Human Action Recognition Network Based on Improved Channel Attention Mechanism
-
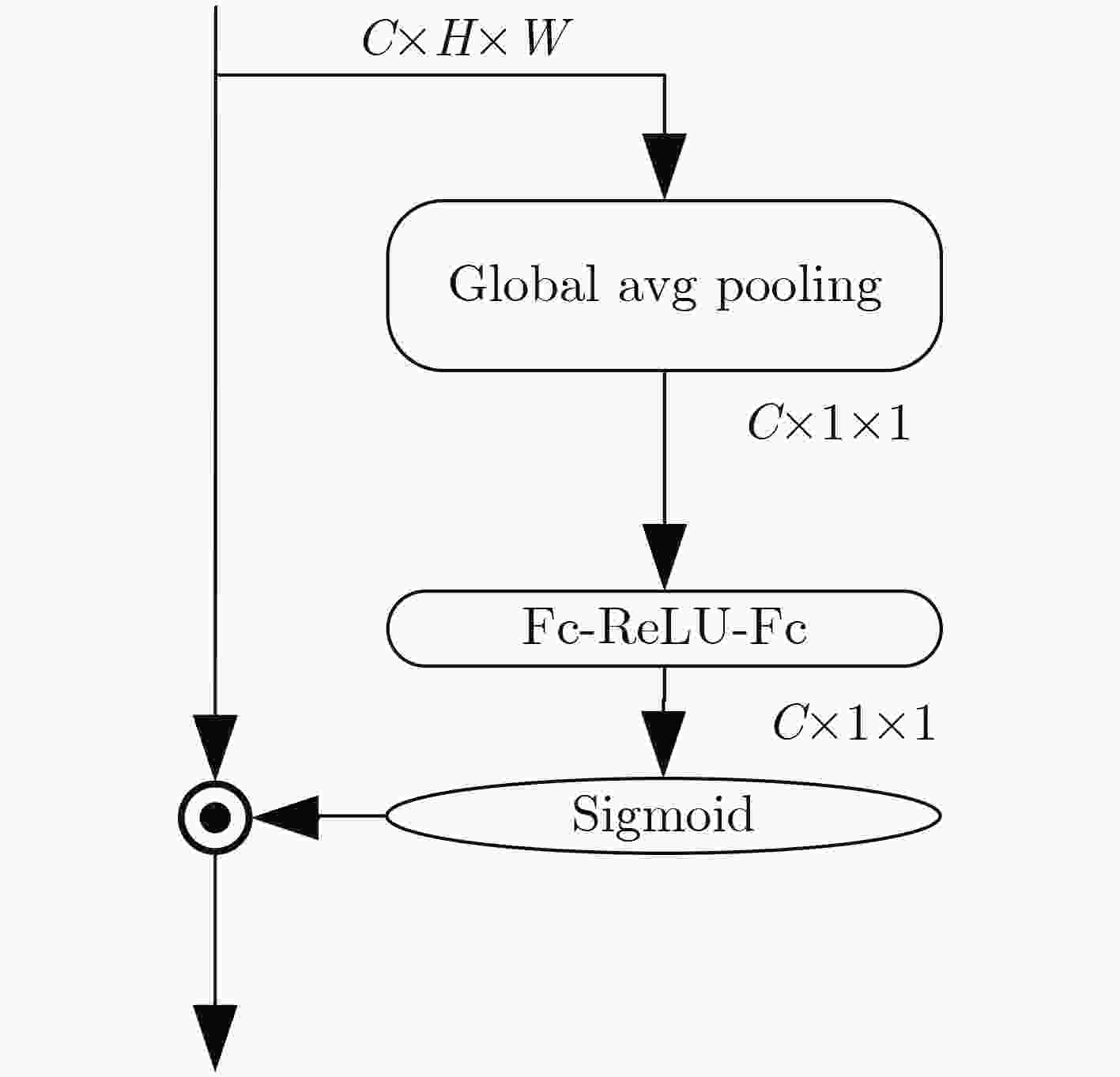
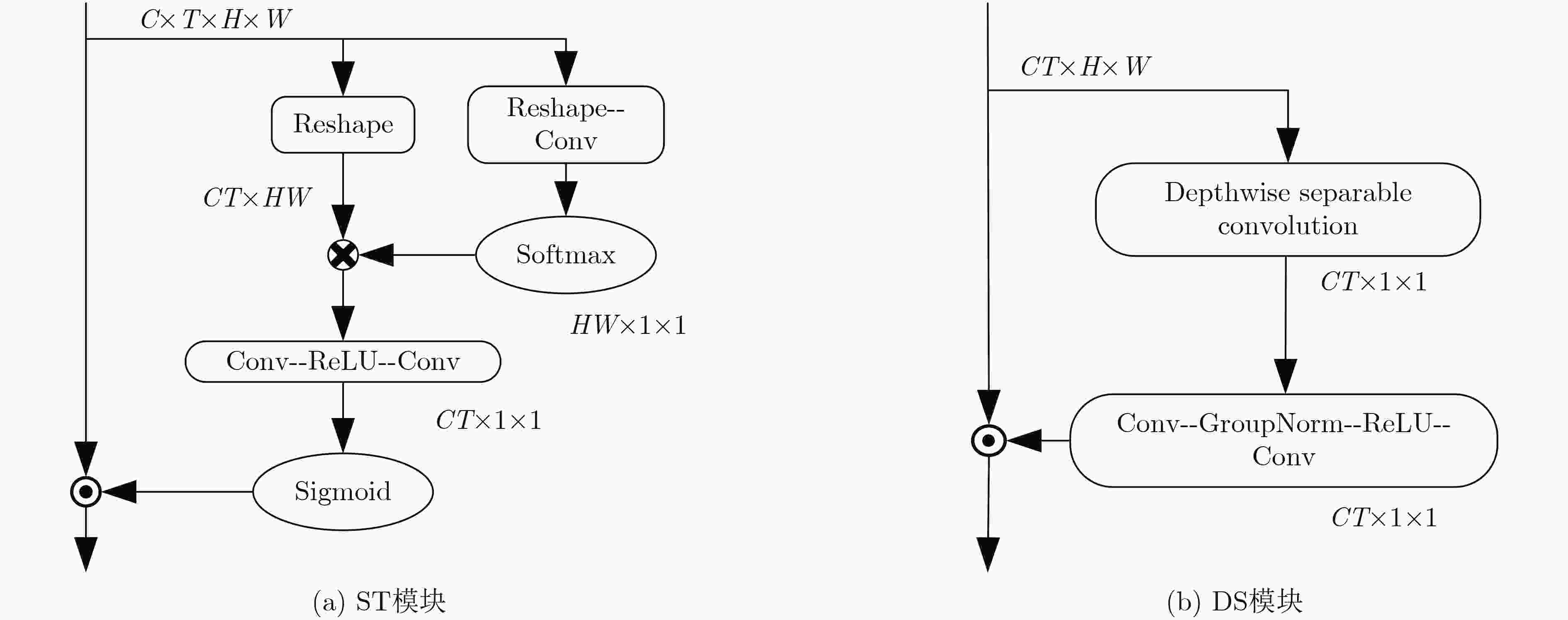
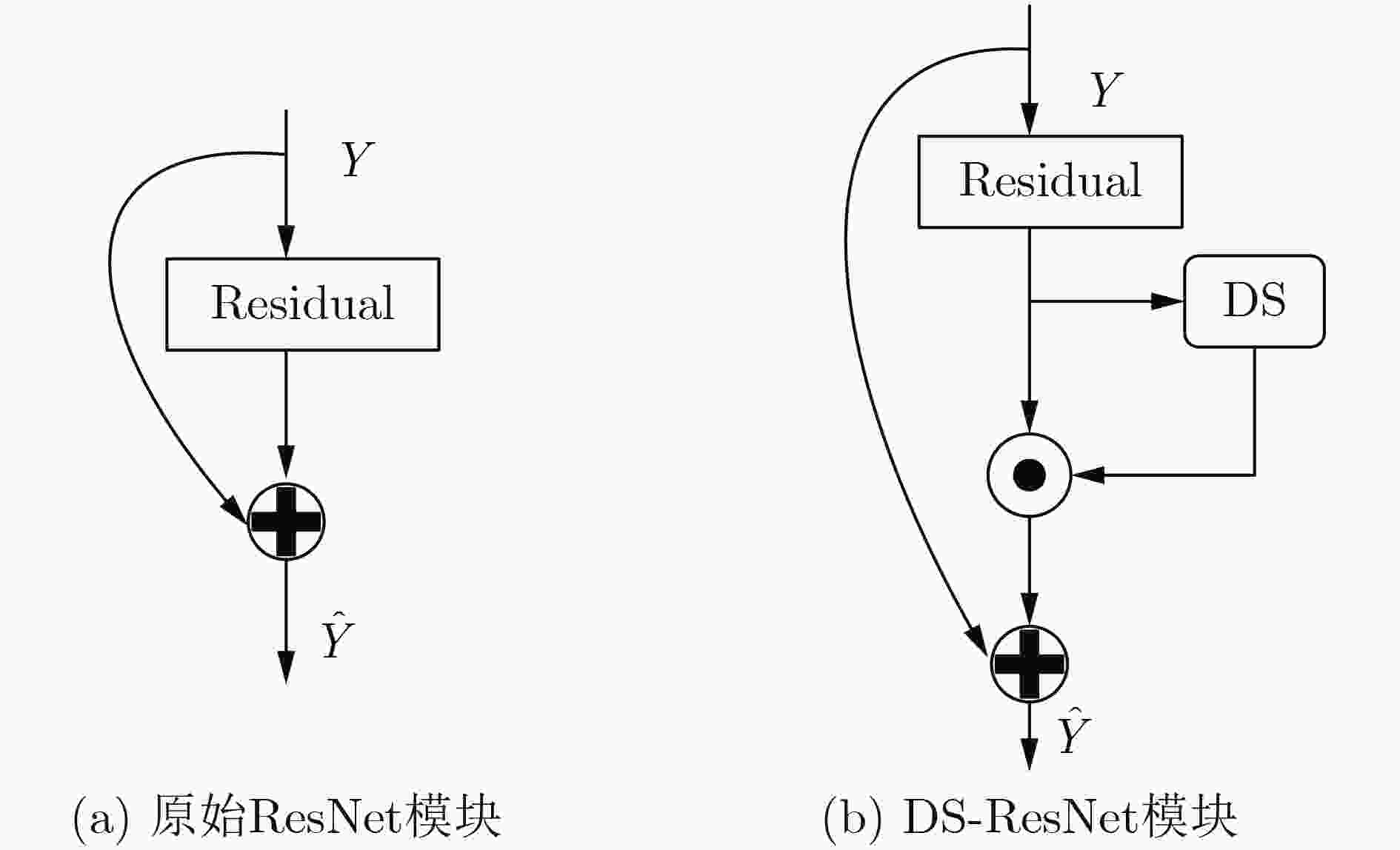
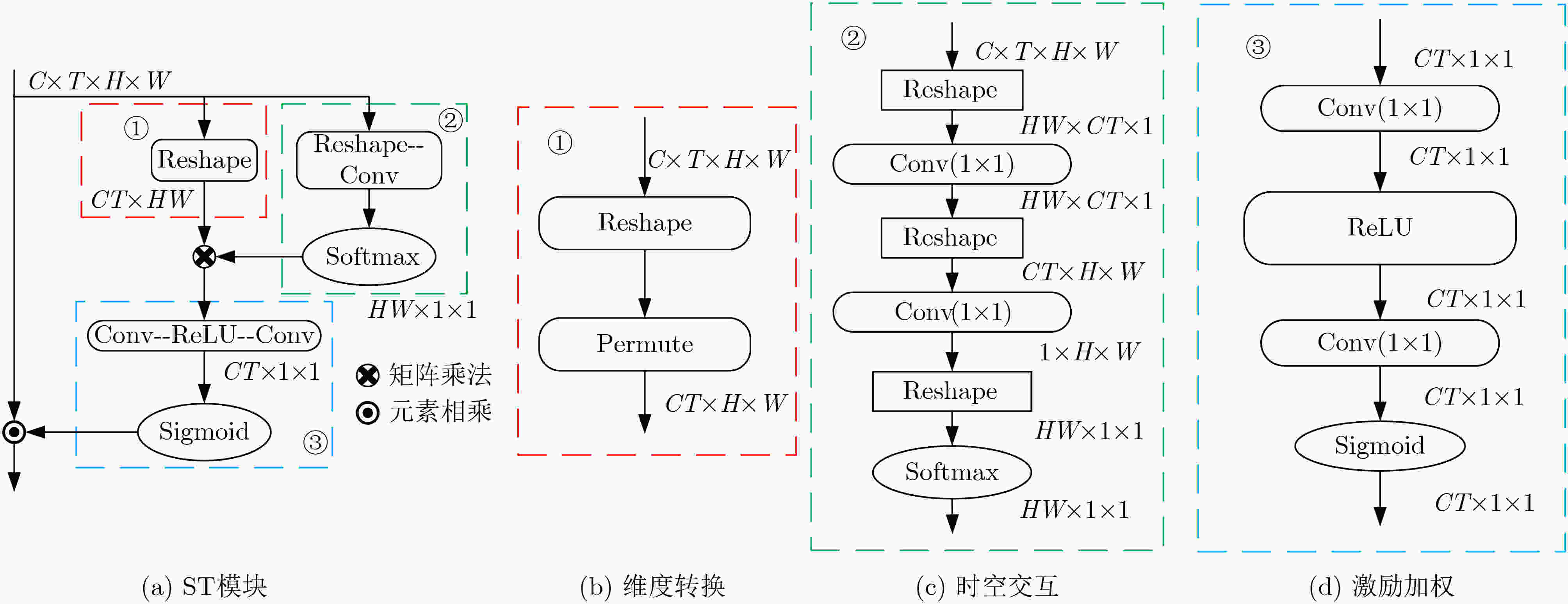
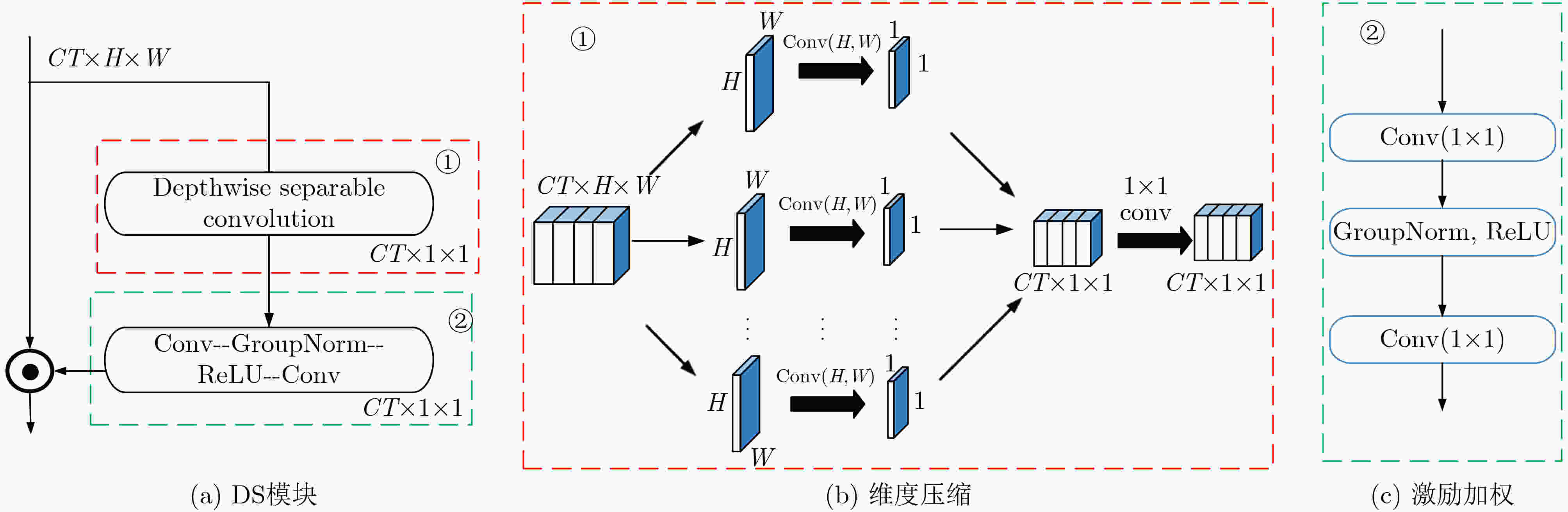
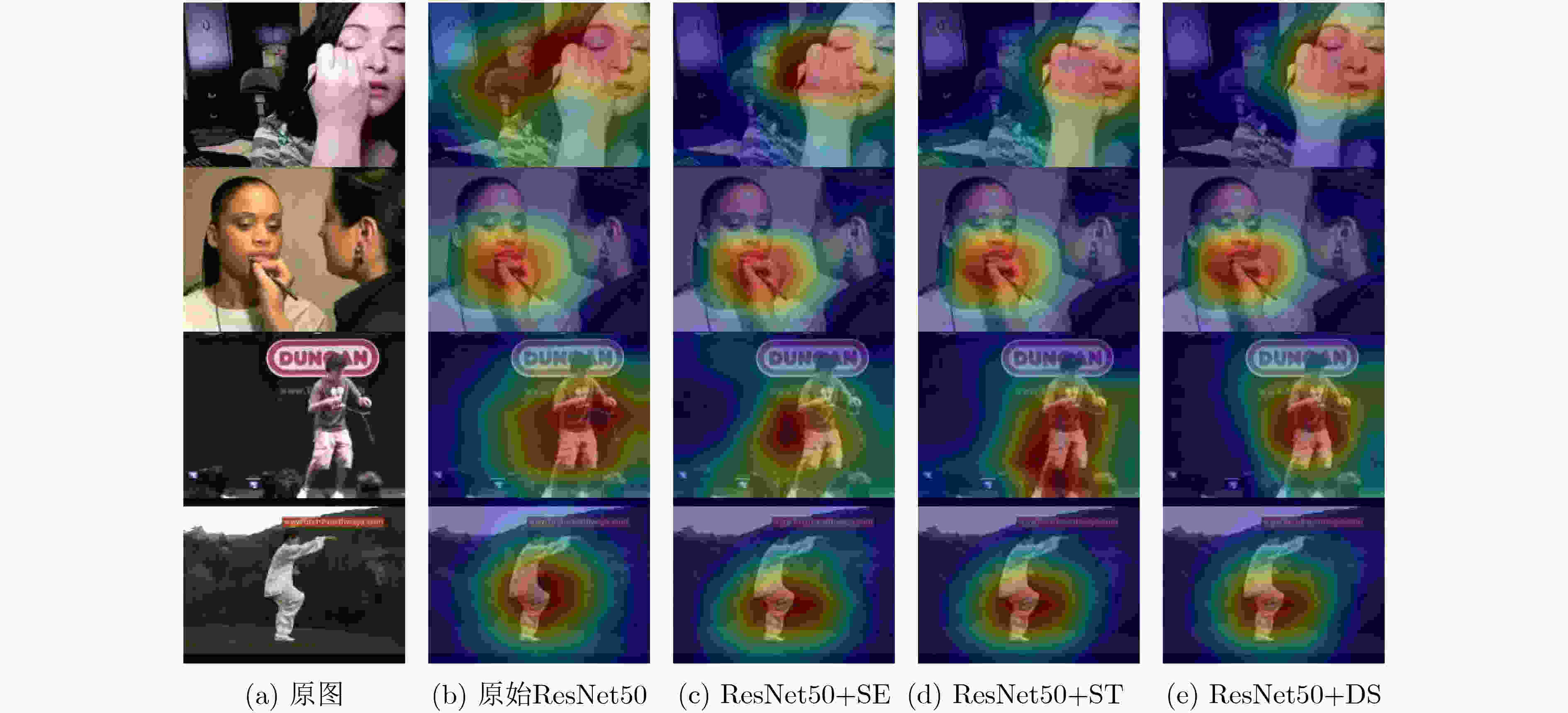
摘要: 针对现有通道注意力机制对各通道信息直接全局平均池化而忽略其局部空间信息的问题,该文结合人体行为识别研究提出了两种改进通道注意力模块,即矩阵操作的时空(ST)交互模块和深度可分离卷积(DS)模块。ST模块通过卷积和维度转换操作提取各通道时空加权信息数列,经卷积得到各通道的注意权重;DS模块首先利用深度可分离卷积获取各通道局部空间信息,然后压缩通道尺寸使其具有全局的感受野,接着通过卷积操作得到各通道注意权重,进而完成通道注意力机制下的特征重标定。将改进后的注意力模块插入基础网络并在常见的人体行为识别数据集UCF101和HDBM51上进行实验分析,实现了准确率的提升。Abstract: To tackle the problem that the existing channel attention mechanism uses global average pooling to generate channel-wise statistics while ignoring its local spatial information, two improved channel attention modules are proposed for human action recognition, namely the Spatial-Temporal (ST) interaction block of matrix operation and the Depth-wise-Separable (DS) block. The ST block extracts the spatiotemporal weighted information sequence of each channel through convolution and dimension conversion operations, and obtains the attention weight of each channel through convolution. The DS block uses firstly depth-wise separable convolution to obtain local spatial information of each channel, then compresses the channel size to make it have a global receptive field. The attention weight of each channel is obtained via convolution operation, which completes feature re-calibration with the channel attention mechanism. The proposed attention block is inserted into the basic network and experimented over the popular UCF101 and HDBM51 datasets, and the results show that the accuracy is improved.
-
表 1 验证注意力模块
表 2 网络参数对比结果
方法 主干网络 参数大小(M) MiCT ResNet-34 26.16 MiCT+SE ResNet-34 26.30 MiCT+DS ResNet-34 26.31 MiCT+ST ResNet-34 30.09 ResNet-50 ResNet-50 23.71 ResNet-50+SE ResNet-50 26.20 ResNet-50+DS ResNet-50 26.22 ResNet-50+ST ResNet-50 86.61 表 3 注意力模块的精度及运行时间比较
方法 准确率(%) 平均运行时间(s) ResNet-50 85.7 0.93 ResNet-50+SE 86.1 1.20 ResNet-50+DS 87.2 2.20 ResNet-50+ST 87.0 3.39 表 4 不同算法在UCF101与HMDB51数据集上识别准确率对比(单流输入)
方法 输入 主干网络 预训练 UCF101(%) HMDB51(%) fps C3D[21] RGB 3D Conv. Sports-1M 44.0 43.9 4.2 TS+LSTM[19] RGB ResNet+LSTM ImageNet 82.0 – – TSN[5] RGB ResNet101 ImageNet 85.7 54.6 8.5 LTC[22] RGB ResNet-50 ImageNet 83.0 52.8 – TLE[20] RGB 3D Conv. ImageNet 86.3 63.2 – TLE[20] RGB BN-Inception ImageNet 86.9 63.5 – I3D[18] RGB BN-Inception ImageNet+Kinetics 84.5 49.8 8.3 P3D[17] RGB ResNet-101 ImageNet+Kinetics 86.8 – 13.4 MiCT[16] RGB ResNet-101 ImageNet+Kinetics 86.1 62.8 4.8 C-LSTM[8] RGB ResNet+LSTM ImageNet 84.96 41.3 8.0 TSN+DS RGB ResNet-101 ImageNet 87.3 64.4 3.6 MiCT+DS RGB ResNet-101 ImageNet 87.0 64.2 2.1 表 5 不同算法在UCF101与HMDB51数据集上识别准确率对比(双流输入)
方法 输入 主干网络 预训练 UCF101(%) HMDB51(%) DTPP[23] RGB+FLOW ResNet-101 ImageNet 89.7 61.1 TS+LSTM[19] RGB+FLOW ResNet+LSTM ImageNet 88.1 – LTC[22] RGB+FLOW ResNet-50 ImageNet 91.7 64.8 TLE[20] RGB+FLOW BN-Inception ImageNet+Kinetics 95.6 70.8 T3D[24] RGB+FLOW ResNet-50 ImageNet+Kinetics 91.7 61.1 I3D[18] RGB+FLOW BN-Inception ImageNet 93.2 69.3 TSM[25] RGB+FLOW ResNet-50 ImageNet+Kinetics 94.5 70.7 MiCT-A RGB+FLOW ResNet-101 ImageNet 94.2 70.0 MiCT-B RGB+FLOW ResNet-101 ImageNet 94.6 70.9 -
[1] IKIZLER-CINBIS N and SCLAROFF S. Object, scene and actions: Combining multiple features for human action recognition[C]. The 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 2010: 494–507. [2] 张良, 鲁梦梦, 姜华. 局部分布信息增强的视觉单词描述与动作识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(3): 549–556. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150410ZHANG Liang, LU Mengmeng, and JIANG Hua. An improved scheme of visual words description and action recognition using local enhanced distribution information[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(3): 549–556. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150410 [3] KARPATHY A, TODERICI G, SHETTY S, et al. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colombus, USA, 2014: 1725–1732. [4] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 568–576. [5] WANG Limin, XIONG Yuanjun, WANG Zhe, et al. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition[C]. The 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Kingdom of the Netherlands, 2016: 20–36. [6] JI Shuiwang, XU Wei, YANG Ming, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221–231. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 [7] ZHU Yi, LAN Zhenzhong, NEWSAM S, et al. Hidden two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition[C]. The 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2018: 363–378. [8] SHARMA S, KIROS R, and SALAKHUTDINOV R. Action recognition using visual attention[C]. The International Conference on Learning Representations 2016, San Juan, The Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, 2016: 1–11. [9] 胡正平, 刁鹏成, 张瑞雪, 等. 3D多支路聚合轻量网络视频行为识别算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(7): 1261–1268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.07.003HU Zhengping, DIAO Pengcheng, ZHANG Ruixue, et al. Research on 3D multi-branch aggregated lightweight network video action recognition algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(7): 1261–1268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.07.003 [10] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [11] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [12] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167v2, 2015. [13] WU Yuxin and HE Kaiming. Group normalization[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Kingdom of the Netherlands, 2018: 3–19. [14] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. [15] 周波, 李俊峰. 结合目标检测的人体行为识别[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1961–1970.ZHOU Bo and LI Junfeng. Human action recognition combined with object detection[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1961–1970. [16] ZHOU Yizhou, SUN Xiaoyan, ZHA Zhengjun, et al. MiCT: Mixed 3D/2D convolutional tube for human action recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 449–458. [17] QIU Zhaofan, YAO Ting, and MEI Tao. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3D residual networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 5534–5542. [18] CARREIRA J and ZISSERMAN A. Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4724–4733. [19] MA C Y, CHEN M H, KIRA Z, et al. TS-LSTM and temporal-inception: Exploiting spatiotemporal dynamics for activity recognition[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2019, 71: 76–87. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2018.09.003 [20] DIBA A, SHARMA V, and VAN GOOL L. Deep temporal linear encoding networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1541–1550. [21] TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4489–4497. [22] VAROL G, LAPTEV I, and SCHMID C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1510–1517. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2712608 [23] ZHU Jiagang, ZHU Zheng, and ZOU Wei. End-to-end video-level representation learning for action recognition[C]. 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 2018: 645–650. [24] DIBA A, FAYYAZ M, SHARMA V, et al. Temporal 3D convnets: New architecture and transfer learning for video classification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.08200v1, 2017. [25] LIN Ji, GAN Chuang, and HAN Song. TSM: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea(south), 2019: 7082–7092. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
