Analysis on Structure and Multiplexing of L1 Signal from Global Positing System III in-orbit Satellites
-
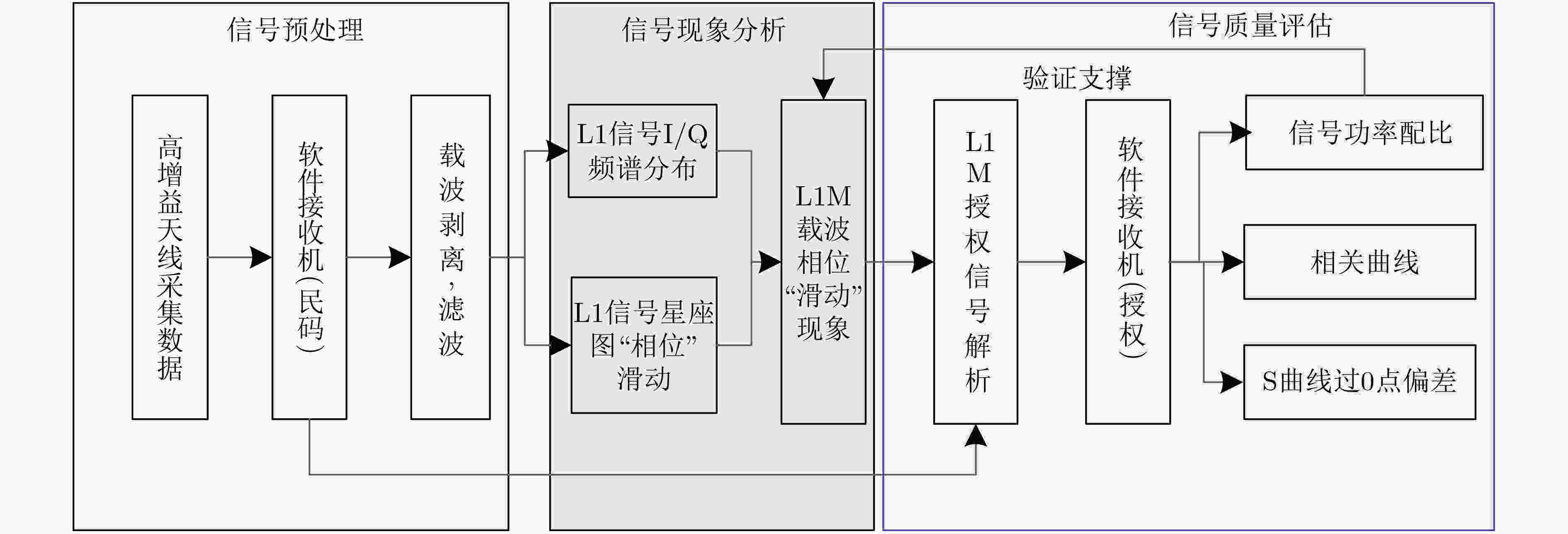
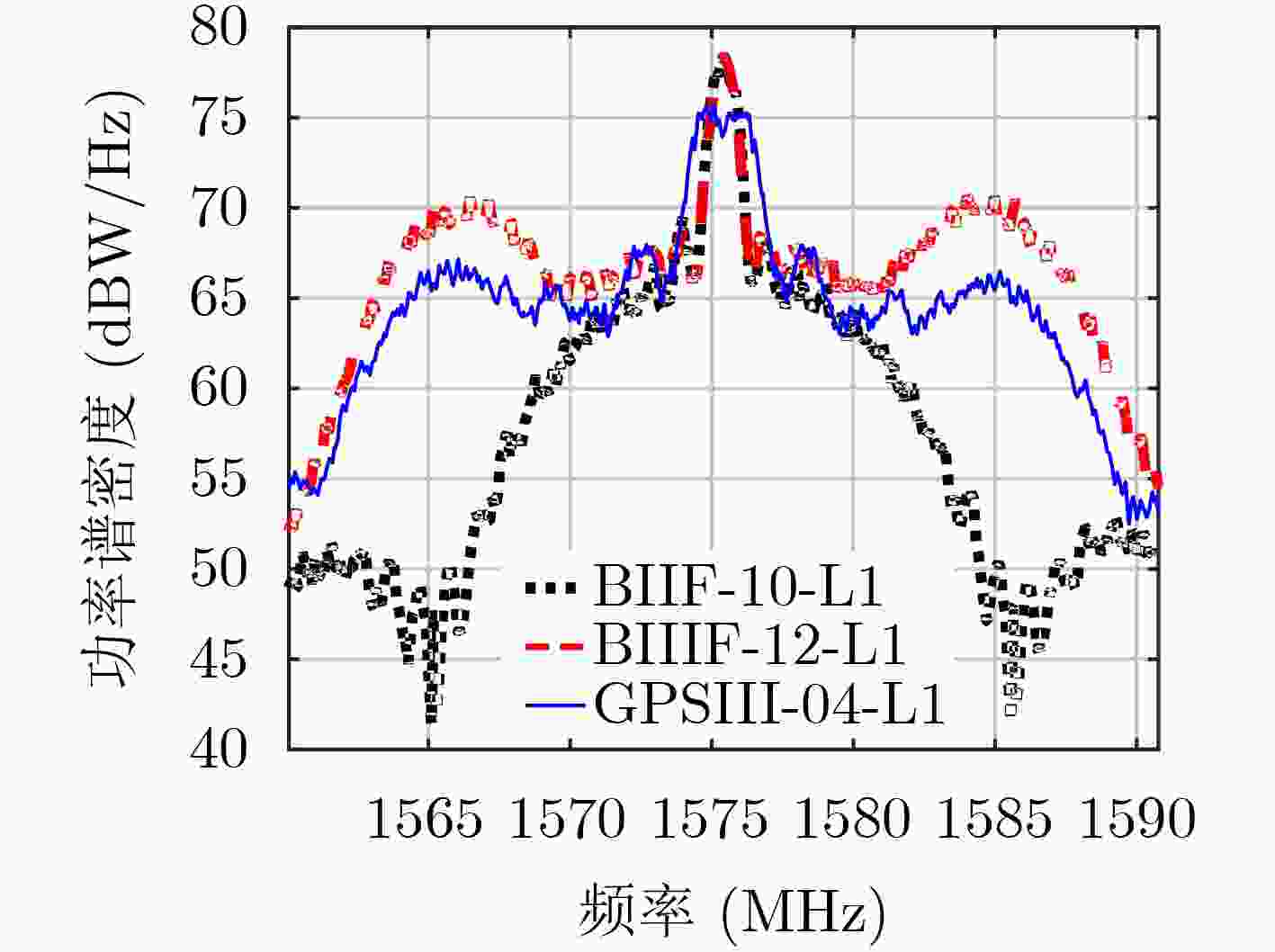
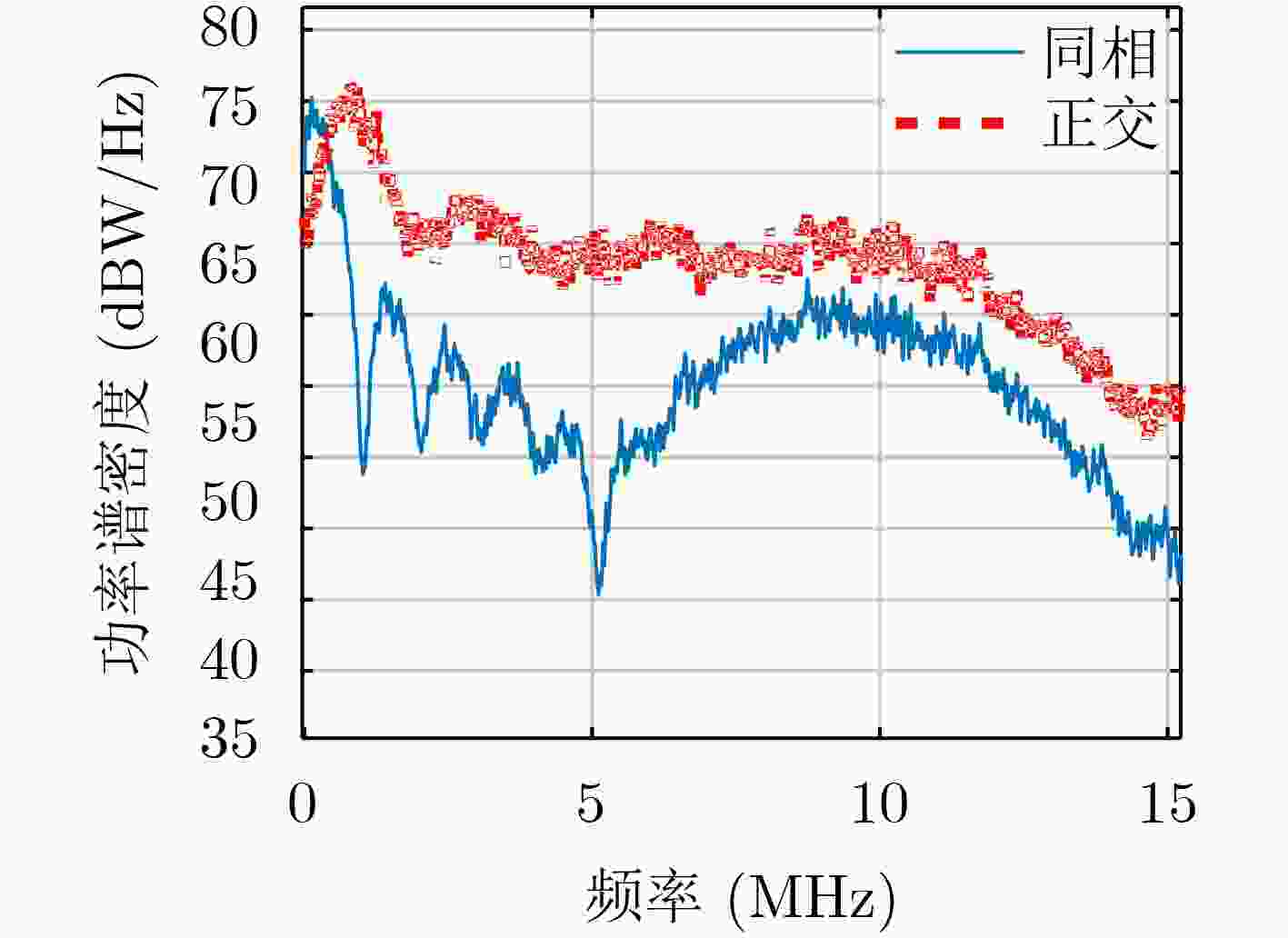
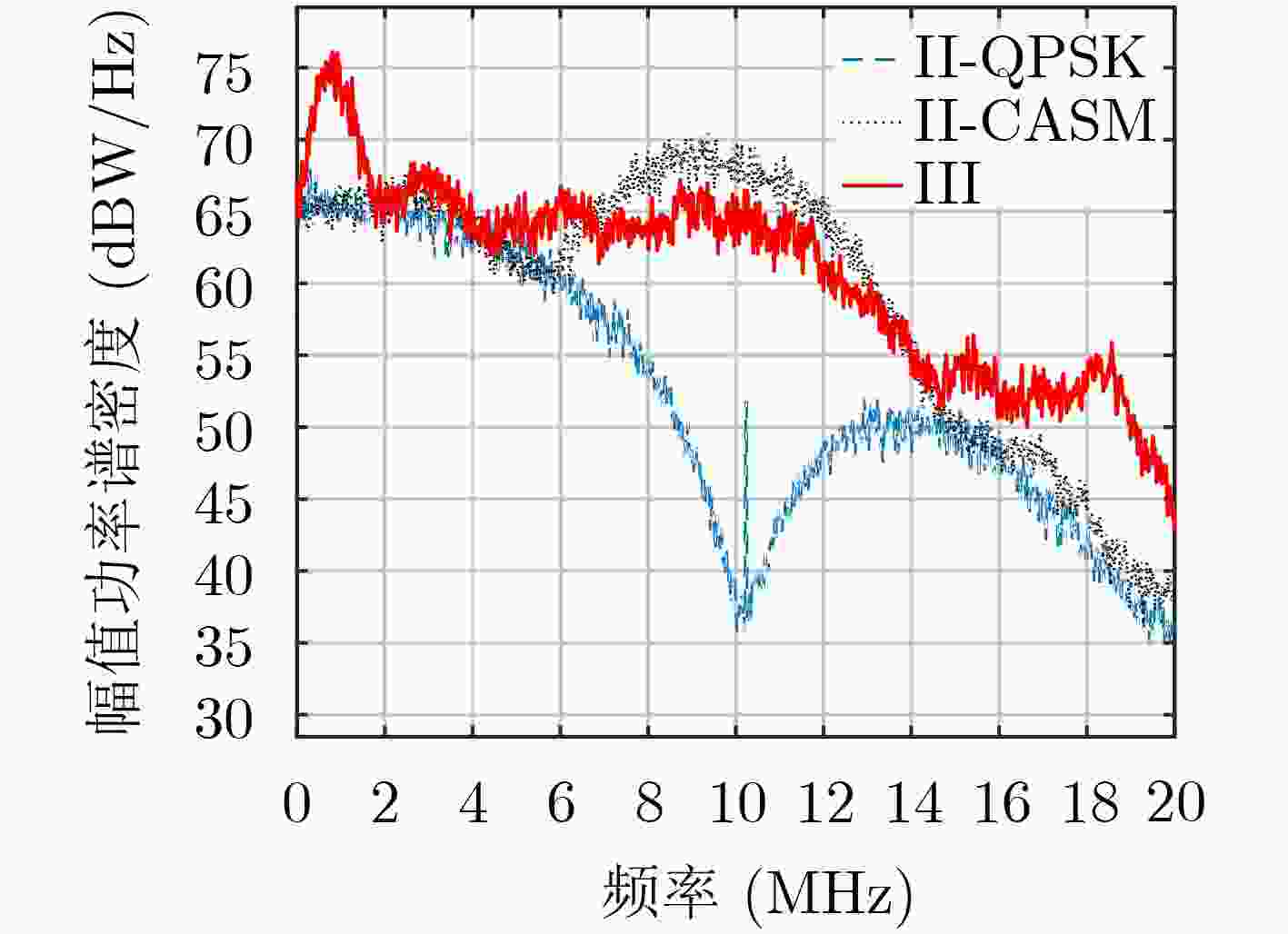
摘要: 导航信号是连接空间卫星和地面用户端的枢纽,是卫星导航定位系统中最重要的部分之一,其优劣直接影响后续的定位、测速、授时等性能。该文利用国家授时中心40 m高增益天线对GPS III首星进行多次信号采集及比对分析工作,从GPS III L1频点调制矢量及频谱分布入手,对L1频点载波相位存在“滑动”现象进行了深入剖析,得出该现象主要源于L1M信号。利用C/A码解析出授权信号M码,定量分析了L1频点信号分量的S曲线过0点偏差以及功率占比,其中L1M S曲线过0点偏差达到0.058 ns,信号功率占比最高可达6.78。该文研究成果可为研究新一代GPS信号的调制方式提供支撑,也可为后续北斗导航卫星系统信号体制设计以及信号质量评估方法提供参考。Abstract: The navigation signal is the hub connecting space satellites and ground users, and is one of the most important parts of the satellite navigation and positioning system. Its advantages and disadvantages directly affect the subsequent positioning, speed measurement, timing and other performance. The 40 m high-gain antenna of the National Time Service Center is used to conduct multiple signal acquisition and comparison analysis of the Global Positing System III (GPS III) first satellite. Starting from the GPS III L1 frequency point modulation vector and frequency spectrum distribution, an in-depth analysis of the "sliding" phenomenon in the carrier phase of the L1 frequency point is carried out, and it is concluded that the phenomenon is mainly derived from the L1M signal. C/A code is used to analyze the authorized signal M code. The S-curve zero-crossing deviation and the power proportion of the L1 frequency point signal component are quantitatively analyzed. Among them, the L1M S-curve zero-crossing deviation reaches 0.058ns, and the signal power proportion is up to 6.78. The research results of this paper can provide support for the research on the modulation methods of the new generation GPS signals, and also provide references for the subsequent Beidou navigation satellite signal system design and signal quality evaluation methods.
-
表 1 GPS L1 信号分量
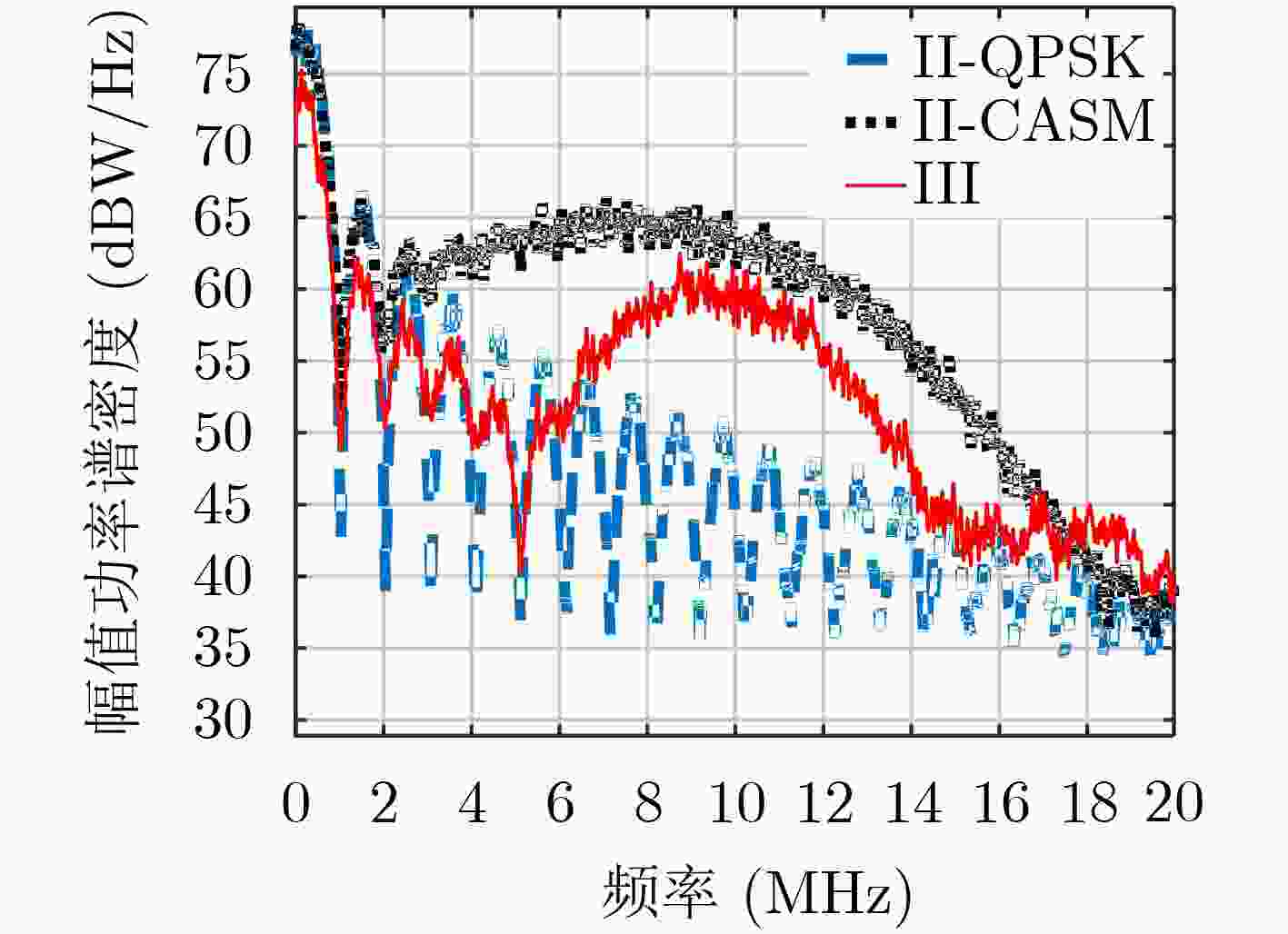
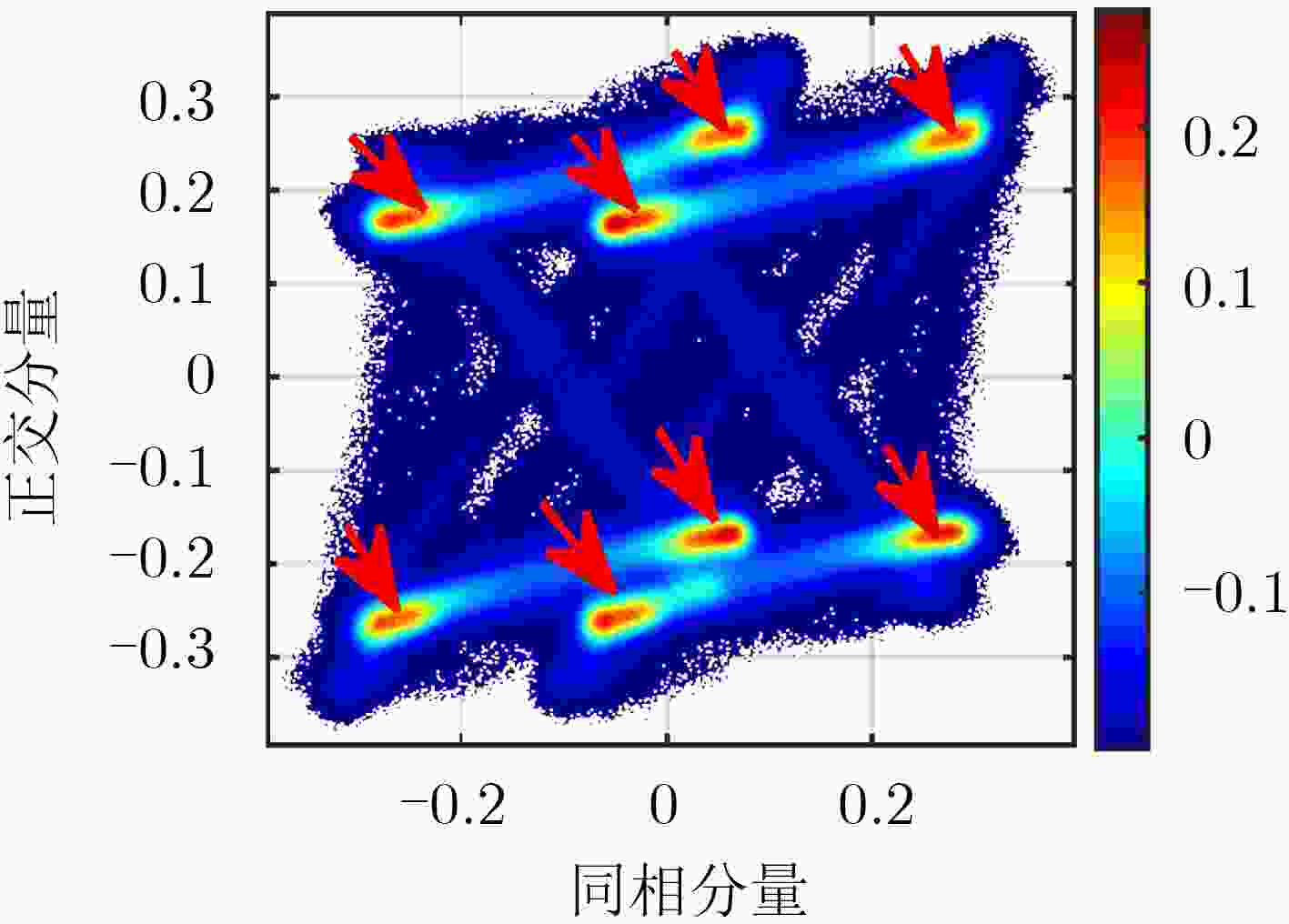
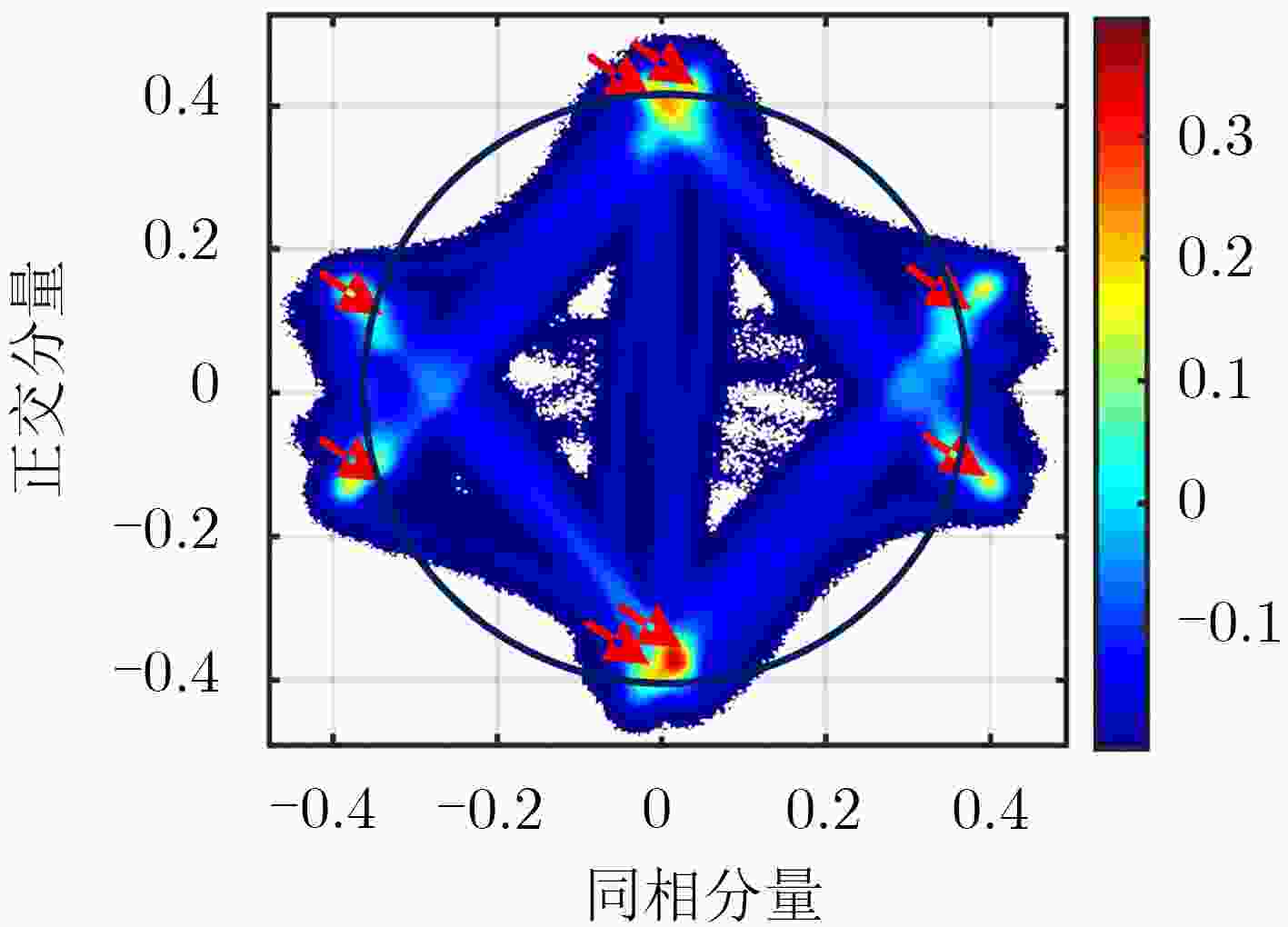
系统 GPS III GPS II 参考 复用方式/分量 未公开 QPSK CASM C/A √ √ √ IS-GPS-200J(2018) L1Cd √ – – IS-GPS-800E(2018) L1Cp √ – – IS-GPS-800E(2018) P(Y) √ √ √ IS-GPS-200J(2018) M √ – √ Marquis and Reigh(2015) 表 2 GPS L1 信号I/Q支路调制方式统计
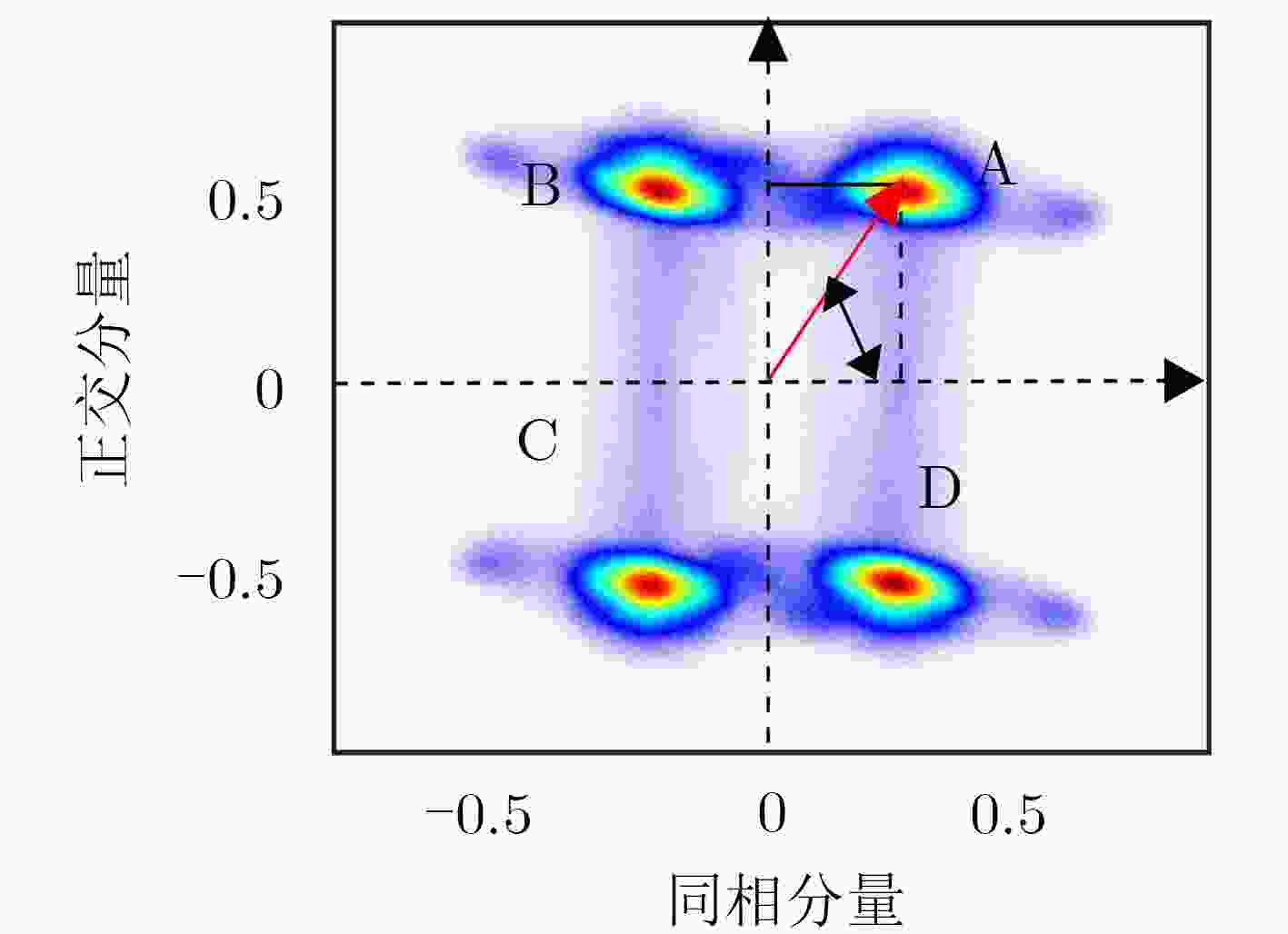
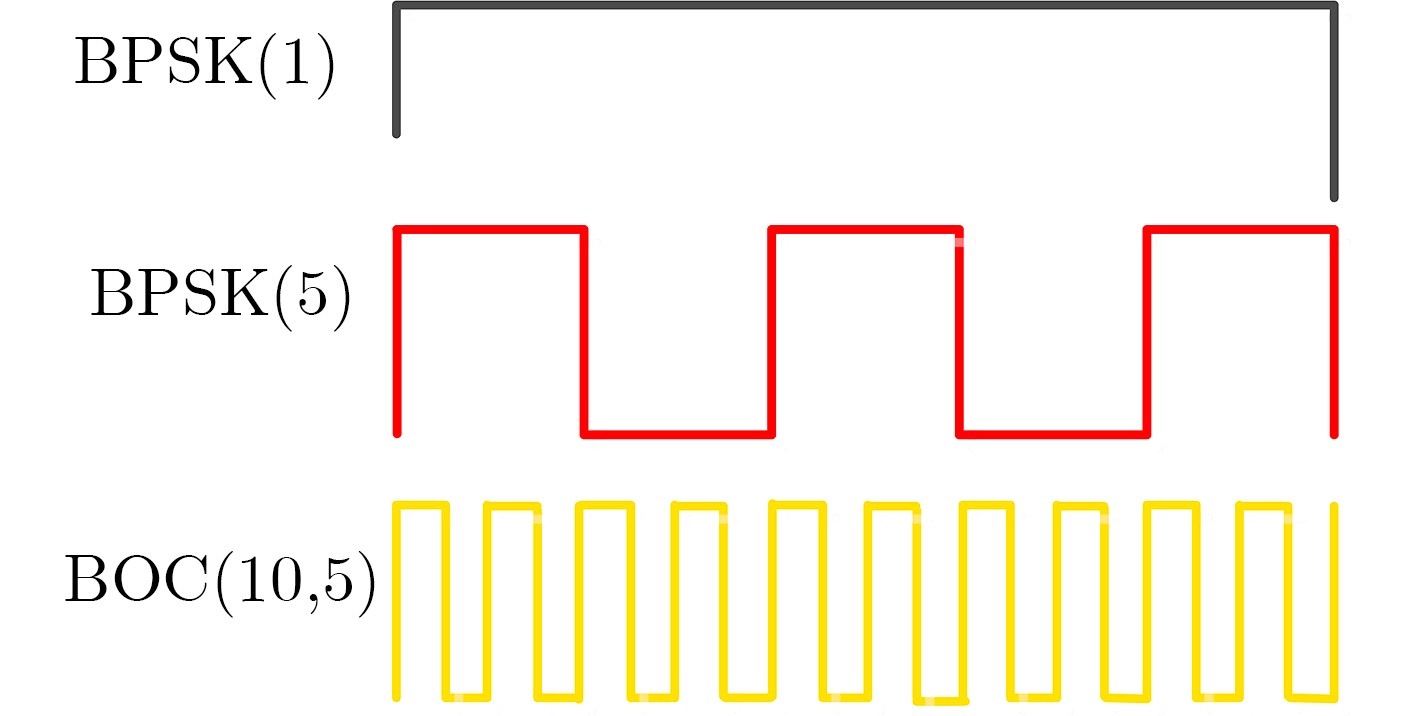
分量/系统 GPS III GPS II 未知 QPSK CASM 同相 BPSK(1) BOC(10,5) BPSK(1) BPSK(1)+ BOC(10,5) 正交 BOC(1,1)+TMBOC(6,1,4/33)+P(Y) BPSK(10) BPSK(10) 表 3 主瓣带宽内星座点幅度相位统计结果
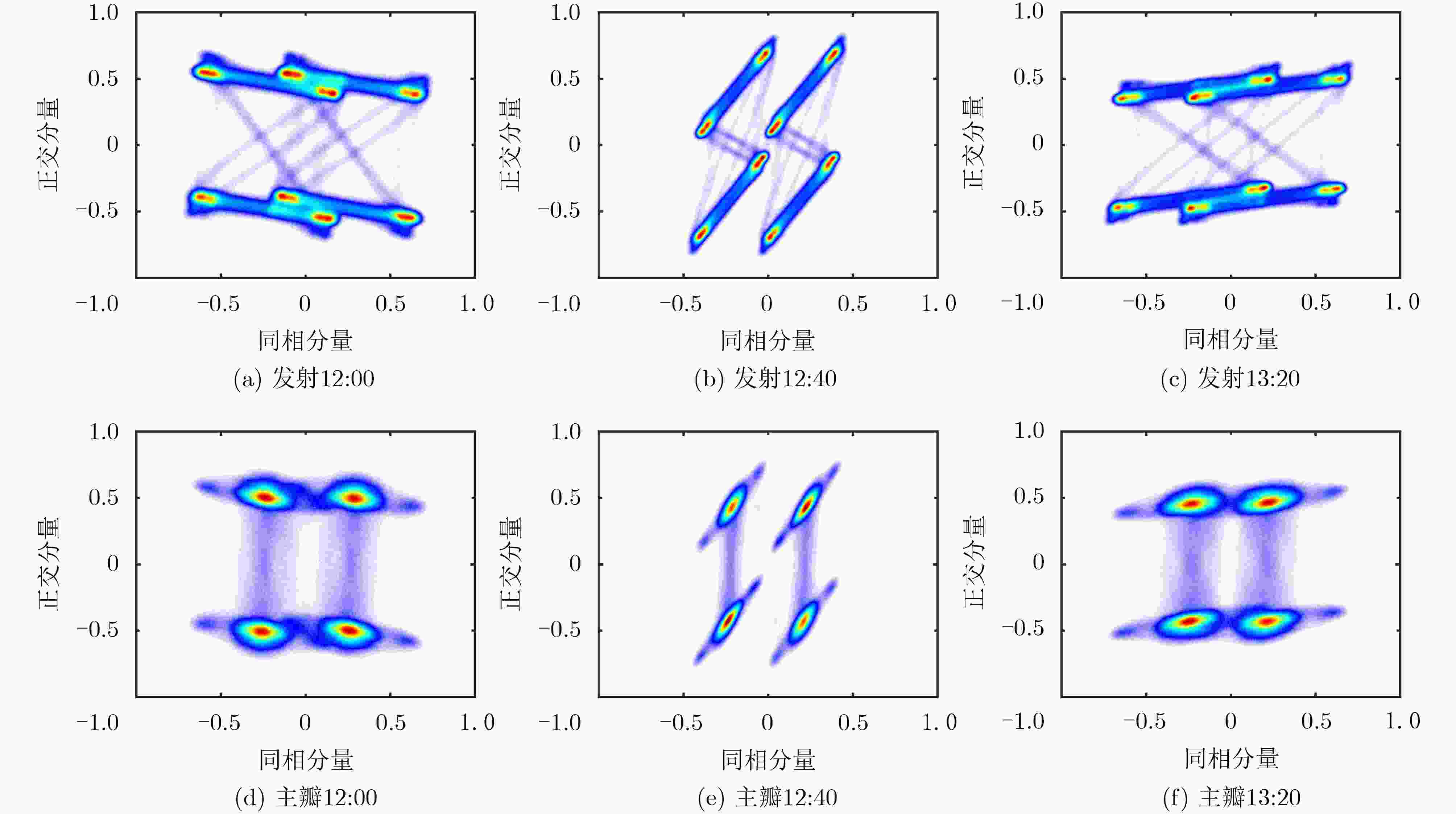
时间 星座点 12:00 12:20 12:40 13:00 13:20 幅值 A 0.57 0.53 0.49 0.48 0.49 B 0.56 0.53 0.49 0.46 0.48 C 0.56 0.53 0.49 0.47 0.47 D 0.57 0.52 0.48 0.48 0.48 相位 A 59.80 60.90 63.23 61.73 61.23 B 115.38 116.22 115.55 117.00 116.52 C 242.08 241.92 241.42 240.62 241.53 D 297.23 297.59 295.54 295.54 295.32 表 4 不同时刻L1频点各信号分量功率配比统计表
信号分量 L1Cd L1Cp L1C/A L1M 数据1 1.00 2.70 2.35 4.67 数据2 1:00 2.68 2.36 6.75 数据3 1:00 2.73 2.39 6.78 数据4 1:00 2.74 2.40 4.66 表 5 L1信号SCB统计表
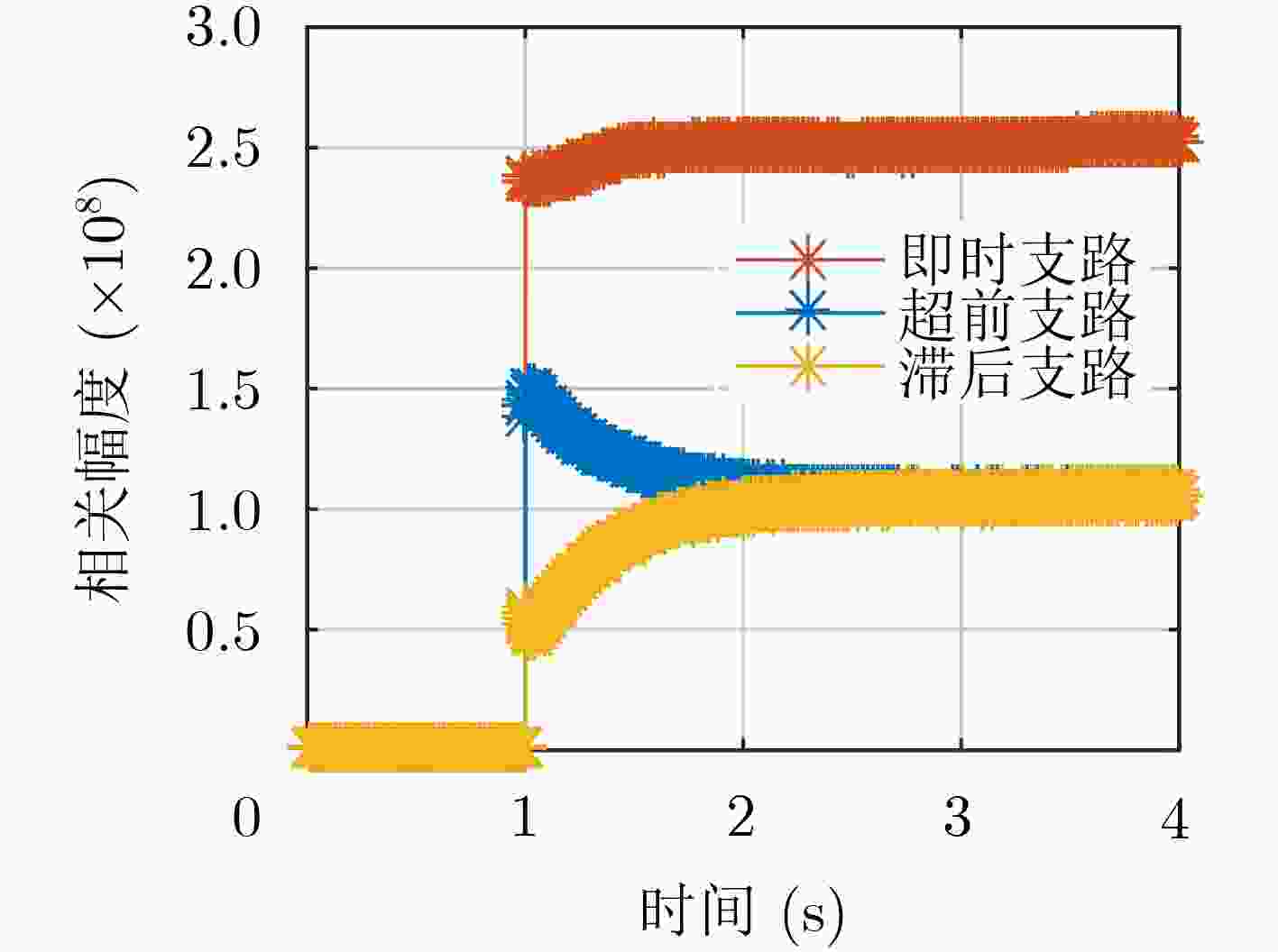
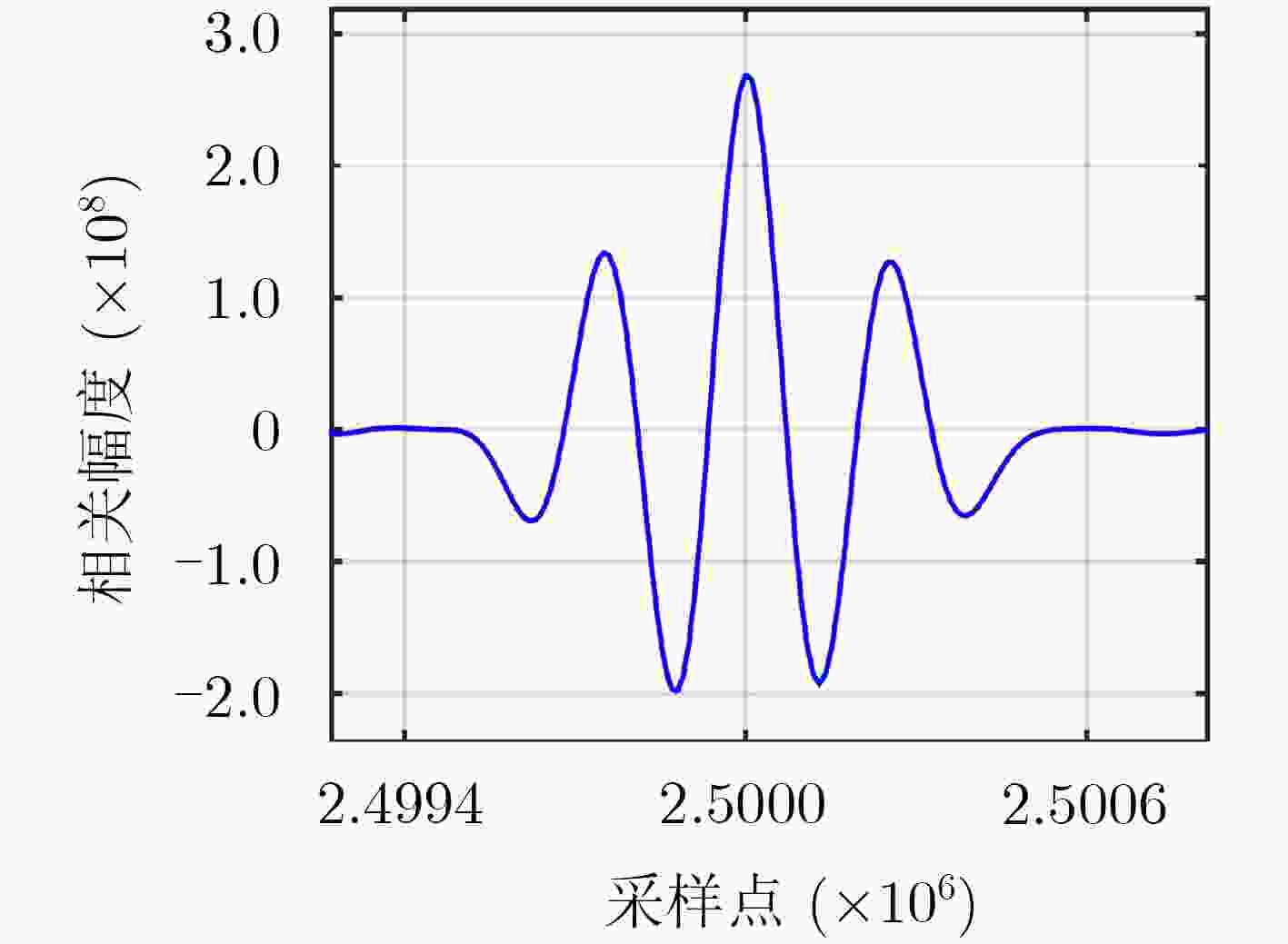
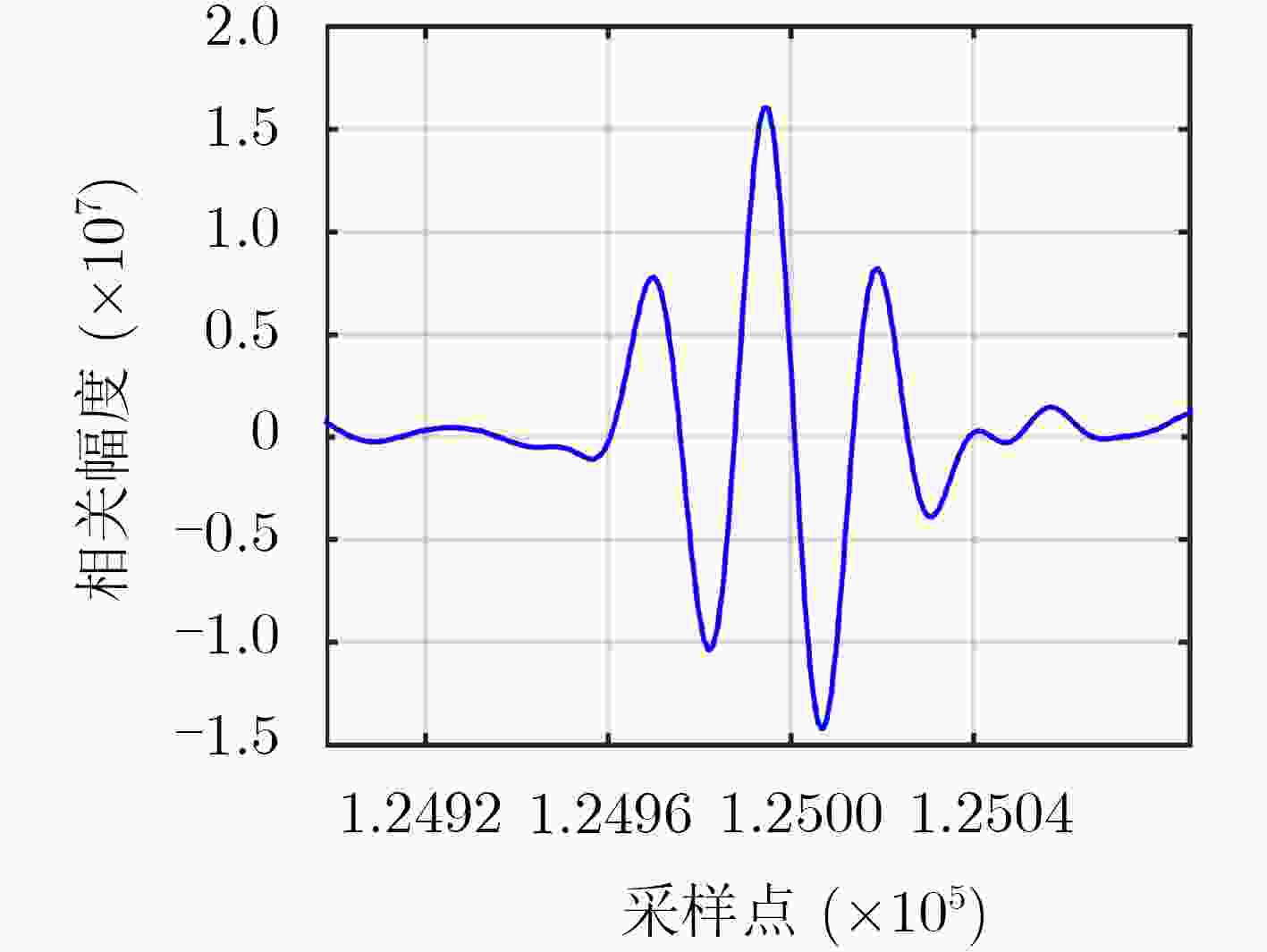
信号分量 L1C/A L1Cd L1Cp L1M 最大相关间隔区(chip) <0.5 <0.5 <0.06 <0.21 SCB (ns) –0.129 –0.135 1.271 0.058 -
[1] 谢钢. 全球导航卫星系统原理: GPS、格洛纳斯和伽利略系统[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013: 15–24.XIE Gang. Principles of GNSS: GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013: 15–24. [2] FAN Tiange, LIN V S, WANG G H, et al. Study of signal combining methodologies for future GPS flexible navigation payload (Part II)[C]. 2008 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Monterey, USA, 2008: 1079–1089. [3] Global Positioning System Directorate Systems Engineering & Integration. IS-GPS-200J NAVSTAR GPS space segment/navigation user segment interfaces[S]. 2018. [4] Global Positioning System Directorate Systems Engineering & Integration. IS-GPS-800E NAVSTAR GPS space segment/user segment L1C interface[S]. 2018. [5] MARQUIS W A and REIGH D L. The GPS block IIR and IIR-M broadcast L-band antenna panel: Its pattern and performance[J]. Navigation, 2015, 62(4): 329–347. doi: 10.1002/navi.123 [6] 贺成艳. GNSS空间信号质量评估方法研究及测距性能影响分析[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院国家授时中心, 2013.HE Chengyan. Research on evaluation methods of GNSS signal quality and the influence of GNSS signal on ranging performance[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National Time Service Center Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013. [7] 卢晓春, 周鸿伟. GNSS空间信号质量分析方法研究[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2010, 40(5): 528–533.LU Xiaochun and ZHOU Hongwei. Methods of analysis for GNSS signal quality[J]. Scientia Sinica:Physica,Mechanica &Astronomica, 2010, 40(5): 528–533. [8] 姚铮, 陆明泉. 新一代卫星导航系统信号设计原理与实现技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2016.YAO Zheng and LU Mingquan. Signal Design Principle and Implementation Technology of A New Generation of Satellite Navigation System[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2016. [9] THOELERT S, HAUSCHILD A, STEIGENBERGER P, et al.GPS IIR-M L1 transmit power redistribution: Analysis of GNSS receiver and high-gain antenna data[C]. The 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Portland, USA, 2017: 1589–1602. [10] 康立, 卢晓春, 王雪, 等. GPS L1频点授权信号质量评估[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 905–911. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170440KANG Li, LU Xiaochun, WANG Xue, et al. Authorized signals quality assessment on GPS L1[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 905–911. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170440 [11] YANG Dejin, RAO Yongnan, SHI Huihui, et al. Quality assessment of Galileo E1A signal[C]. China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Beijing, China, 2019: 1589–1602. [12] 卢晓春, 贺成艳, 王雪, 等. 卫星导航信号评估系统设计及信号性能评估[J]. 时间频率学报, 2016, 39(3): 225–246. doi: 10.13875/j.issn.1674-0637.2016-03-0225-22LU Xiaochun, HE Chengyan, WANG Xue, et al. Design of GNSS monitoring and assessment system and assessment of GNSS signal-in-space[J]. Journal of Time and Frequency, 2016, 39(3): 225–246. doi: 10.13875/j.issn.1674-0637.2016-03-0225-22 [13] SOELLNER M, KURZHALS C, HECHENBLAIKNER G, et al. GNSS offline signal quality assessment[C]. ION GNSS 2008, Institute of Navigation, Savannah, USA, 2008: 909–920. [14] HE Chengyan, GUO Ji, LU Xiaochun, et al. A new evil waveforms evaluating method for new BDS navigation signals[J]. GPS Solutions, 2018, 22(2): 37. doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0698-x -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
