Coalition Structure Generation Constrained by Trust and Utility Relationship
-
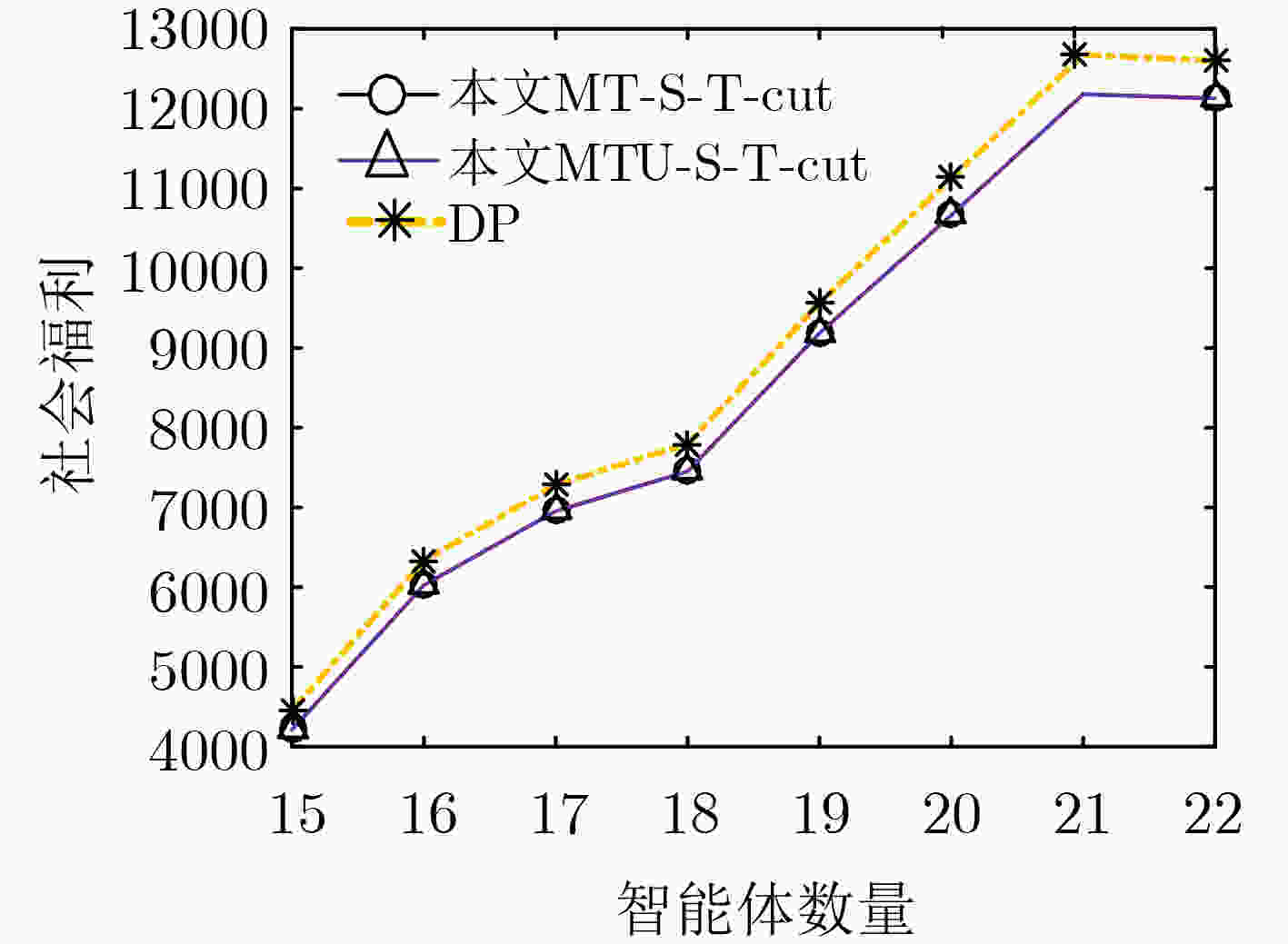
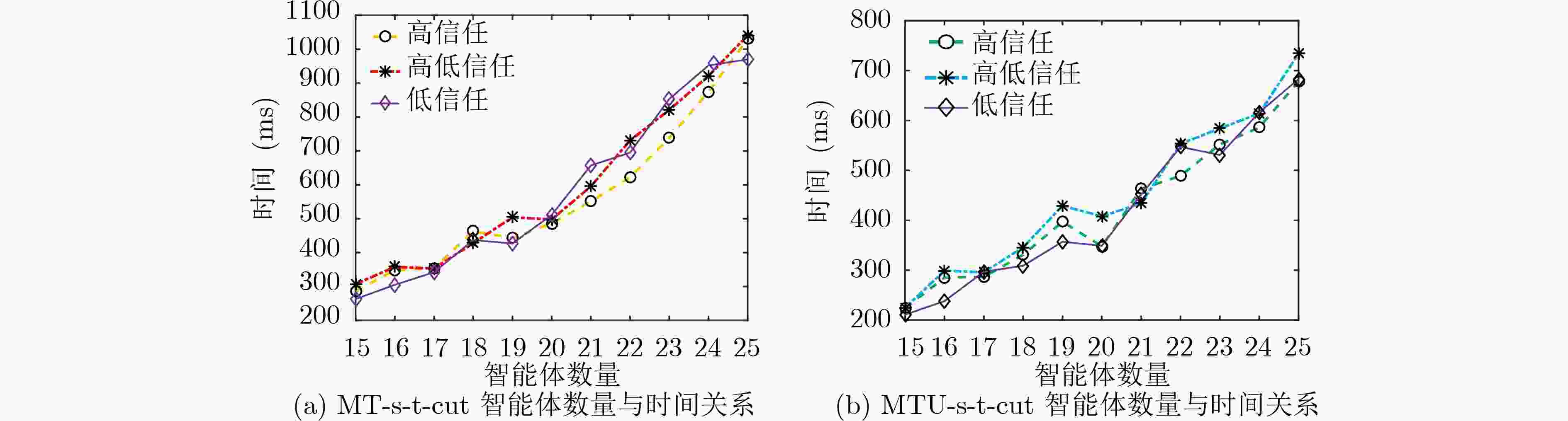
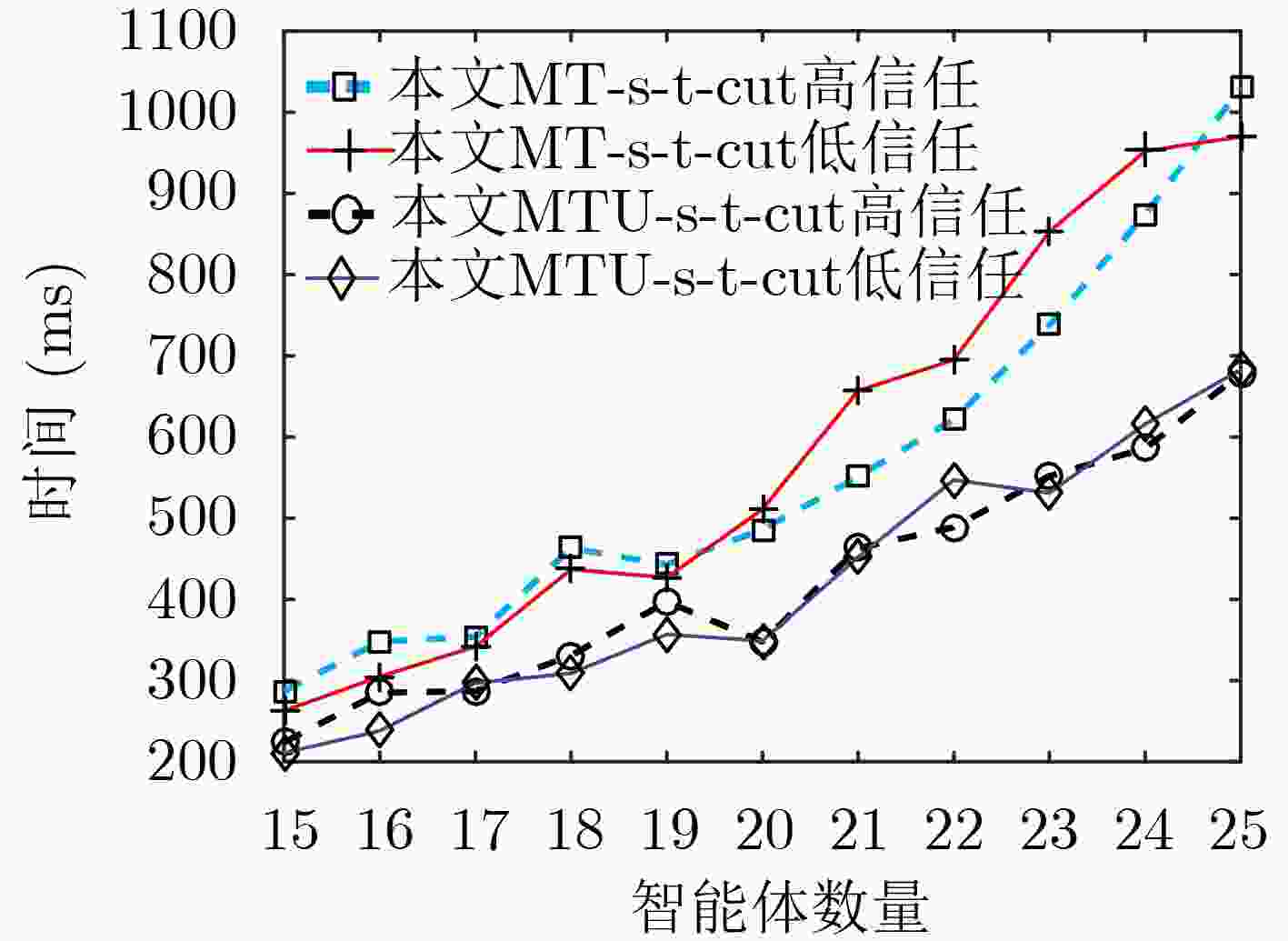
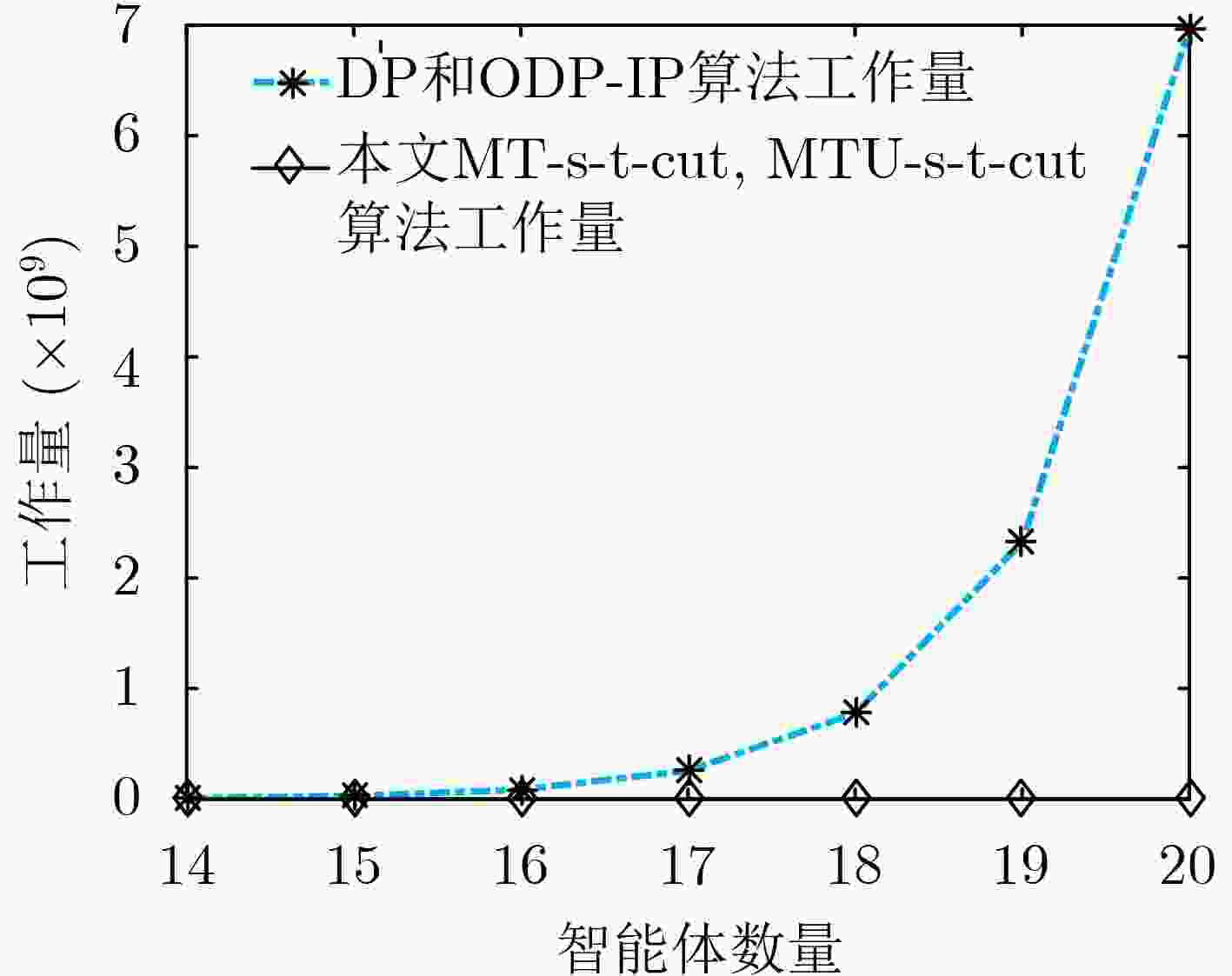
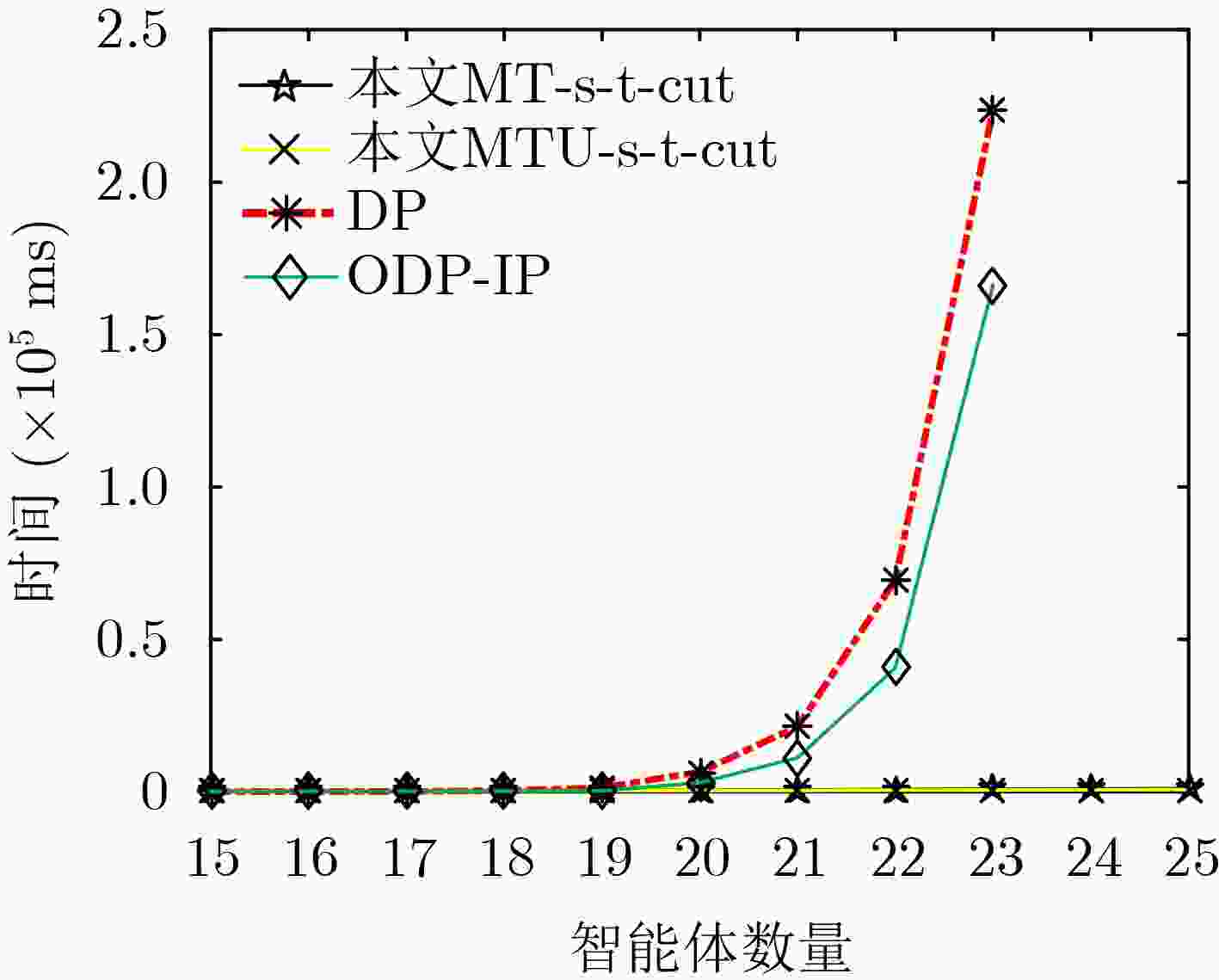
摘要: 联盟结构生成是分布式人工智能的重要研究内容,一般仅依据智能体效用生成任意数量的联盟,这导致最优联盟结构生成的计算复杂度NP难。实际上,信任是合作的基础,信任关系对最终效用有直接的影响,应该综合考虑信任和效用关系。针对以上问题,该文扩展效用约束为信任和效用约束,用信任和效用二元组表示,以此作为联盟结构生成的依据。借鉴图割的s-t-cut算法,研究了基于信任和效用关系的联盟结构生成,在保证智能体个体理性和联盟稳定(无块)的前提下,使用信任和效用关系对网络进行切割,从而形成联盟。由此,该文提出了两种多项式时间的精确算法:信任关系约束下的MT-s-t-cut算法和信任效用关系约束下的MTU-s-t-cut算法,这两种算法均能够在多项式时间内得到最优联盟结构。仿真实验验证了信任关系影响所形成的联盟结构,社会整体效用随智能体数量的增加而增加,并且算法的运行时间远小于动态规划法(DP)和ODP-IP算法。Abstract: The coalition structure generation is an important domain of distributed artificial intelligence. Most coalition formation models are only based on the utility, and any number of coalitions are permitted, which makes it be NP complexity difficult to generate the optimal coalition structure. Actually, Trust is the base of cooperation and has direct effect on the final utility. So, not only utility but also trust relationship should be seriously considered. To this end, the utility constraint is extended to trust and utility constraint, a two-tuples is used to represent utility and trust, which is the base of coalition structure generation. Inspired by the classic s-t-cut algorithm for graph cut, coalition structure generation constrained by trust and utility relationship is investigated. Assuming that individual rationality of agents and the stability of coalition (there is no block) is satisfied, the network is cut by the relationship of utility and trust to formation coalitions. The proposed algorithms of coalition structure generation named MT-s-t-cut and MTU-s-t-cut (Trust s-t-cut) can output the optimal coalition structure in polynomial time. The results of simulated experiments show that the social utility increases with the number of agents, and the running time of the algorithms are far less than that of Dynamic Programming (DP) and Optimal Dynamic Programming and Integer Partition (ODP-IP) algorithms.
-
表 1 算法1:MT-s-t-cut算法
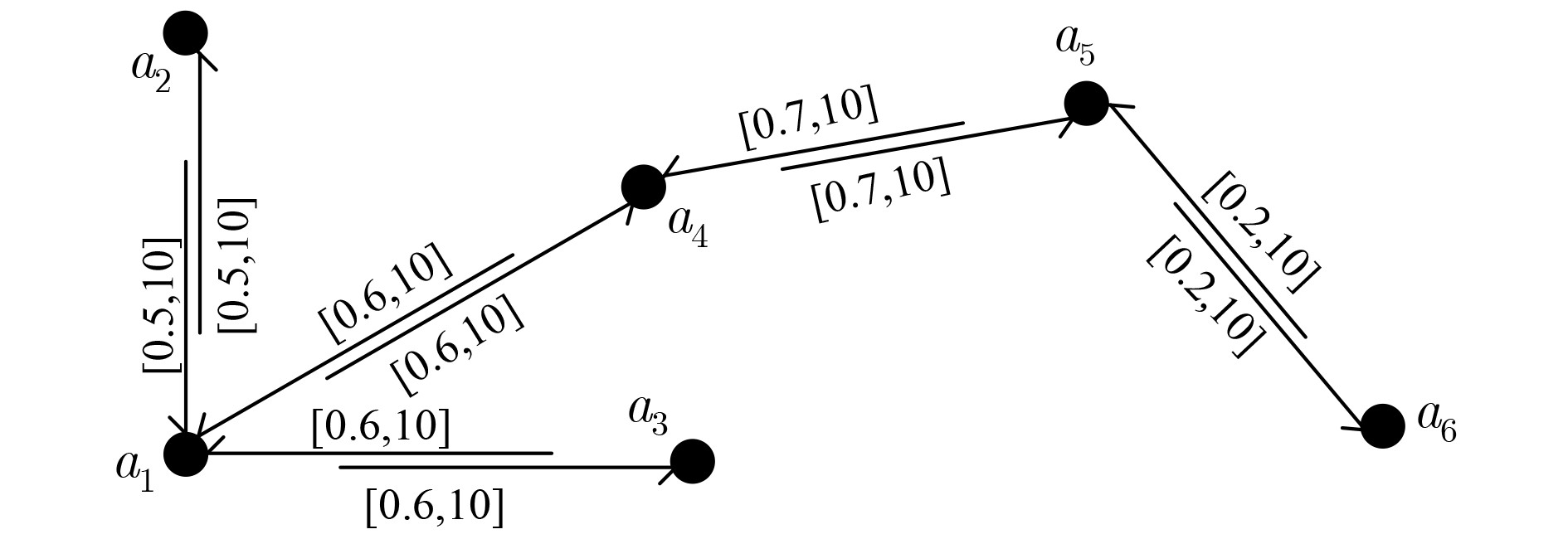
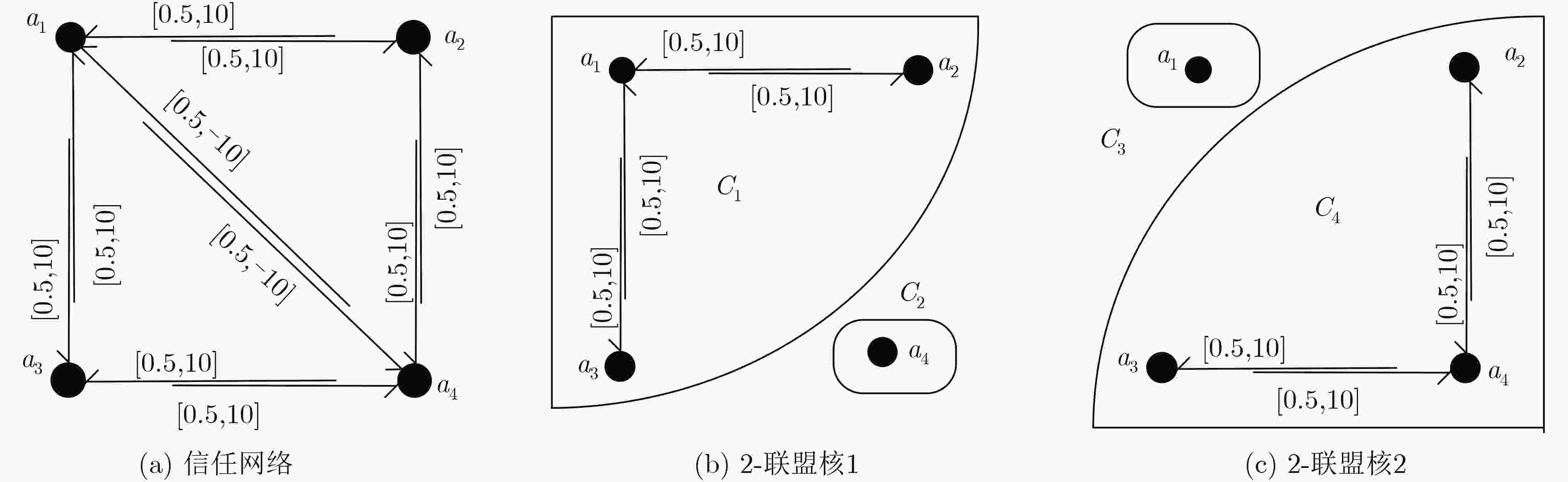
输入:$G = < A,E,\omega ,\rho > $ 输出:${C_1},{C_2}$ //(1) 计算传递概率和效用 For all Agent ${a_i},{a_j} \in A$ ${P_{ij}}$,$\varOmega {}_{ij}$ Endfor //(2) 进行图割生成CS For all Agent $ {a}_{s},{a}_{t}\in A $ Do while exist a path p from $ {a}_{s} $ to $ {a}_{t} $ in the residual
network GfDo ${\rm{cf}}\left( p \right){\rm{ }} \leftarrow {\rm{min}}\left\{ {{\rm{cf}}\left( {{a_i},{a_j}} \right)|\left( {{a_i},{a_j}} \right){\rm{ in }}\;p} \right\}$ For each edge $ < {a_i},{a_j} > $ in p ${P_{ij}} \leftarrow {P_{ij}} - {\rm{cf}}(p)$ ${P_{ji}} \leftarrow {P_{ji}} + {\rm{cf}}(p)$ Endfor EndDo If $(V({C_1}) + V({C_2})) < (V(C) + V(C'))$ then ${C_1} \leftarrow C,{C_2} \leftarrow C'$ Endif EndDo Endfor 表 2 算法2:MTU-s-t-cut算法
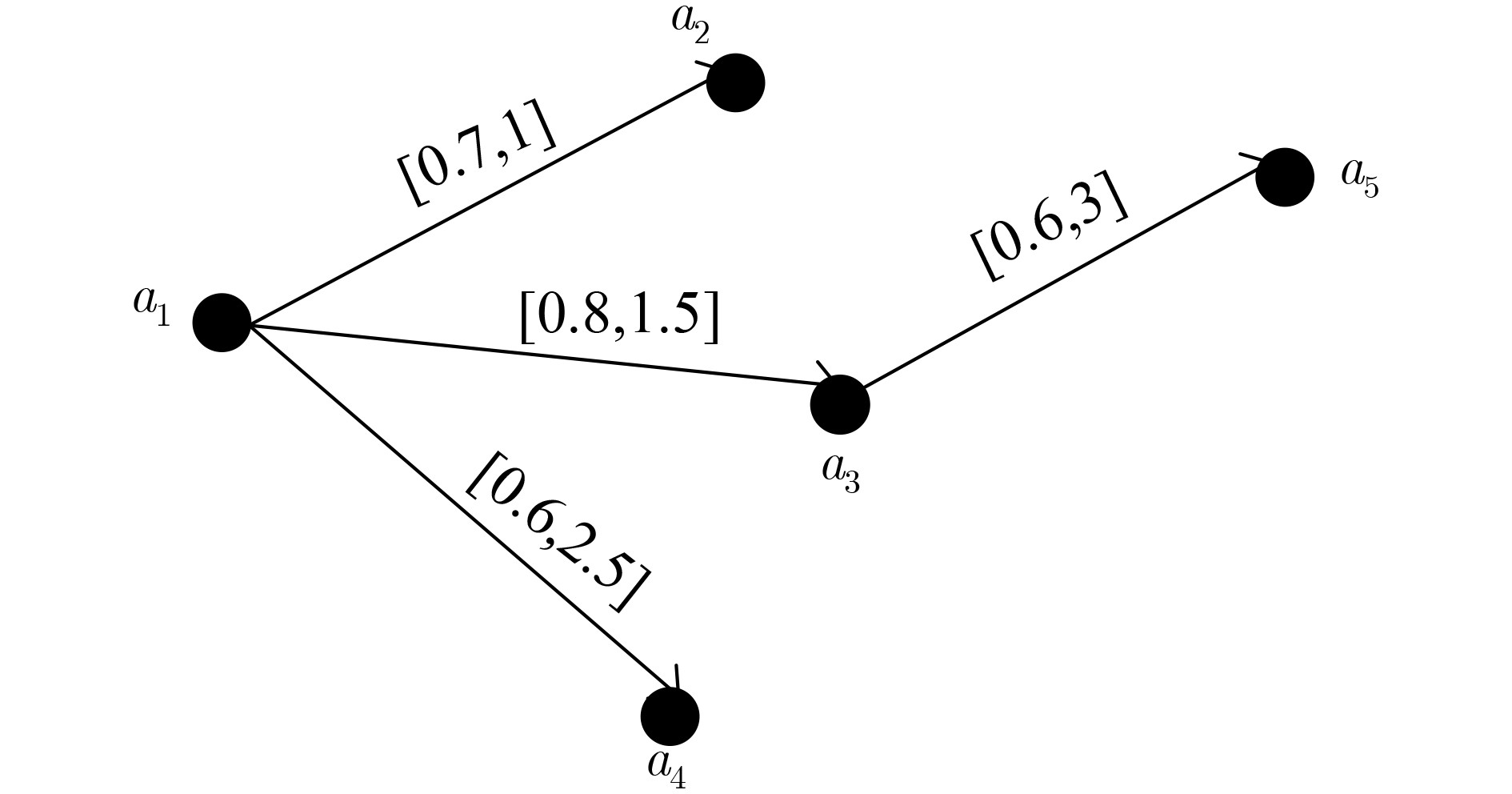
输入:$G = < A,E,\omega ,\rho > $ 输出:${C_1},{C_2}$ //(1) 计算传递概率和效用 For all Agent $ {a}_{s},{a}_{t}\in A $ ${P_{ij}}$,$\varOmega {}_{ij}$ Endfor //(2) 计算信任效用关系 For each edge $ < {a_i},{a_j} > \notin E$ ${f_{\rho ,\omega }}({a_i},{a_j})$ Endfor //(3) 进行图割生成联盟 For all Agent $ {a}_{s},{a}_{t}\in A $ Do while exist a path p from $ {a}_{s} $ to $ {a}_{t} $ in the residual
network GfDo ${\rm{cf}}\left( p \right){\rm{ }} \leftarrow {\rm{min}}\left\{ {cf\left( {{a_i},{a_j}} \right)|\left( {{a_i},{a_j}} \right){\rm{ in }}p} \right\}$ For each edge $ < {a_i},{a_j} > $ in p ${f_{\rho ,\omega }}({a_i},{a_j}) \leftarrow {f_{\rho ,\omega }}({a_i},{a_j}) - {\rm{cf}}(p)$ ${f_{\rho ,\omega }}({a_j},{a_i}) \leftarrow {f_{\rho ,\omega }}({a_j},{a_i}) + {\rm{cf}}(p)$ Endfor EndDo If ${\rm{SW}}({\rm{CS}}) < {\rm{SW}}({\rm{CS}}')$ then ${\rm{CS}} \to {\rm{CS'}}$ Endif EndDo Endfor -
[1] 智慧, 王飞跃, 黄子菊. 大规模MIMO系统中联合用户分组和联盟博弈的动态导频分配方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1686–1693. doi: 10.11999/5EIT190445ZHI Hui, WANG Feiyue, and HUANG Ziju. Dynamic pilot allocation scheme for joint user grouping and alliance game in massive MIMO systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1686–1693. doi: 10.11999/5EIT190445 [2] CHANGDER N, AKNINE S, and DUTTA A. An imperfect algorithm for coalition structure generation[C]. The Thirty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hawaii, USA, 2019: 9923–9924. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33019923. [3] UEDA S, IWASAKI A, CONITZER V, et al. Coalition structure generation in cooperative games with compact representations[J]. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2018, 32(4): 503–533. doi: 10.1007/s10458-018-9386-z [4] GALLARDO J M, JIMÉNEZ N, and JIMÉNEZ-LOSADA A. Nontransferable utility games with fuzzy coalition restrictions[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2018, 349: 42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2017.08.004 [5] KARAKAYA M and KLAUS B. Hedonic coalition formation games with variable populations: Core characterizations and (im)possibilities[J]. International Journal of Game Theory, 2017, 46(2): 435–455. doi: 10.1007/s00182-016-0533-y [6] İNAL H. The existence of a unique core partition in coalition formation games[J]. Games and Economic Behavior, 2019, 114: 215–231. d. doi: 10.1016/j.geb.2019.01.009 [7] DENG Yuan, SHEN Weiran, and TANG Pingzhong. Coalitional permutation manipulations in the gale-Shapley algorithm[C]. The 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 928–936. [8] LIN Dianchao and JABARI S E. Transferable utility games based intersection control for connected vehicles[C]. 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 2019: 3496–3501. [9] RAHWAN T, MICHALAK T P, WOOLDRIDGE M, et al. Coalition structure generation: A survey[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2015, 229: 139–174. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2015.08.004 [10] 王海艳, 杨文彬, 王随昌, 等. 基于可信联盟的服务推荐方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2014, 37(2): 301–311. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2014.00301WANG Haiyan, YANG Wenbin, WANG Suichang, et al. A service recommendation method based on trustworthy community[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2014, 37(2): 301–311. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2014.00301 [11] SLESS L, HAZON N, KRAUS S, et al. Forming k coalitions and facilitating relationships in social networks[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 259: 217–245. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2018.03.004 [12] 童向荣, 张伟, 龙宇. Agent主观信任的传递性[J]. 软件学报, 2012, 23(11): 2862–2870. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2012.04303TONG Xiangrong, ZHANG Wei, and LONG Yu. Transitivity of Agent subjective trust[J]. Journal of Software, 2012, 23(11): 2862–2870. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2012.04303 [13] WANG Xiaofeng, SU Jinshu, WANG Baosheng, et al. Trust description and propagation system: Semantics and axiomatization[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 90: 81–91. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2015.09.030 [14] MAO Chengying, XU Changfu, and HE Qiang. A cost-effective algorithm for inferring the trust between two individuals in social networks[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 164: 122–138. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.10.027 [15] KARGER D R. Global min-cuts in RNC, and other ramifications of a simple min-cut algorithm[C]. The 4th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, Austin, USA, 1993: 21–30. doi: 10.1145/313559.313605 [16] BRÂNZEI S and LARSON K. Coalitional affinity games[C]. The 8th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Budapest, Hungary, 2009: 1319–1320. [17] YEH D Y. A dynamic programming approach to the complete set partitioning problem[J]. Bit Numerical Mathematics, 1986, 26(4): 467–474. doi: 10.1007/BF01935053 [18] MICHALAK T, RAHWAN T, ELKIND E, et al. A hybrid exact algorithm for complete set partitioning[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 230: 14–50. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2015.09.006 [19] WU Feng and RAMCHURN S D. Monte-Carlo tree search for scalable coalition formation[C]. The 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 407–413. -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
