Super-resolution Reconstruction Detection Method for DeepFake Hard Compressed Videos
-
摘要: 经典的深度伪造(DeepFake)视频检测方法一般使用卷积神经网络进行检测,但在强压缩深度伪造换脸视频数据集上表现较差,并会对真实数据做出大量误检测。针对这个问题,该文提出一种基于超分辨率重建的强压缩深度伪造视频检测方法。该方法基于深度神经网络检测模型,通过融入超分辨率重建技术,恢复强压缩视频所损失的空间与时间信息,进而提升对强压缩视频的检测准确率。使用FaceForensics++及DFDC数据集进行实验,针对强压缩的深度伪造视频,该方法较ResNet50提高了单帧以及视频的测试准确率,有效缓解强压缩真实视频的误检测问题。Abstract: The forensics methods of DeepFake video generally use convolution neural networks. However, these methods perform poorly on hard compressed DeepFake datasets and make a large number of false detections on real data. To solve the problem above, a method of hard compressed DeepFake video detection based on deep neural network model is proposed, which improves the detection accuracy of hard compressed video by incorporating super-resolution reconstruction technology and recovering the loss of the spatial and temporal information during hard compression. Experiments are performed with the FaceForensics++ Datasets and DFDC (the DeepFake Detection Challenge) Datasets for hard compressed DeepFake video, which improve the test accuracy of single frame and video compared to ResNet50, and effectively alleviate the problem of false detection of real video with hard compression.
-
表 1 负样本生成的伪代码
输入:图像路径path,图像标签$L$,真实图像${i_r}$ 输出:伪造图像${i_f}$ 参数:随机数${r_1}$, ${r_2}$,转换矩阵${m_t}$,特征点坐标${p_{68}}$。 (1) begin (2) for ${i_r}$ in path: (3) ${i_r}$=dlib.align(${i_r}$) //人脸对齐 (4) if $L$= 1: (5) if ${r_1}$ < 0.5 (6) face = cv2.warpAffine(${i_r}$, ${m_t}$* size, (size,
size)) //仿射变换(7) face = cv2.GaussianBlur(face, (5, 5)) //高斯
模糊(8) if ${r_2}$ < 0.5 (9) part_mask = dlib.mask(${i_r}$, ${p_{68}}$) //特征
点标定(10) ${i_f}$ =${i_r}$ * (1 - part_mask) +${i_f}$ *
part_mask(11) ${i_r}$ = ${i_f}$ (12) $L$ = 0 (13) else: (14) continue (15) return ${i_r}$ (16) end 表 2 改进的ResNet50结构参数
网络层 conv_1 conv_2 conv_3 conv_4 conv_5 fc 输出大小 112×112 56×56 28×28 14×14 7×7 1×1 改进后的ResNet50 7×7, 64, stride2 3×3 maxpool,stride2 $ \left[\begin{array}{c}1\times 1, \\ 3\times 3, \\ 1\times 1, \end{array}\begin{array}{c}64\\ 64\\ 256\end{array}\right]\times 3$ $ \left[\begin{array}{c}1\times 1, \\ 3\times 3, \\ 1\times 1, \end{array}\begin{array}{c}256\\ 256\\ 1024\end{array}\right]\times 6$ $ \left[\begin{array}{c}1\times 1, \\ 3\times 3, \\ 1\times 1, \end{array}\begin{array}{c}256\\ 256\\ 1024\end{array}\right]\times 6$ $ \left[\begin{array}{c}1\times 1, \\ 3\times 3, \\ 1\times 1, \end{array}\begin{array}{c}512\\ 512\\ 2048\end{array}\right]\times 3$ average pool, softmax+tanh -
[1] 陈宇飞, 沈超, 王骞, 等. 人工智能系统安全与隐私风险[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(10): 2135–2150. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190415CHEN Yufei, SHEN Chao, WANG Qian, et al. Security and privacy risks in artificial intelligence systems[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(10): 2135–2150. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190415 [2] Faceswap: Deepfakes software for all[EB/OL]. https://github.com/deepfakes/faceswap, 2018. [3] KORSHUNOVA I, SHI Wenzhe, DAMBRE J, et al. Fast face-swap using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3697–3705. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.397. [4] Faceswap-GAN[EB/OL]. https://github.com/shaoanlu/faceswap-GAN, 2019. [5] Keras-VGGFace: VGGFace implementation with Keras framework[EB/OL]. https://github.com/rcmalli/keras-vggface, 2019. [6] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [7] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [8] ZHOU Peng, HAN Xintong, MORARIU V I, et al. Two-Stream neural networks for tampered face detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1831–1839. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.229. [9] AFCHAR D, NOZICK V, YAMAGISHI J, et al. MesoNet: A compact facial video forgery detection network[C]. 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Hong Kong, China, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/WIFS.2018.8630761. [10] MATERN F, RIESS C, and STAMMINGER M. Exploiting visual artifacts to expose deepfakes and face manipulations[C]. 2019 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Waikoloa Village, USA, 2019: 83–92. doi: 10.1109/WACVW.2019.00020. [11] 胡永健, 高逸飞, 刘琲贝, 等. 基于图像分割网络的深度假脸视频篡改检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 162–170. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200077HU Yongjian, GAO Yifei, LIU Beibei, et al. Deepfake videos detection based on image segmentation with deep neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 162–170. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200077 [12] RÖSSLER A, COZZOLINO D, VERDOLIVA L, et al. Faceforensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2019.00009. [13] LI Yuezun and LYU Siwei. Exposing deepFake videos by detecting face warping artifacts[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 46–52. [14] SCHWARZ H, MARPE D, and WIEGAND T. Overview of the scalable video coding extension of the H. 264/AVC standard[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2007, 17(9): 1103–1120. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2007.905532 [15] PARK S C, PARK M K, and KANG M G. Super-resolution image reconstruction: a technical overview[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2003, 20(3): 21–36. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2003.1203207 [16] JO Y, Oh S W, KANG J, et al. Deep video super-resolution network using dynamic upsampling filters without explicit motion compensation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3224–3232. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00340. [17] NAH S, KIM T H, and LEE K M. Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 257–265. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.35. [18] RÖSSLER A, COZZOLINO D, VERDOLIVA L, et al. FaceForensics: A large-scale video dataset for forgery detection in human faces[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09179, 2018. [19] NICHOLAS D, ANDREW G, PER K, et al. Deepfakes detection dataset by Google & jigsaw[EB/OL]. 