Improved Design of Constant Power Consumption Circuit Based on Differential Pass-transistor Precharge Logic
-
摘要: 通过分析差分传输管预充电逻辑(DP2L)的电路结构,发现该电路还无法达到完全的功耗恒定特性,仍然存在被功耗攻击的风险。针对该问题,该文对DP2L的电路结构进行改进,并用Hspice对改进前后的电路进行模拟仿真测试。实验表明:改进后的DP2L电路结构具有更好的功耗恒定特性,更能满足该逻辑电路的设计要求。
-
关键词:
- 功耗攻击 /
- 功耗恒定 /
- 双轨预充电逻辑 /
- 差分传输管预充电逻辑
Abstract: By analyzing the circuit structure of Differential Pass-transistor Precharge Logic (DP2L), it is found that the circuit can not achieve the complete constant power consumption, and there is still a risk of being attacked by power attack. To solve this problem, the circuit structure of DP2L is improved by this paper, and the circuits before and after the improvement are simulated using Hspice. The experimental results show that the improved DP2L circuit structure has better characteristics of constant power consumption and can better meet the design requirements of the logic circuit. -
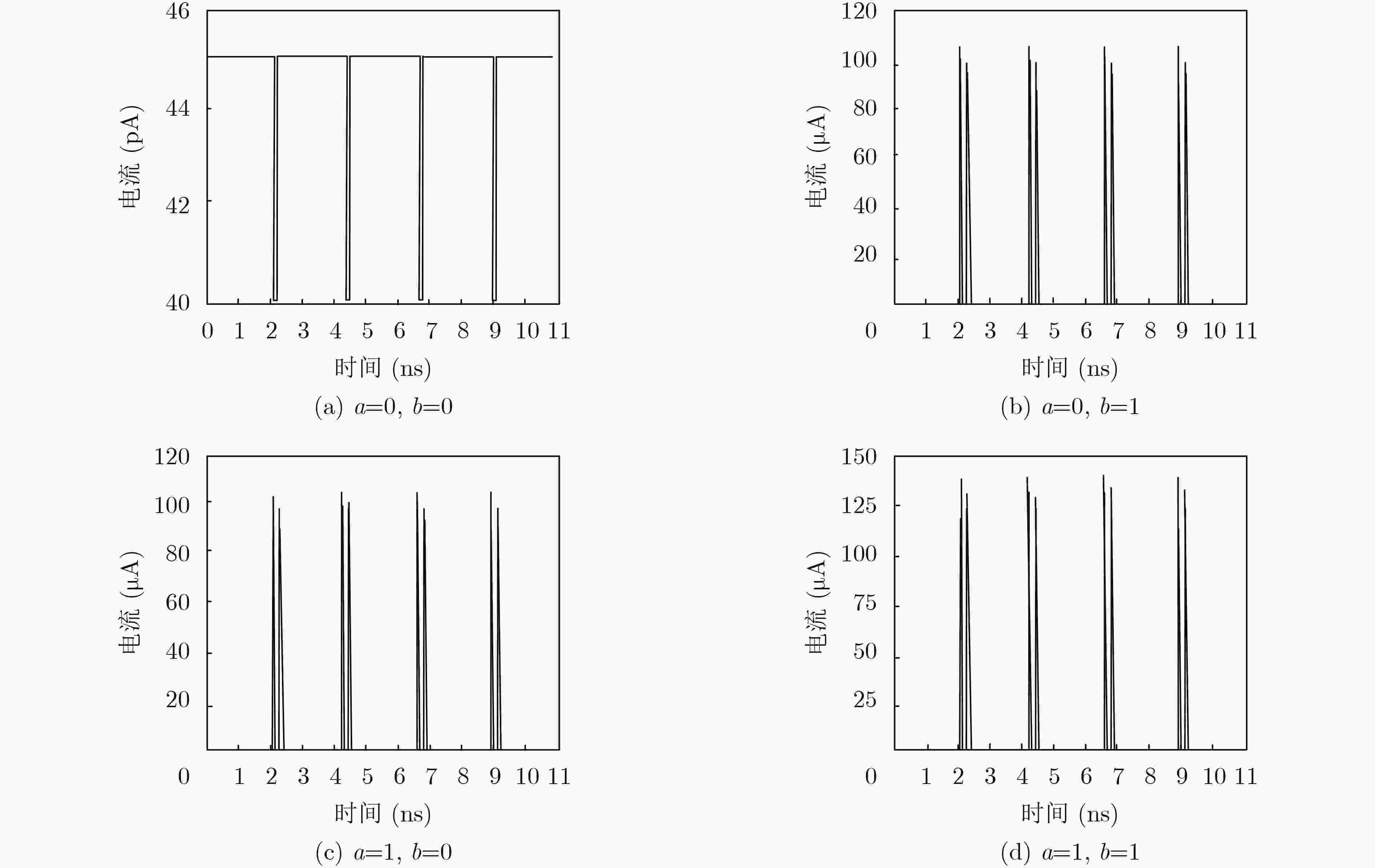
表 1 改进前DP2L单轨电路相关参数
输入条件 $a$=0, $b$=0 $a$=0, $b$=1 $a$=1, $b$=0 $a$=1, $b$=1 “0→1”翻转电流(μA) / 48.86 87.82 62.12 “1→0”翻转电流(μA) / 58.17 38.75 97.74 NED(%) 33.05 表 2 改进后DP2L单轨电路相关参数
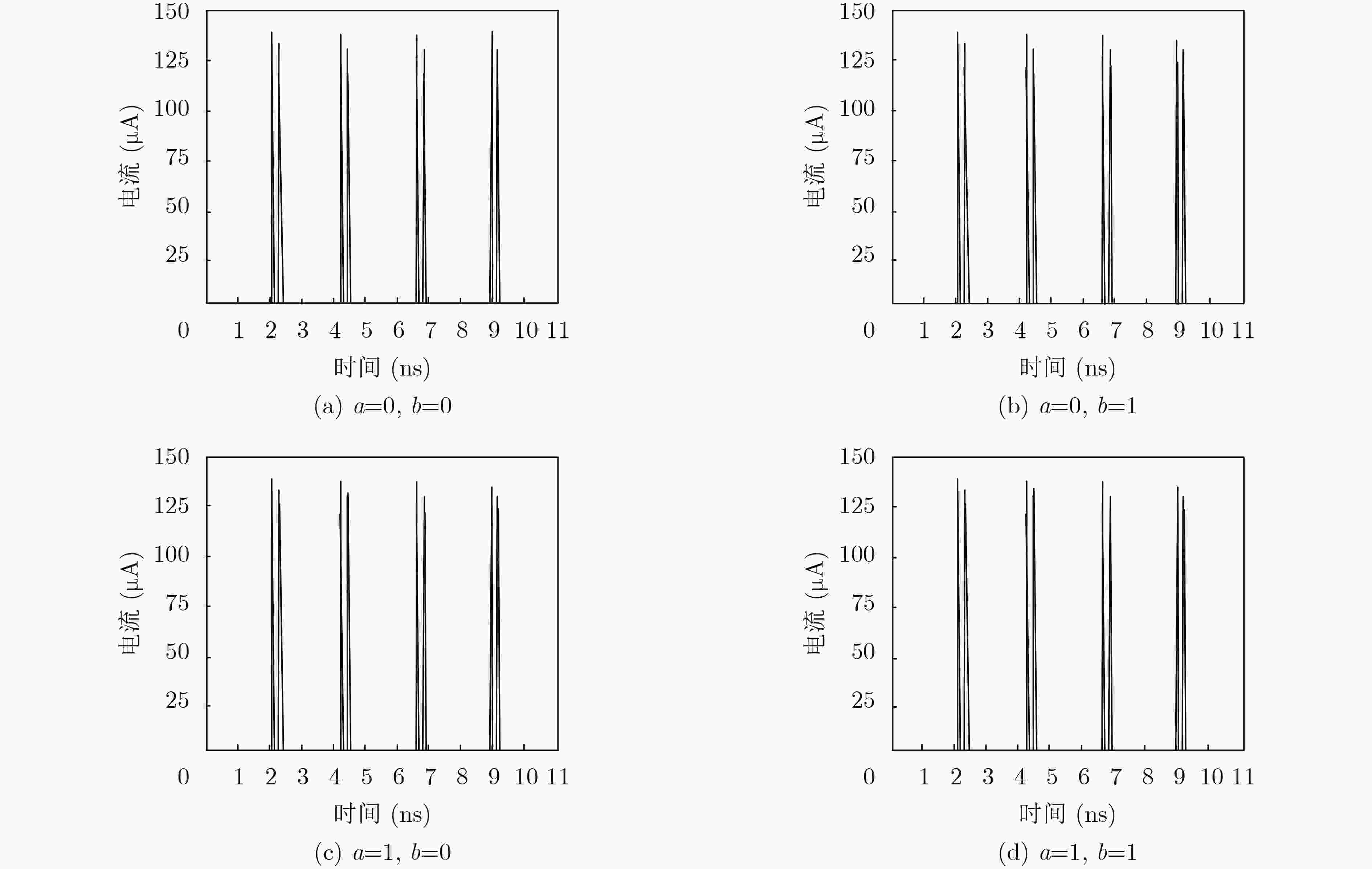
输入条件 $a$=0, $b$=0 $a$=0, $b$=1 $a$=1, $b$=0 $a$=1, $b$=1 “0→1”翻转电流(μA) / 108.32 107.65 140.18 “1→0”翻转电流(μA) / 97.96 98.31 136.58 NED(%) 25.58 表 3 改进后DP2L双轨电路相关参数
输入条件 $a$=0, $b$=0 $a$=0, $b$=1 $a$=1, $b$=0 $a$=1, $b$=1 “0→1”翻转电流(μA) 139.12 139.01 139.67 139.51 “1→0”翻转电流(μA) 136.73 136.51 136.95 136.82 NED(%) 0.40 表 4 同类型逻辑实现的“或”门标准化能量偏差对比
逻辑电路 WDDL 改进前DP2L双轨电路 LBDL 改进后DP2L双轨电路 NED(%) 11.50 5.36 3.23 0.40 -
[1] 黄海, 冯新新, 刘红雨, 等. 基于随机加法链的高级加密标准抗侧信道攻击对策[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 348–354. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171211HUANG Hai, FENG Xinxin, LIU Hongyu, et al. Random addition-chain based countermeasure against side-channel attack for advanced encryption standard[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 348–354. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171211 [2] 陈华, 习伟, 范丽敏, 等. 密码产品的侧信道分析与评估[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1836–1845. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190853CHEN Hua, XI Wei, FAN Limin, et al. Side channel analysis and evaluation on cryptographic products[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1836–1845. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190853 [3] UTYAMISHEV D and PARTIN-VAISBAND I. Real-time detection of power analysis attacks by machine learning of power supply variations on-chip[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2020, 39(1): 45–55. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2018.2883971 [4] ASHOK P and VETTUVANAM SOMASUNDARAM K B. Charge balancing symmetric pre-resolve adiabatic logic against power analysis attacks[J]. IET Information Security, 2019, 13(6): 692–702. doi: 10.1049/iet-ifs.2018.5136 [5] MESSERGES T S, DABBISH E A, and SLOAN R H. Examining smart-card security under the threat of power analysis attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2002, 51(5): 541–552. doi: 10.1109/TC.2002.1004593 [6] SENGUPTA A, MAZUMDAR B, YASIN M, et al. Logic locking with provable security against power analysis attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2020, 39(4): 766–778. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2019.2897699 [7] GOHIL N N and VEMURI R R. Automated synthesis of differential power attack resistant integrated circuits[C]. 2019 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference, Dayton, USA, 2019: 204–211. doi: 10.1109/NAECON46414.2019.9057882. [8] ZHENG Zhen and YAN Yingjian. Design of a power randomization circuit for block ciphers[C]. The IEEE 4th International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Microsystems, Beijing, China, 2019: 6–11. doi: 10.1109/ICICM48536.2019.8977152. [9] KUMAR S D and THAPLIYAL H. Exploration of non-volatile MTJ/CMOS circuits for DPA-resistant embedded hardware[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2019, 55(12): 3401308. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2019.2943053 [10] HWANG D D, TIRI K, HODJAT A, et al. AES-based security coprocessor IC in 0.18-μm CMOS with resistance to differential power analysis side-channel attacks[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(4): 781–792. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.870913 [11] AVITAL M, LEVI I, KEREN O, et al. CMOS based gates for blurring power information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2016, 63(7): 1033–1042. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2546387 [12] TIRI K, AKMAL M, and VERBAUWHEDE I. A dynamic and differential CMOS logic with signal independent power consumption to withstand differential power analysis on smart cards[C]. The 28th European Solid-state Circuits Conference, Florence, Italy, 2002: 403–406. [13] TIRI K and VERBAUWHEDE I. A logic level design methodology for a secure DPA resistant ASIC or FPGA implementation[C]. The Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, Paris, France, 2004: 246–251. doi: 10.1109/DATE.2004.1268856. [14] 钱浩宇, 汪鹏君, 丁代鲁, 等. 基于SABL的防御差分功耗分析移位寄存器设计[J]. 电子技术应用, 2017, 43(2): 40–43. doi: 10.16157/j.issn.0258-7998.2017.02.008QIAN Haoyu, WANG Pengjun, DING Dailu, et al. Design of resistant differential power analysis shift register based on SABL[J]. Application of Electronic Technique, 2017, 43(2): 40–43. doi: 10.16157/j.issn.0258-7998.2017.02.008 [15] BUCCI M, GIANCANE L, LUZZI R, et al. A flip-flop for the DPA resistant three-phase dual-rail pre-charge logic family[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2012, 20(11): 2128–2132. doi: 10.1109/tvlsi.2011.2165862 [16] YU Weize and WEN Yiming. Leveraging balanced logic gates as strong PUFs for securing IoT against malicious attacks[J]. Journal of Electronic Testing, 2019, 35(6): 853–865. doi: 10.1007/s10836-019-05833-9 [17] BELLIZIA D, SCOTTI G, and TRIFILETTI A. TEL logic style as a countermeasure against side-channel attacks: Secure cells library in 65nm CMOS and experimental results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2018, 65(11): 3874–3884. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2861738 [18] 乐大珩. 抗功耗攻击的密码芯片电路级防护关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011.YUE Daheng. Research on circuit-level design against power analysis attack for cryptographic chip[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011. [19] 王晨旭. 密码芯片抗功耗攻击技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.WANG Chenxu. Research on the power analysis resistant technology of cryptographic IC[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. [20] 乐大珩, 李少青, 张民选. 基于LBDL逻辑的抗DPA攻击电路设计方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2009, 31(6): 18–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2009.06.004YUE Daheng, LI Shaoqing, and ZHANG Minxuan. An LBDL based VLSI design method to counteract DPA attacks[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2009, 31(6): 18–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2009.06.004 -





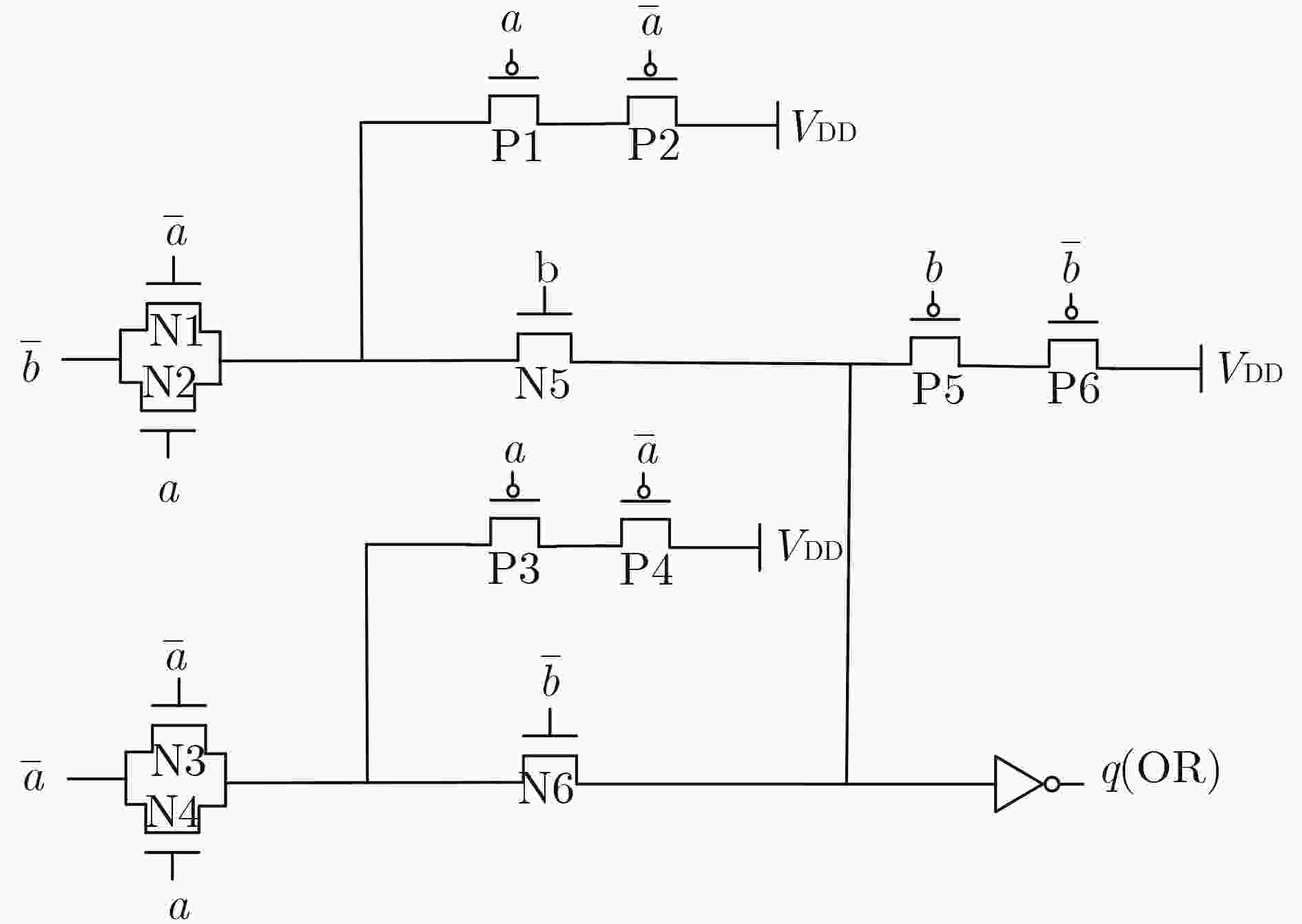
 下载:
下载:
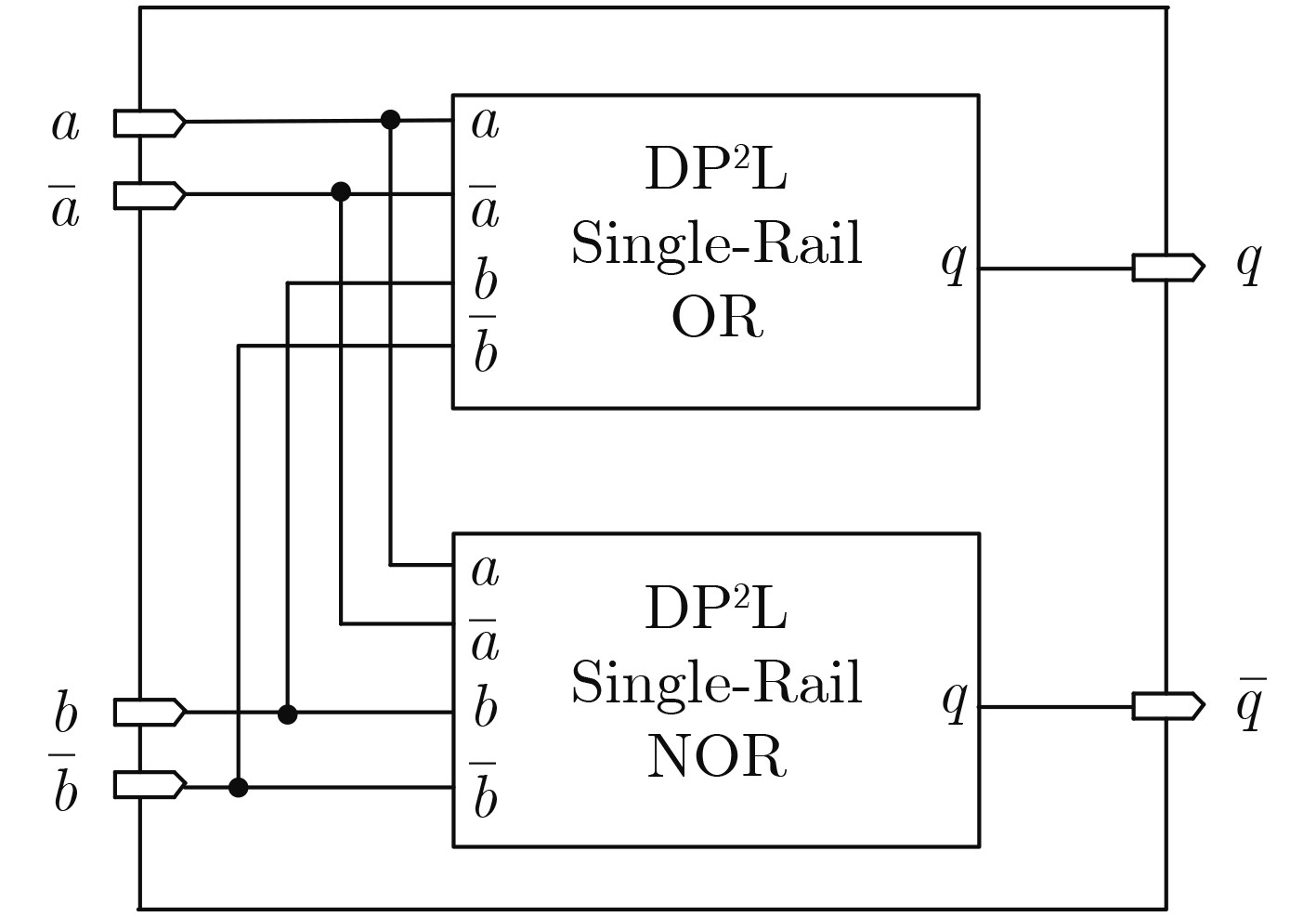
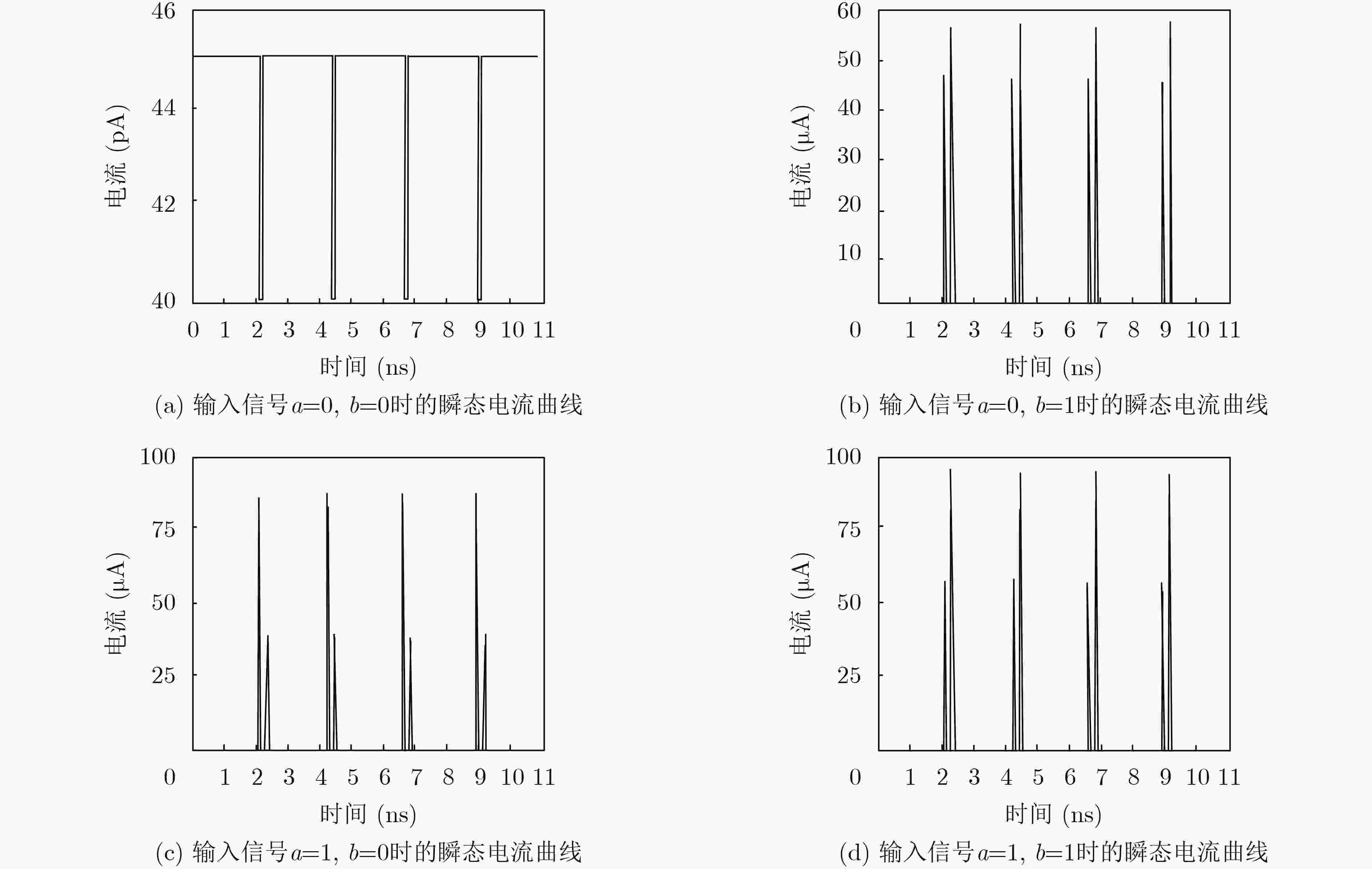
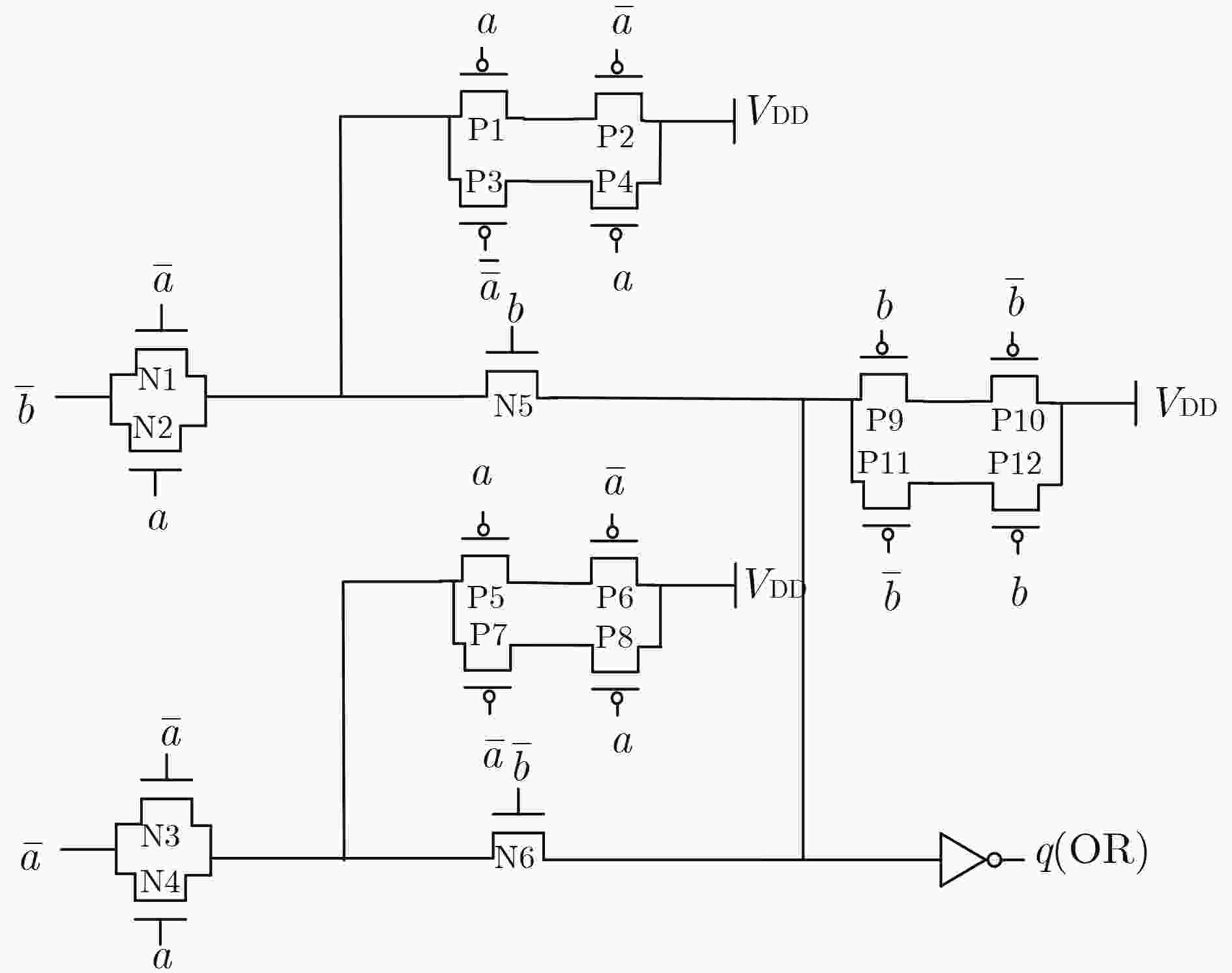


 下载:
下载:
