Cooperative Inversion of Winter Wheat Covered Surface Soil Moisture Based on Sentinel-1/2 Remote Sensing Data
-
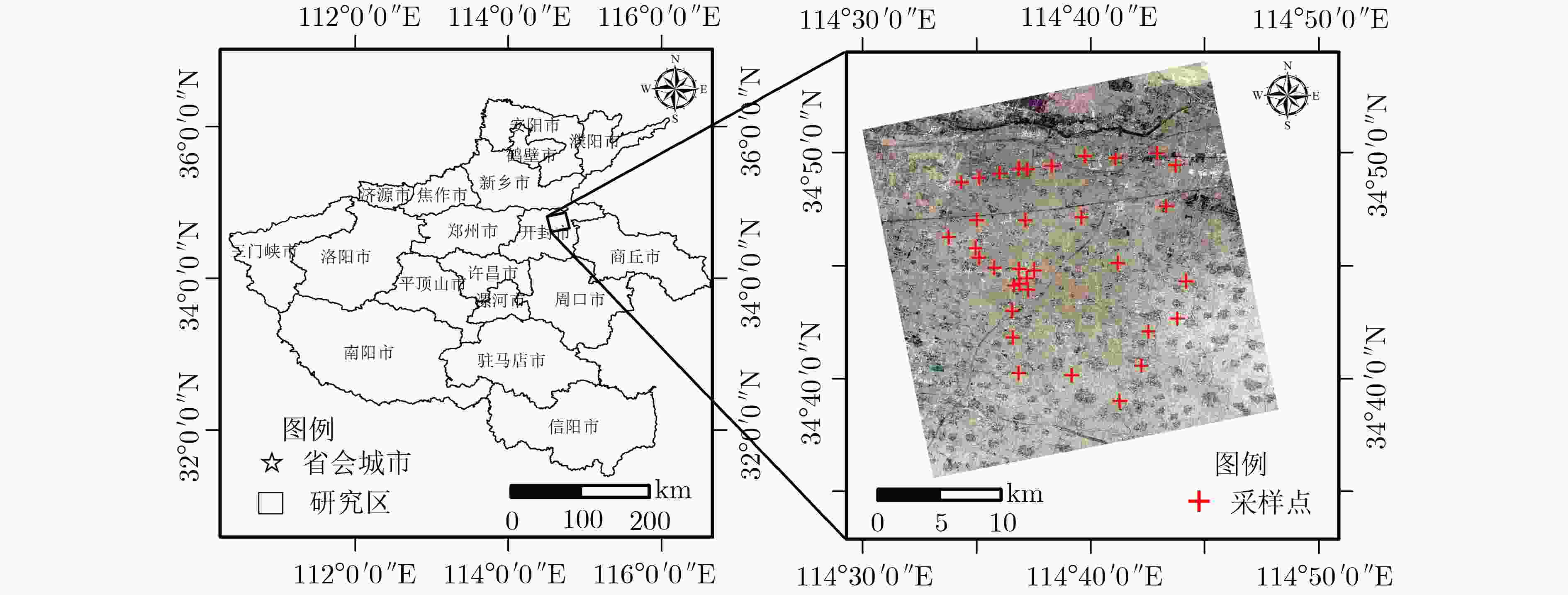
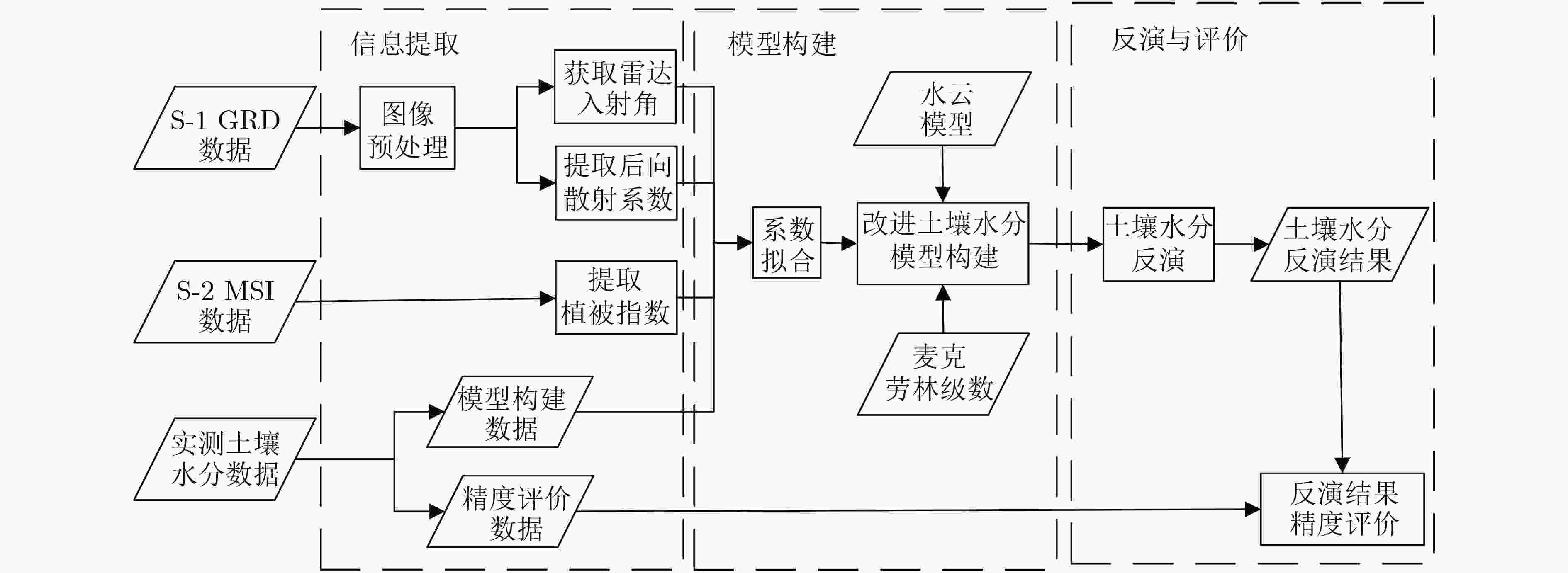
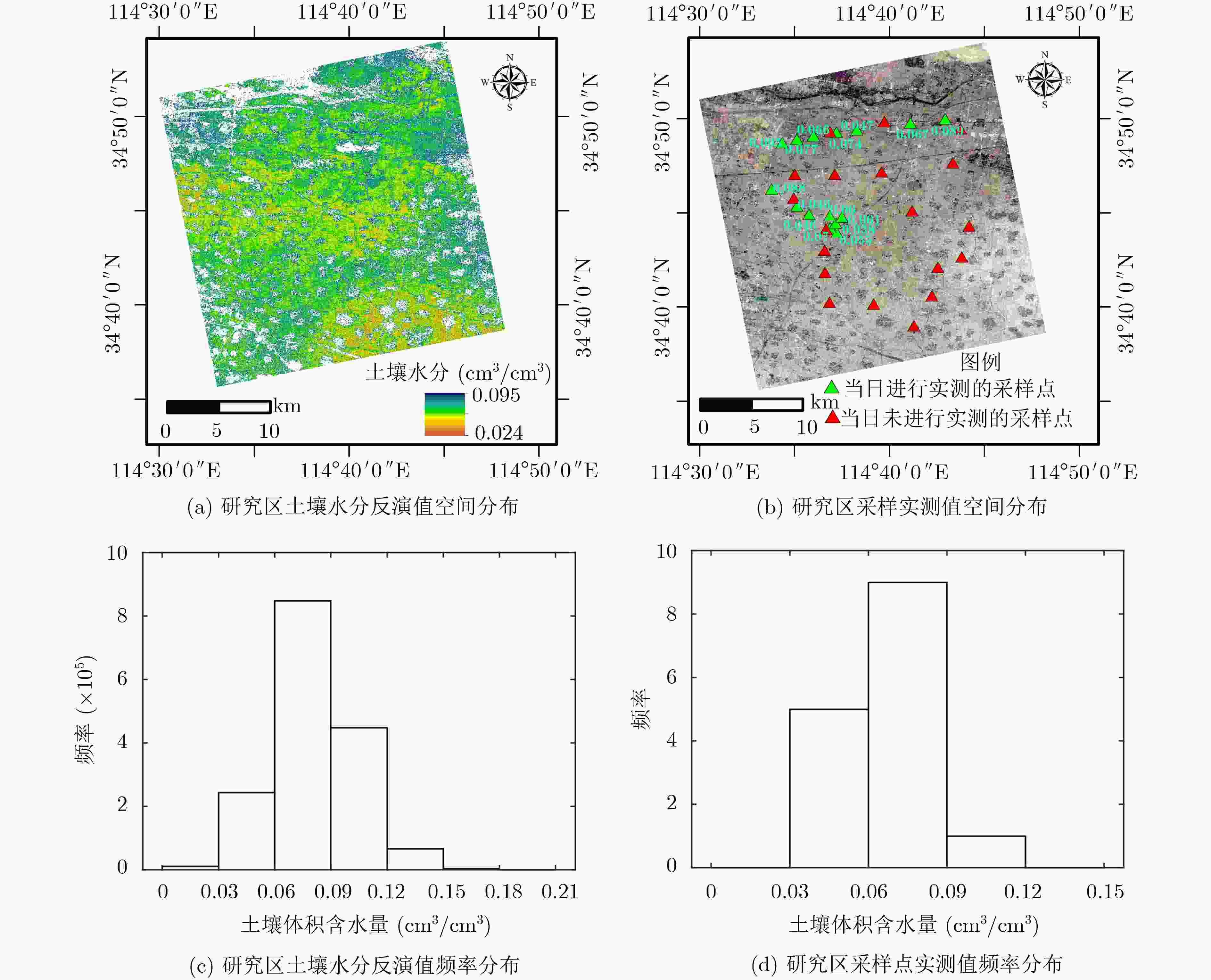
摘要: 冬小麦是我国重要粮食作物之一,对冬小麦覆盖地表土壤水分进行监测有助于解决因土壤供水导致的冬小麦歉收和农业用水浪费等问题。为了降低冬小麦覆盖地表土壤水分微波遥感反演过程中冬小麦对雷达后向散射系数的影响,该文基于Sentinel-1携带的合成孔径雷达(SAR)数据和Sentinel-2携带的多光谱成像仪(MSI)数据,结合水云模型,开展冬小麦覆盖地表土壤水分协同反演研究。首先,基于MSI数据,该文定义了一种新的植被指数,即融合植被指数(FVI),用于冬小麦含水量反演;然后,该文发展了一种基于主被动遥感数据的冬小麦覆盖地表土壤水分反演半经验模型,校正冬小麦在土壤水分反演过程中对雷达后向散射系数的影响;最后,以河南省某地冬小麦农田为研究区域,开展归一化水体指数(NDWI)和FVI两种指数与VV, VH, VV/VH 3种极化组合而成的6种反演方式下的土壤水分反演对比实验。结果表明:以FVI为植被指数,能够更好地去除冬小麦在土壤水分反演过程中对雷达后向散射系数的影响;6种反演方式中,FVI与VV/VH组合下的反演效果最优,其决定系数为0.7642,均方根误差为0.0209 cm3/cm3,平均绝对误差为0.0174 cm3/cm3,展示了该文所提土壤水分反演模型的研究价值和应用潜力。
-
关键词:
- 雷达土壤水分反演 /
- 水云模型 /
- 融合植被指数 /
- Sentinel-1/2
Abstract: Winter wheat is one of the most important food crops in China. Monitoring the soil moisture over winter wheat covered surface can help to solve the problem of poor harvest of winter wheat and waste of agricultural water due to soil water supply. In order to reduce the influence of winter wheat on radar backscattering coefficient in the process of microwave remote sensing retrieval of soil moisture covered by winter wheat, based on the Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data carried by Sentinel-1 and the MultiSpectral Imager (MSI) data carried by Sentinel-2, combined with the water cloud model, the collaborative inversion of soil moisture over winter wheat mulching surface is carried out. Firstly, based on the MSI data from Sentinel-2, a new vegetation index called Fusion Vegetation Index (FVI) is defined for inversion of winter wheat moisture. Secondly, a semi-empirical soil moisture inversion model based on active and passive remote sensing data is developed to correct the influence of winter wheat on radar backscatter coefficient. Finally, by taking a winter wheat field in Henan Province as the study area, the comparative experiments of soil moisture inversion are carried out under six combinations, which are composed of two vegetation indexes, Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) and FVI respectively, and three types of polarization data, VV, VH and VV/VH respectively. Through the experimental results, FVI shows a better performance than NDWI in reducing the influence of winter wheat on radar backscatter coefficient. Meanwhile, among the six inversion combinations, the one of FVI and VV/VH achieves the optimal inversion precision, with a determination coefficient of 0.7642, a Root Mean Square Error of 0.0209 cm3/cm3, and a Mean Absolute Error of 0.0174 cm3/cm3, demonstrating the application potential of the soil inversion model developed in this paper. -
表 1 基于水云模型和本文所发展模型的土壤水分反演精度对比结果
反演模型 反演组合方式 R2 RMSE 水云模型 VV-NDWI 0.6915 0.0245 VV-FVI 0.7212 0.0243 本文所发展模型 VV/VH-NDWI 0.7266 0.0240 VV/VH-FVI 0.7642 0.0209 表 2 本文所发展模型的6种组合反演方式下土壤水分反演精度对比结果
反演组合方式 R2 RMSE MAE VH-NDWI 0.4727 0.0326 0.0263 VV-NDWI 0.6733 0.0253 0.0202 VV/VH-NDWI 0.7266 0.0240 0.0202 VH-FVI 0.5151 0.0289 0.0246 VV-FVI 0.6791 0.0249 0.0219 VV/VH-FVI 0.7642 0.0209 0.0174 -
李震, 廖静娟. 合成孔径雷达地表参数反演模型与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 209–305.LI Zhen and LIAO Jingjuan. Model and Method for Inversion of Synthetic Surface Radar Surface Parameters[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 209–305. 闵林, 王宁, 毋琳, 等. 基于多源雷达遥感技术的黄河径流反演研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1590–1598. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190494MIN Lin, WANG Ning, WU Lin, et al. Inversion of Yellow River runoff based on multi-source radar remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1590–1598. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190494 杜兰, 魏迪, 李璐, 等. 基于半监督学习的SAR目标检测网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783DU Lan, WEI Di, LI Lu, et al. SAR target detection network via semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783 张祥, 陈报章, 赵慧, 等. 基于时序Sentinel-1A数据的农田土壤水分变化检测分析[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2017, 32(2): 338–345. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2017.2.0338ZHANG Xiang, CHEN Baozhang, ZHAO Hui, et al. Soil moisture change detection over bare agricultural area by means of time-series Sentinel-1A SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2017, 32(2): 338–345. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2017.2.0338 陈婷婷, 潘耀忠, 孙林. 基于多时相Sentinel-1SAR地表土壤水分反演的Alpha近似模型改进[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(5): 1269–1278. doi: 10.11766/trxb201807270361CHEN Tingting, PAN Yaozhong, and SUN Lin. Modification of alpha approximation model based for retrieving soil moisture data based on multi-temporal sentinel-1 SAR[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(5): 1269–1278. doi: 10.11766/trxb201807270361 韩玲, 秦小宝, 陈鲁皖. 双极化SAR数据反演裸露地表土壤水分[J]. 测绘工程, 2018, 27(2): 7–12. doi: 10.19349/j.cnki.issn1006-7949.2018.02.002HAN Ling, QIN Xiaobao, and CHEN Luwan. Inversion of soil moisture on bare surface by dual polarization SAR data[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 27(2): 7–12. doi: 10.19349/j.cnki.issn1006-7949.2018.02.002 林利斌, 鲍艳松, 左泉, 等. 基于Sentinel-1与FY-3C数据反演植被覆盖地表土壤水分[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2018, 33(4): 750–758. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2018.4.0750LIN Libin, BAO Yansong, ZUO Quan, et al. Soil moisture retrieval over vegetated areas based on sentinel-1 and FY-3C data[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2018, 33(4): 750–758. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2018.4.0750 郭二旺, 郭乙霏, 罗蔚然, 等. 基于Landsat8和Sentinel-1A数据的焦作广利灌区夏玉米土壤墒情监测方法研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2019(7): 22–25, 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2019.07.005GUO Erwang, GUO Yifei, LUO Weiran, et al. Soil moisture retrieval of summer maize in the irrigation area based on sentinel-1A[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2019(7): 22–25, 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2019.07.005 郭交, 刘健, 宁纪锋, 等. 基于Sentinel多源数据的农田地表土壤水分反演模型构建与验证[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(14): 71–78. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.14.009GUO Jiao, LIU Jian, NING Jifeng, et al. Construction and validation of soil moisture retrieval model in farmland based on Sentinel multi-source data[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(14): 71–78. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.14.009 PRÉVOT L, CHAMPION I, and GUYOT G. Estimating surface soil moisture and leaf area index of a wheat canopy using a dual-frequency (C and X bands) scatterometer[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1993, 46(3): 331–339. doi: 10.1016/0034-4257(93)90053-Z TACONET O, BENALLEGUE M, VIDAL-MADJAR D, et al. Estimation of soil and crop parameters for wheat from airborne radar backscattering data in C and X bands[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1994, 50(3): 287–294. doi: 10.1016/0034-4257(94)90078-7 BAGHDADI N, EL HAJJ M, ZRIBI M, et al. Calibration of the water cloud model at C-band for winter crop fields and grasslands[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(9): 969. doi: 10.3390/rs9090969 BAO Yansong, LIN Libin, WU Shanyu, et al. Surface soil moisture retrievals over partially vegetated areas from the synergy of Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 data using a modified water-cloud model[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2018, 72: 76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2018.05.026 杜伟娜, 徐爱功, 宋耀鑫, 等. 新型SAR传感器一级地距产品绝对辐射定标方法[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2016, 28(4): 30–34. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2016.04.05DU Weina, XU Aigong, SONG Yaoxin, et al. Absolute radiometric calibration of level-1 detected ground range products of new SAR sensors[J]. Remote Sensing for Land &Resources, 2016, 28(4): 30–34. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2016.04.05 MOHAN M M P, RAJITHA K, and VARMA M R R. Integration of soil moisture as an auxiliary parameter for the anchor pixel selection process in SEBAL using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1A images[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(3): 1214–1231. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1658239 MOREAU S, BOSSENO R, GU Xingfa, et al. Assessing the biomass dynamics of Andean bofedal and totora high-protein wetland grasses from NOAA/AVHRR[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 85(4): 516–529. doi: 10.1016/s0034-4257(03)00053-1 GAO Bocai. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1996, 58(3): 257–266. doi: 10.1016/s0034-4257(96)00067-3 SIBANDA M, MUTANGA O, and ROUGET M. Examining the potential of Sentinel-2 MSI spectral resolution in quantifying above ground biomass across different fertilizer treatments[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 110: 55–65. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.005 KONG Jinling, YANG Jing, ZHEN Peipei, et al. A coupling model for soil moisture retrieval in sparse vegetation covered areas based on microwave and optical remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(12): 7162–7173. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2018.2849009 ATTEMA E P W and ULABY F T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud[J]. Radio Science, 1978, 13(2): 357–364. doi: 10.1029/rs013i002p00357 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
