A Vision-based Method for 3D Pose Estimation of Non-cooperative Space Target
-
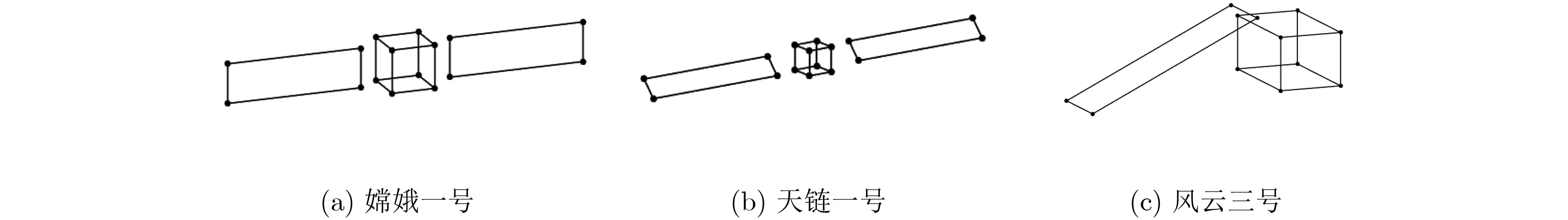
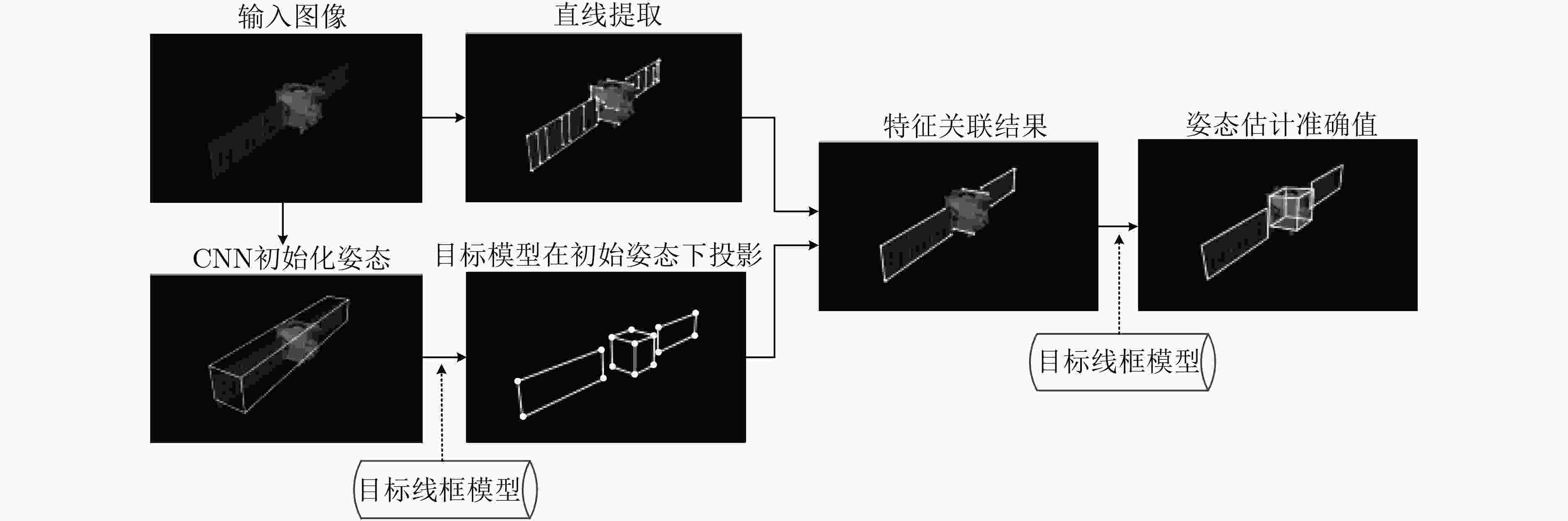
摘要: 基于视觉的非合作空间目标3维姿态估计,关键在于建立观测图像与目标模型的特征关联。当前方法往往通过采用复杂的多维特征、产生候选关联结果的方式确保特征关联的准确性,难以兼顾算法效率。为解决以上问题,该文提出一种结合深度学习技术的姿态估计方法,首先通过深度神经网络得到姿态初值,然后基于姿态初值建立图像和目标模型之间的特征关联,进而求解目标姿态。所提方法中,深度神经网络提供了稳定的姿态初值,缩小了特征关联的候选空间;在姿态初值的支撑下采取了更为高效的特征提取与匹配方法。仿真实验表明,该文方法相比于现有方法更好地兼顾了算法准确率和效率。Abstract: Establishing correspondence between the target model and the input image is an important step for the pose estimation of non-cooperative space target. Current methods always rely on complex image features and generation of candidate, which can be costly and time consuming. To solve the problems above, this paper proposes a pose estimation method that first conducts initial estimation based on deep neural network and then