Correntropy Extreme Learning Machine Based on Spatial Pyramid Matching and Local Receptive Field
-
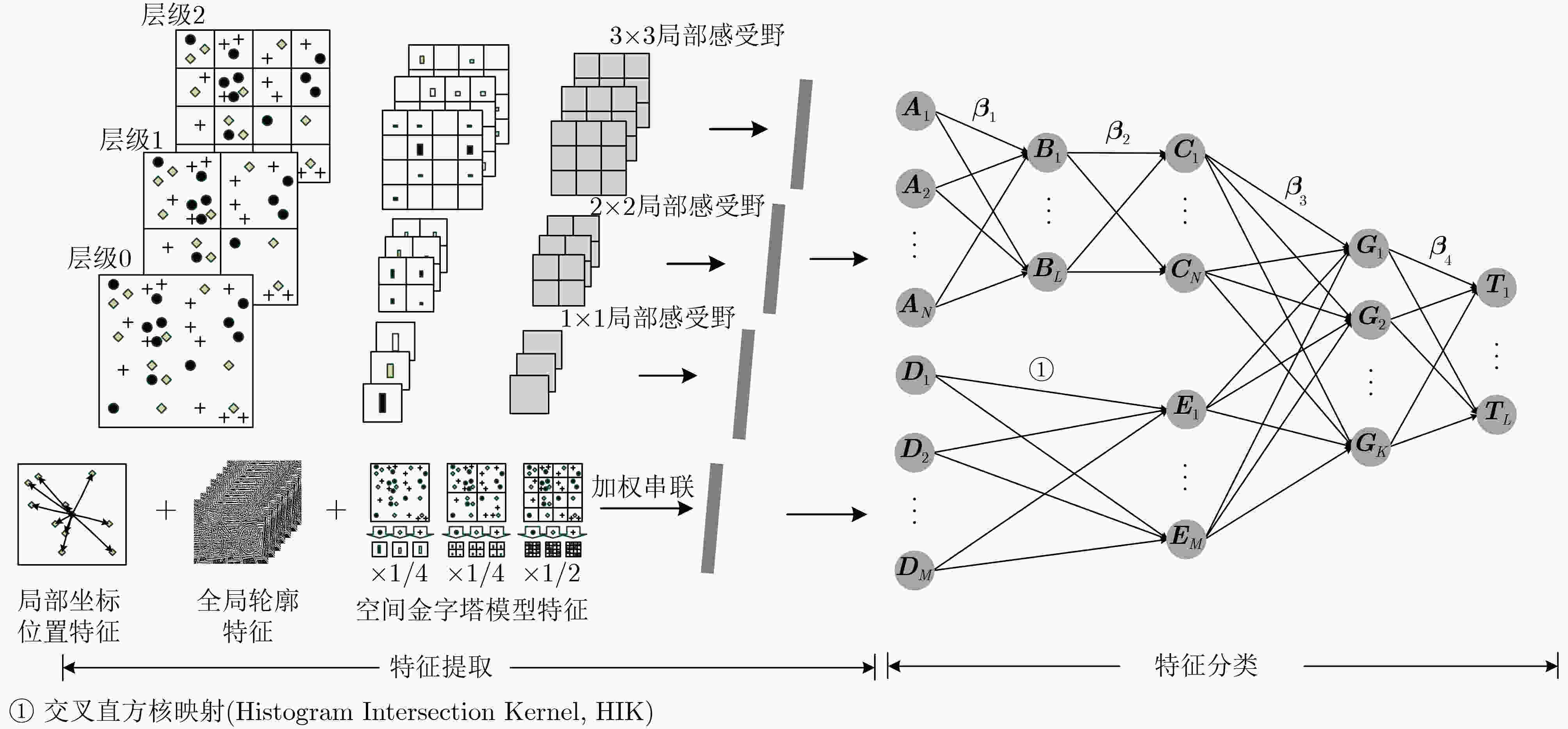
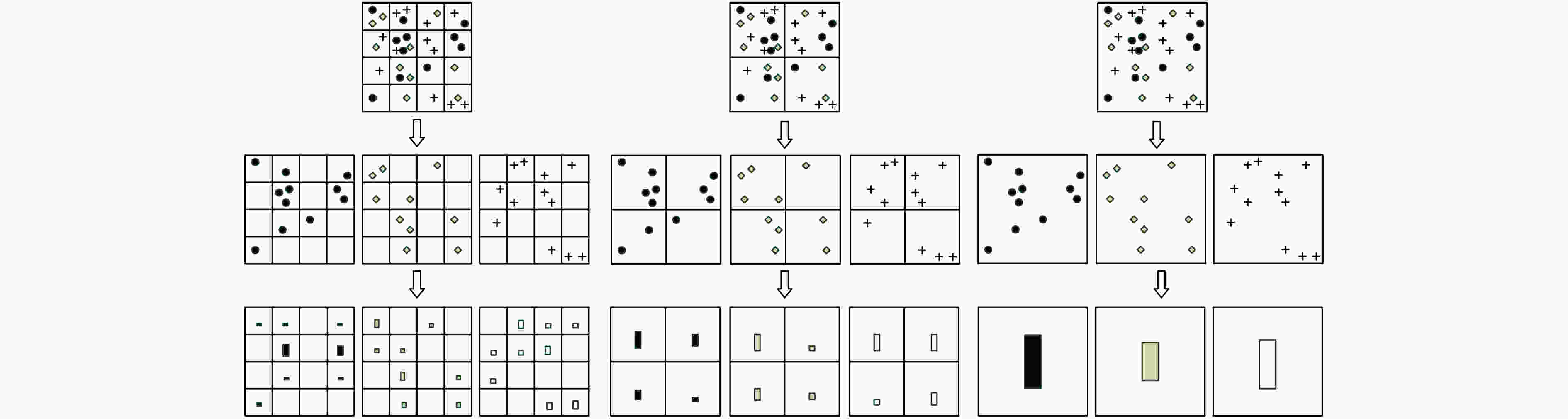
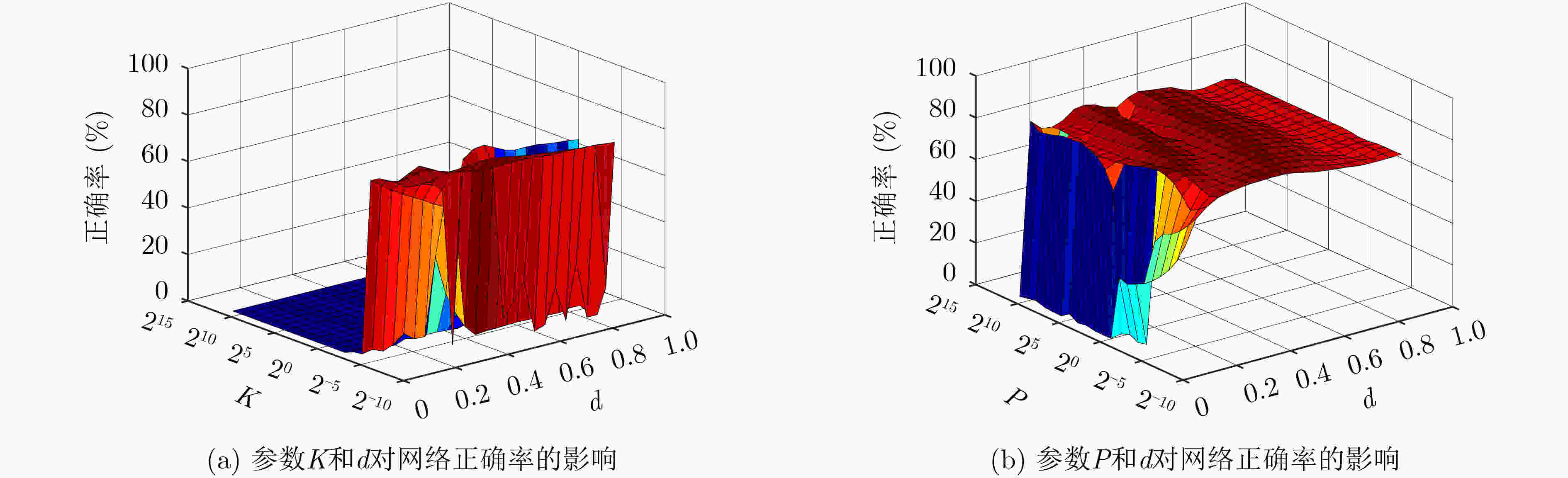
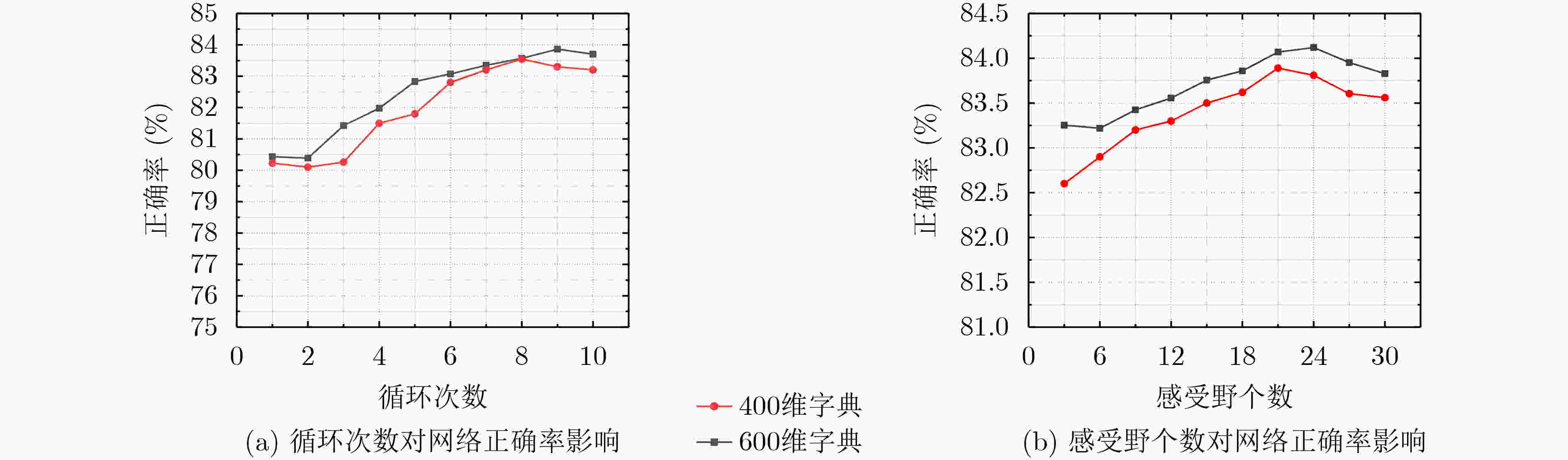
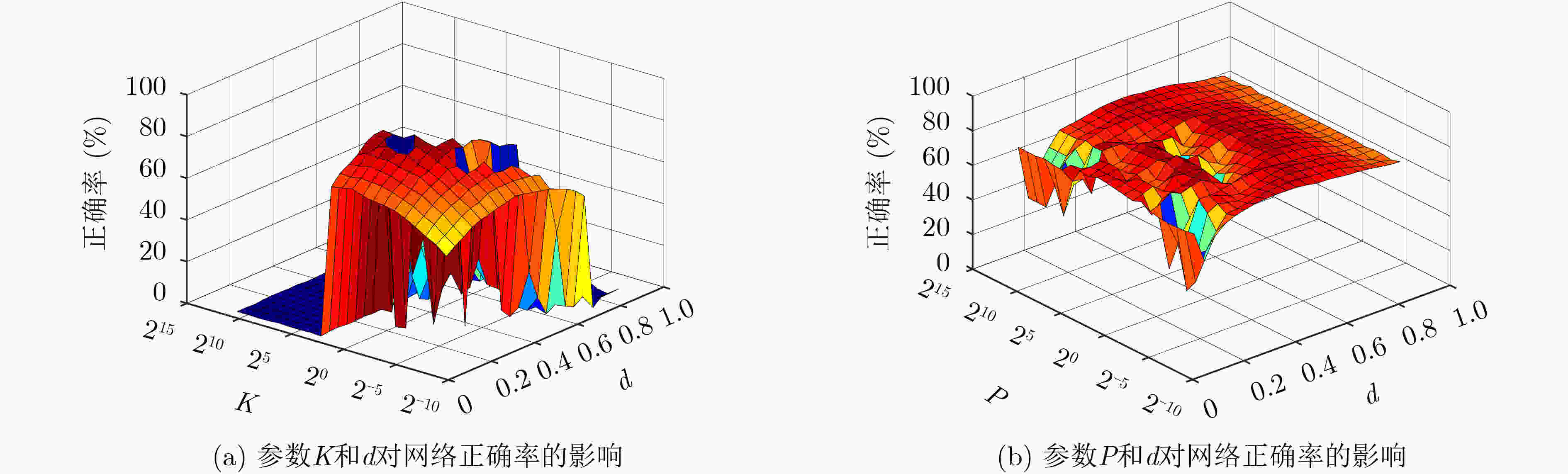
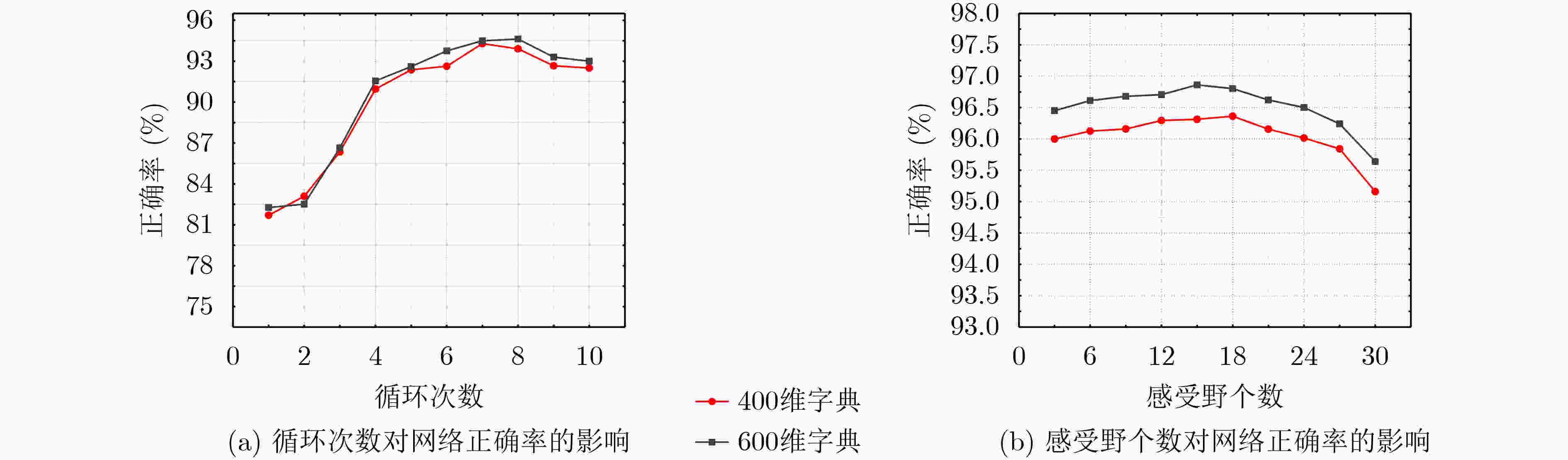
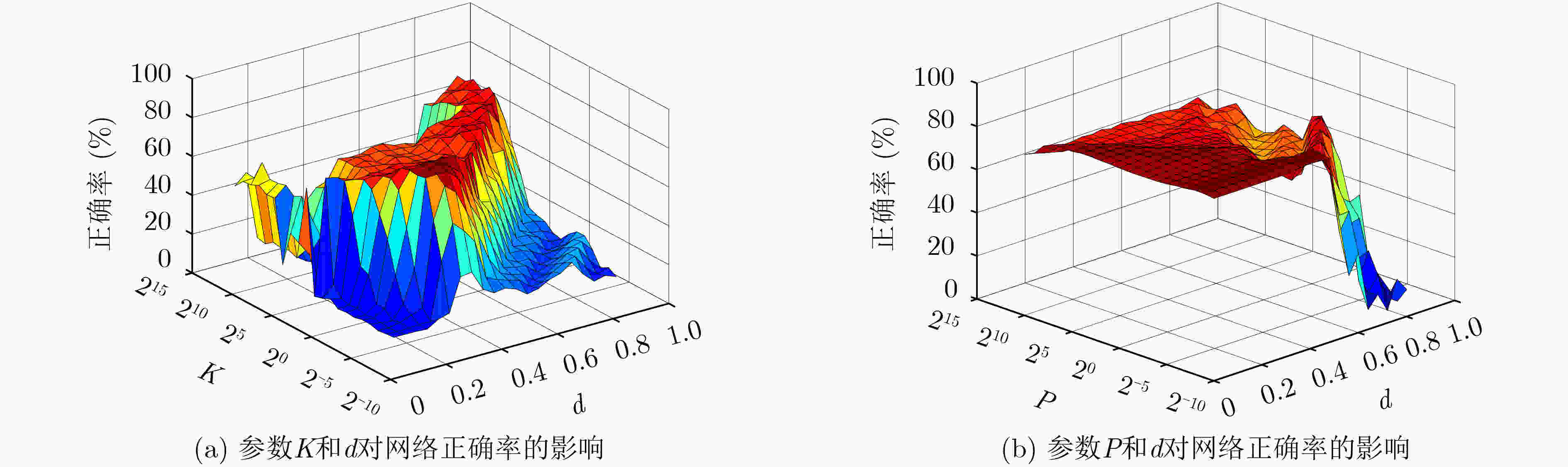
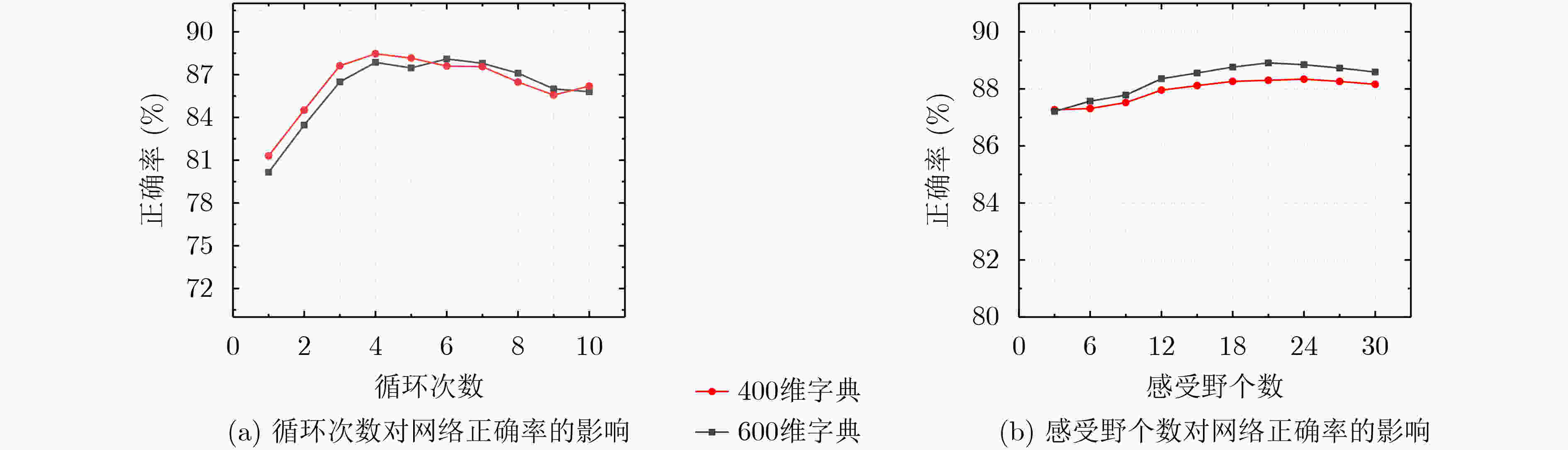
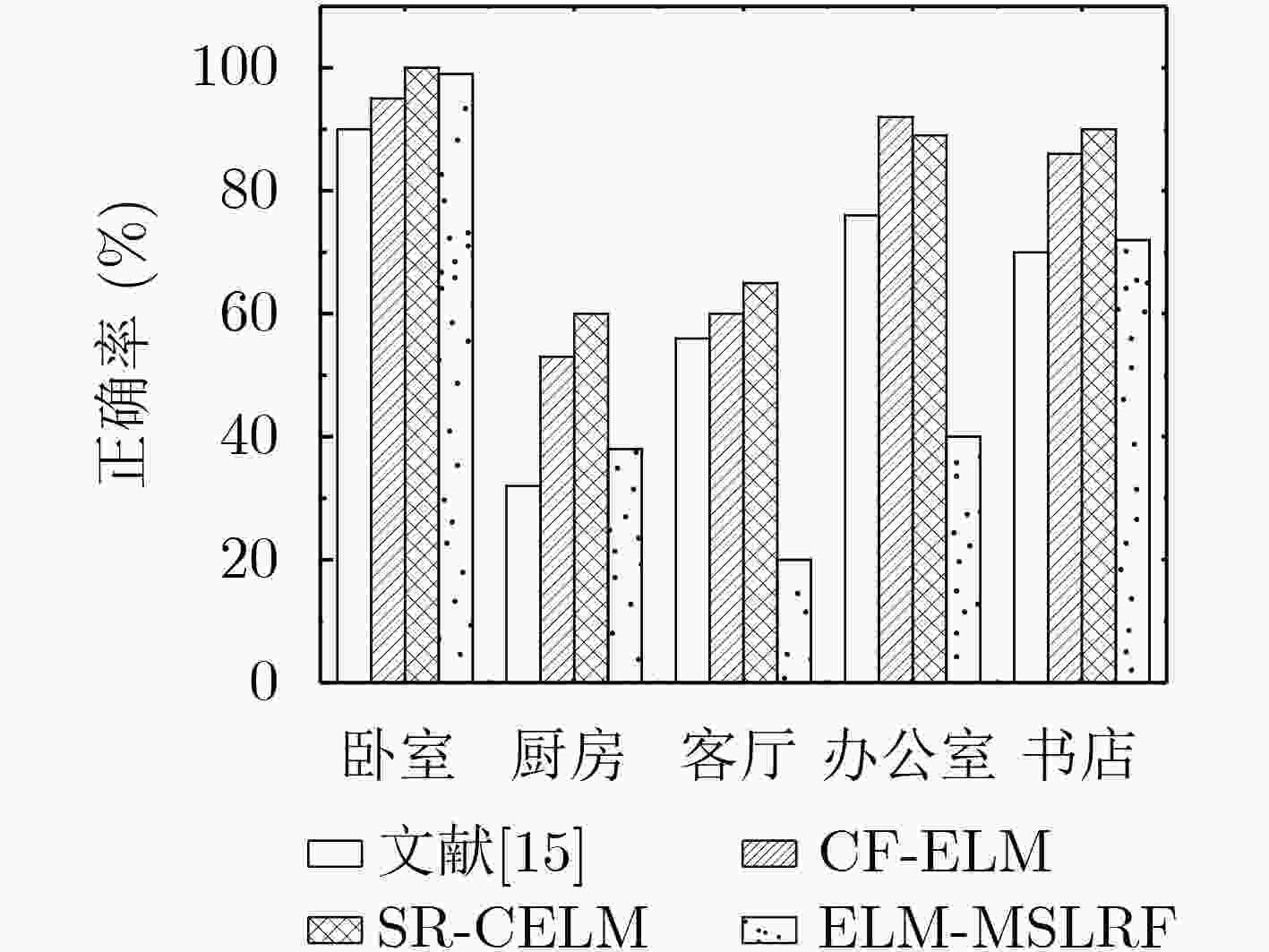
摘要: 针对空间金字塔词袋模型中空间特征分布信息利用效率低,各类特征融合不充分的问题,该文提出空间金字塔与局部感受野相结合的相关熵极限学习机(SR-CELM)。在特征提取部分,利用多尺度局部感受野对生成的多层级的字典特征分布图进行卷积,并引入局部位置特征和全局轮廓特征。在特征分类部分,提出一种新的网络以融合各部分特征。同时在传统极限学习机训练方法的基础上利用相关熵准则构建判别性约束,推导出权重更新公式以求解网络的输出权重。为验证SR-CELM的有效性,该文分别在数据库Caltech 101, MSRC和15 Scene上进行实验。实验表明SR-CELM能够充分利用特征中可辨识信息,提高分类正确率。Abstract: Considering the problems of inefficient use of spatial information between features and inadequate fusion of different features, a Correntropy Extreme Learning Machine based on Spatial pyramid matching and local Receptive field(SR-CELM) is proposed. In feature extraction part, multi-scale local receptive fields are used to convolve the generated multi-level dictionary feature distribution map, and local position features and global contour features are introduced. In feature classification part, a new network is proposed to fuse the features of each part. Based on the traditional extreme learning machine training method, a discriminative constraint is constructed by using the relevant entropy criterion, and the weight update formula is used to solve the output weight of the new network. In order to verify the effectiveness of the SR-CELM, experiments are performed on the databases Caltech 101, MSRC and 15 Scene. The experiments show that SR-CELM can make full use of the identifiable information in the features and improve the classification accuracy.
-
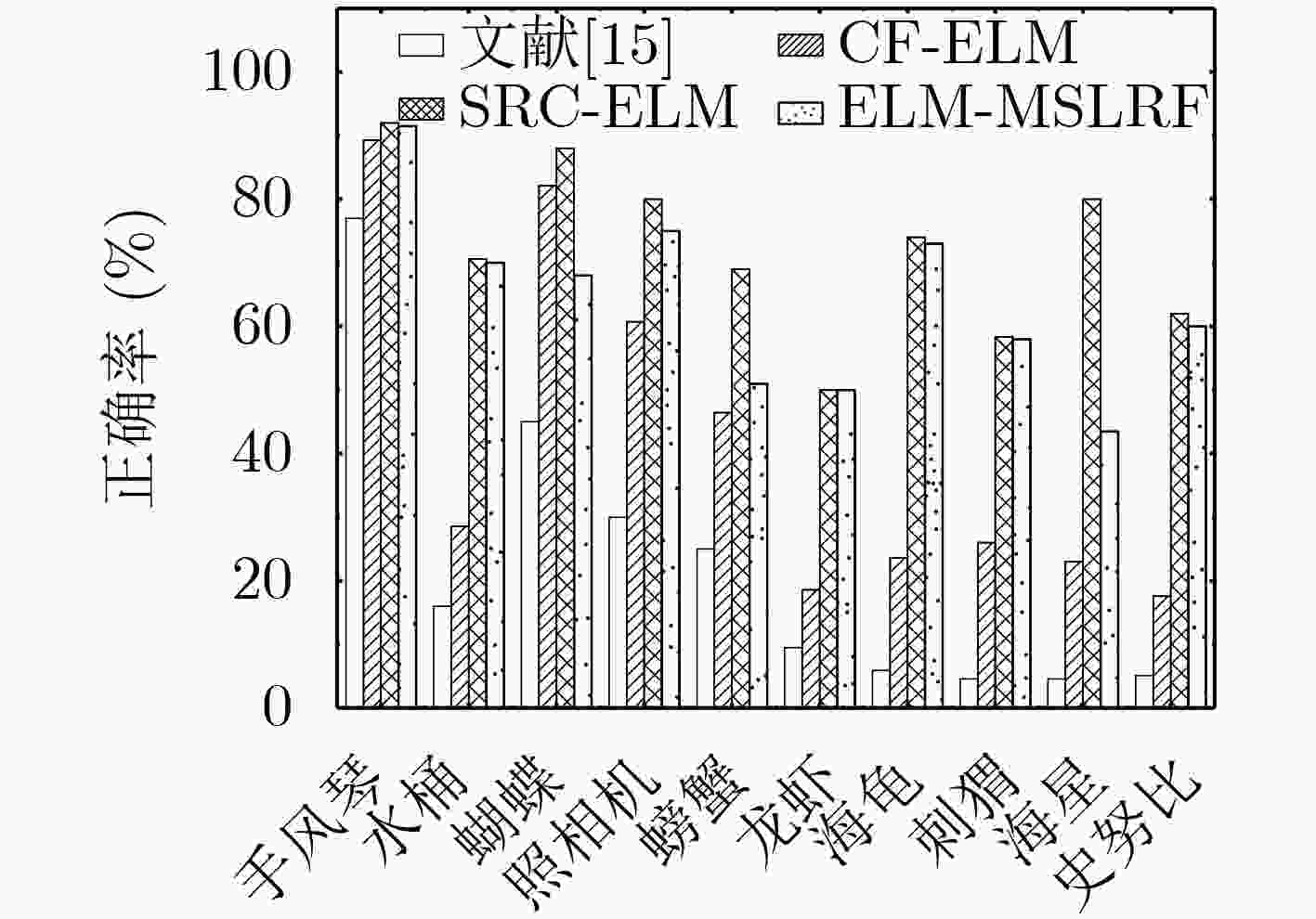
表 1 Caltech 101正确率(%)与训练时间(s)
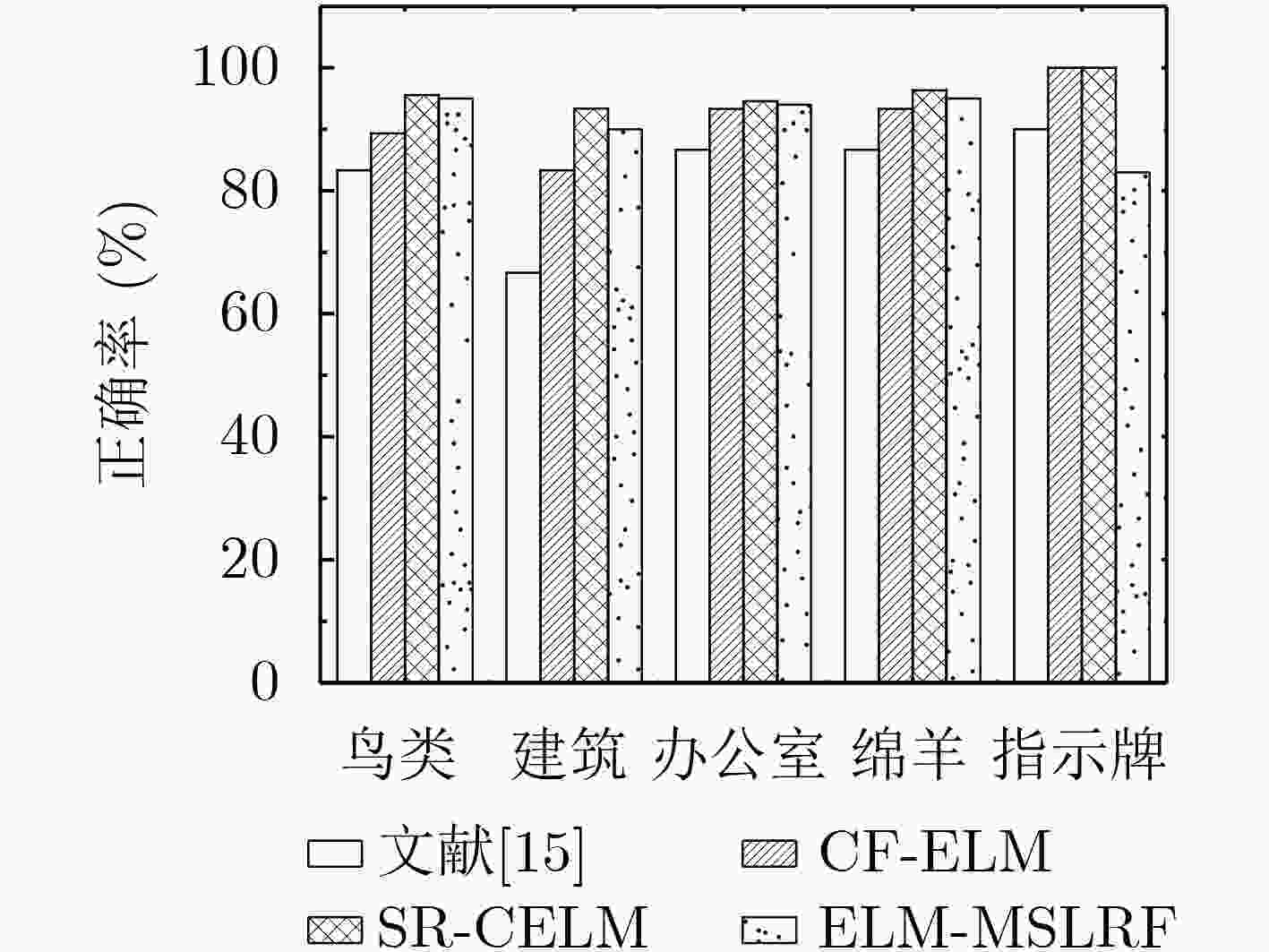
表 2 MSRC正确率(%)与训练时间(s)
-
[1] CSURKA G, DANCE C R, FAN Lixin, et al. Visual categorization with bags of keypoints[C]. Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 2004: 1–22. [2] LAZEBNIK S, SCHMID C, and PONCE J. Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories[C]. 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2006: 2169–2178. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2006.68. [3] LI Qing, PENG Qiang, CHEN Junzhou, et al. Improving image classification accuracy with ELM and CSIFT[J]. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2019, 21(5): 26–34. doi: 10.1109/MCSE.2018.108164708 [4] HUANG Guangbin, ZHU Qinyu, and SIEW C K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1/3): 489–501. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 [5] PARK J M and KIM J H. Online recurrent extreme learning machine and its application to time-series prediction[C]. 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Anchorage, USA, 2017: 1983–1990. doi: 10.1109/ijcnn.2017.7966094. [6] LIU Zheng, WEI Jin, and YING Mu. Variances-constrained weighted extreme learning machine for imbalanced classification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 403: 45–52. [7] 刘彬, 杨有恒, 赵志彪, 等. 一种基于正则优化的批次继承极限学习机算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1734–1742. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190502LIU Bin, YANG Youheng, ZHAO Zhibiao, et al. A batch inheritance extreme learning machine algorithm based on regular optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1734–1742. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190502 [8] HUANG Guangbin, BAI Zuo, KASUN L L C, et al. Local receptive fields based extreme learning machine[J]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2015, 10(2): 18–29. doi: 10.1109/mci.2015.2405316 [9] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New York, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [10] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [11] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298594. [12] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [13] XING Hongjie and WANG Xinmei. Training extreme learning machine via regularized correntropy criterion[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2013, 23(7/8): 1977–1986. doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-1184-y [14] 吴超, 李雅倩, 张亚茹, 等. 用于表示级特征融合与分类的相关熵融合极限学习机[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 386–393. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190186WU Chao, LI Yaqian, ZHANG Yaru, et al. Correntropy-based fusion extreme learning machine for representation level feature fusion and classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 386–393. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190186 [15] 李雅倩, 吴超, 李海滨, 等. 局部位置特征与全局轮廓特征相结合的图像分类方法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(7): 1726–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.07.026LI Yaqian, WU Chao, LI Haibin, et al. Image classification method combining local position feature with global contour feature[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(7): 1726–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.07.026 [16] HUANG Jinghong, YU Zhuliang, CAI Zhaoquan, et al. Extreme learning machine with multi-scale local receptive fields for texture classification[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 28(3): 995–1011. doi: 10.1007/s11045-016-0414-3 [17] KONIUSZ P, YAN Fei, GOSSELIN P H, et al. Higher-order occurrence pooling for bags-of-words: Visual concept detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 313–326. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2545667 [18] WANG Jinjun, YANG Jianchao, YU Kai, et al. Locality-constrained Linear Coding for image classification[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 13–18. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540018. [19] 肖文华, 包卫东, 陈立栋, 等. 一种用于图像分类的语义增强线性编码方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 791–797. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140743XIAO Wenhua, BAO Weidong, CHEN Lidong, et al. A semantic enhanced linear coding for image classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 791–797. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140743 [20] LI Weisheng, DONG Peng, XIAO Bin, et al. Object recognition based on the region of interest and optimal bag of words model[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 172: 271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.01.083 [21] KHAN R, BARAT C, MUSELET D, et al. Spatial histograms of soft pairwise similar patches to improve the bag-of-visual-words model[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2015, 132: 102–112. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2014.09.005 [22] 姜轩. 基于深度学习的场景图像分类算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.JIANG Xuan. Research on scene image classification algrithm based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
