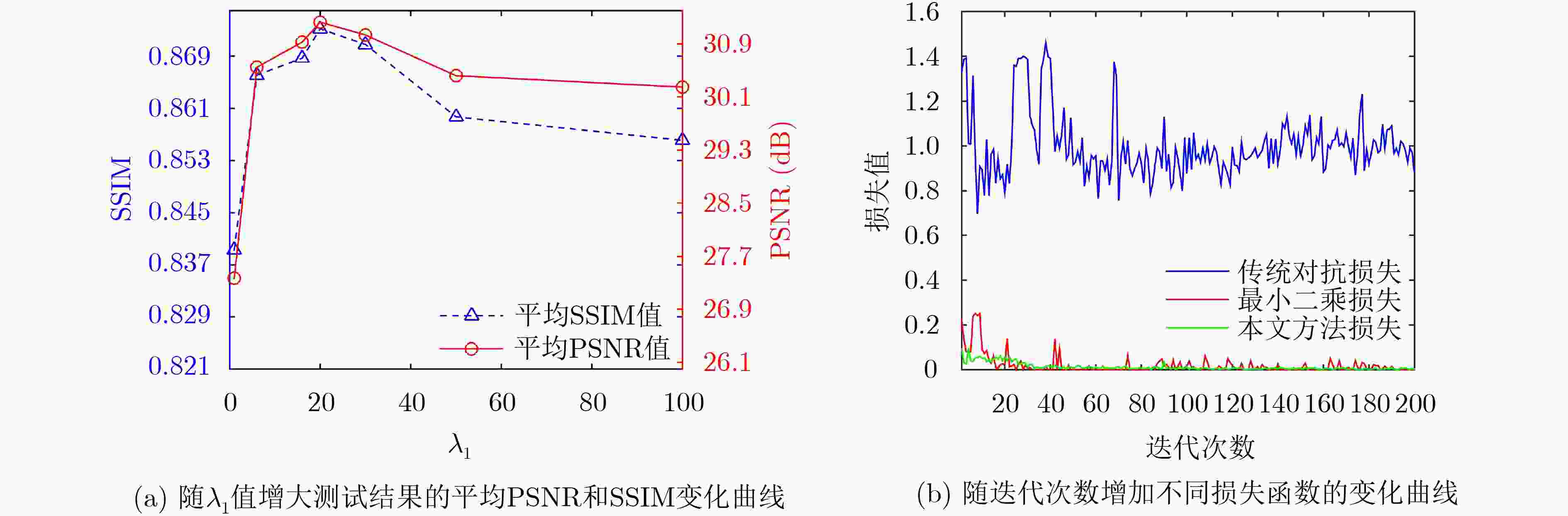
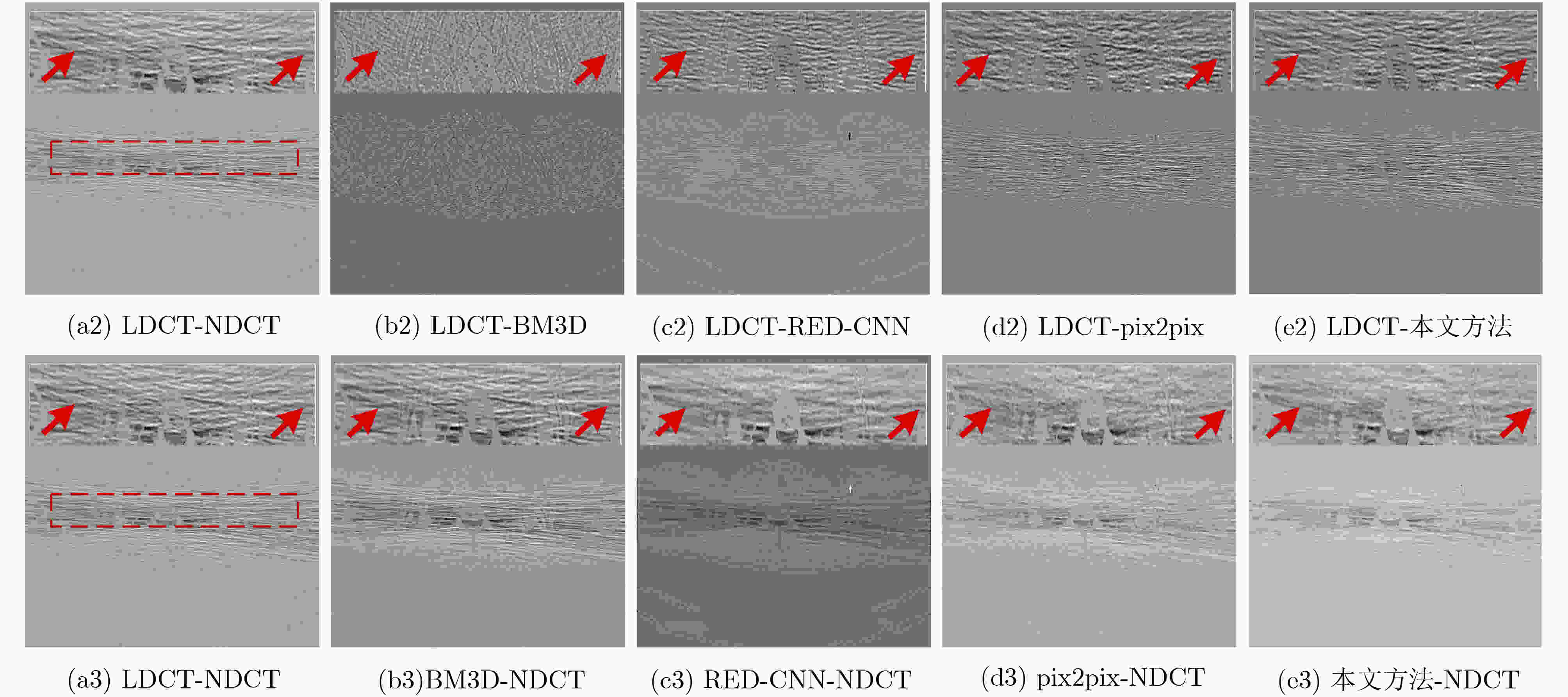
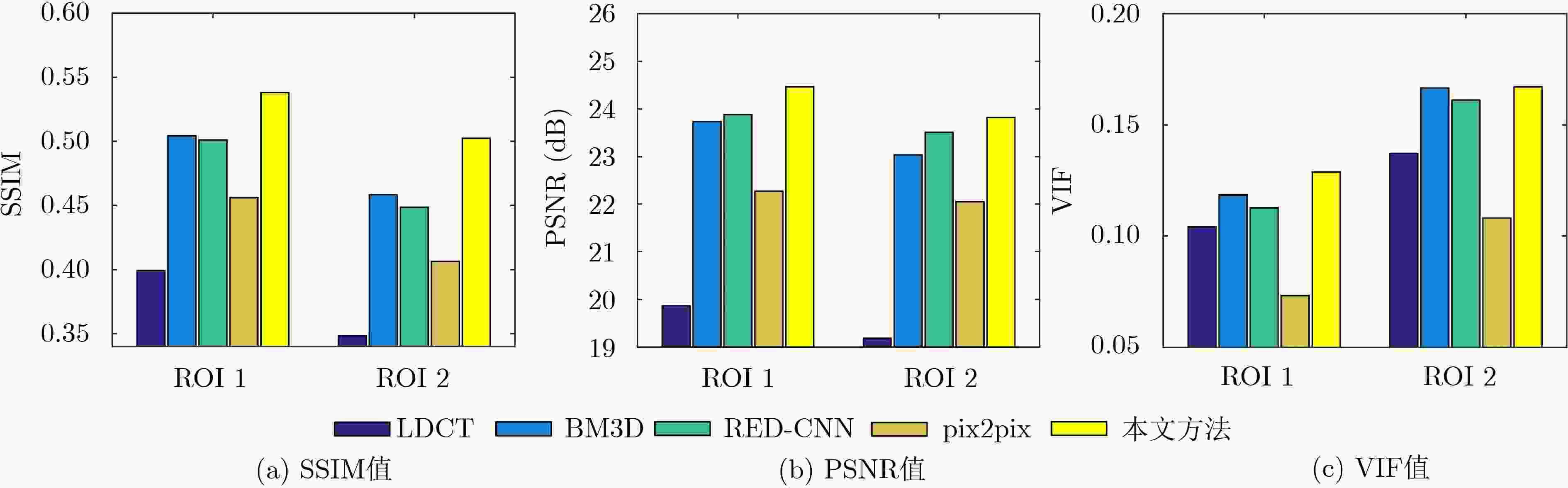
图 7 图3所示降噪图像局部ROI的量化指标值
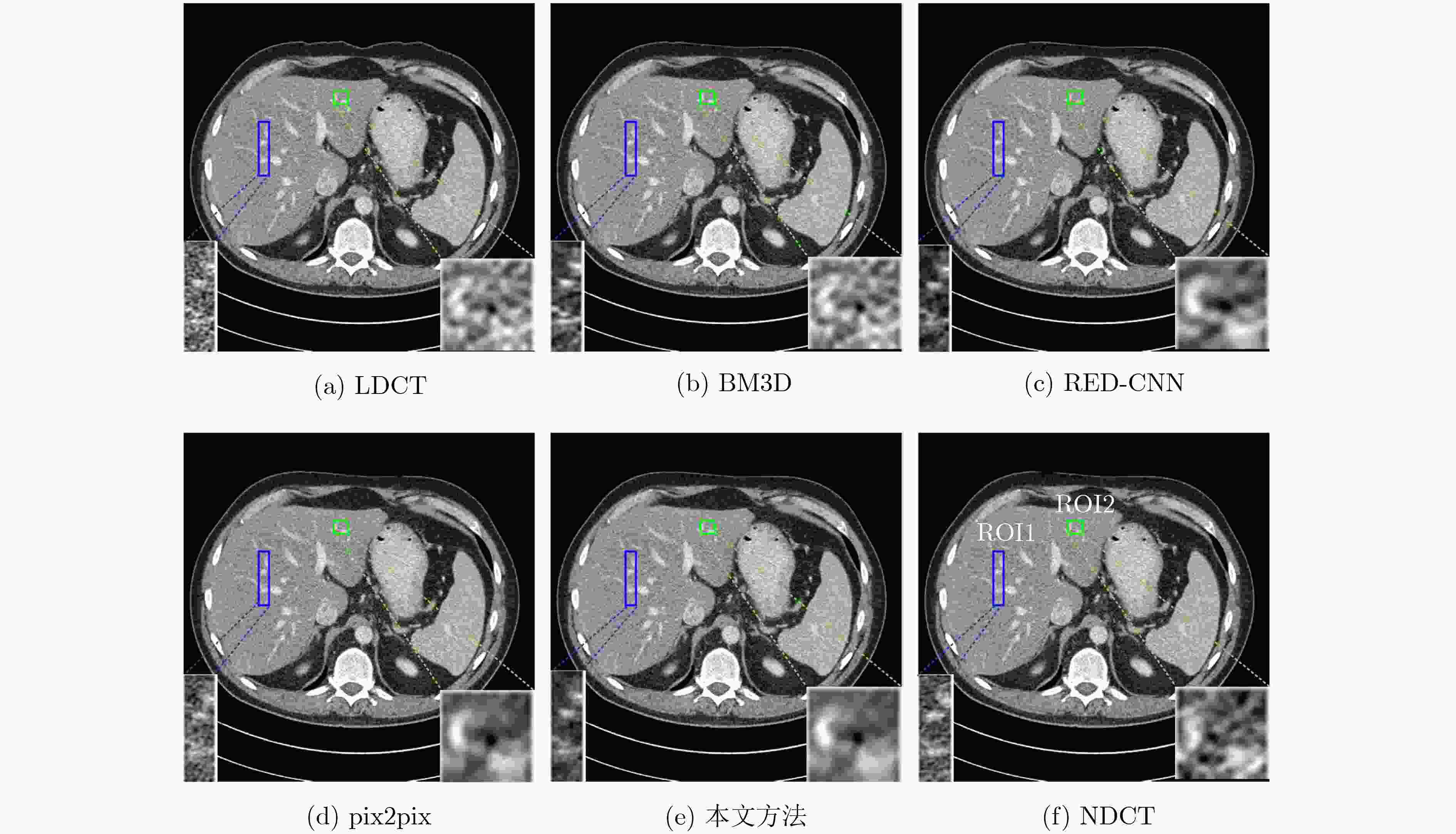
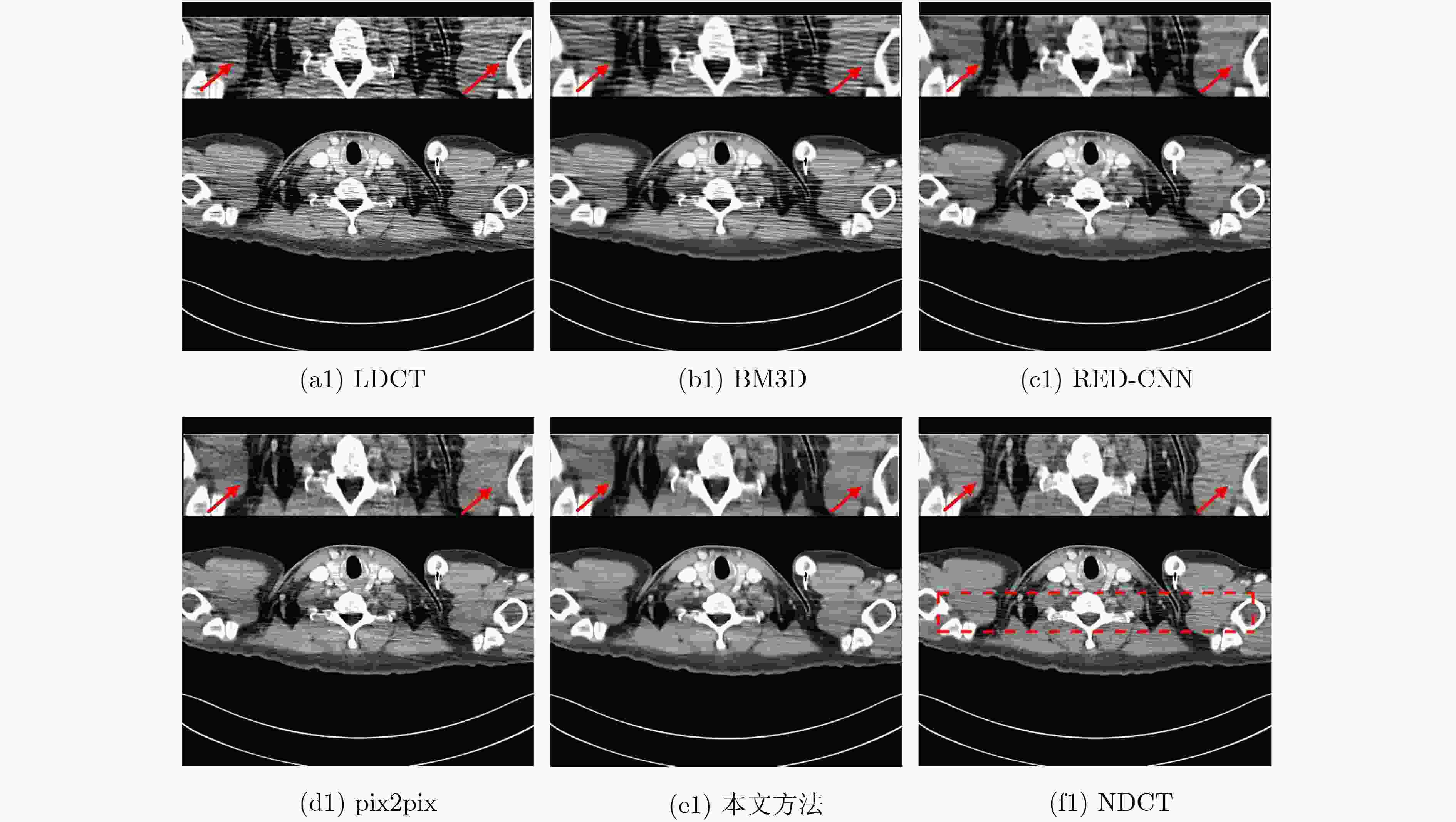
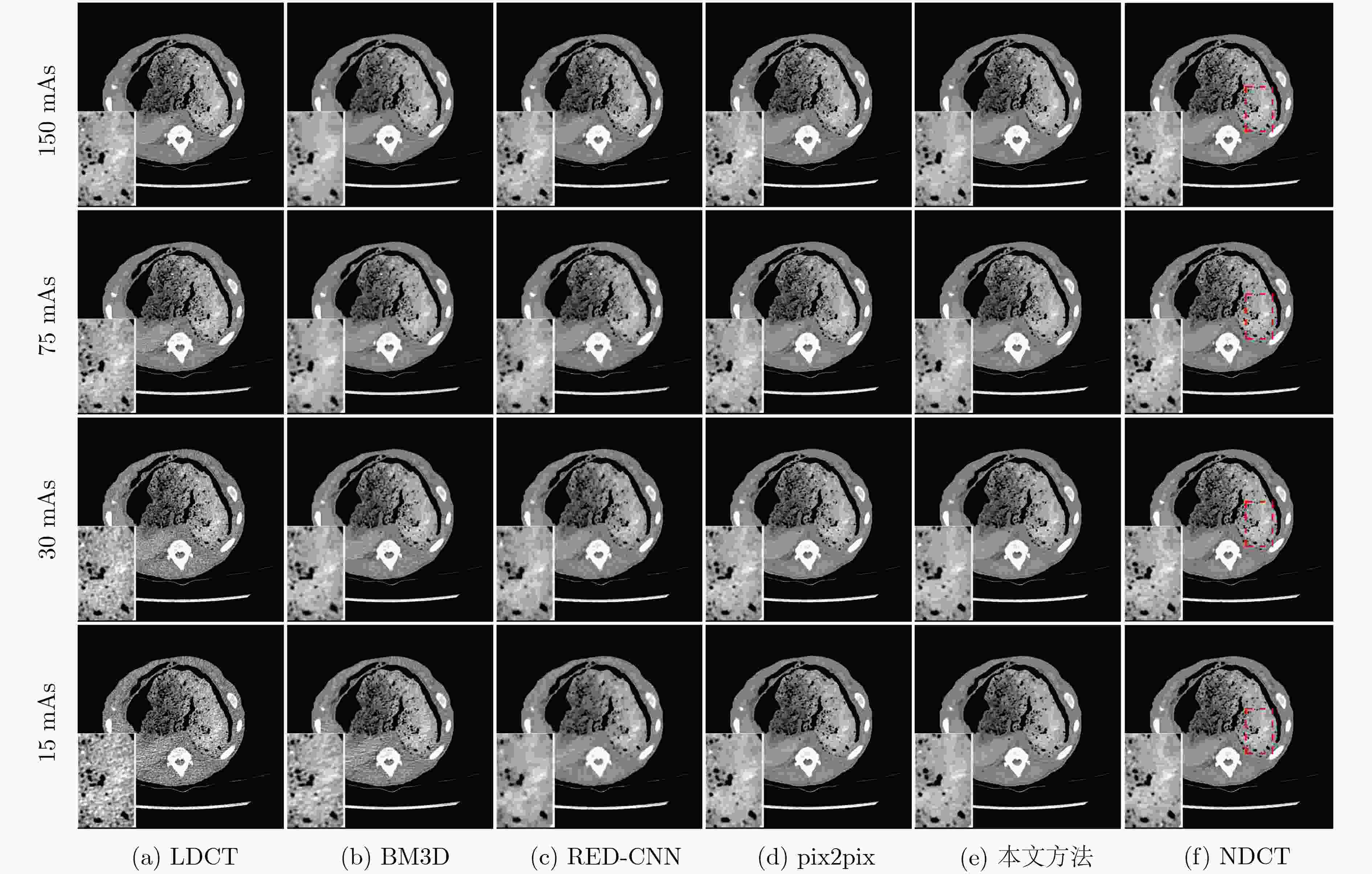
表 1 图6所示降噪图像的定量比较
150 mAs 75 mAs 30 mAs 15 mAs SSIM PSNR(dB) VIF SSIM PSNR(dB) VIF SSIM PSNR(dB) VIF SSIM PSNR(dB) VIF LDCT 0.9135 32.4367 0.3912 0.8827 29.7393 0.3087 0.8572 28.4505 0.2561 0.8232 25.6776 0.1867 BM3D 0.9346 32.7401 0.4810 0.9181 30.6341 0.4062 0.8996 30.6095 0.3547 0.8595 27.8316 0.2616 RED-CNN 0.9137 31.1185 0.3478 0.8944 28.9783 0.2960 0.9003 30.4194 0.3113 0.8930 29.1218 0.2858 pix2pix 0.9244 32.7808 0.4130 0.9084 30.8796 0.3585 0.9224 32.9193 0.3986 0.9118 31.3273 0.3537 本文方法 0.9484 34.6459 0.5030 0.9408 32.6691 0.4580 0.9453 34.1737 0.4776 0.9403 33.1630 0.4457 表 2 网络结构消融对算法性能的影响
子模块 SSIM PSNR (dB) 多路卷积 噪声水平
估计子网w/o多路卷积 √ 0.8684 30.3736 w/o噪声水平估计子网 √ 0.8696 31.0011 本文方法 √ √ 0.8732 31.2266 表 3 不同算法的测试时间对比
算法 BM3D RED-CNN pix2pix 本文方法 测试时间(s/张) 1.2078 8.6900 0.0710 0.1085 -
[1] 张权. 低剂量X线CT重建若干问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 东南大学, 2015.ZHANG Quan. A study on some problems in image reconstruction for low-dose CT system[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Southeast University, 2015. [2] HSIEH J. Computed Tomography: Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances[M]. Bellingham, USA: SPIE Press, 2009. [3] BRENNER D J and HALL E J. Computed tomography-an increasing source of radiation exposure[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2007, 357(22): 2277–2284. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra072149 [4] NAIDICH D P, MARSHALL C H, GRIBBIN C, et al. Low-dose CT of the lungs: Preliminary observations[J]. Radiology, 1990, 175(3): 729–731. doi: 10.1148/radiology.175.3.2343122 [5] CHEN Hu, ZHANG Yi, ZHANG Weihua, et al. Low-dose CT via convolutional neural network[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(2): 679–694. doi: 10.1364/BOE.8.000679 [6] SHAN Hongming, ZHANG Yi, YANG Qingsong, et al. 3-D convolutional encoder-decoder network for low-dose CT via transfer learning from a 2-D trained network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1522–1534. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2832217 [7] CHEN Hu, ZHANG Yi, KALRA M K, et al. Low-dose CT with a residual encoder-decoder convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2524–2535. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2715284 [8] WU Dufan, KIM K, FAKHRI G E, et al. A cascaded convolutional neural network for X-ray low-dose CT image denoising[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.04267, 2017. [9] WOLTERINK J M, LEINER T, VIERGEVER M A, et al. Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2536–2545. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2708987 [10] YANG Qingsong, YAN Pingkun, ZHANG Yanbo, et al. Low-Dose CT image denoising using a generative adversarial network with wasserstein distance and perceptual loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1348–1357. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2827462 [11] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 27th Conference and Workshop on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Cambridge, United States, 2014: 2672–2680. [12] BAO Jianmin, CHEN Dong, WEN Fang, et al. CVAE-GAN: Fine-grained image generation through asymmetric training[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2745–2754. [13] ZHENG Jin, MA Haocheng, and PENG Lihui. A CNN-based image reconstruction for electrical capacitance tomography[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/IST48021.2019.9010096. [14] ZHANG Zhijun and JI Xiaopeng. GAN network solves the problem of image segmentation across data[C]. 2019 IEEE 4th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chengdu, China, 2019. doi: 10.1109/iaeac47372.2019.8998056. [15] KIM D W, CHUNG J R, and JUNG S W. GRDN: Grouped residual dense network for real image denoising and GAN-based real-world noise modeling[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, USA, 2019. [16] HE Zhang, VISHWANATH S, and VISHAL M P. Image de-raining using a conditional generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(11): 3943–3956. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2920407 [17] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1125–1134. [18] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4608–4622. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2839891 [19] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. [20] AAPM. Low dose CT grand challenge[EB/OL]. http://www.aapm.org/GrandChallenge/LowDoseCT/, 2017. [21] Piglet Dataset[EB/OL]. http://homepage.usask.ca/~xiy525/. [22] DIEDERK P K and JIMMY L B. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Ithaca, USA, 2015. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