conducts accurate estimation through correspondence between the known target model and the input image is proposed. The deep neural network provides the stable initial value which reduces the candidates of correspondence between the target model and image. In addition, a more efficient feature extraction and matching method is adopted in this paper instead of complex multi-dimensional features. The simulation results show that the method proposed performs well both in efficiency and accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Pose estimation /
- Space target /
- Deep learning /
- Feature matching
-
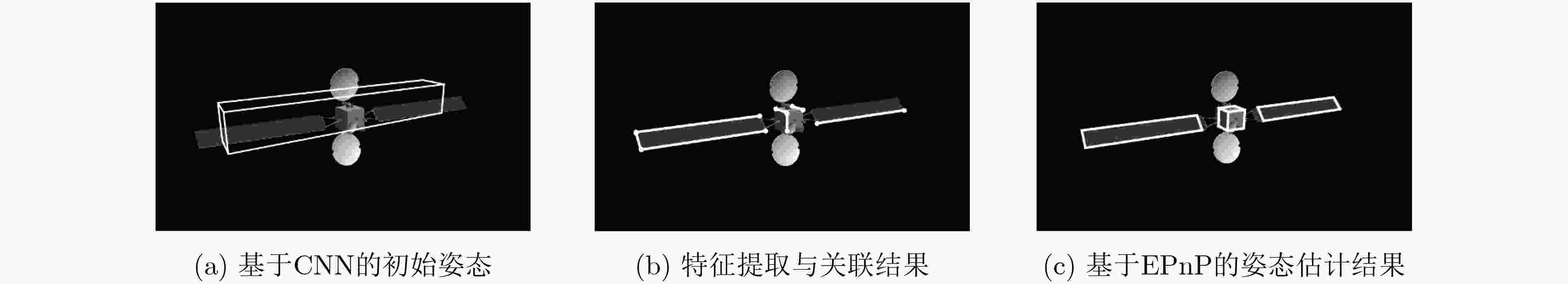
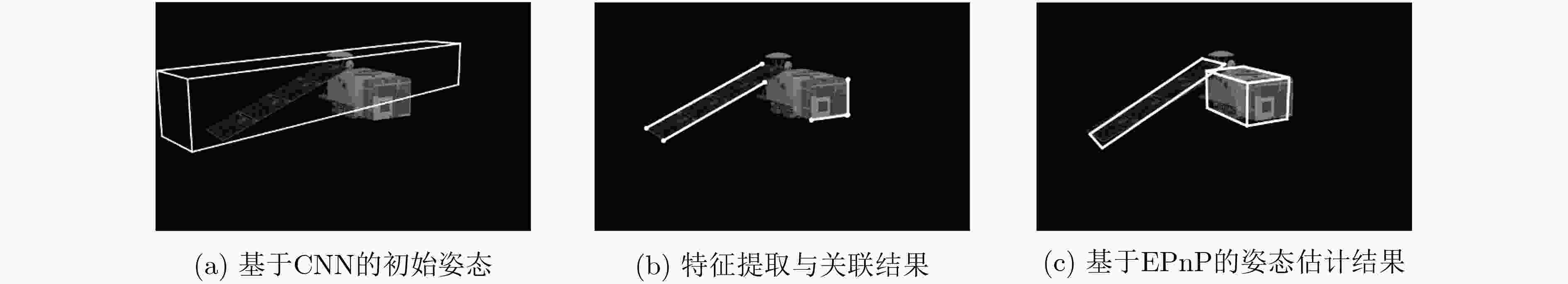
表 1 本文方法姿态估计结果
目标编号 (a) (b) (c) $\{ {\bar \varphi _{\rm{e}}},{\bar \gamma _{\rm{e}}},{\bar \theta _{\rm{e}}}\} $(°) {2.7, 2.9, 2.8} {2.3, 2.2, 2.7} {2.6, 2.5, 3} $\psi $(°) 2.8 2.4 2.7 ${\boldsymbol{\bar t}_{\rm{e}}}$(m) 0.6 0.53 0.51 -
[1] 周叶剑, 张磊, 王虹现, 等. 多站ISAR空间目标姿态估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3182–3188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160603ZHOU Yejian, ZHANG Lei, WANG Hongxian, et al. Attitude estimation for space satellite targets with multistatic ISAR systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3182–3188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160603 [2] 王阳. 基于轮廓线匹配的目标姿态求解研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.WANG Yang. Research and implementation of contour matching-based solution for target attitude[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2014. [3] SHARMA S, VENTURA J, and D’AMICO S. Robust model-based monocular pose initialization for noncooperative spacecraft rendezvous[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2018, 55(6): 1414–1429. doi: 10.2514/1.A34124 [4] ZHANG Xin, JIANG Zhiguo, ZHANG Haopeng, et al. Vision-based pose estimation for textureless space objects by contour points matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2342–2355. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2815879 [5] RUBIO A, VILLAMIZAR M, FERRAZ L, et al. Efficient monocular pose estimation for complex 3D models[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, USA, 2015: 1397–1402. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2015.7139372. [6] 宋平, 杨小冈, 蔡光斌, 等. 单站光测图像中空间目标姿态估计[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2020, 41(9): 165–170. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2020.09.031SONG Ping, YANG Xiaogang, CAI Guangbin, et al. Attitude estimation for space object based on optical image[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2020, 41(9): 165–170. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2020.09.031 [7] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2564–2571. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126544. [8] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/b:visi.0000029664.99615.94 [9] SHARMA S, BEIERLE C, and D’AMICO S. Pose estimation for non-cooperative spacecraft rendezvous using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2018. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2018.8396425. [10] 李想. 基于深度学习的空间非合作目标姿态估计算法设计[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.LI Xiang. Design of attitude estimation algorithm for space non-cooperative targets based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. [11] PAVLAKOS G, ZHOU Xiaowei, CHAN A, et al. 6-DoF object pose from semantic keypoints[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Singapore, 2017. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2017.7989233. [12] ZAKHAROV S, SHUGUROV I, and ILIC S. DPOD: 6D pose object detector and refiner[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019. [13] 张慧娟, 熊芝, 劳达宝, 等. 基于EPNP算法的单目视觉测量系统研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(5): 180–185.ZHANG Huijuan, XIONG Zhi, LAO Dabao, et al. Monocular vision measurement system based on EPNP algorithm[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(5): 180–185. [14] XIANG Yu, MOTTAGHI R, and SAVARESE S. Beyond PASCAL: A benchmark for 3D object detection in the wild[C]. 2014 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, USA, 2014. doi: 10.1109/WACV.2014.6836101. [15] 钱旭冉, 朱明, 蔡栩. 基于Blender的天文数据三维可视化[J]. 天文研究与技术, 2015, 12(2): 204–211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7673.2015.02.010QIAN Xuran, ZHU Ming, and CAI Xu. A study of 3D visualization of astronomical data based on the blender[J]. Astronomical Research and Technology, 2015, 12(2): 204–211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7673.2015.02.010 [16] 贲进, 童晓冲, 张永生, 等. 球面等积网格系统生成算法与软件模型研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2007, 36(2): 187–191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2007.02.013BEN Jin, TONG Xiaochong, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Research on generating algorithm and software model of discrete global grid systems[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2007, 36(2): 187–191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2007.02.013 [17] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [18] CHO N G, YUILLE A, LEE S W, et al. A novel linelet-based representation for line segment detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(5): 1195–1280. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2703841 [19] 胡海霞, 李钢. 几何特性二元关系的直线匹配[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2014, 19(9): 1338–1348. doi: 10.11834/jig.20140911HU Haixia and LI Gang. Line matching based on binary relations of geometric attributes[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2014, 19(9): 1338–1348. doi: 10.11834/jig.20140911 -





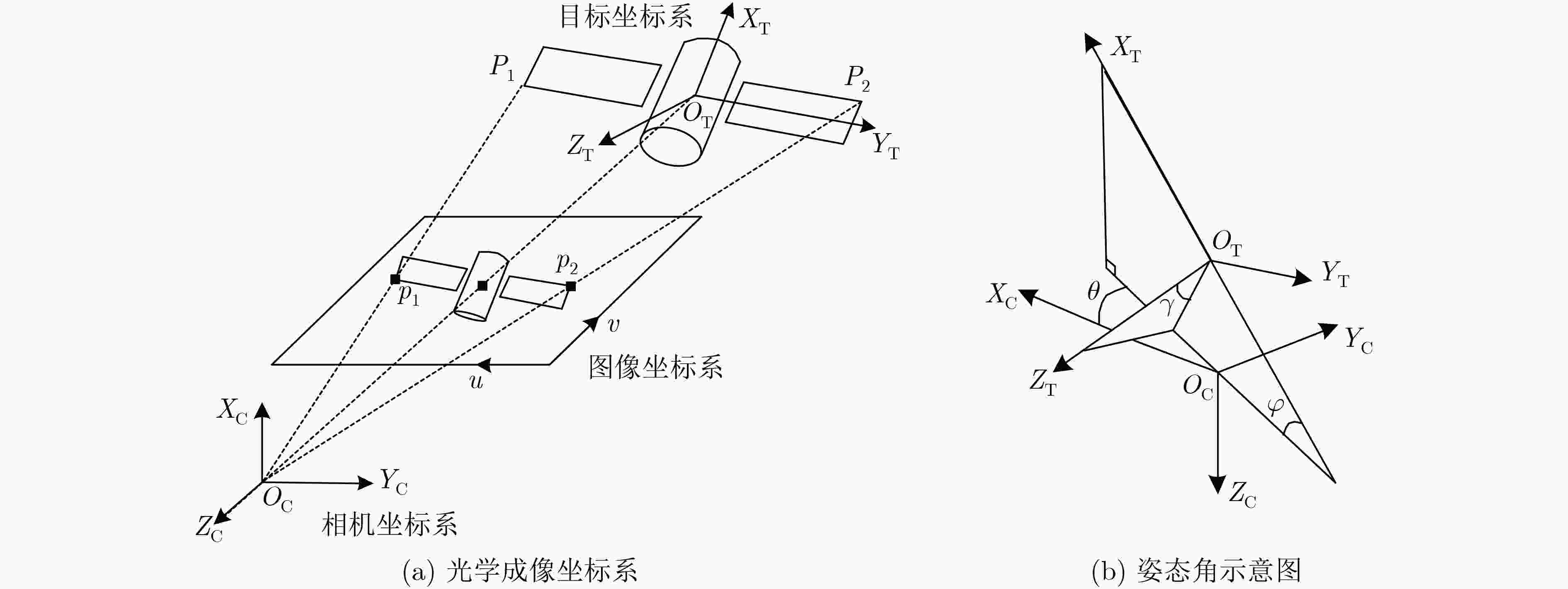
 下载:
下载:

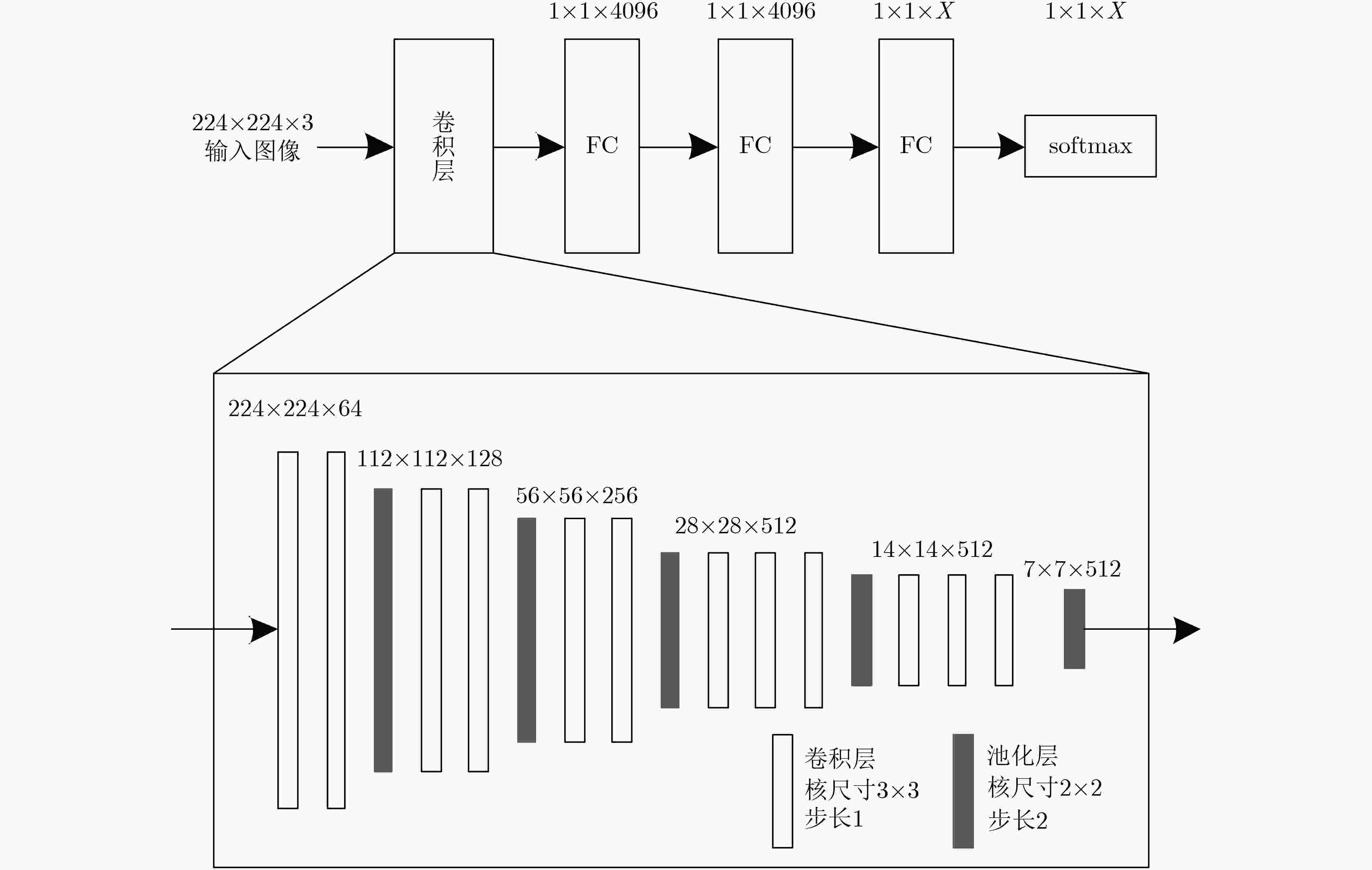
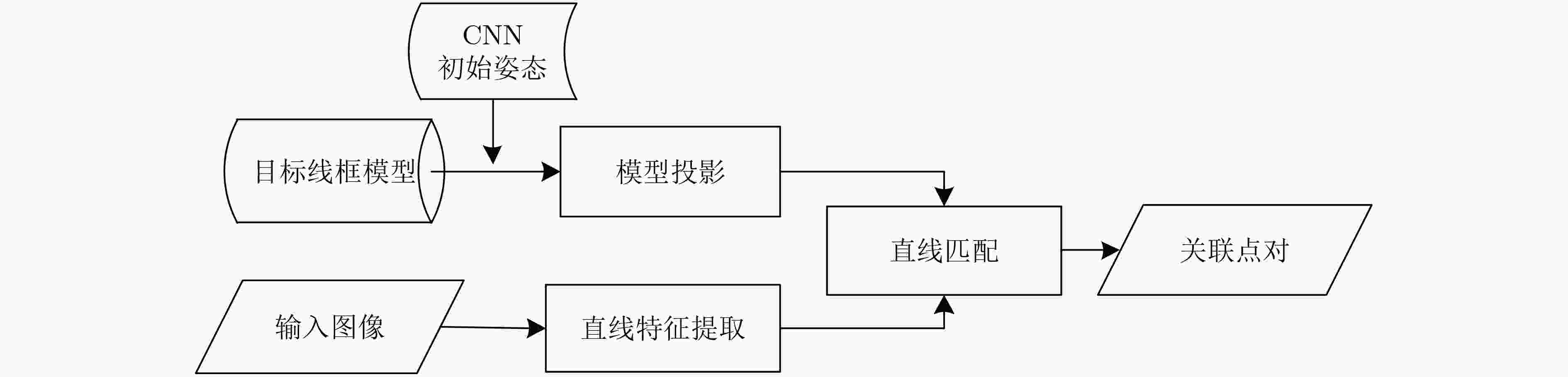
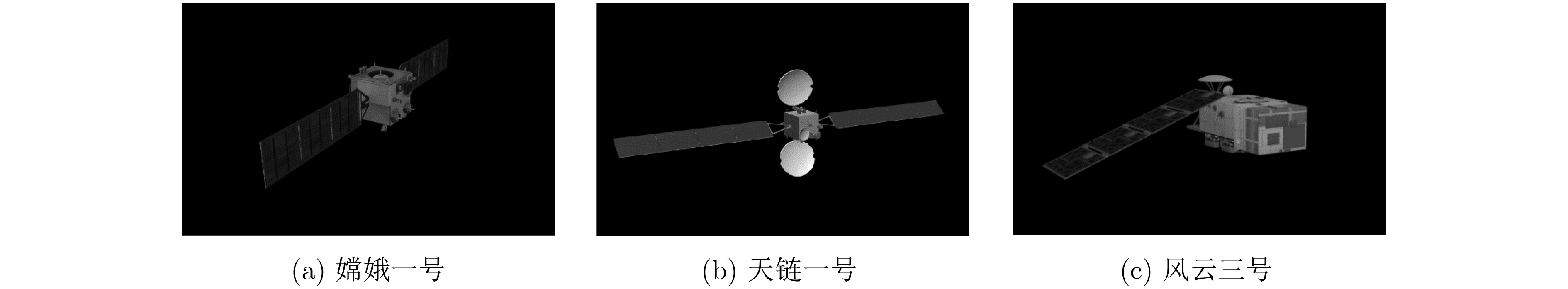
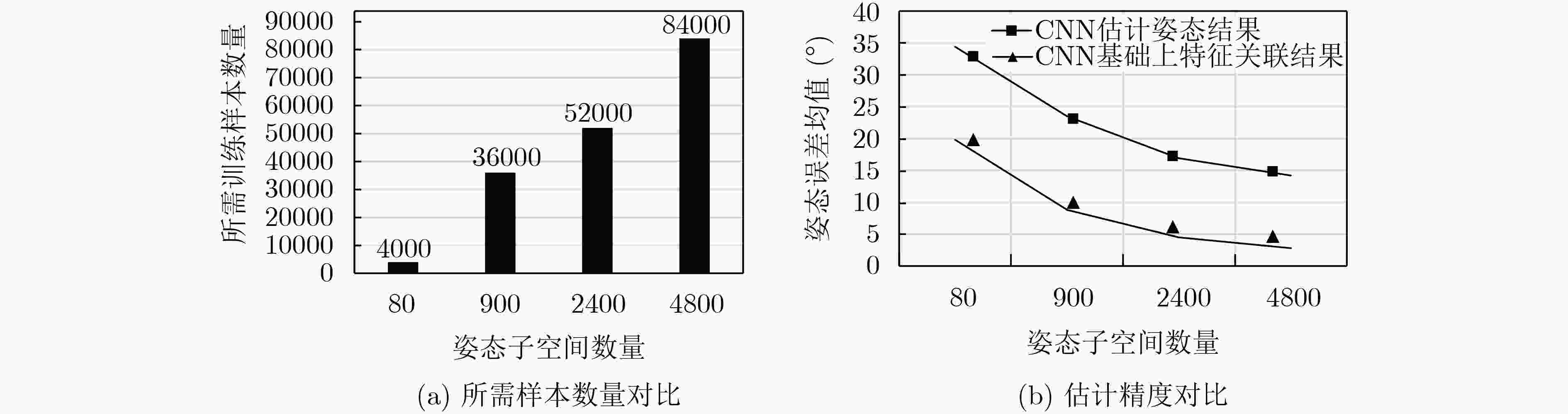
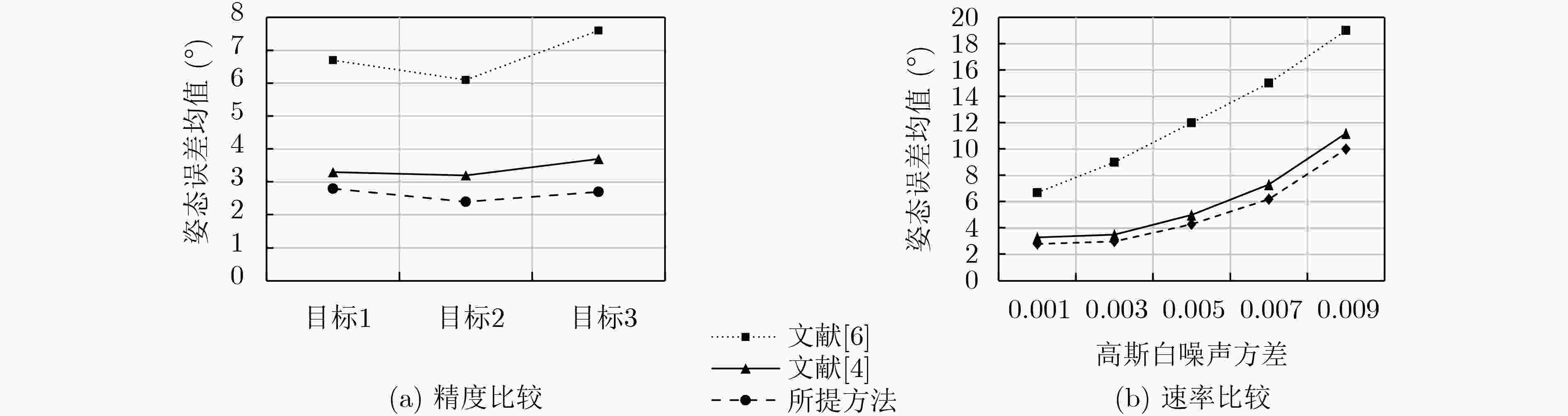
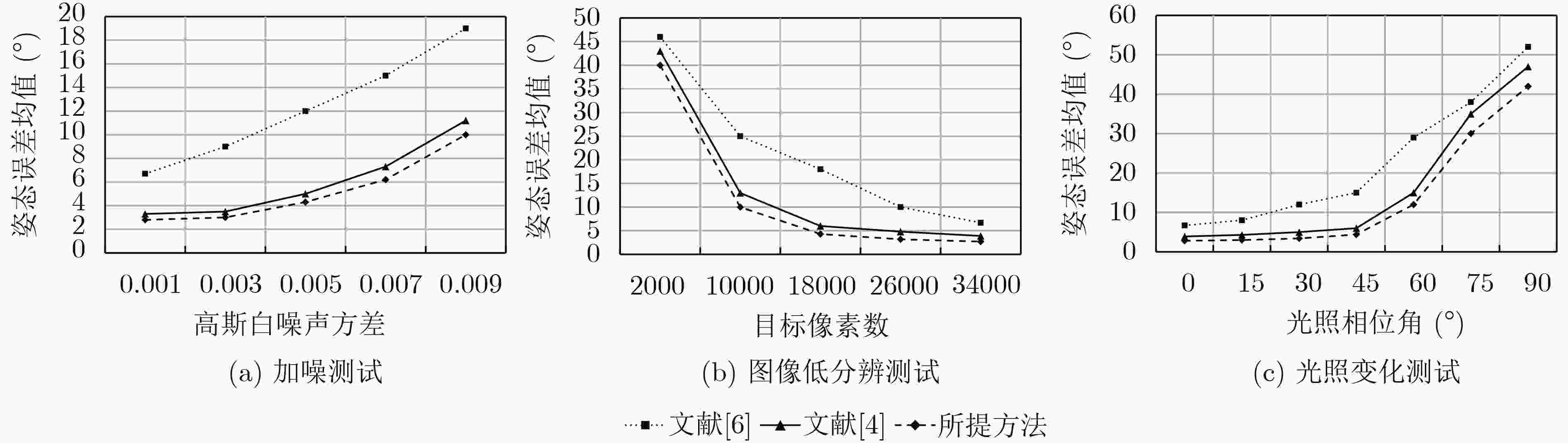
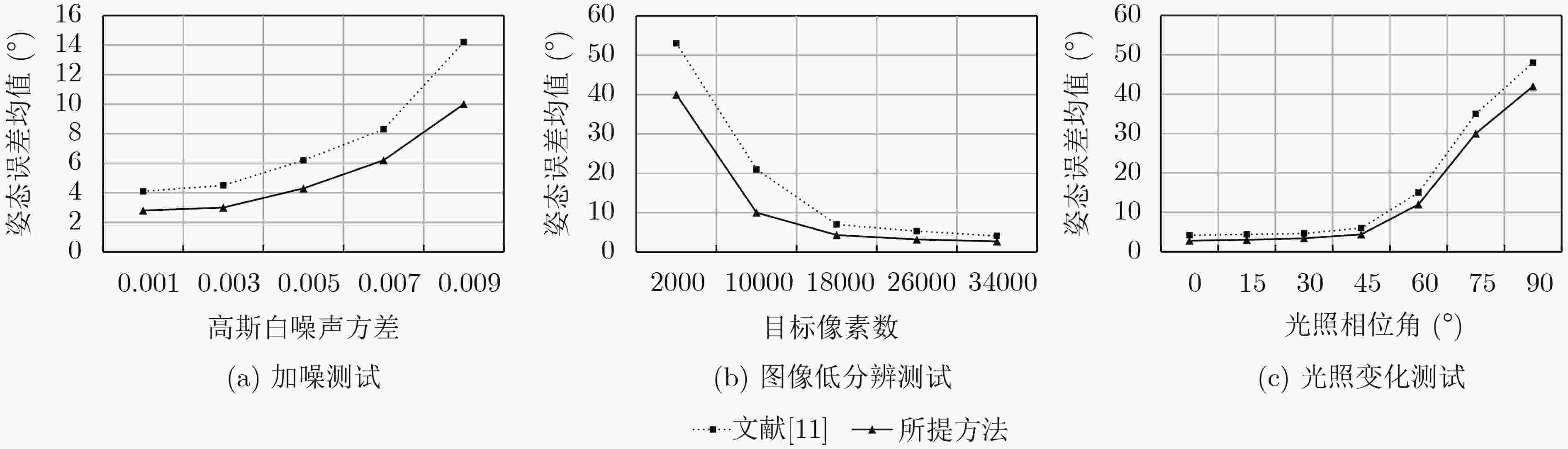


 下载:
下载:
