Sea Clutter Data Augmentation Method Based on Deep Generative Adversarial Network
-
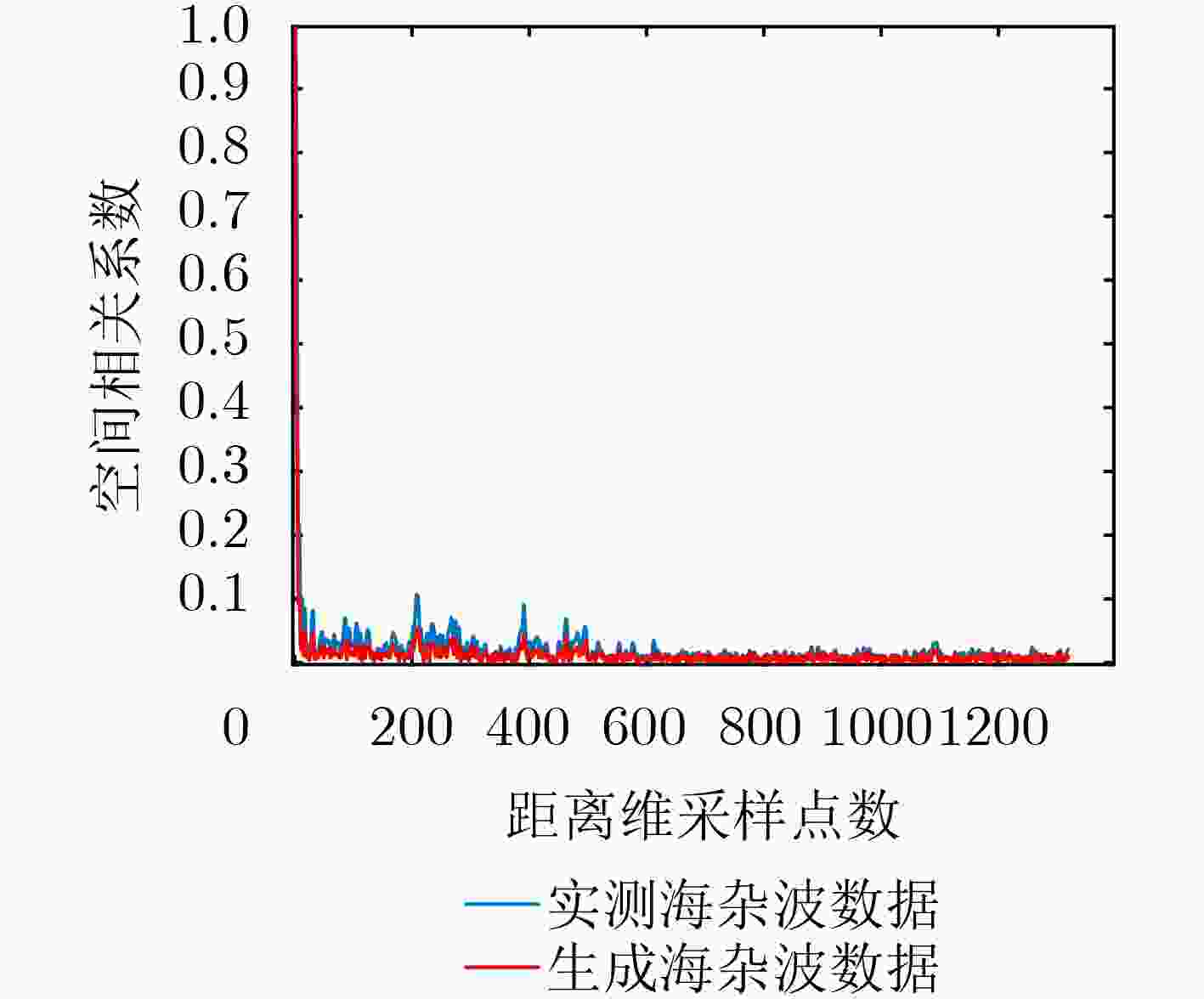
摘要: 海杂波数据稀缺,获取海杂波数据成本高、周期长,极大地限制了海杂波特性研究及海洋遥感应用。该文主要研究了基于深度生成性对抗网络(GAN)的海杂波数据生成方法,通过扩展传统的GAN框架,形成了1维海杂波数据生成和鉴别模型,基于实测海杂波数据集,进行对抗网络生成和鉴别模型训练,分析了生成模型所生成的海杂波数据的幅度分布特性和时间、空间相关性。基于实测数据验证了该方法能够生成更多、更多样、与真实海杂波数据分布相近的海杂波数据。Abstract: Due to the scarcity of sea clutter data, the high cost and long period of obtaining sea clutter data greatly limit the research of sea clutter characteristics and the application of ocean remote sensing. The method of sea clutter data generation based on the Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) is studied. By extending the traditional GAN framework, a one-dimensional sea clutter data generation and identification model is formed. Based on the radar measured sea clutter data set, the generation and identification model training in the adversarial network is carried out. The amplitude distribution characteristics and time and spatial correlation of the sea clutter data generated by the model are analyzed. Based on the measured data, it is verified that the method can generate more sea clutter data with more variety, and similar distribution to the real sea clutter data.
