A Personalized QoS-based Resource Allocation for Cellular-Vehicle to Everything Network and Vehicle Ad-hoc Network Heterogeneous Vehicular Network
-
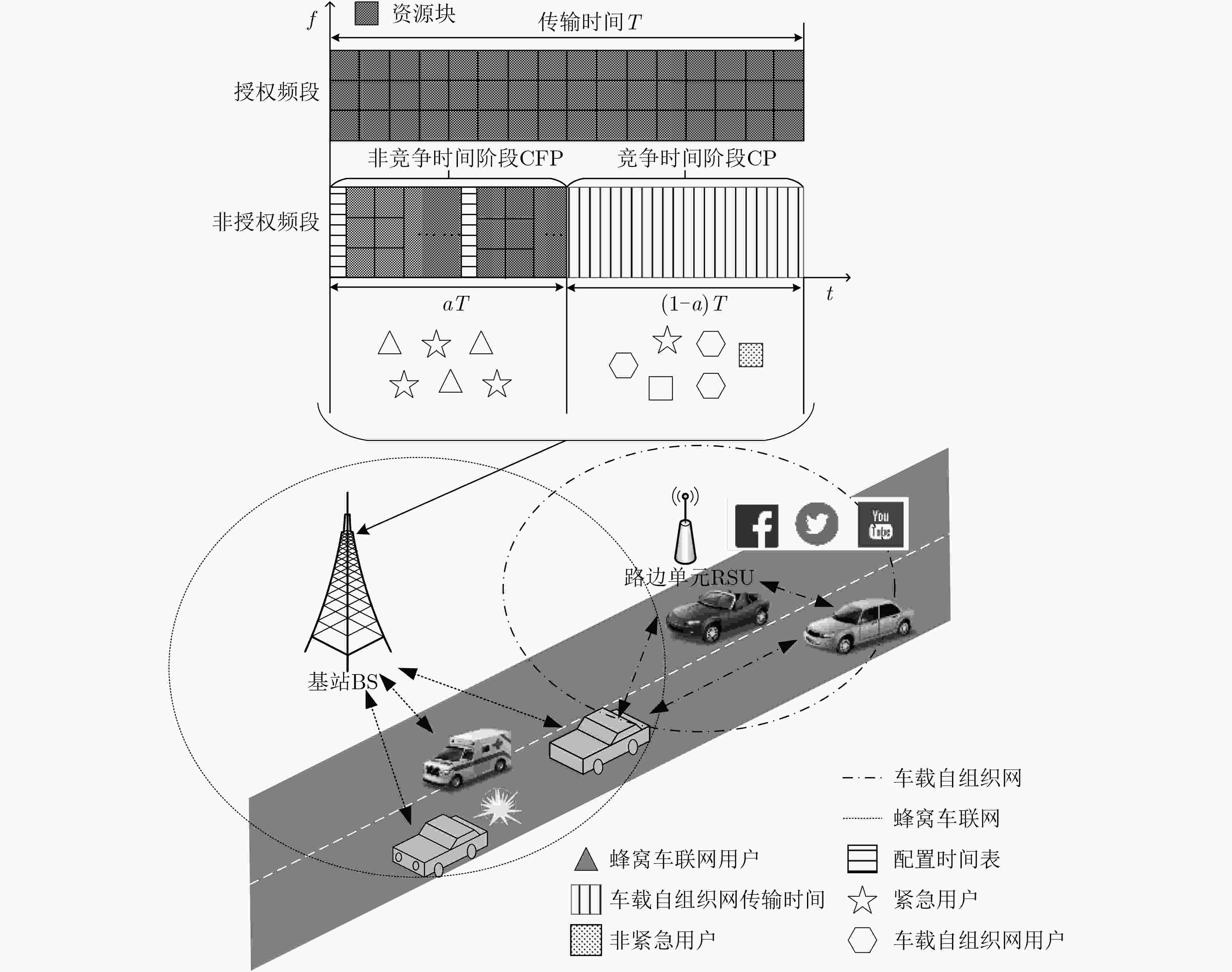
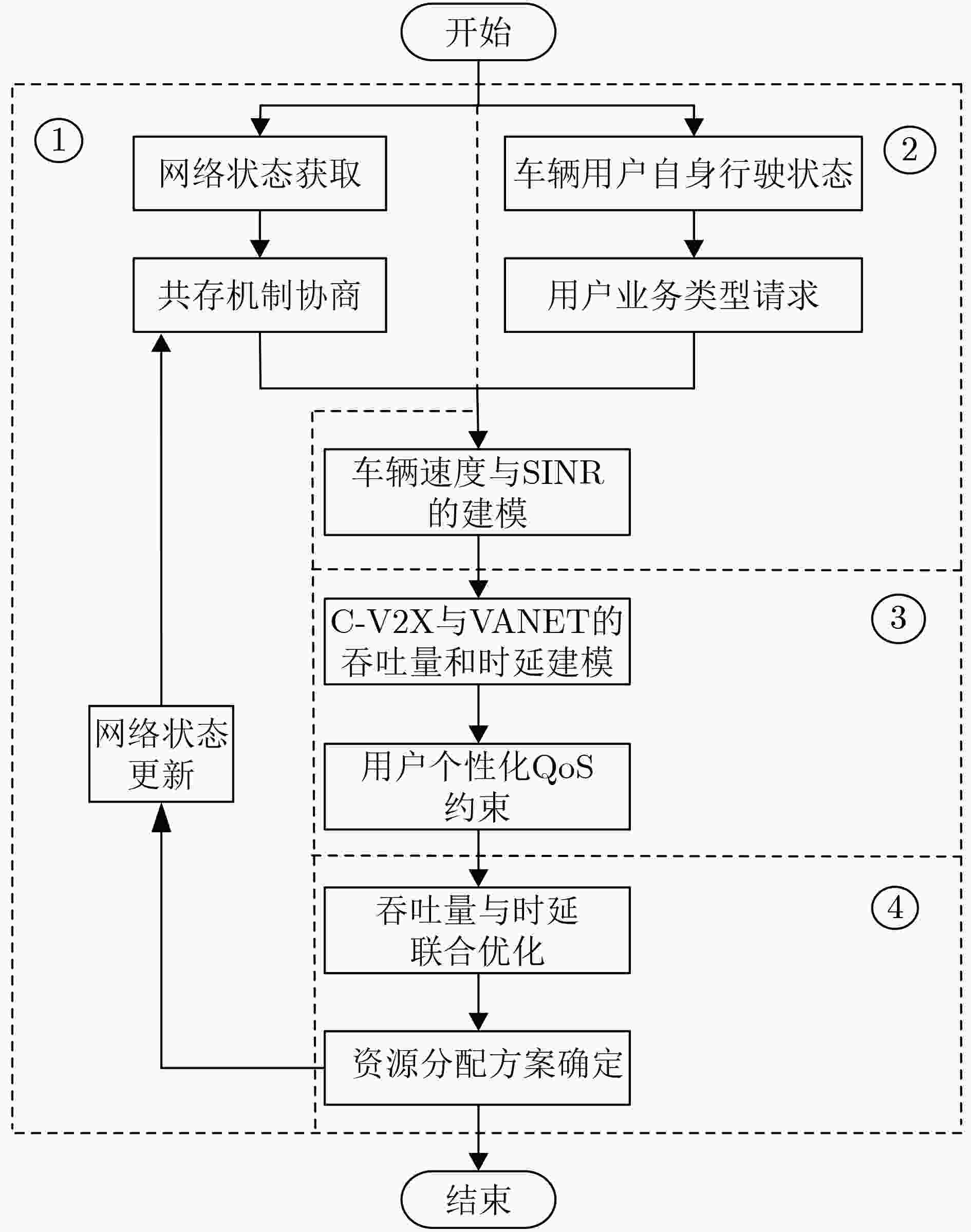
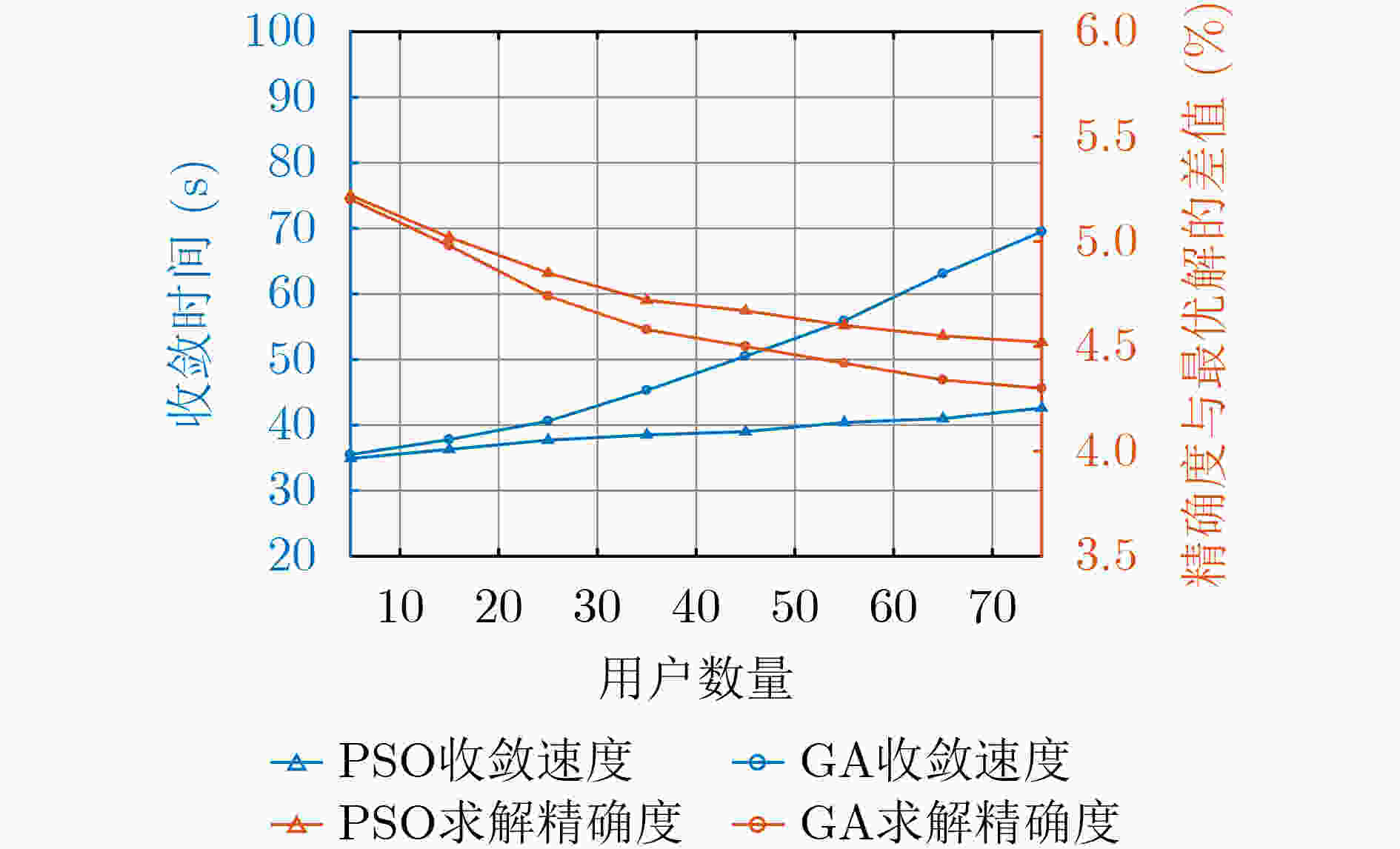
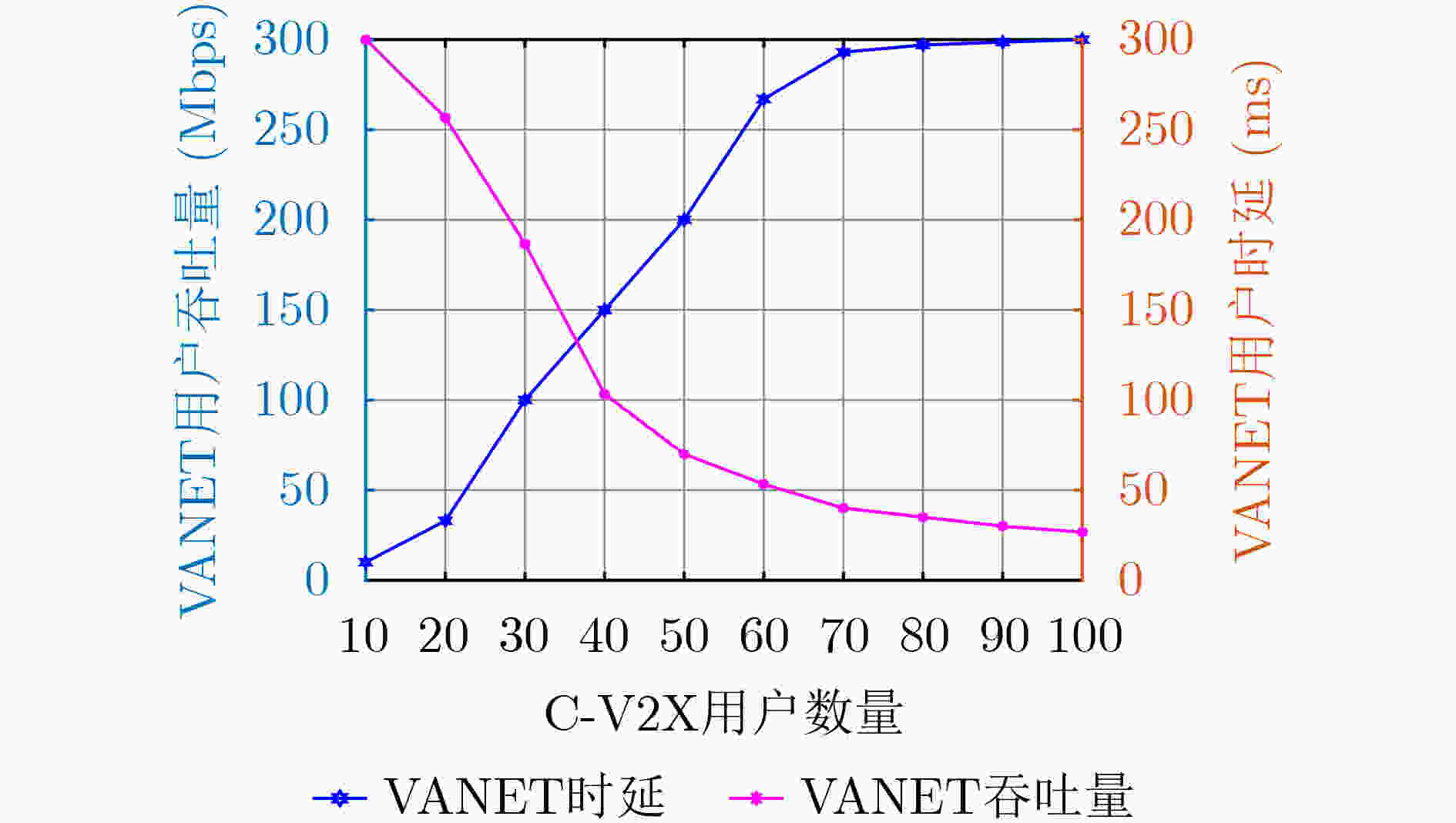
摘要: 蜂窝车联网(C-V2X)与车载自组织网络(VANET)的异构融合能够有效提高网络容量。然而,不同网络在非授权频段上共存而引起的信道冲突会导致系统吞吐量降低和用户接入时延增大,无法满足车联网用户对服务质量(QoS)的需求。针对该问题,该文提出一种基于用户个性化QoS需求的时频资源分配方法。首先,分别对C-V2X 和 VANET 的吞吐量和时延进行建模分析,刻画用户数据传输时间配置与吞吐量和时延的数学关系;然后,基于上述模型构建吞吐量-时延联合优化函数,根据用户的个性化QoS需求实现异构网络中吞吐量和时延的优化;最后,提出一种基于改进多目标粒子群优化的时延-吞吐量联合优化算法(DT-JOA)进行求解。仿真结果表明,该文所提网络资源分配算法可以有效地保证用户的个性化QoS需求,提升异构网络综合性能。Abstract: The heterogeneous integration of Cellular-Vehicle to everything (C-V2X) and Vehicle Ad-hoc NETwork (VANET) can effectively increase network capacity. However, the channel conflicts caused by the coexistence of different networks on the unlicensed frequency bands will cause the system throughput to decrease and the user access delay to increase, which can not satisfy the Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. Considering this problem, a time-frequency resource allocation method based on personalized QoS is proposed. Firstly, the throughput and delay models of C-V2X and VANET are established respectively to determine the mathematical relationship between user data transmission time configuration and throughput and delay. Then, based on the above mathematical models, a Delay-Throughput Joint Optimization Algorithm (DT-JOA) is established to optimize throughput and delay in a heterogeneous network according to the personalized QoS requirements of users. Finally, a joint optimization algorithm for delay and throughput based on Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is proposed. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can meet the personalized QoS requirements of users and significantly improve the comprehensive performance of heterogeneous networks.
-
表 1 基于PSO的联合优化算法
输入:最大迭代次数: maxgen, 粒子群数量: pop, 学习因子:C1,C2。 输出:Pareto最优解. (1) 初始化:v, p, Pbest, Gbest, ω, t. (2) while t < maxgen do (3) for i = 1, 2, ···, pop do (4) 计算适应度 F(xi) (5) if F(xi(t)) < F(xi(t+1)) then (6) 更新局部Pbest= xi(t+1); (7) end if (8) if F(Gbest(t)) < F(Gbest(t+1)) then (9) 更新全局 Gbest (t+1) < Pbest (t+1) (10) end if (11) 针对每个粒子进行 (12) 速度比较 ${v_i}(t + 1)$; (13) 位置比较 ${x_i}(t + 1)$; (14) end for (15) t++; (16) end for (17) end while 表 2 仿真参数
参数 数值 仿真区域 1000 m×1000 m 发射功率 43 dBm 功率增益因子 –31.5 dB 车辆数量 100 接收功率门限 –75 dBm SINR门限 20 dB EU容忍最大时延 50 ms nEU最低数据速率 5 Mbps 子信道带宽 15 kHz 子信道数量 12 数据包大小 512 B 噪声功率 –114 dBm 车辆行驶速度 30~120 km/h MAC层 IEEE 802.11 p 仿真时间 500 s 仿真次数 50 -
[1] 钱志鸿, 田春生, 郭银景, 等. 智能网联交通系统的关键技术与发展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 2–19. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190787QIAN Zhihong, TIAN Chunsheng, GUO Yinjing, et al. The key technology and development of intelligent and connected transportation system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 2–19. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190787 [2] 张海霞, 李腆腆, 李东阳, 等. 基于车辆行为分析的智能车联网关键技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 36–49. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190820ZHANG Haixia, LI Tiantian, LI Dongyang, et al. Research on vehicle behavior analysis based technologies for intelligent vehicular networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 36–49. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190820 [3] CHEN Shanzhi, HU Jinling, YAN Shi, et al. Vehicle-to-everything (v2x) services supported by LTE-based systems and 5G[J]. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, 2017, 1(2): 70–76. doi: 10.1109/MCOMSTD.2017.1700015 [4] ABBAS F, FAN Pingzhi, KHAN Z, et al. A novel low-latency V2V resource allocation scheme based on cellular V2X communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(6): 2185–2197. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2865173 [5] QI Weijing, LANDFELDT B, SONG Qingyang, et al. Traffic differentiated clustering routing in DSRC and C-V2X hybrid vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(7): 7723–7734. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2990174 [6] WANG Pengfei, DI Boya, ZHANG Hongliang, et al. Cellular V2X communications in unlicensed spectrum: Harmonious coexistence With VANET in 5G systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(8): 5212–5224. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2839183 [7] WEI Qing, LI Wang, FENG Zhiyong, et al. Wireless resource management in LTE-U driven heterogeneous V2X communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(8): 7508–7522. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2823313 [8] HUANG Xumin, YU Rong, KANG Jiawen, et al. Exploring mobile edge computing for 5G-enabled software defined vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2017, 24(6): 55–63. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2017.1600387 [9] DUO Ran, WU C, YOSHINAGA T, et al. SDN-based handover scheme in cellular/IEEE 802.11p Hybrid vehicular networks[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(4): 1082. doi: 10.3390/s20041082 [10] LI Xiaoshuai, MA Lin, SHANKARAN R, et al. Joint power control and resource allocation mode selection for safety-related V2X communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 7970–7986. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2921352 [11] AMADEO M, CAMPOLO C, and MOLINARO A. Enhancing IEEE 802.11p/WAVE to provide infotainment applications in VANETs[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2012, 10(2): 253–269. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2010.09.013 [12] CHEN Chen, WANG Baoji, and ZHANG Rongqing. Interference hypergraph-based resource allocation (IHG-RA) for NOMA-integrated V2X networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(1): 161–170. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875670 [13] DI Boya, SONG Lingyang, and LI Yonghui. Sub-channel assignment, power allocation, and user scheduling for non-orthogonal multiple access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(11): 7686–7698. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2606100 [14] LEE K, KIM J, PARK Y, et al. Latency of cellular-based V2X: Perspectives on TTI-proportional latency and TTI-independent latency[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 15800–15809. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2731777 [15] TONG Weiyang, CHOWDHURY S, and MESSAC A. A multi-objective mixed-discrete particle swarm optimization with multi-domain diversity preservation[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 53(3): 471–488. doi: 10.1007/s00158-015-1319-8 [16] PRASAD S and RAMESH J. Partial transmit sequence based PAPR reduction with GA and PSO optimization techniques[C]. 2017 International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS), Coimbatore, India, 2017: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICIIECS.2017.8276004. -





 下载:
下载:
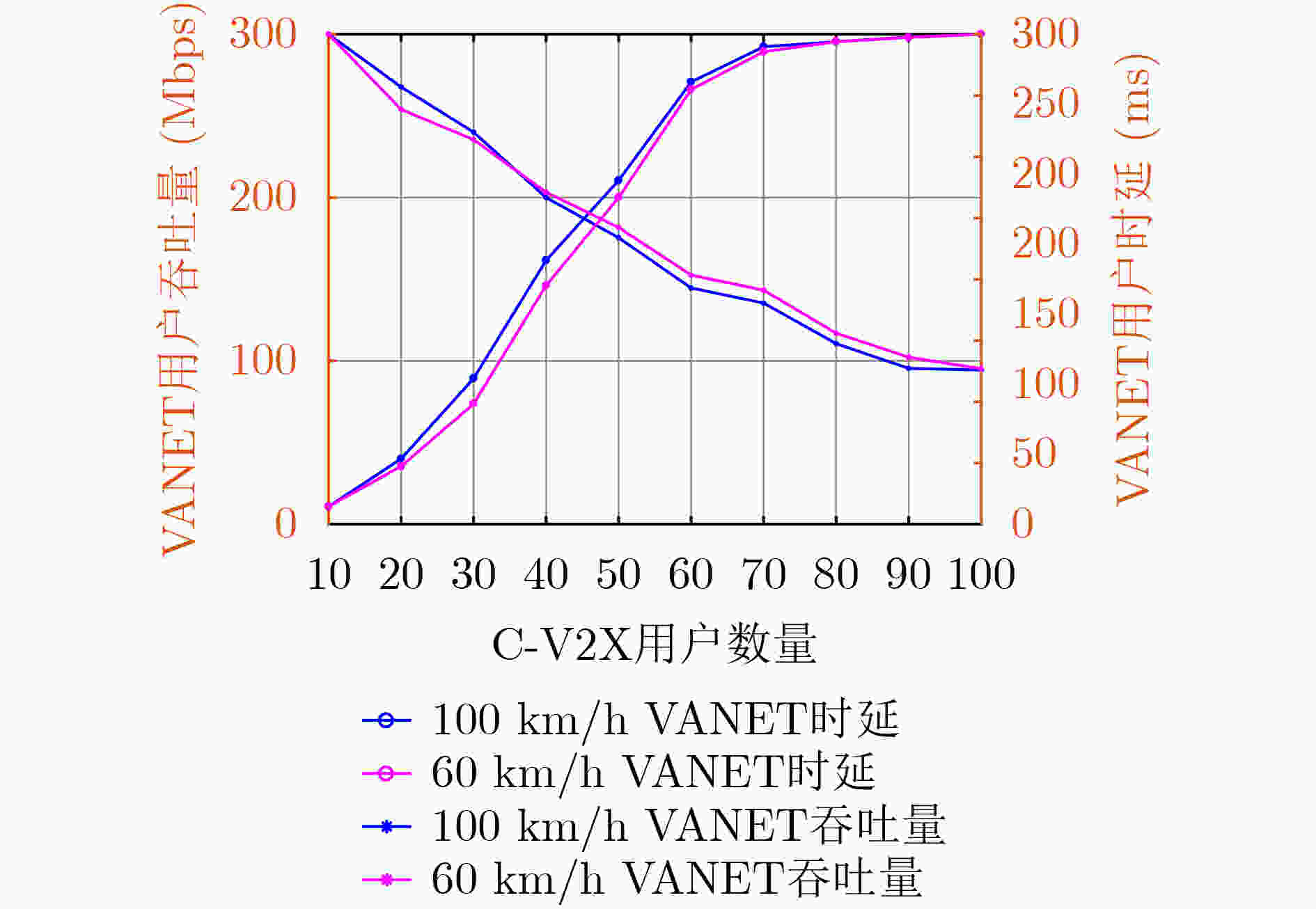
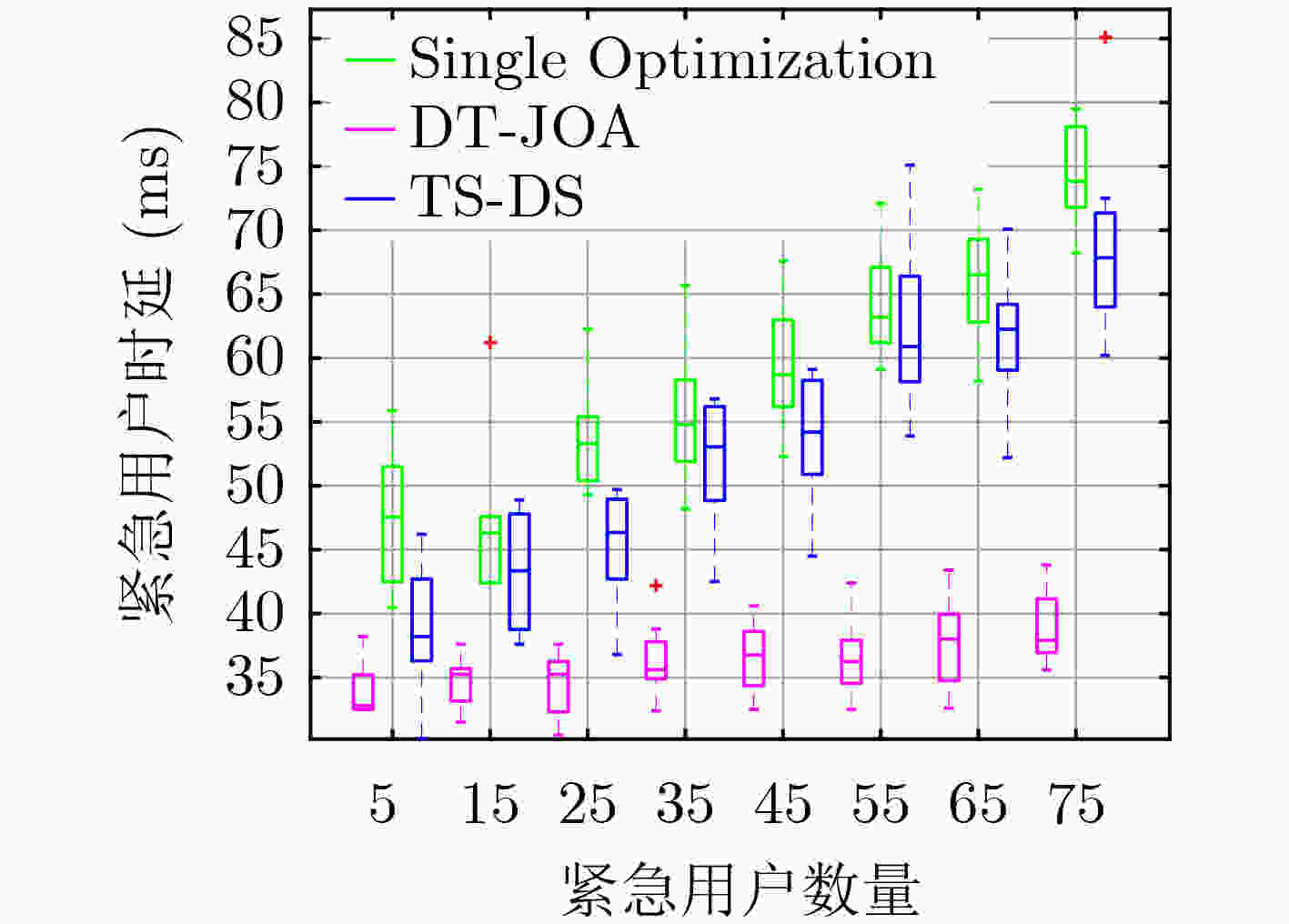
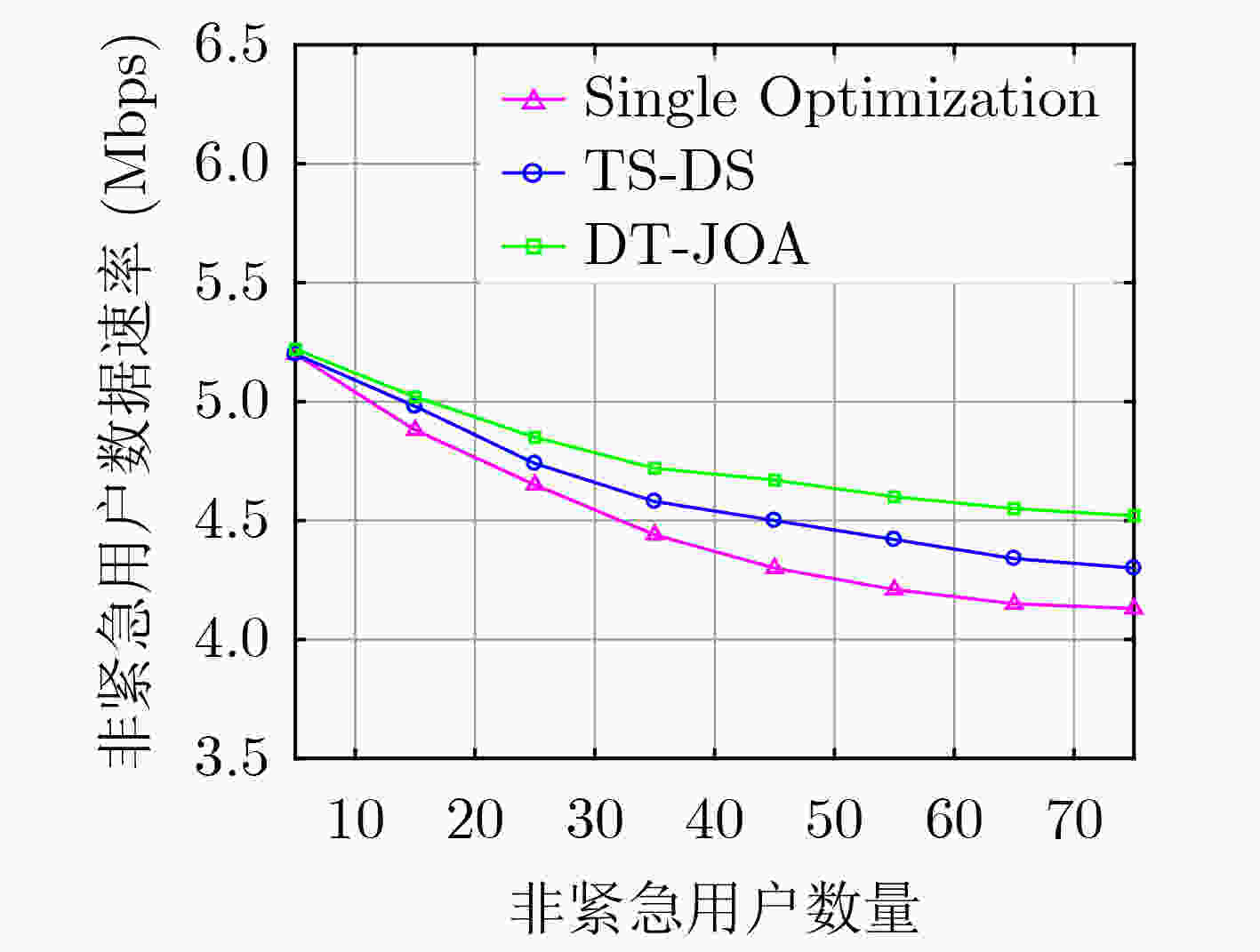


 下载:
下载:
