Radar Signal Modulation Type Recognition Based on Denoising Convolutional Neural Network
-
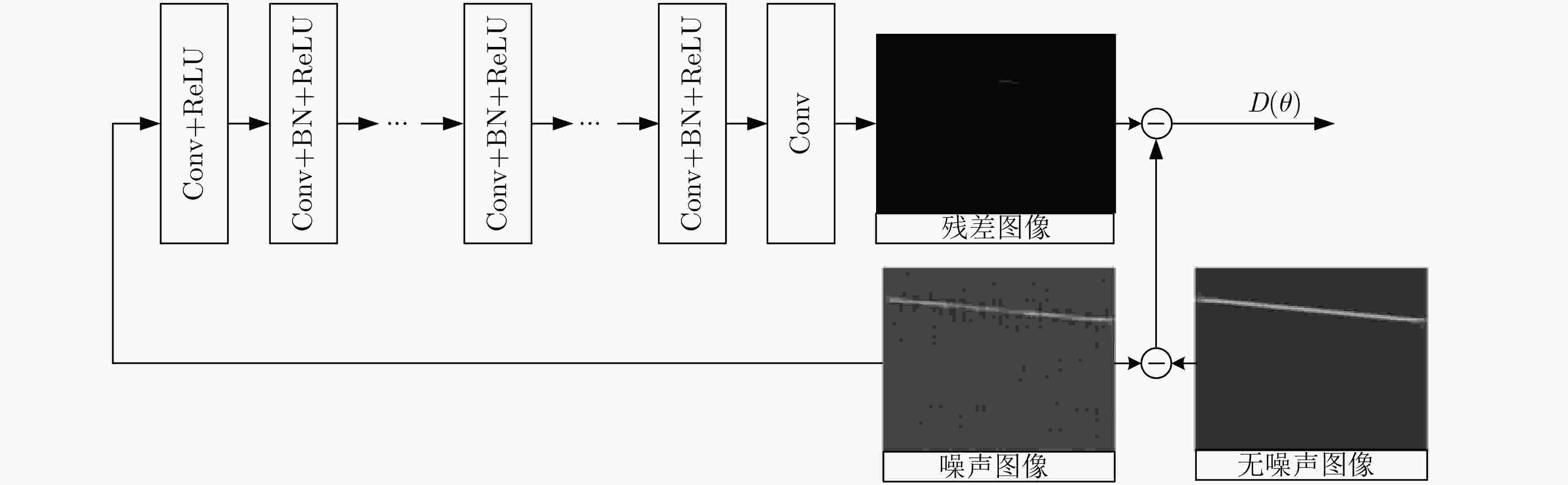
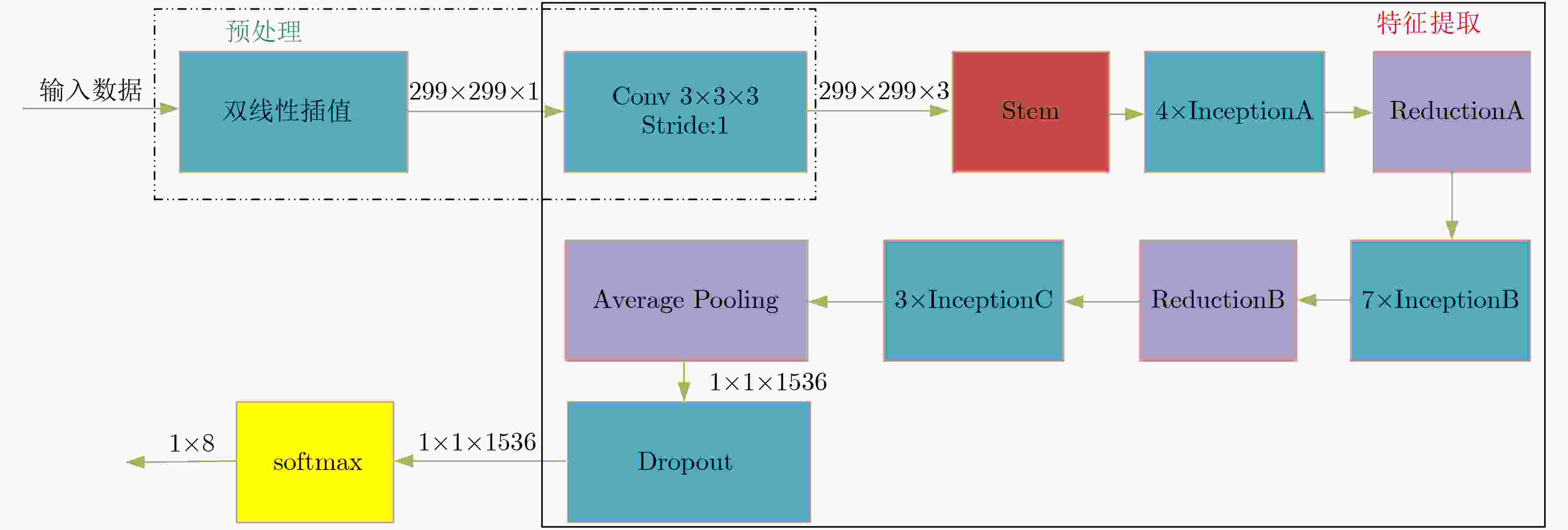
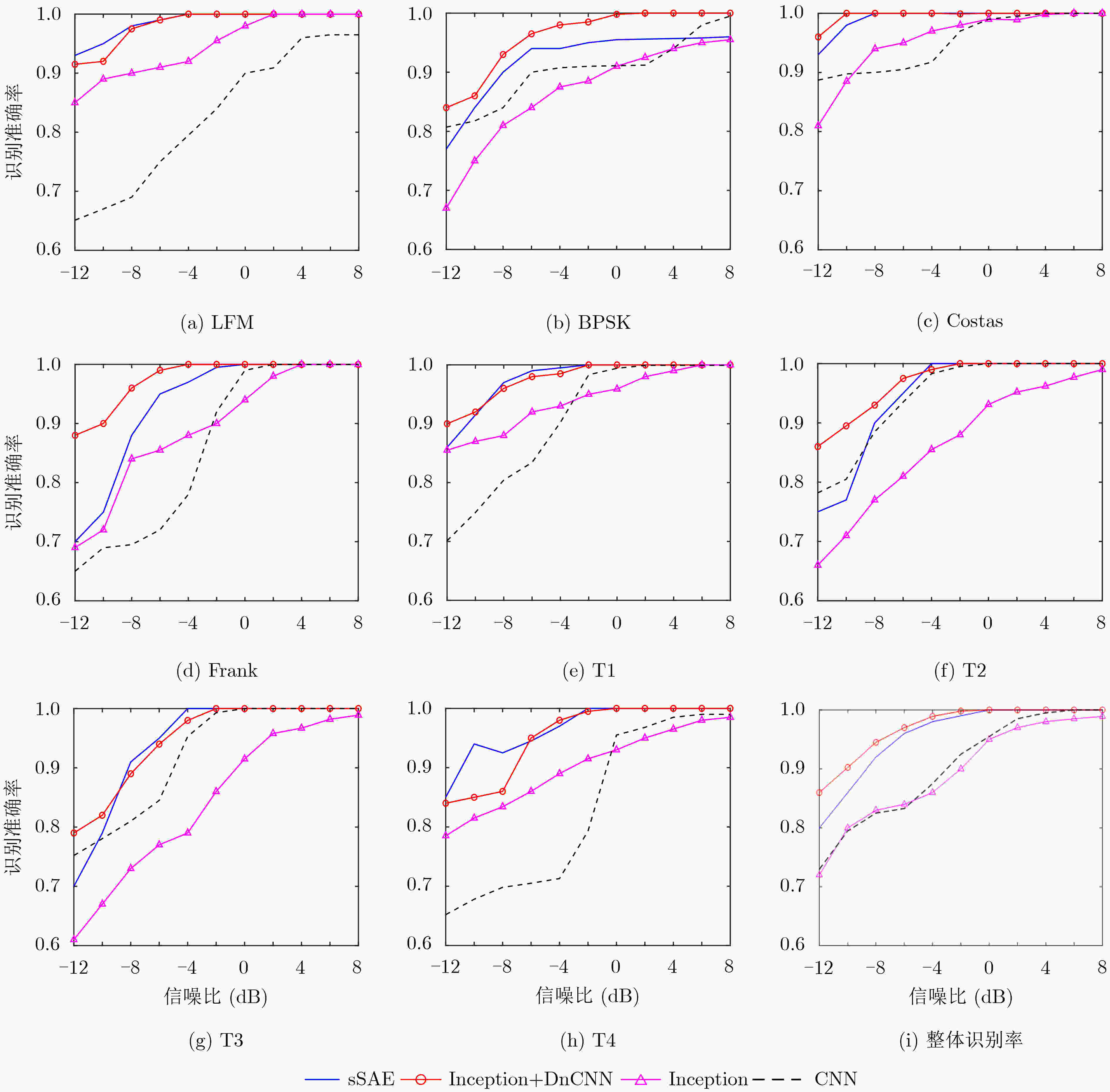
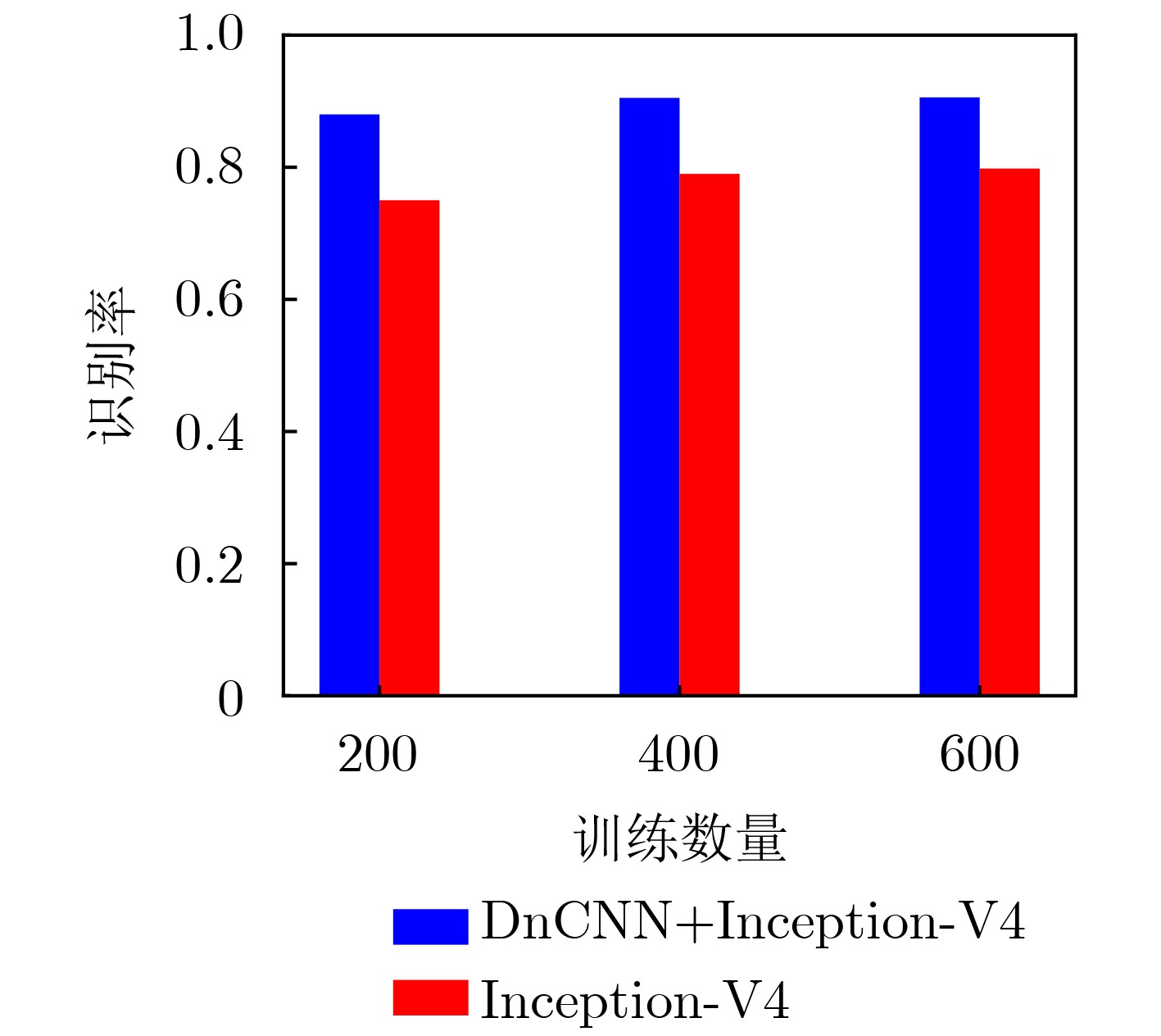
摘要: 针对低截获概率雷达(LPI)信号处理复杂,低信噪比条件下识别率低的问题,该文提出一种基于去噪卷积神经网络和Inception网络的信号分类识别系统。首先对8种LPI雷达信号进行Choi-Williams分布(CWD)时频变换,得到2维时频图像,然后使用去噪卷积神经网络进行时频图像去噪处理,最后将图像发送到Inception-V4网络进行特征提取,并使用softmax分类器进行分类,实现LPI雷达信号的有效分类识别。仿真结果表明,该方法在–10 dB信噪比(SNR)下,识别率仍然可以达到90%以上。
-
关键词:
- 低截获概率雷达信号 /
- Choi-Williams分布时频变换 /
- 去噪卷积神经网络 /
- Inception-V4网络
Abstract: Considering the problems of Low Probability of Intercept (LPI) radar signal processing complexity and low recognition rate under the condition of low SNR, a signal classification and recognition system based on Denoising Convolution Neural Network (DnCNN) and Inception network is proposed. Firstly, eight kinds of LPI radar signals are transformed by Choi Williams Distribution (CWD) to obtain two-dimensional time-frequency images. Then, the denoising convolution neural network is used to denoise the time-frequency images. Finally, the images are sent to the Inception-v4 network for feature extraction, and the softmax classifier is used for classification to realize the effective classification and recognition of LPI radar signals. Simulation results show that the recognition rate of this method can still reach more than 90% under –10 dB Signal-Noise Ratio (SNR). -
表 1 仿真参数
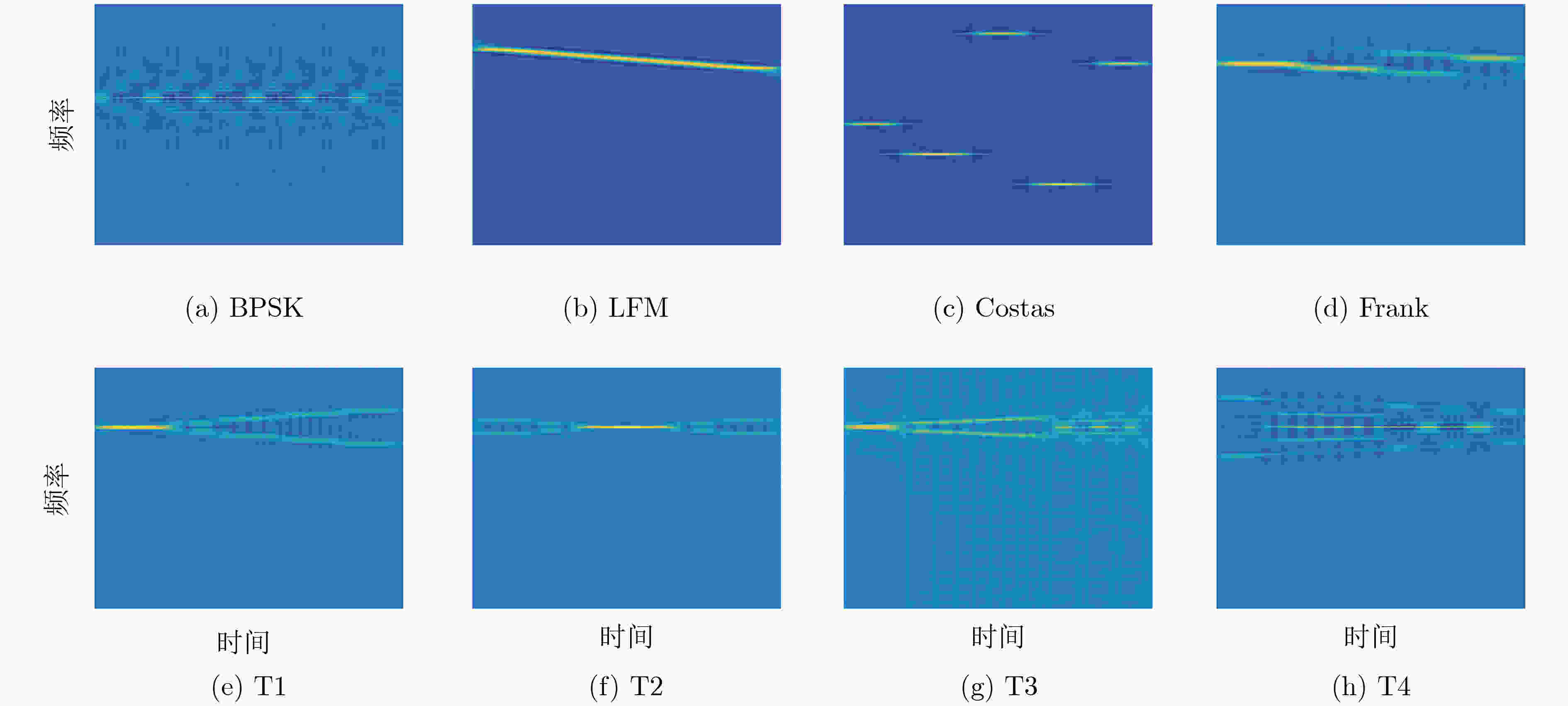
信号类型 信号参数 参数取值范围 LFM 信号长度$N$ $[{\rm{512}},1024]$ 带宽$\Delta f$ $U({1 /{16}},{1 / 8})$ 初始频率${f_0}$ $U({1 / {16}},{1 / 8})$ Costas 信号长度$N$ $[{\rm{512}},1024]$ 序列数量${N_c}$ $[3,6]$ 基准频率${f_{\min }}$ $U({1 / {24}},{1 / {20}})$ Frank 载频${f_c}$ $U({1 / 8},{1 / 4})$ 循环相位码${\rm{cpp}}$ $[4,6]$ 步进频率$M$ $[4,8]$ Barker 巴克码长度${N_c}$ $\{ 7,11,13\} $ 载频${f_c}$ $U({1 / 8},{1 / 4})$ 码数量${N_p}$ $[100,300]$ 循环相位码${\rm{cpp}}$ $[1,5]$ T1~T4 信号长度$N$ ${\rm{[512}},1024]$ 整体码元周期$T$ $[0.07,0.1]$ 码序列段数$k$ $[4,6]$ 表 2 时频图去噪峰值信噪比(dB)
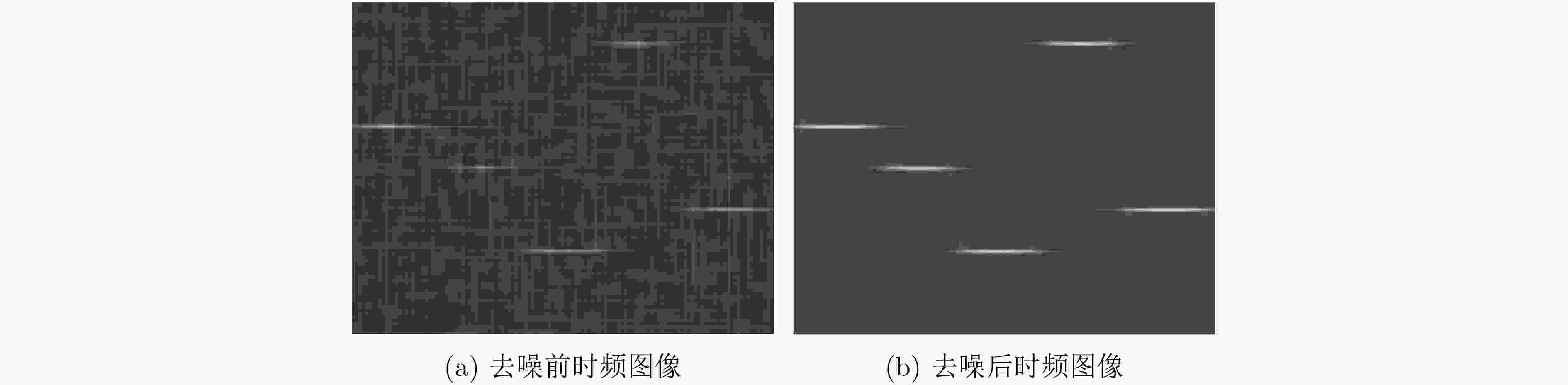
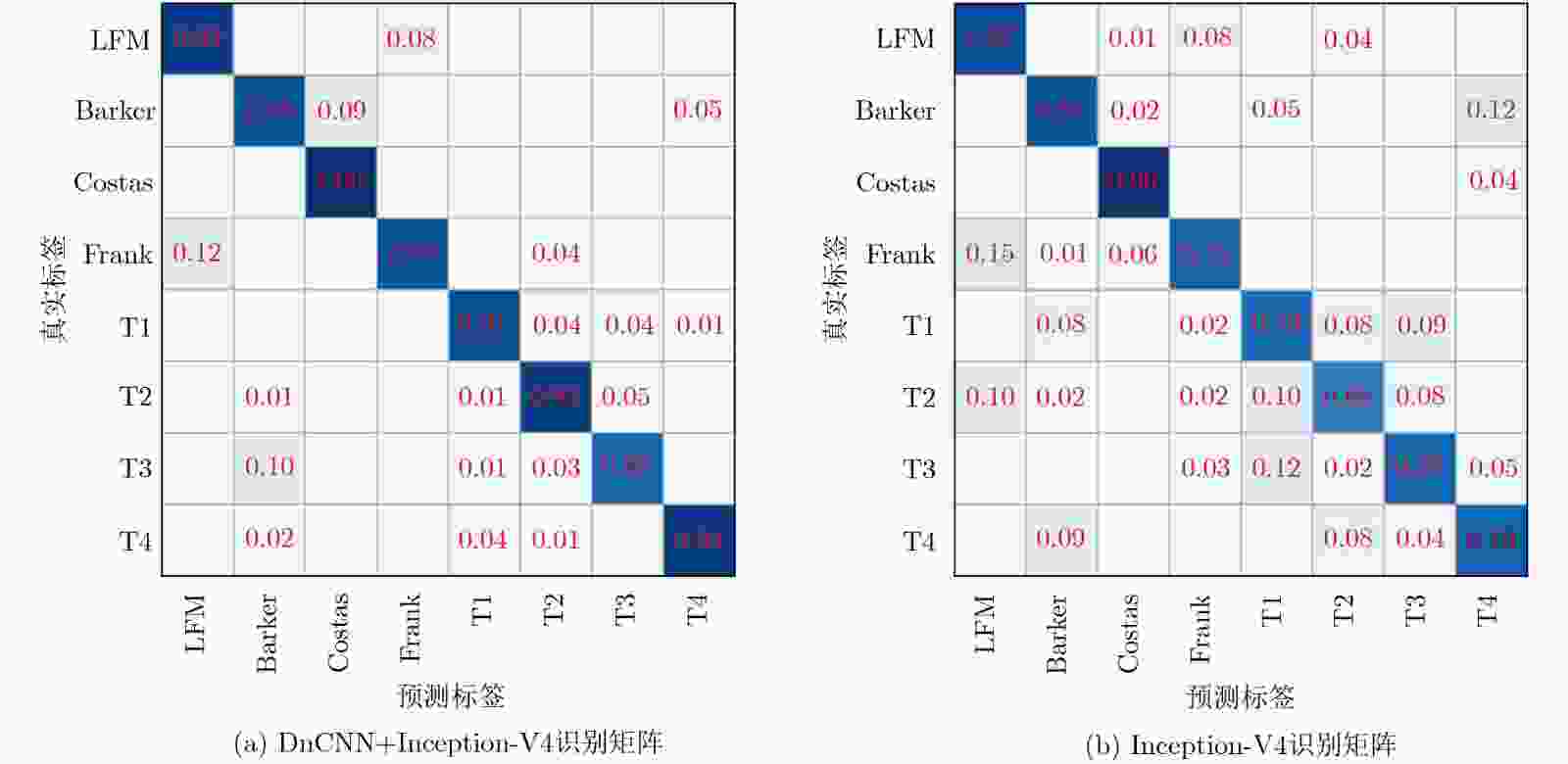
信号类型 雷达信号信噪/视频图像峰值信噪比 –10 –6 –2 2 LFM 34.02 34.56 35.67 37.12 Costas 32.15 33.31 34.55 35.01 Frank 30.35 31.16 32.09 33.32 BPSK 28.89 29.34 29.57 30.21 T1 31.44 32.02 33.10 33.98 T2 31.54 32.34 33.55 34.18 T3 30.21 31.23 31.96 32.44 T4 29.98 30.65 31.33 32.46 -
[1] 陈涛, 柳立志, 郭立民. 基于MWC压缩采样宽带接收机的雷达信号脉内调制识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 867–874. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170612CHEN Tao, LIU Lizhi, and GUO Limin. Intra-pulse modulation recognition of radar signals based on MWC compressed sampling wideband receiver[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 867–874. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170612 [2] TÜMEN V, SÖYLEMEZ Ö F, and ERGEN B. Facial emotion recognition on a dataset using convolutional neural network[C]. 2017 International Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing Symposium, Malatya, Turkey, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/IDAP.2017.8090281. [3] ZHANG Ming, DIAO Ming, and GUO Limin. Convolutional neural networks for automatic cognitive radio waveform recognition[J] IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 11074–11082. doi: 10.1109/access.2017.2716191. [4] 郭立民, 陈鑫, 陈涛. 基于AlexNet模型的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(3): 1000–1008. doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20171056GUO Limin, CHEN Xin, and CHEN Tao. Radar signal modulation type recognition based on AlexNet model[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition, 2019, 49(3): 1000–1008. doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20171056 [5] QIN Xin, ZHA Xiong, HUANG Jie, et al. Radar waveform recognition based on deep residual network[C]. The 8th IEEE Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, Chongqing, China, 2019: 892–896. doi: 10.1109/ITAIC.2019.8785588. [6] 郭立民, 寇韵涵, 陈涛, 等. 基于栈式稀疏自编码器的低信噪比下低截获概率雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 875–881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170588GUO Limin, KOU Yunhan, CHEN Tao, et al. Low probability of intercept radar signal recognition based on stacked sparse Auto-encoder[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 875–881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170588 [7] GUO Qiang, YU Xin, and RUAN Guoqing. LPI radar waveform recognition based on deep convolutional neural network transfer learning[J]. Symmetry, 2019, 11(4): 540. doi: 10.3390/sym11040540 [8] XIAO Yihan, LIU Wenjian, and GAO Lipeng. Radar signal recognition based on transfer learning and feature fusion[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020, 25(4): 1563–1571. doi: 10.1007/s11036-019-01360-1 [9] ZHANG Ming, DIAO Ming, GAO Lipeng, et al. Neural networks for radar waveform recognition[J]. Symmetry, 2017, 9(5): 75. doi: 10.3390/sym9050075 [10] QU Zhiyu, MAO Xiaojie, and DENG Zhian. Radar signal intra-pulse modulation recognition based on convolutional neural network[J] IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 43874–43884. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2864347. [11] LIU Yabo and LIU Yi. Modulation recognition with pre-denoising convolutional neural network[J]. Electronics Letters, 2020, 56(5): 255–257. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.3586 [12] WU Yushuang, LI Xiukun, and WANG Yang. Extraction and classification of acoustic scattering from underwater target based on Wigner-Ville distribution[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2018, 138: 52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2018.03.026 [13] TIAN Xiaodi, SUN Xiaodong, YU Xiaohui, et al. Modulation pattern recognition of communication signals based on fractional low-order Choi-Williams distribution and convolutional neural network in impulsive noise environment[C]. The 19th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology, Xi’an, China, 2019: 188–192. doi: 10.1109/ICCT46805.2019.8947208. [14] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [15] 邓祾. 基于DnCNN函数的分水岭算法[J]. 海南热带海洋学院学报, 2019, 26(5): 69–75. doi: 10.13307/j.issn.2096-3122.2019.05.12DENG Ling. Watershed algorithm based on DnCNN function[J]. Journal of Hainan Tropical Ocean University, 2019, 26(5): 69–75. doi: 10.13307/j.issn.2096-3122.2019.05.12 [16] LENZ B, HASSELBRUCH H, GROßMANN H, et al. Application of CNN networks for an automatic determination of critical loads in scratch tests on a-C: H: W coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 393: 125764. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125764 [17] EMARA T, AFIFY H M, ISMAIL F H, et al. A modified inception-v4 for imbalanced skin cancer classification dataset[C]. The 14th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems, Cairo, Egypt, 2019: 28–33. doi: 10.1109/ICCES48960.2019.9068110. [18] JOSHI K, YADAV R, and ALLWADHI S. PSNR and MSE based investigation of LSB[C]. 2016 International Conference on Computational Techniques in Information and Communication Technologies, New Delhi, India, 2016: 280–285. doi: 10.1109/ICCTICT.2016.7514593. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