-
表 1 生成器、辨别器网络参数
生成器网络 判别器网络 Layer Act./Norm Output shape Layer Act./Norm Output shape Fully Linear ReLU Conv1d Leaky ReLU 64×2048 BatchNorm1d 1×256 Conv1d Leaky ReLU 128×512 Conv1d ReLU 512×512 Conv1d Leaky ReLU 256×128 Conv1d ReLU 256×1024 Conv1d Leaky ReLU 512×128 Conv1d ReLU 128×1024 Conv1d Leaky ReLU 1024×16 Conv1d ReLU 64×4096 Fully Linear sigmoid 1×1 Conv1d Tanh 1×8192 -
[1] 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089 [2] DING Hao, GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, et al. Modeling of heavy tailed sea clutter based on the generalized central limit theory[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1591–1595. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2596322 [3] TITI G W and MARSHALL D F. The ARPA/NAVY mountaintop program: Adaptive signal processing for airborne early warning radar[C]. 1996 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, USA, 1996: 1165–1168. [4] DROSOPOULOS A. Description of the OHGR database[R]. Technical Note 94–14, 1994. [5] GRECO M, STINCO P, GINI F, et al. Impact of sea clutter nonstationarity on disturbance covariance matrix estimation and CFAR detector performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1502–1513. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545205 [6] 王帅. 基于人工智能(GAN)的影像技术探究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京师范大学, 2019. [7] 雷志勇, 黄忠平, 吴刚, 等. 机载L波段雷达海杂波幅度分布特性分析[J]. 电波科学学报, 2019, 34(5): 558–566.LEI Zhiyong, HUANG Zhongping, WU Gang, et al. Analysis of sea clutter distribution with L-band airborne radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2019, 34(5): 558–566. [8] 刘恒燕, 宋杰, 熊伟, 等. 大入射余角海杂波相关特性分析及幅度拟合[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2018, 33(3): 307–312. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.1673-1522.2018.03.009LIU Hengyan, SONG Jie, XIONG Wei, et al. Sea clutter correlation analysis and amplitude fitting for large grazing angle[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2018, 33(3): 307–312. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.1673-1522.2018.03.009 [9] 傅俊滔, 周国安, 陈红. 基于ZMNL的Pareto杂波模拟改进方法[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2019, 39(4): 19–21, 28.FU Juntao, ZHOU Guoan, and CHEN Hong. Improved method of Pareto clutter simulation based on ZMNL[J]. Journal of Projectiles,Rockets,Missiles and Guidance, 2019, 39(4): 19–21, 28. [10] 王坤峰, 左旺孟, 谭营, 等. 生成式对抗网络: 从生成数据到创造智能[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 769–774.WANG Kunfeng, ZUO Wangmeng, TAN Ying, et al. Generative adversarial networks: from generating data to creating intelligence[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 769–774. [11] 徐雅楠, 刘宁波, 丁昊, 等. 利用CNN的海上目标探测背景分类方法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(12): 2505–2514.XU Yanan, LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, et al. Background classification method for marine target detection based on CNN[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(12): 2505–2514. [12] 丁昊, 刘宁波, 董云龙, 等. 雷达海杂波测量试验回顾与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006DING Hao, LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, et al. Overview and prospects of radar sea clutter measurement experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006 [13] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[C]. Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal Canada, 2014: 1–23. [14] ZHANG Zhimian, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. [15] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, and BOTTOU L. Wasserstein GAN[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydneym, Australia, 2017: 1–32. [16] GULRAJANI I, AHMED F, ARJOVSKY M, et al. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5767–5777. [17] 关键, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. 实测海杂波数据空间相关性研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2012, 27(5): 943–953.GUAN Jian, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Spatial correlation property with measured sea clutter data[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2012, 27(5): 943–953. -





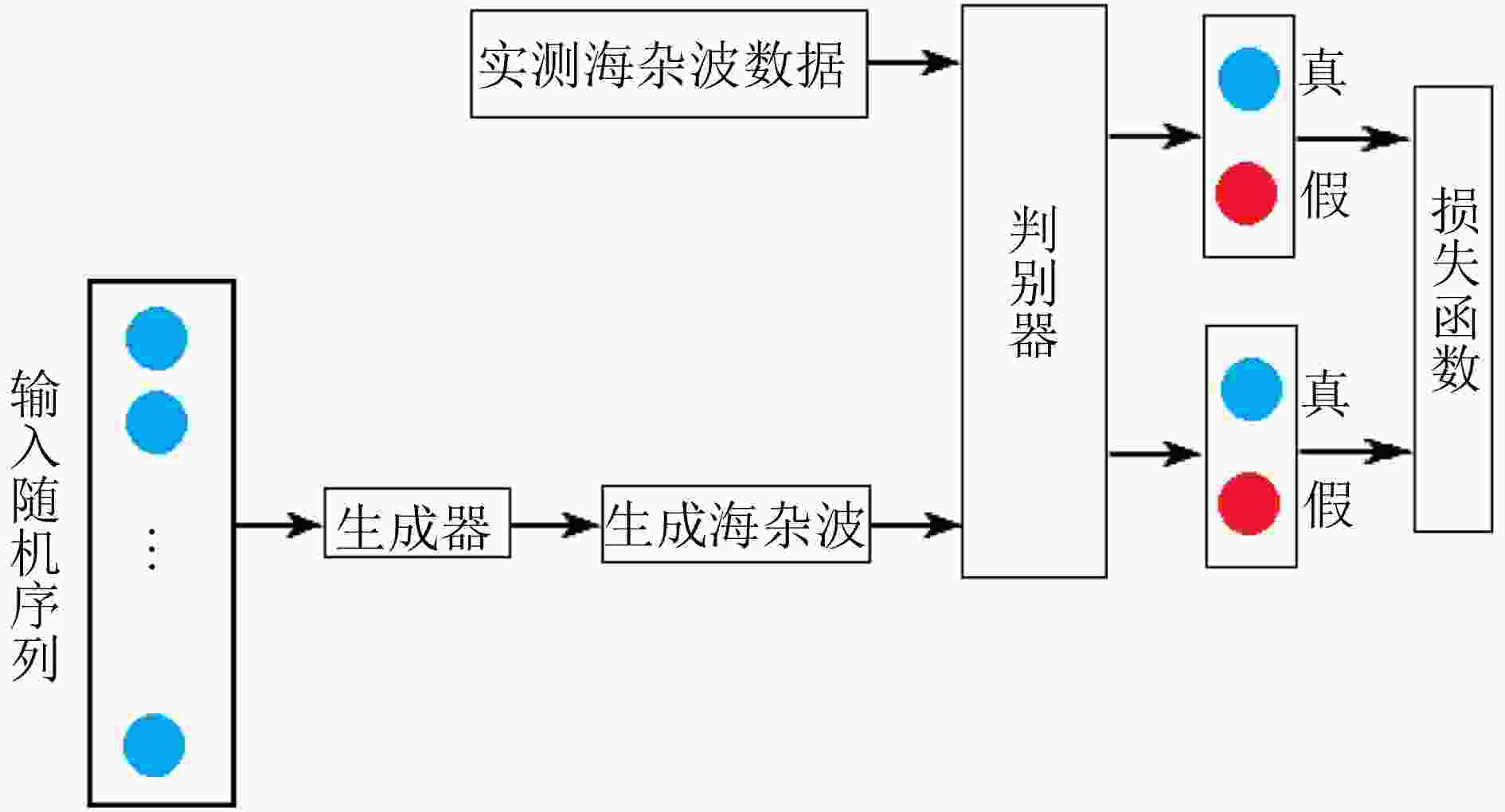
 下载:
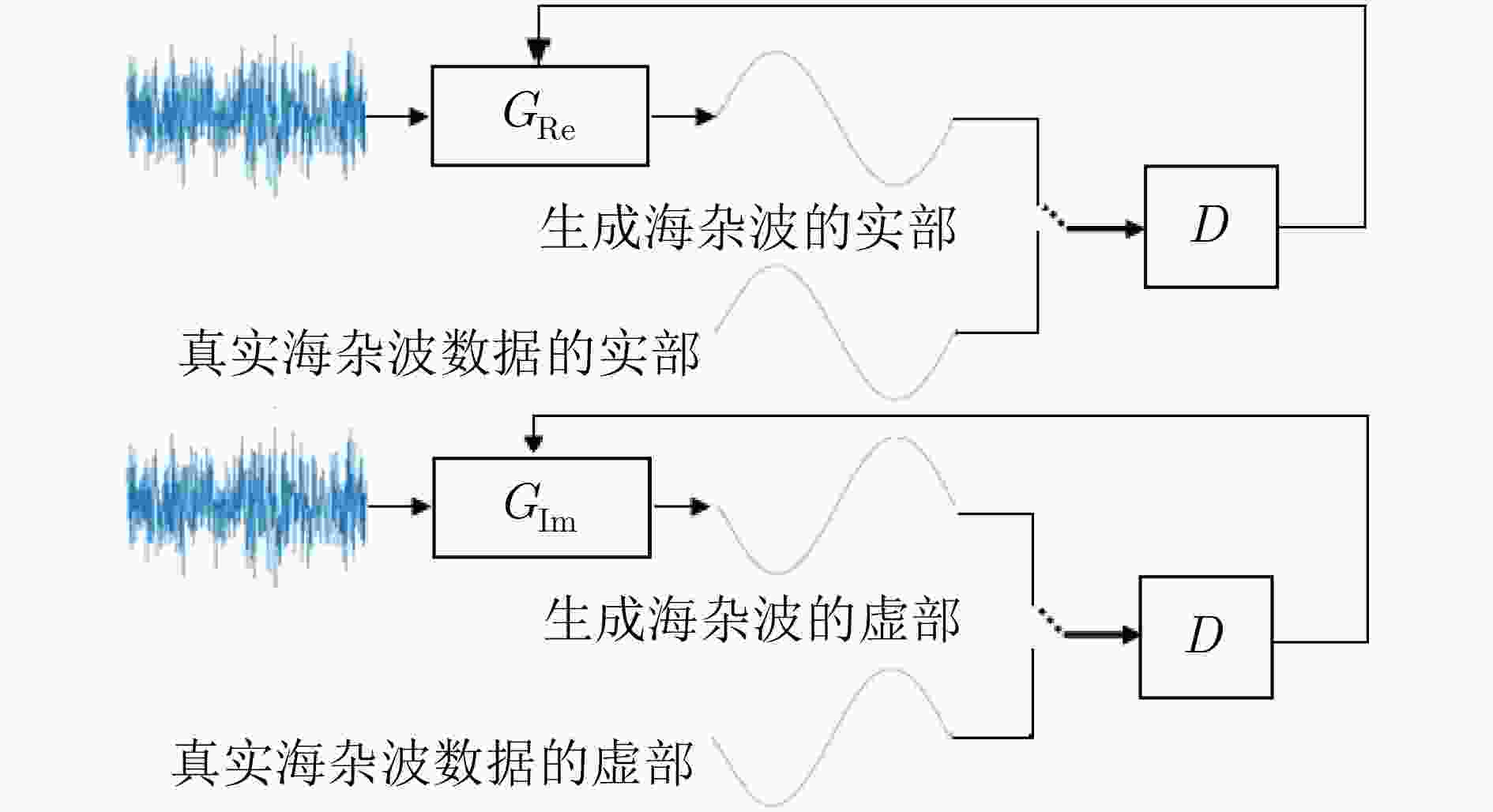
下载:
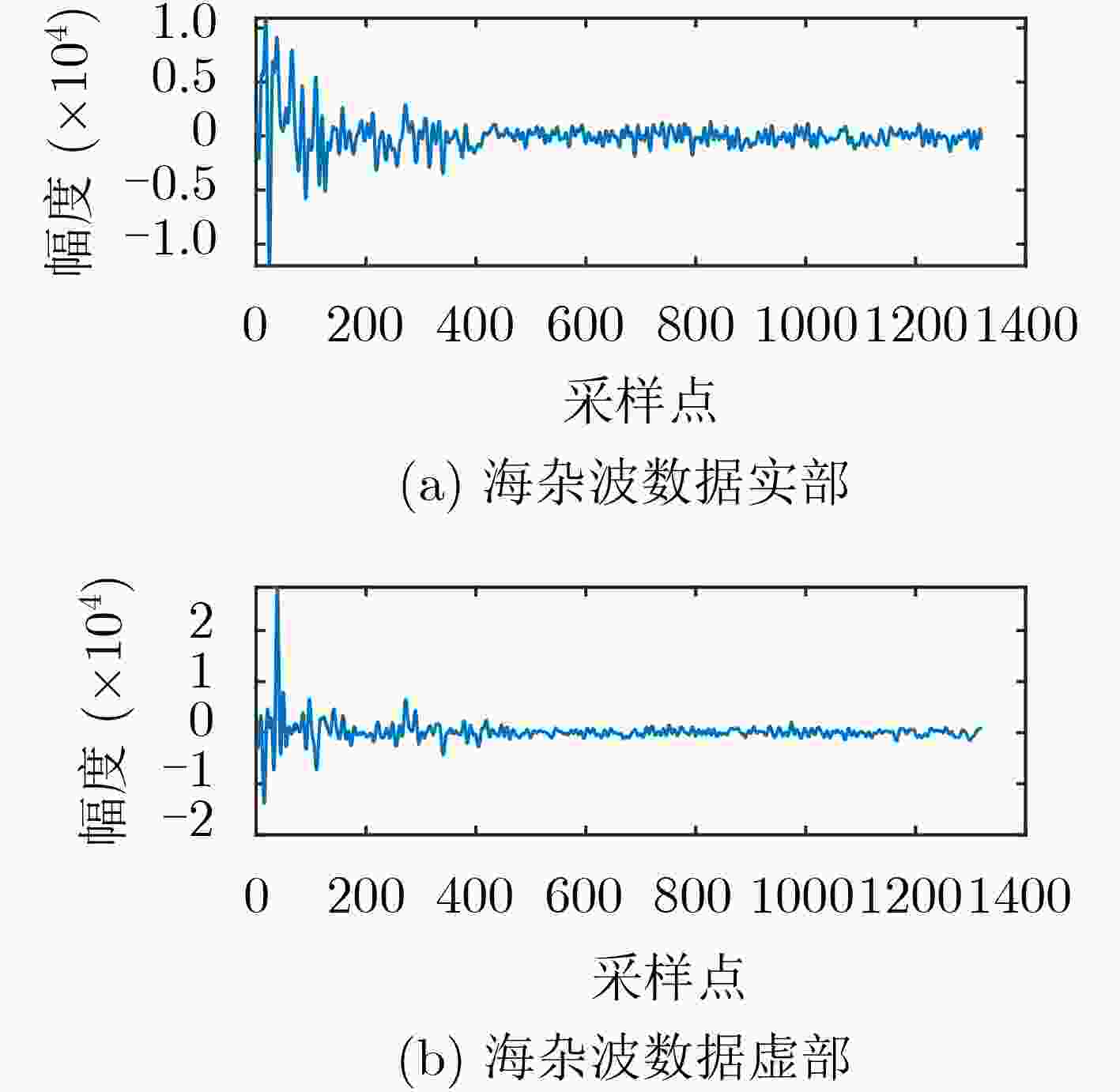
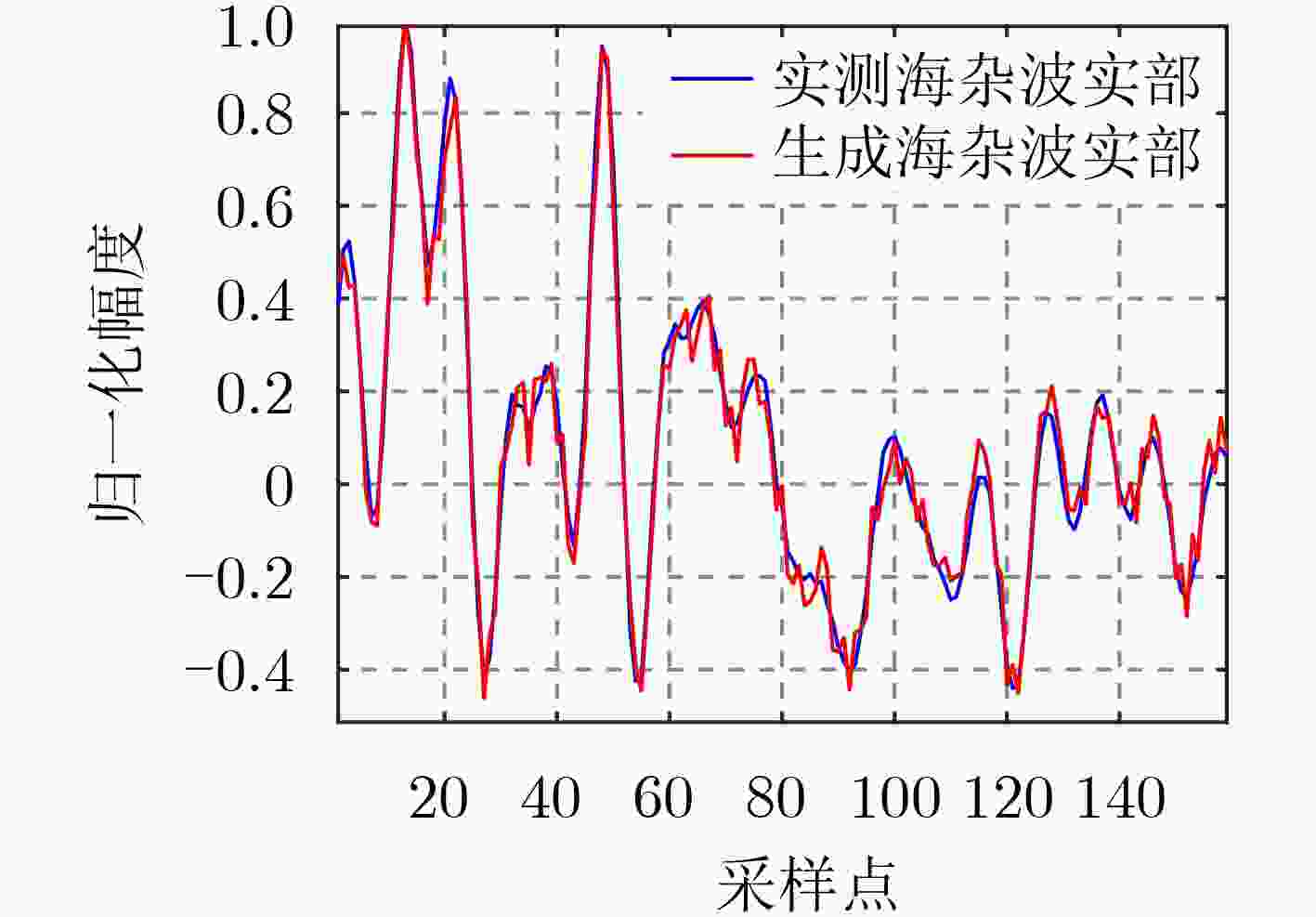

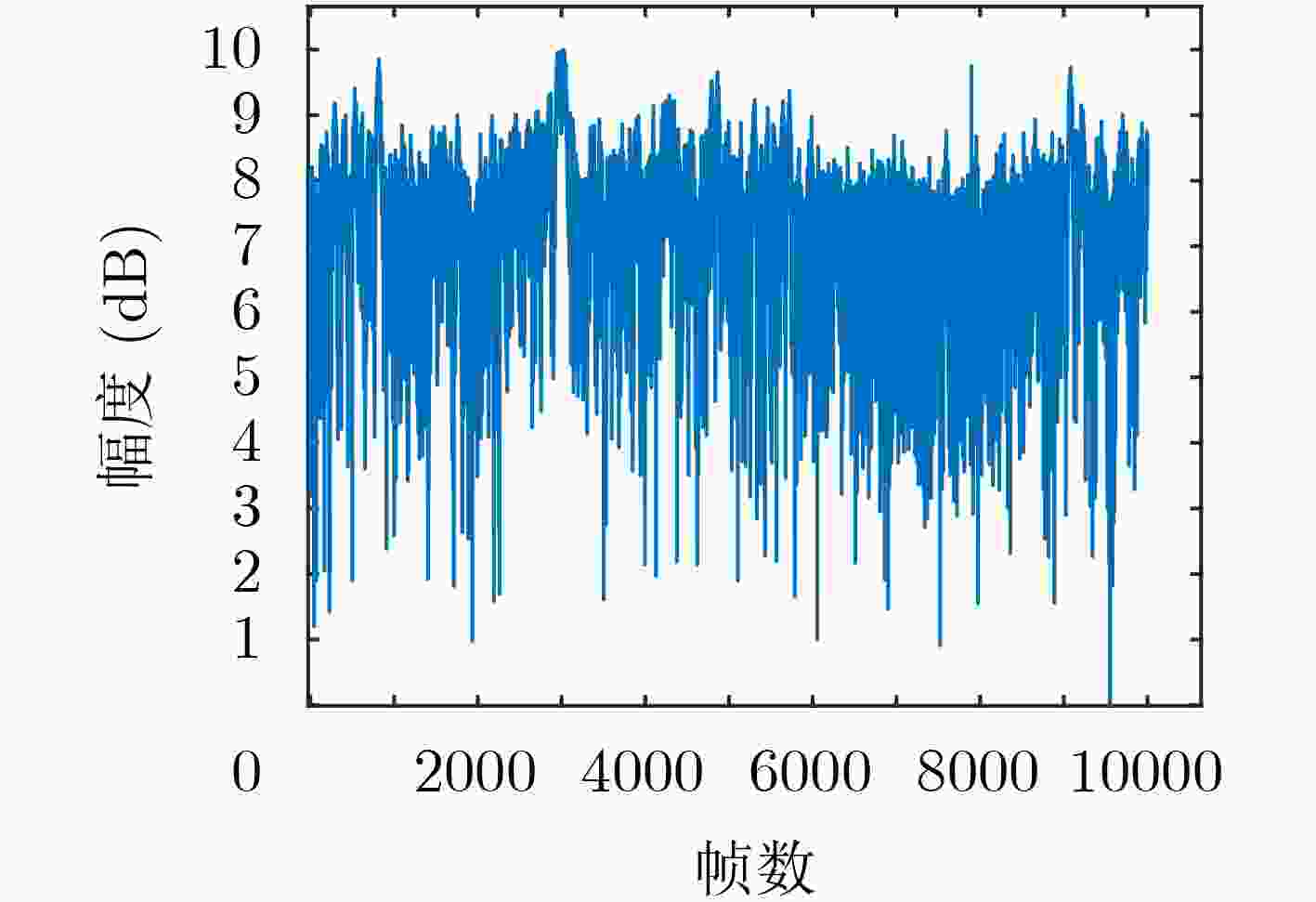
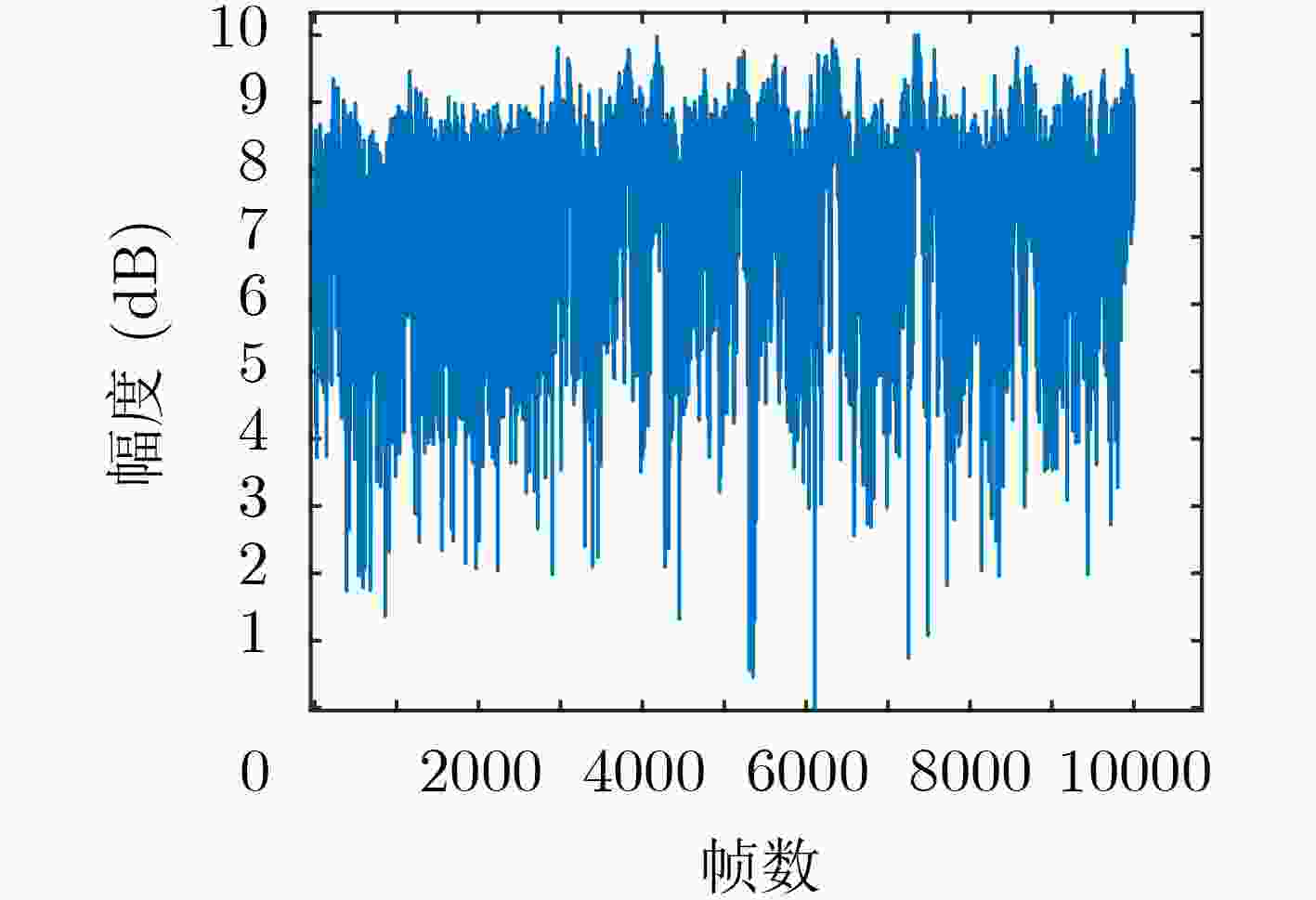
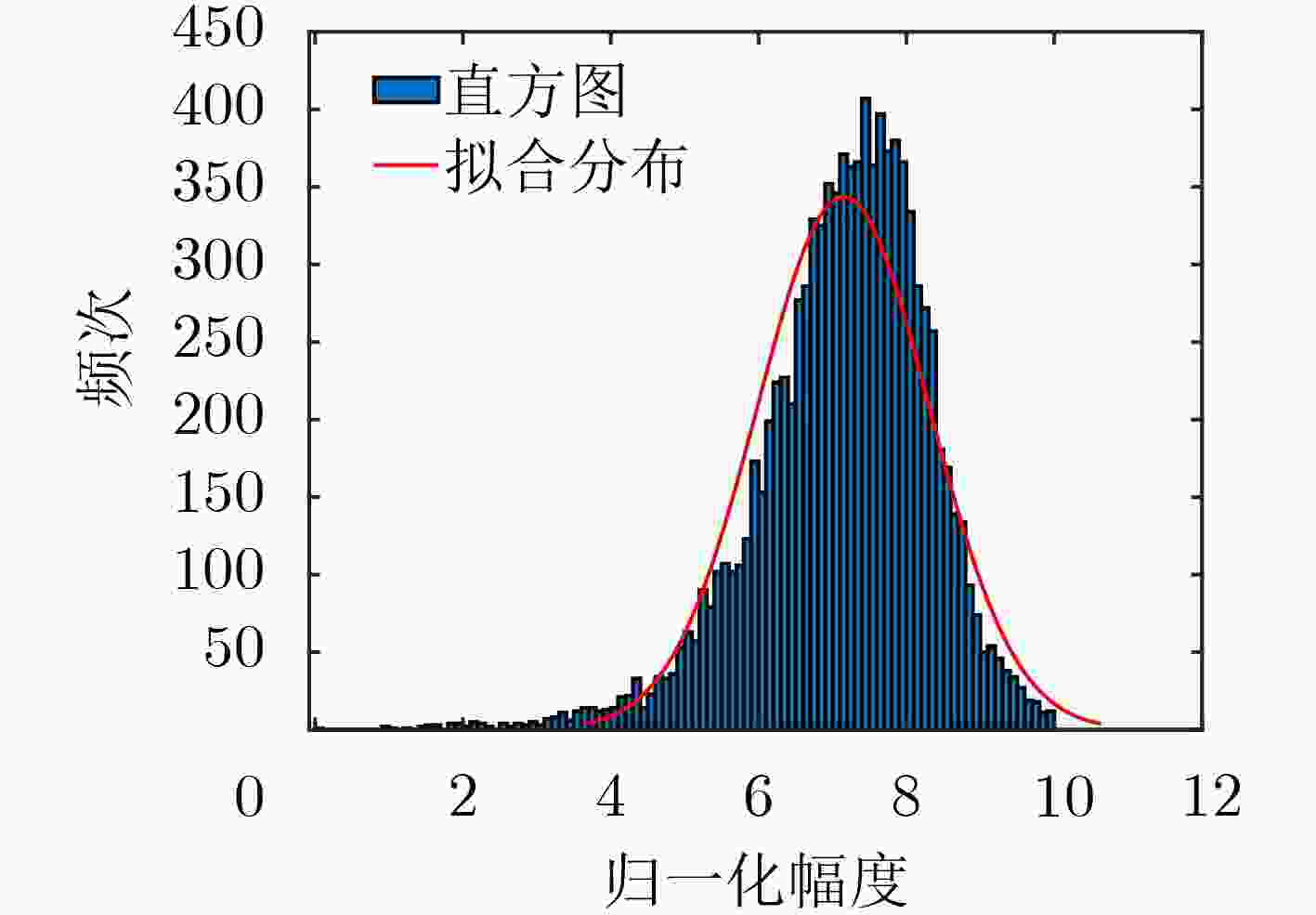
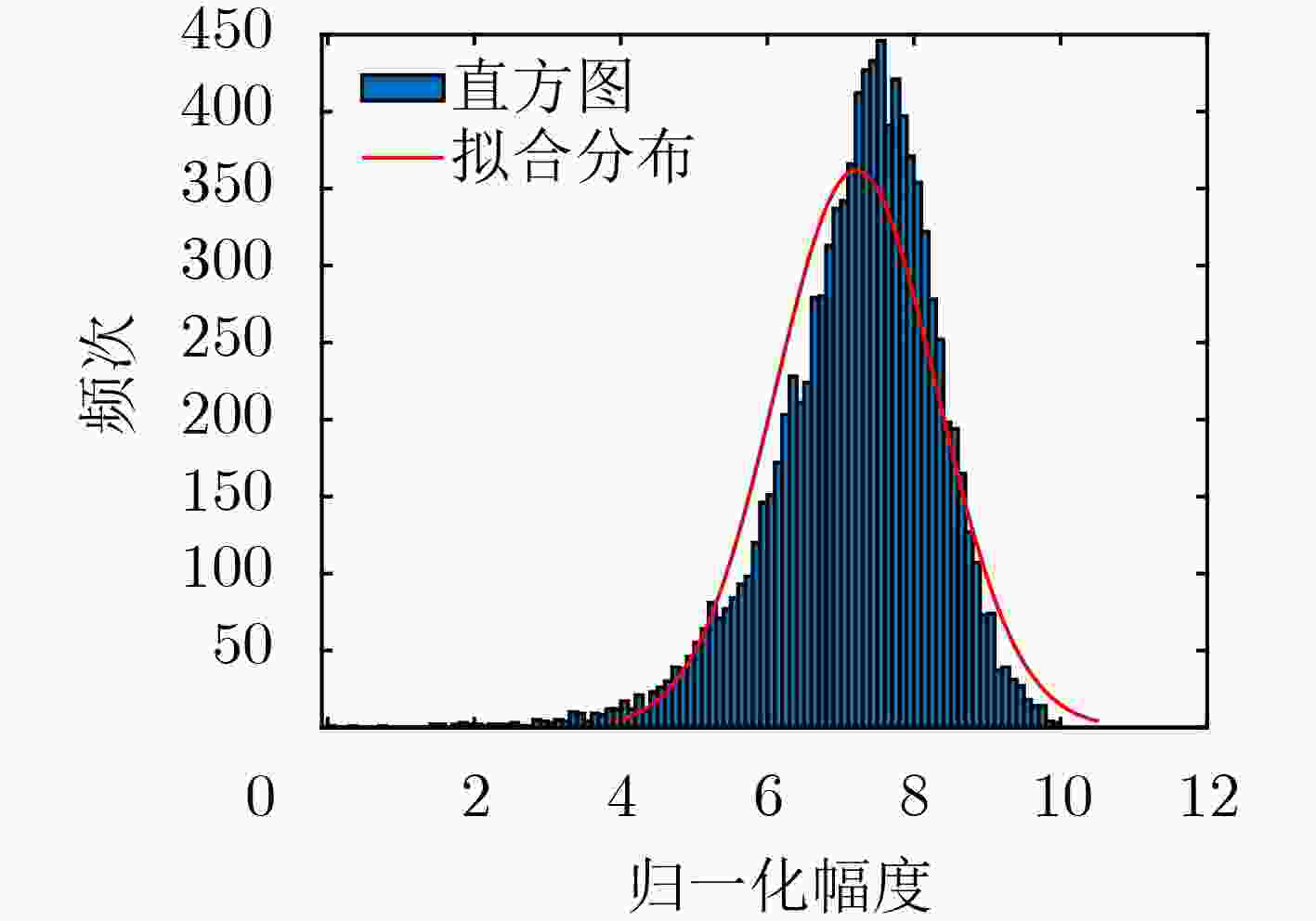
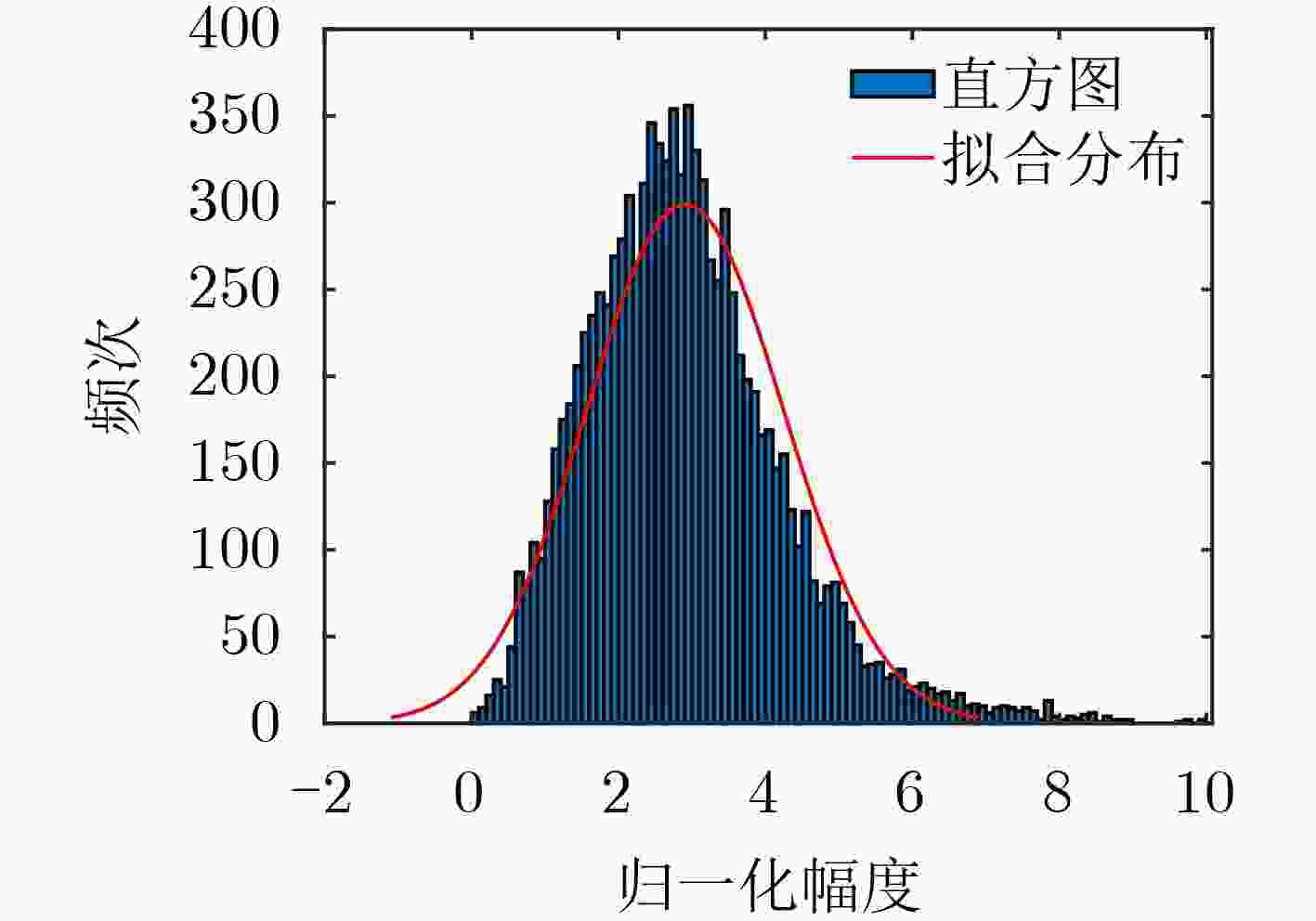
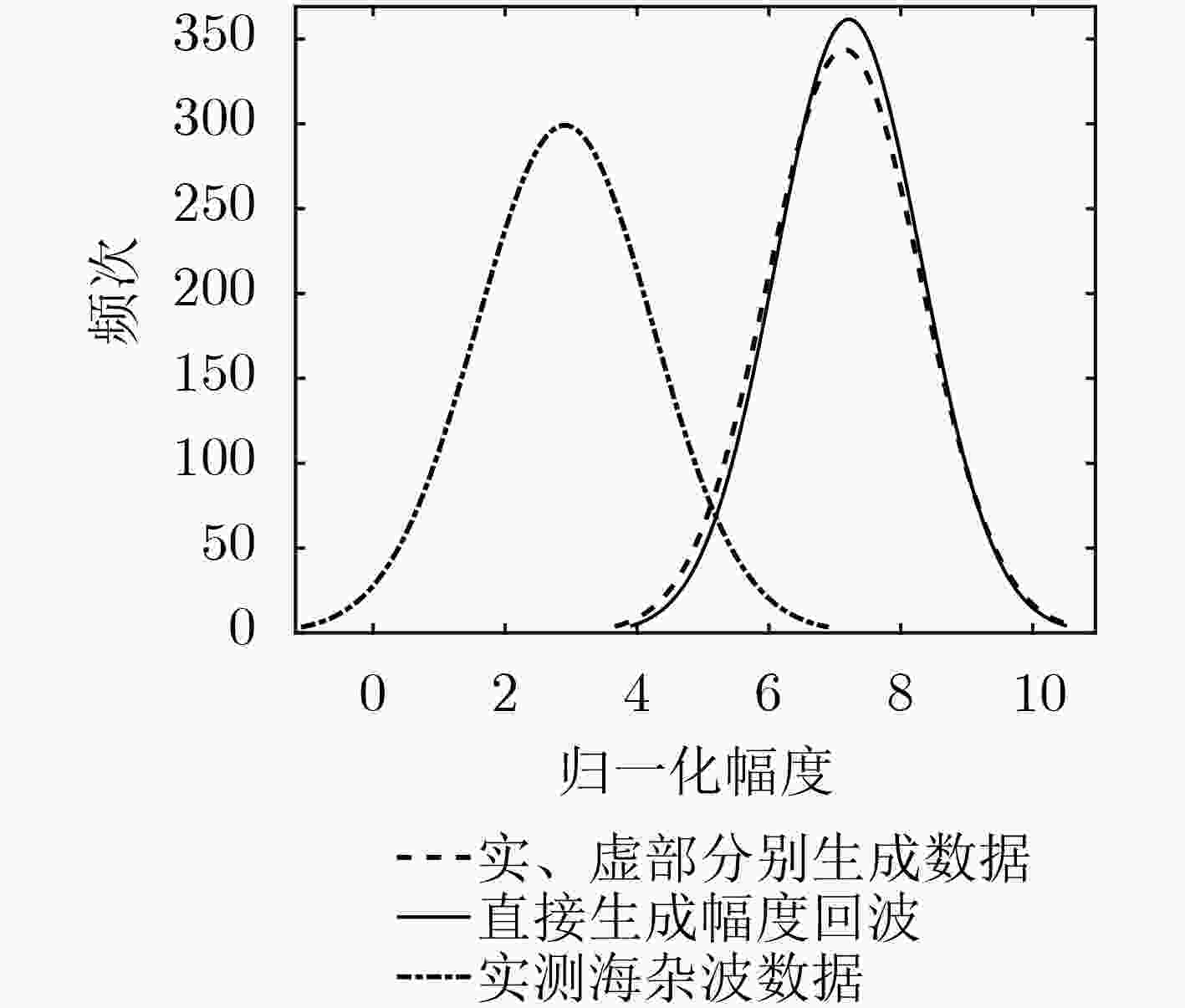
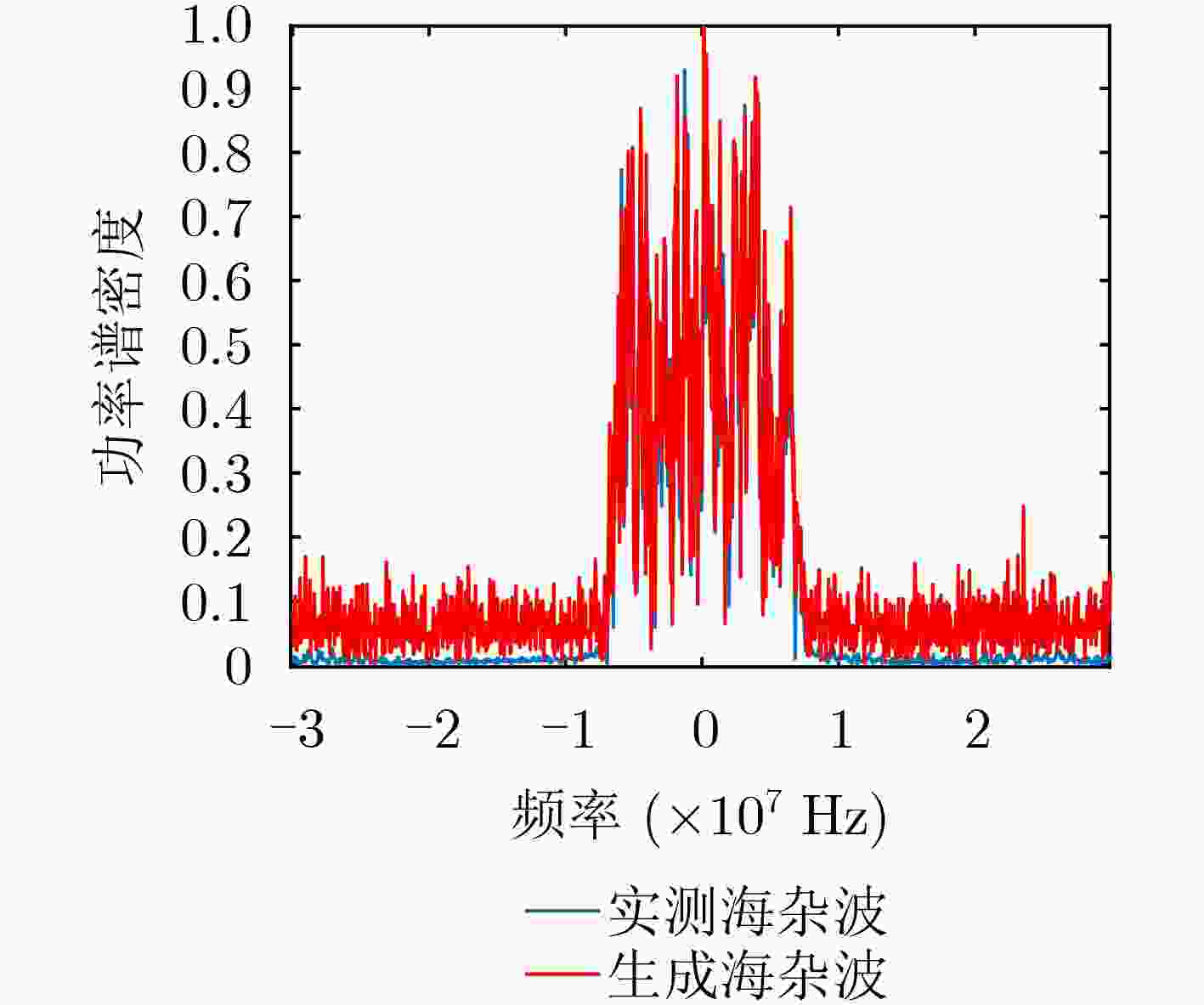
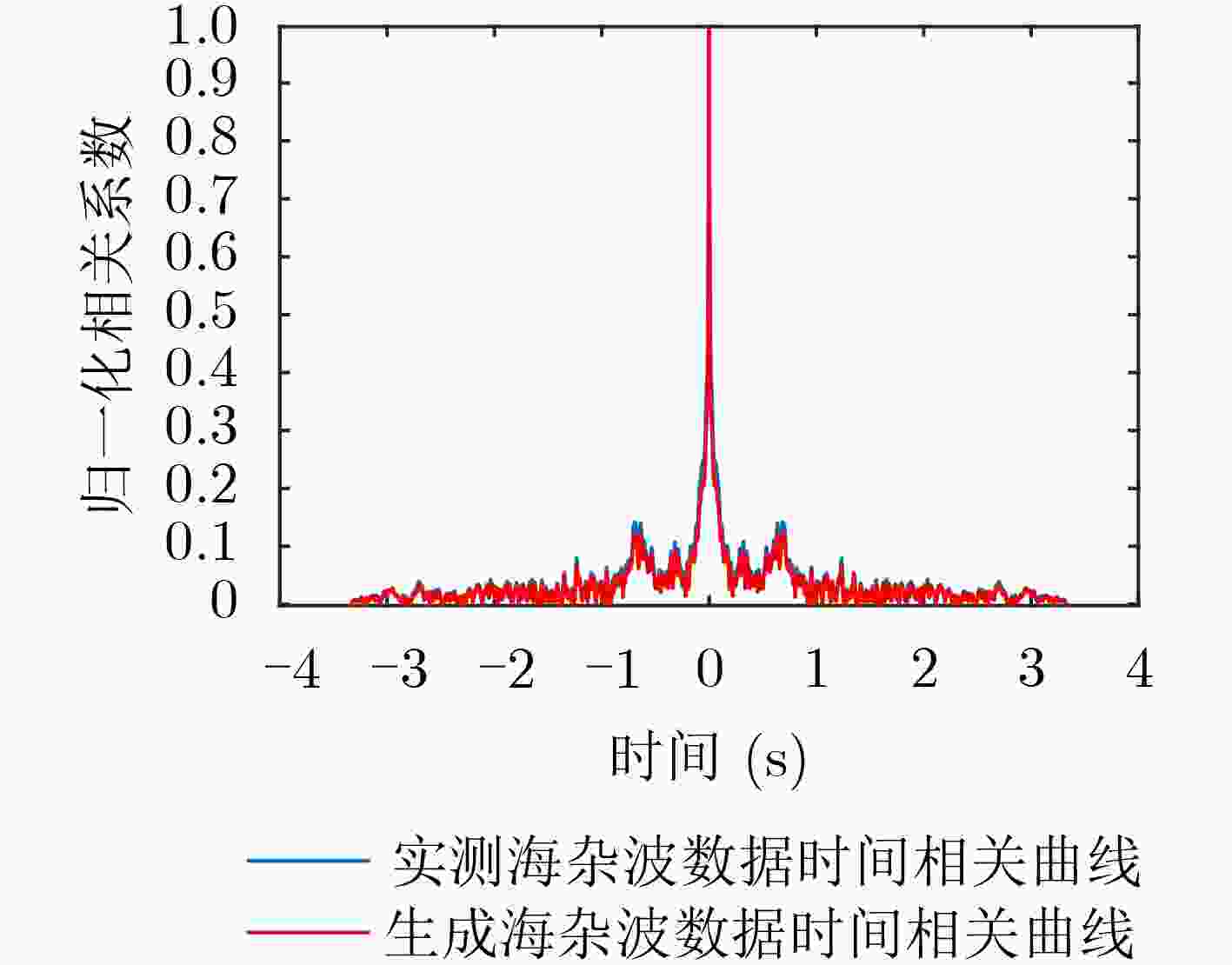


 下载:
下载:
