ReliefF-Pearson Based Olfactory ElectroEncephaloGram Channel Selection
-
摘要: 基于脑电(EEG)信号的气味识别研究在嗅觉功能客观评价及嗅觉障碍疾病诊断等方面具有重要的应用价值。在实际应用场景中使用过多EEG通道会带来诸多不便,因此研究如何选择EEG通道尤为重要。该文针对嗅觉EEG信号分类中的通道选择问题,提出了一种新型的基于ReliefF-Pearson的嗅觉EEG通道选择算法。该算法结合ReliefF的权值思想和Pearson系数的相关性原理对EEG通道进行选择。结果表明,与传统基于ReliefF的通道选择算法相比,该文所提算法在保证一定分类准确率的同时能够显著减少使用的通道数量,并且通道选择的结果不依赖人为经验和分类器。此外,使用该方法获取的通道,其空间分布与已有的嗅觉神经生理学位置相一致,进一步证实了该方法的科学性和有效性。该文所提算法为嗅觉EEG通道选择的研究提供了新思路。
-
关键词:
- 嗅觉脑电 /
- 通道选择 /
- 气味识别 /
- ReliefF-Pearson
Abstract: The study of odor recognition based on ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) signals has important application value to objectively evaluating olfactory function and diagnosing olfactory disorders. Because of the inconvenience caused by using too many EEG channels in practical application scenarios, it is particularly important to study how to choose EEG channels. In this paper, a new ReliefF-Pearson channel selection algorithm is proposed to solve the channel selection problem in the classification of olfactory EEG signals. The algorithm combines the weight idea of ReliefF and the correlation principle of Pearson coefficient to select EEG channels. Experimental results show that compared with the traditional ReliefF-based channel selection algorithm, the proposed algorithm could significantly reduce the number of channels used while ensuring a certain classification accuracy, and the result of channel selection does not depend on human experience and classifiers. In addition, the spatial distribution of the selected channels is consistent with the existing olfactory neurophysiological position, which further confirms the scientificity and effectiveness of this method. The proposed method provides new idea for the research of olfactory EEG channel selection. -
表 1 基于全通道不同频带的PSD特征分类准确率(标准差)(%)
分类器 全特征 θ频带 α频带 β频带 γ频带 KNN 83.76(14.97) 33.28(10.32) 36.15(9.66) 58.55(11.76) 89.07(10.49) SVM 79.02(9.94) 20.51(4.92) 25.04(12.53) 64.43(14.49) 92.61(6.86) RF 85.83(8.74) 31.60(8.15) 35.51(9.71) 62.41(10.81) 86.55(9.60) 表 2 基于γ频带的不同通道选择算法的分类准确率(通道数目)(%)
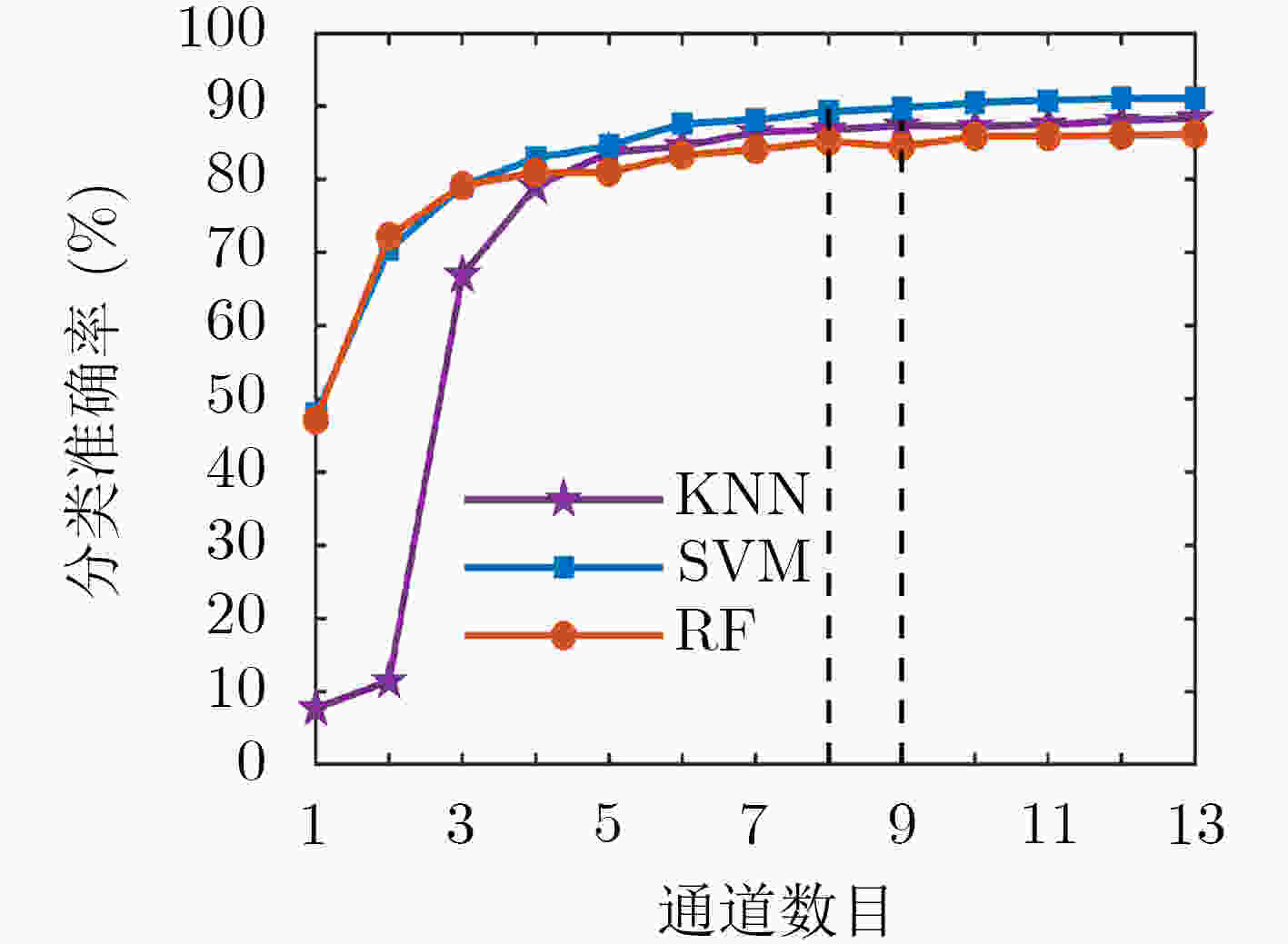
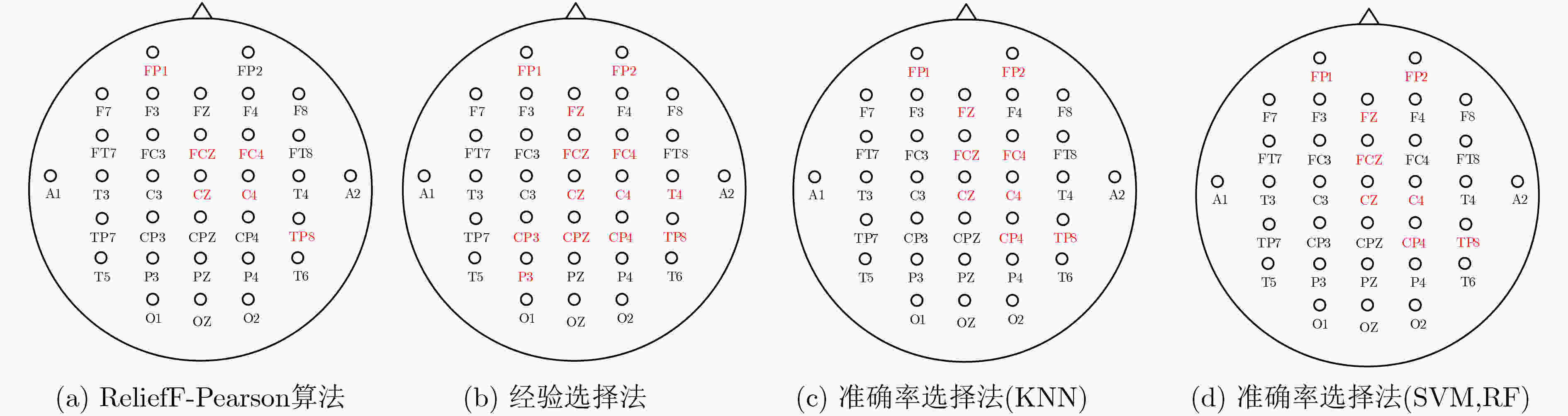
分类器 经验选择法 准确率选择法 ReliefF-Pearson算法 KNN 88.35(13通道) 87.37(9通道) 84.52(6通道) SVM 91.15(13通道) 89.31(8通道) 88.51(6通道) RF 86.23(13通道) 85.19(8通道) 80.14(6通道) -
[1] CHEN Miaochuan, FANG Shuhui, and FANG Li. The effects of aromatherapy in relieving symptoms related to job stress among nurses[J]. International Journal of Nursing Practice, 2015, 21(1): 87–93. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14596 [2] KROUPI E, VESIN J M, and EBRAHIMI T. Subject-independent odor pleasantness classification using brain and peripheral signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2016, 7(4): 422–434. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2015.2496310 [3] EZZATDOOST K, HOJJATI H, and AGHAJAN H. Decoding olfactory stimuli in EEG data using nonlinear Features: A pilot study[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2020, 341: 108780. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108780 [4] 陈万忠, 王晓旭, 张涛. 基于可调Q因子小波变换的识别左右手运动想象脑电模式研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 530–536. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171191CHEN Wanzhong, WANG Xiaoxu, and ZHANG Tao. Research of discrimination between left and right hand motor imagery EEG patterns based on tunable Q-factor wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 530–536. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171191 [5] 王斐, 吴仕超, 刘少林, 等. 基于脑电信号深度迁移学习的驾驶疲劳检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2264–2272. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180900WANG Fei, WU Shichao, LIU Shaolin, et al. Driver fatigue detection through deep transfer learning in an electroencephalogram-based system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2264–2272. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180900 [6] 佘青山, 陈希豪, 高发荣, 等. 基于感兴趣脑区LASSO-Granger因果关系的脑电特征提取算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(5): 1266–1270. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150851SHE Qingshan, CHEN Xihao, GAO Farong, et al. Feature extraction of electroencephalography based on LASSO-Granger causality between brain region of interest[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(5): 1266–1270. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150851 [7] 单海军, 朱善安. 基于Relief-SBS的脑机接口通道选择[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33(2): 350–356. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160059SHAN Haijun and ZHU Shan’an. A novel channel selection method for brain-computer interface based on Relief-SBS[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(2): 350–356. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160059 [8] LAN Tian, ERDOGMUS D, ADAMI A, et al. Salient EEG channel selection in brain computer interfaces by mutual information maximization[C]. 2015 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 2006: 7064–7067. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2005.1616133. [9] LAL T N, SCHRODER M, HINTERBERGER T, et al. Support vector channel selection in BCI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 51(6): 1003–1010. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.827827 [10] ZHANG Jianhai, CHEN Ming, ZHAO Shaokai, et al. Relieff-based EEG sensor selection methods for emotion recognition[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1558. doi: 10.3390/s16101558 [11] PENG Hong, WANG Yongzong, CHAO Jinlong, et al. Stability study of the optimal channel selection for emotion classification from EEG[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Kansas City, USA, 2017: 2031–2036. doi: 10.1109/BIBM.2017.8217973. [12] ROBNIK-ŠIKONJA M and KONONENKO I. Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF[J]. Machine Learning, 2003, 53(1/2): 23–69. doi: 10.1023/a:1025667309714 [13] TONG Laiyuan, ZHAO Jinchuang, and FU Wenli. Emotion recognition and channel selection based on EEG signal[C]. The 2018 11th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Changsha, China, 2018: 101–105. doi: 10.1109/ICICTA.2018.00031. [14] 王永宗. 面向情绪识别的脑电特征组合及通道优化选择研究[D]. [硕士论文], 兰州大学, 2018.WANG Yongzong. Study on feature combination and channel optimization selection of EEG for emotion recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], Lanzhou University, 2018. [15] AHLGREN P, JARNEVING B, and ROUSSEAU R. Requirements for a cocitation similarity measure, with special reference to Pearson’s correlation coefficient[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 2003, 54(6): 550–560. doi: 10.1002/asi.10242 [16] ZHANG Xiaonei, HOU Huirang, and MENG Qinghao. EEG-based odor recognition using channel-frequency convolutional neural network[C]. 2019 Chinese Control Conference, Guangzhou, China, 2019: 7763–7767. doi: 10.23919/ChiCC.2019.8865904. [17] AYDEMIR O. Olfactory recognition based on EEG Gamma-band activity[J]. Neural Computation, 2017, 29(6): 1667–1680. doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00966 [18] ZHENG Weilong and LU Baoliang. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2015, 7(3): 162–175. doi: 10.1109/TAMD.2015.2431497 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