2019. https://ai.googleblog.com/2019/09/contributing-data-to-deepfake-detection.html. [20] LIU Ziwei, LUO Ping, WANG Xiaogang, et al. Deep learning face attributes in the wild[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, USA, 2015: 3730–3738. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.425. [21] SHRIVASTAVA A, GUPTA A, and GIRSHICK R. Training Region-Based object detectors with online hard example mining[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 761–769. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.89. -





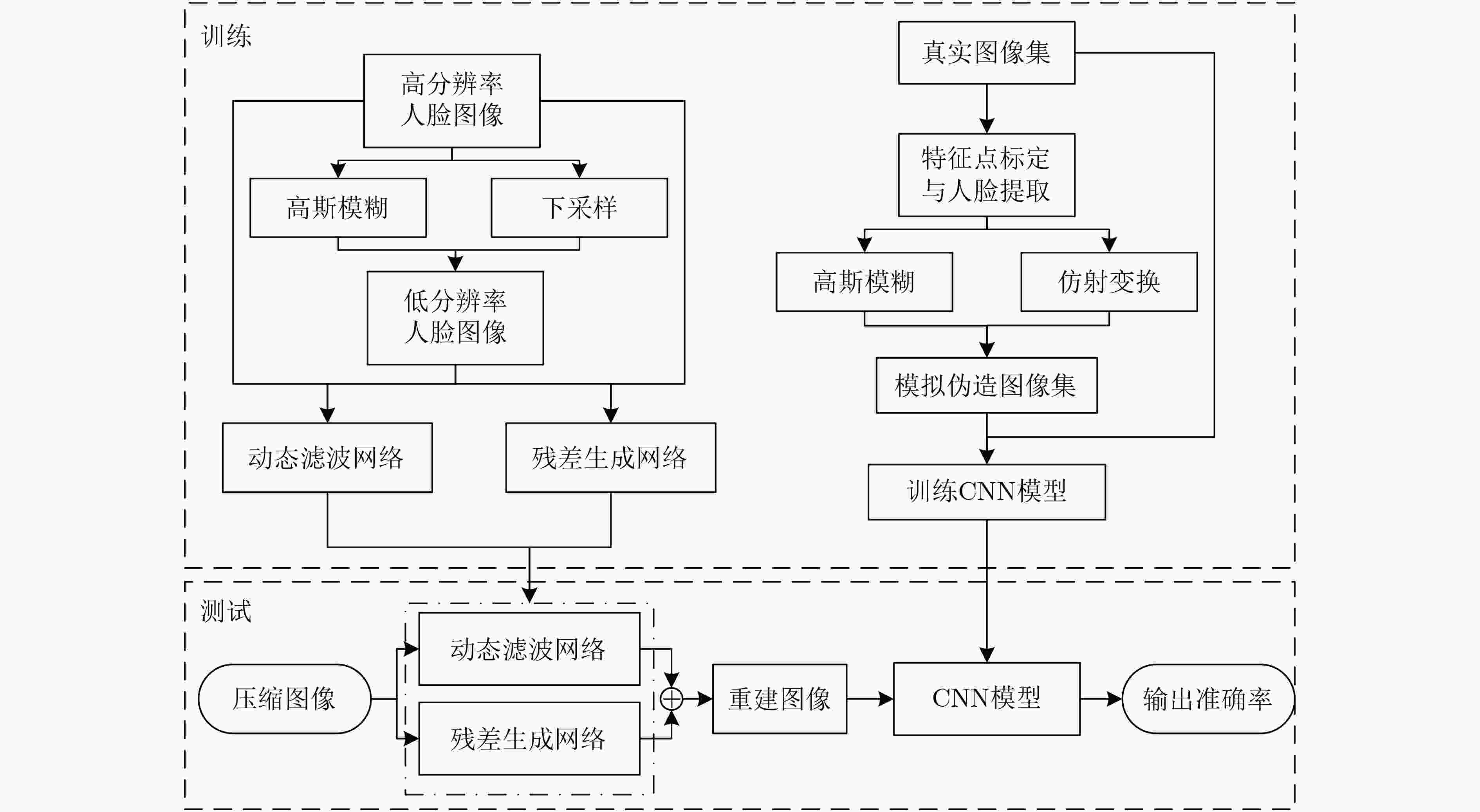
 下载:
下载:
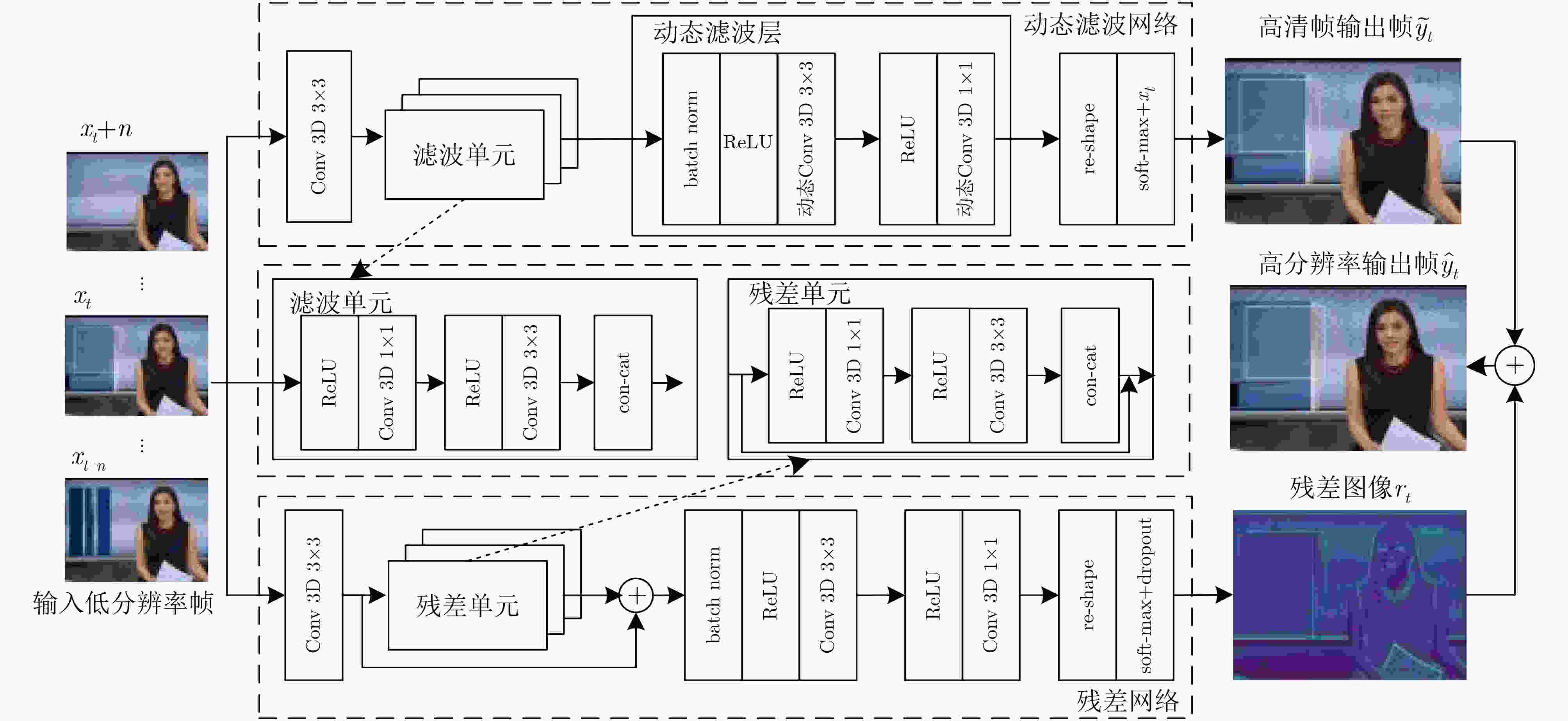
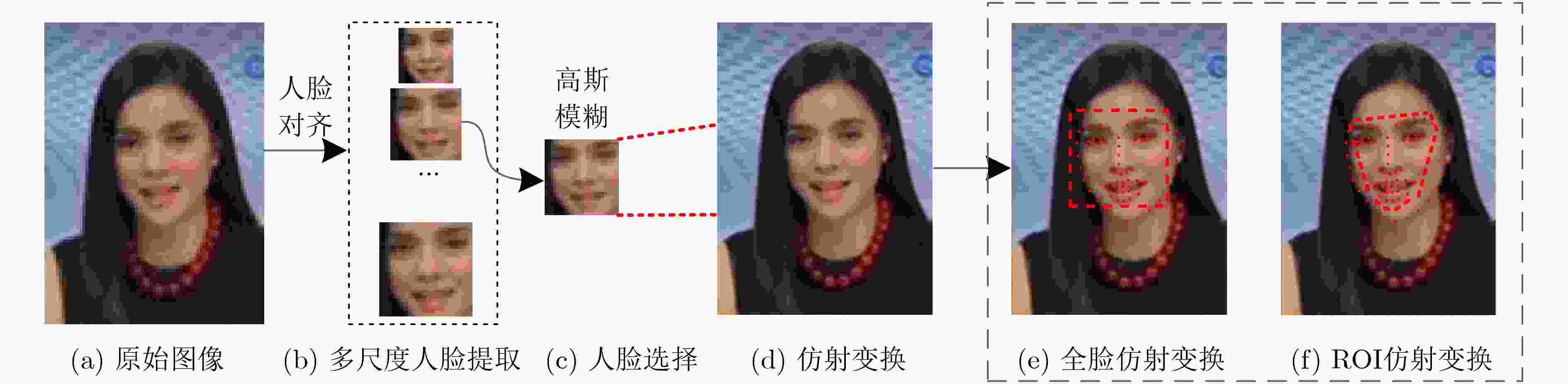
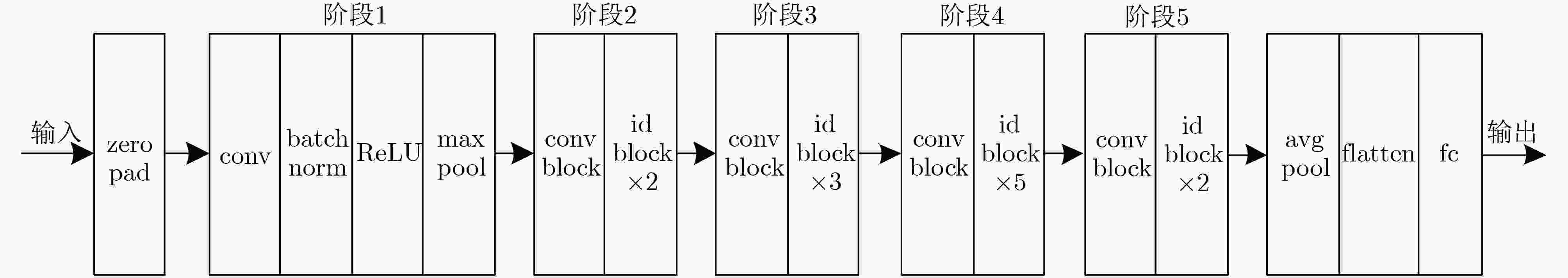
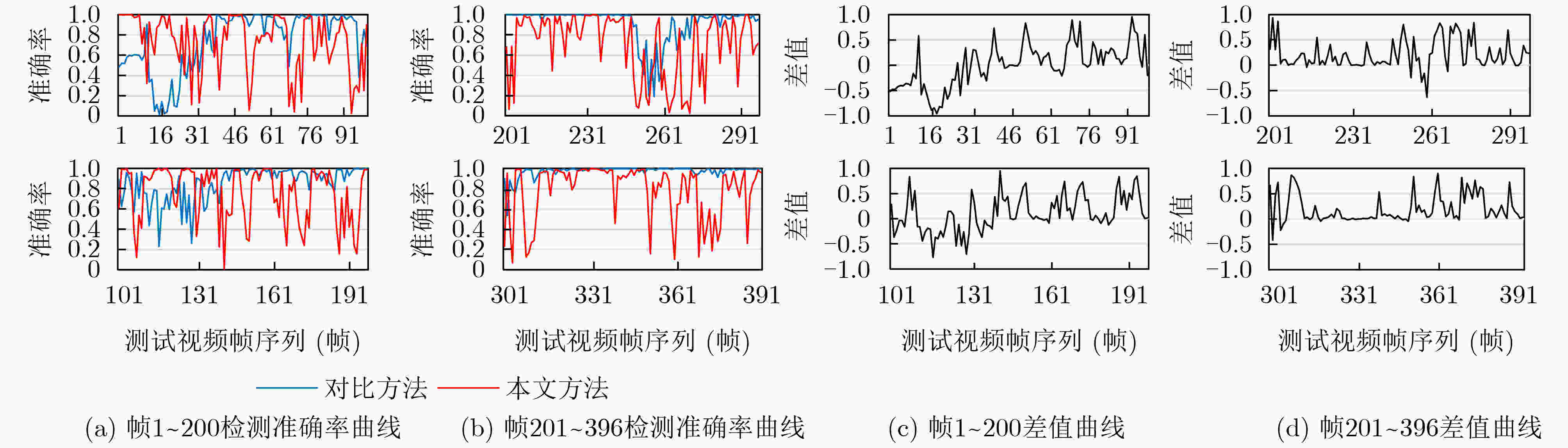
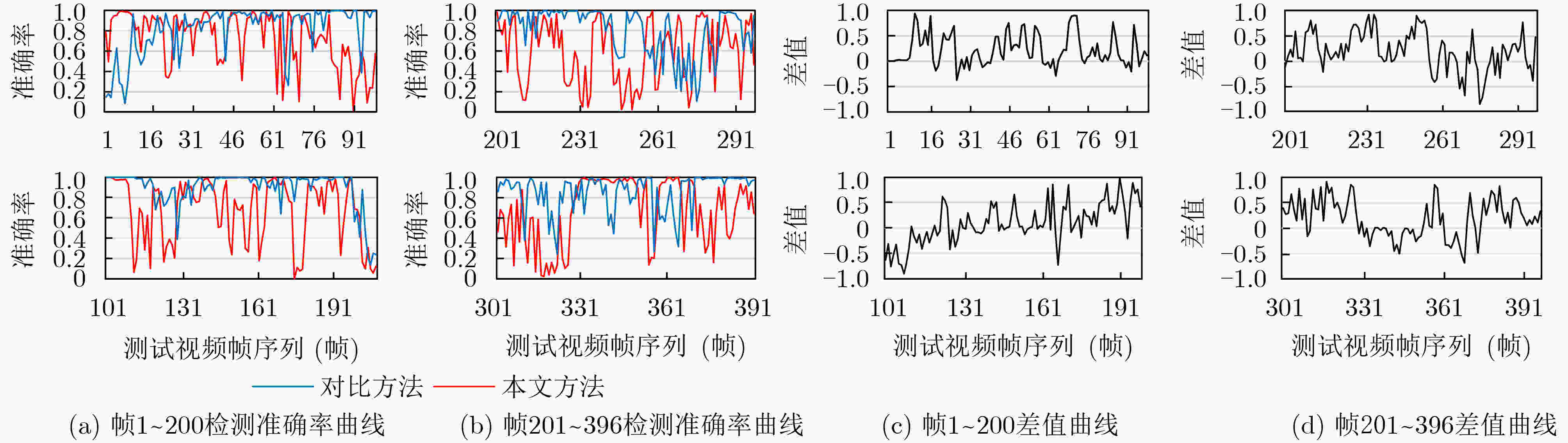
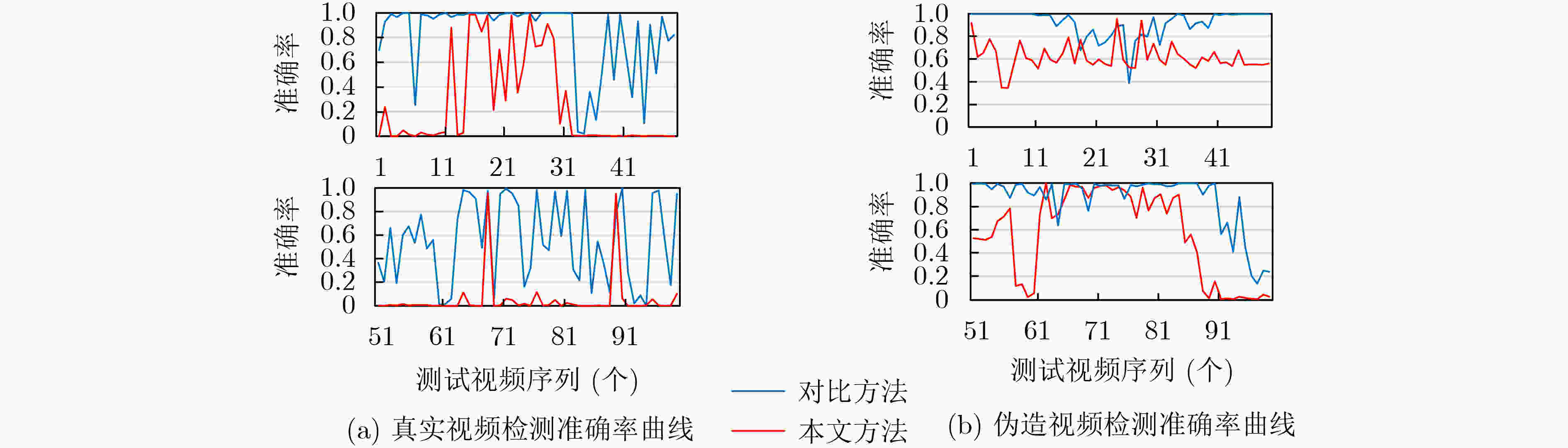
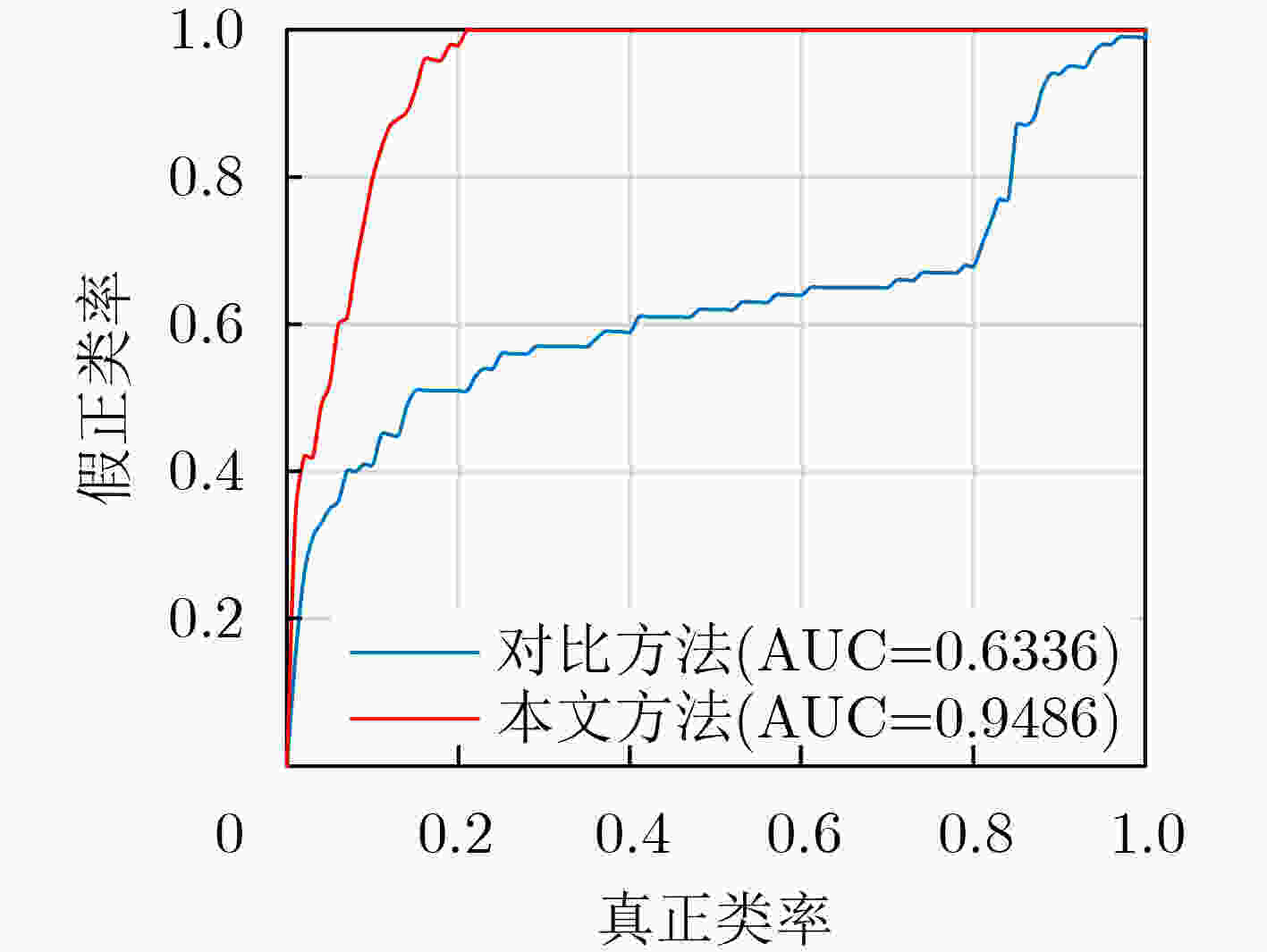


 下载:
下载:
