Robust Sea Clutter Suppression Method for Multichannel Airborne Radar
-
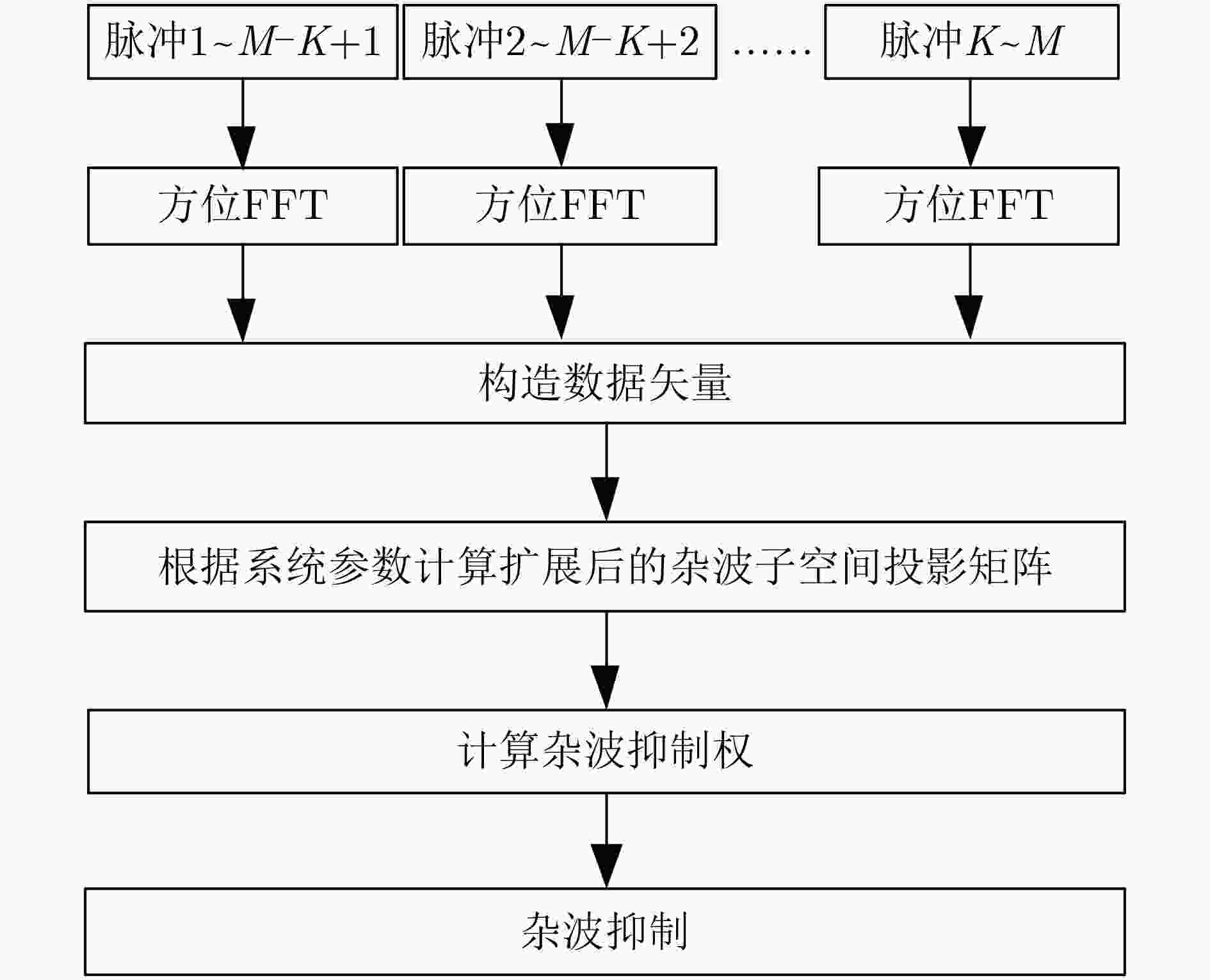
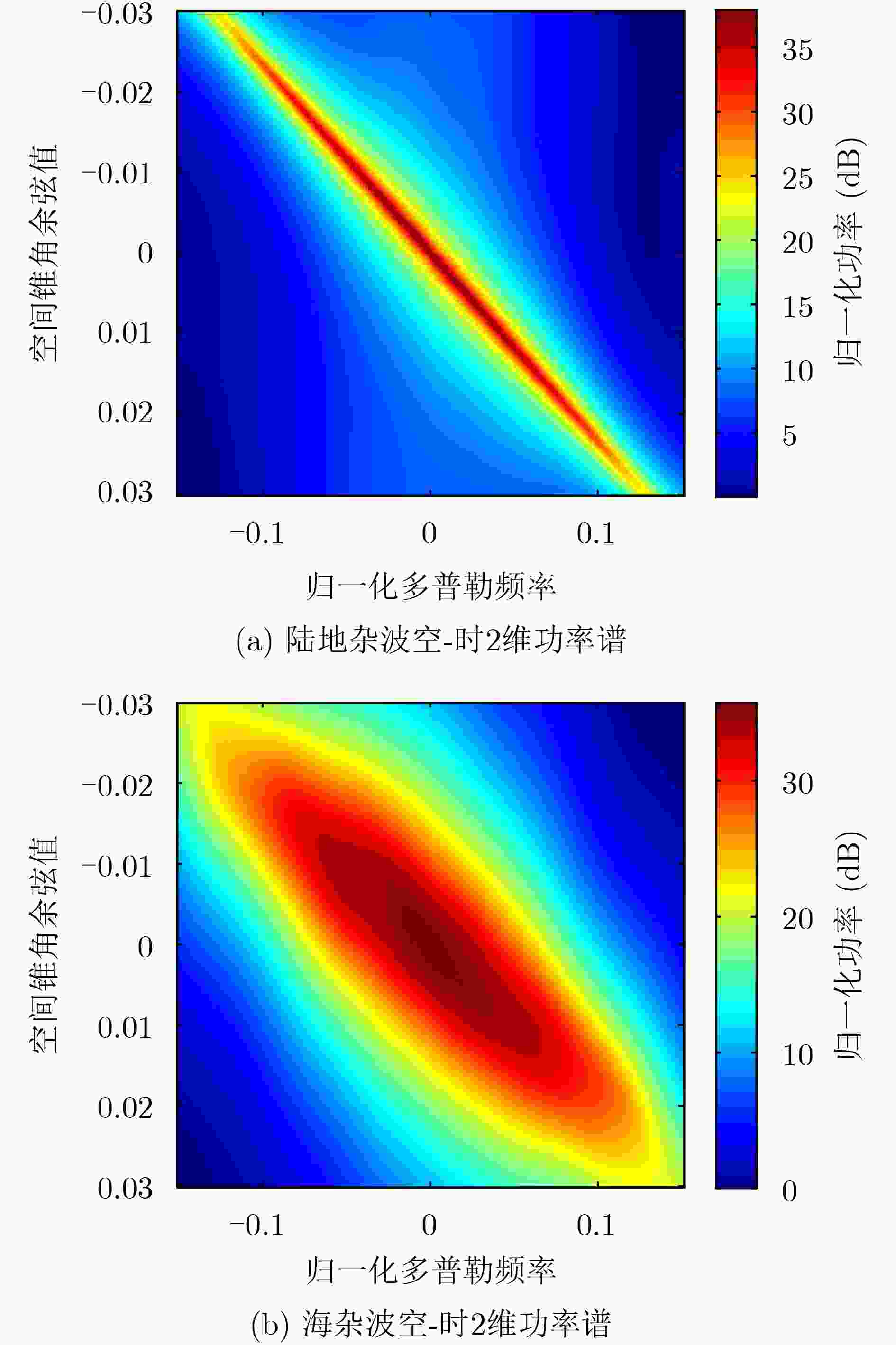
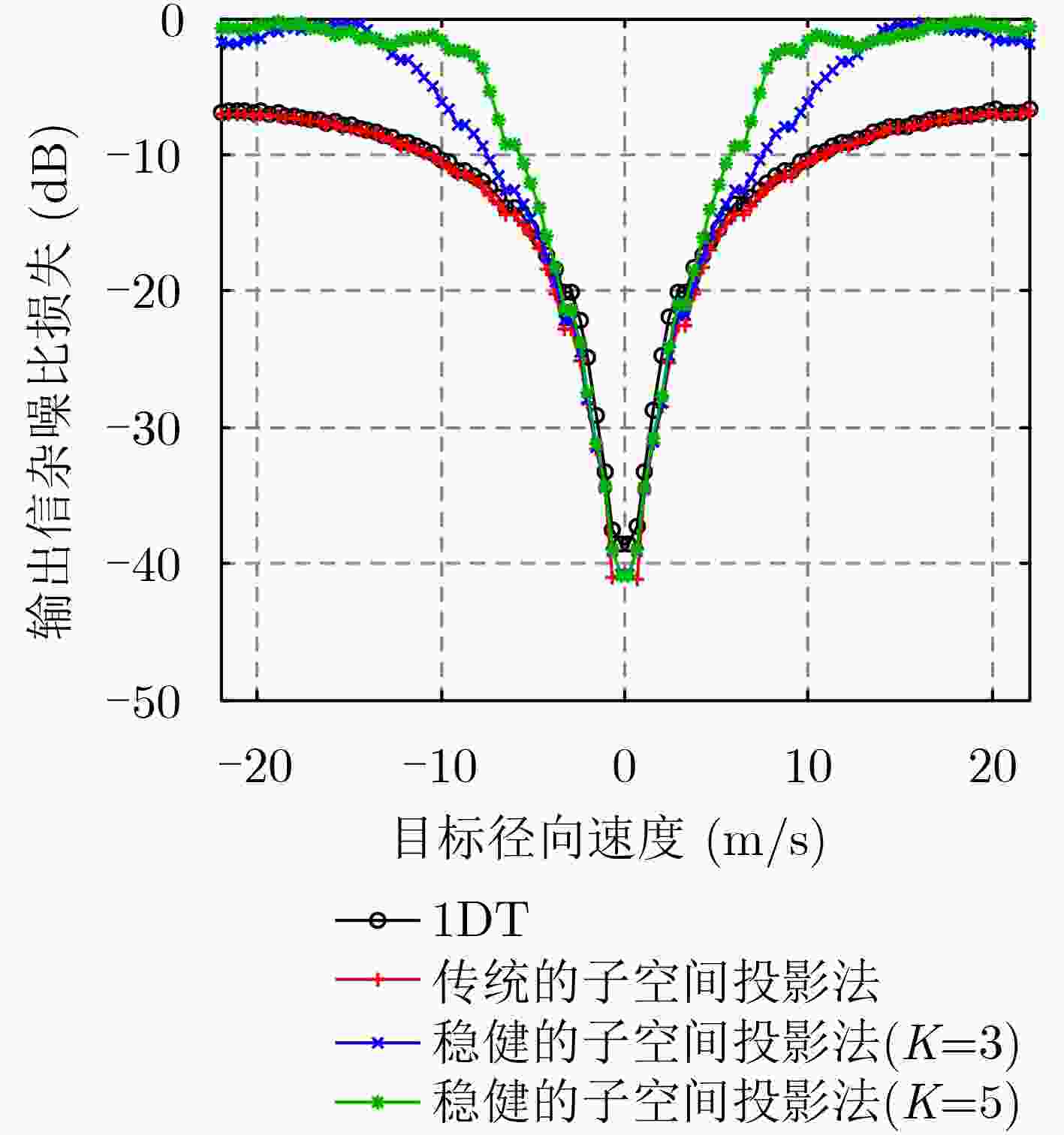
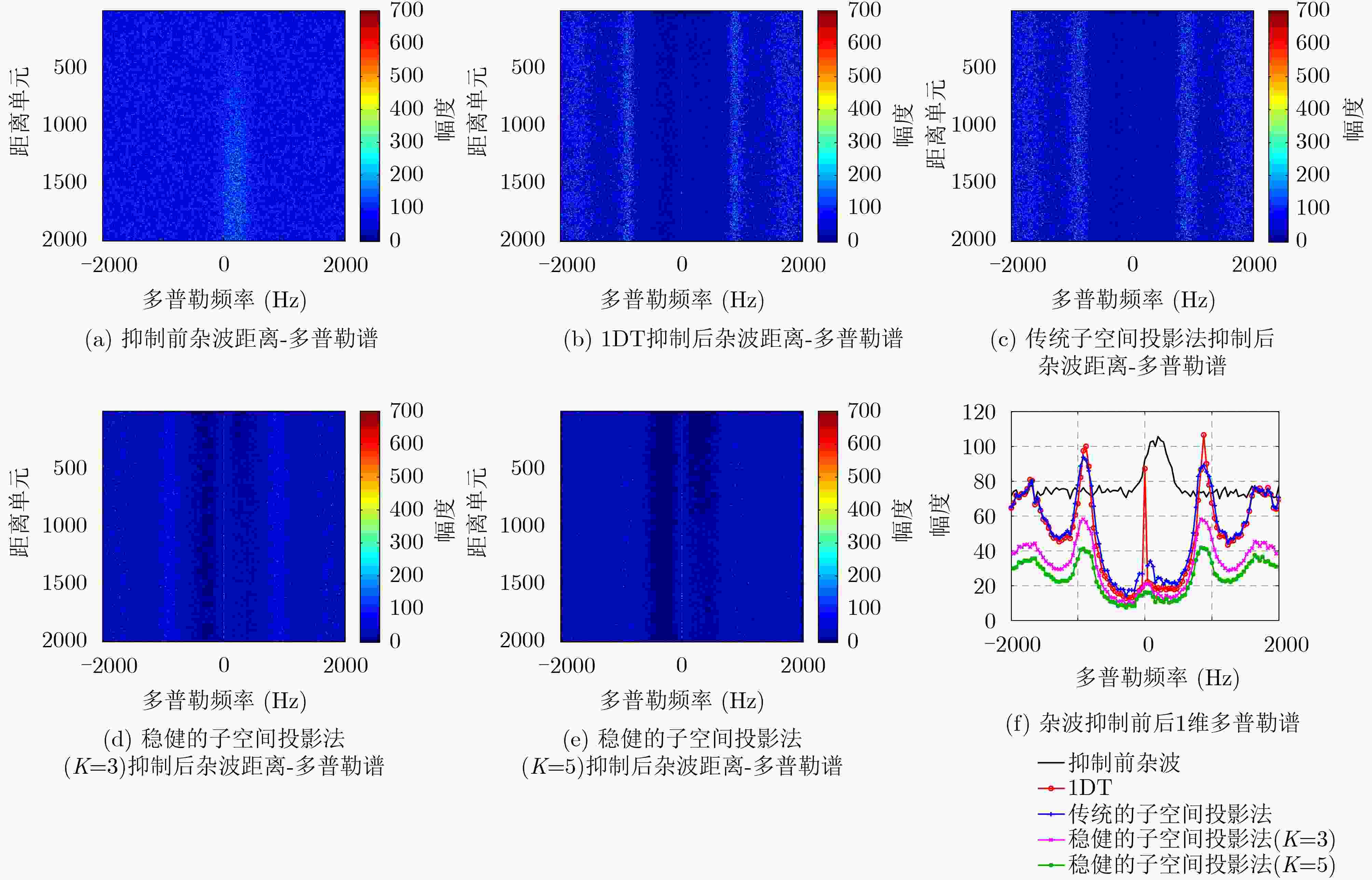
摘要: 在机载预警雷达对海洋背景运动目标的探测过程中,雷达平台的高速运动状态使得海杂波多普勒谱发生严重展宽现象,影响目标的检测性能。针对此问题,空-时自适应处理是一种有效的杂波抑制技术,该技术利用杂波的空-时2维耦合特性进行杂波抑制。但相对于陆地杂波而言,海杂波的内部复杂运动特性使得杂波空-时谱发生展宽现象,导致杂波多普勒频率与空间锥角不再保持一一对应关系,从而影响杂波抑制效果。针对海杂波的运动特性,该文提出一种稳健的基于子空间投影的杂波抑制处理算法,所提算法通过滤波凹口自适应展宽技术和先滑窗滤波后自适应处理技术来提高杂波抑制的稳健性。最后通过仿真的海杂波数据和实测海杂波数据验证了所提算法的有效性。Abstract: During the marine moving target detection for airborne early warning radar, the high-speed movement of the radar platform causes the serious broadening of the sea clutter Doppler spectrum, which affects the target detection performance. To solve this problem, a clutter suppression method called Space-Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) is effective, which exploits the space-time coupling characteristics of clutter. However, compared with the land clutter, the motion characteristics of sea clutter lead to the broadening of the clutter space-time spectrum, resulting in the clutter Doppler frequency and the spatial cone angle no longer maintaining a one-to-one correspondence; thus the clutter suppression performance significantly degrades. According to the motion characteristics of sea clutter, a robust subspace projection method is proposed in this paper. This method improves the robustness of clutter suppression by using the adaptive notch broadening technique and the filter then adapt technique. Finally, the effectiveness of this method is verified through the simulation results and the real-measured sea clutter data.
-
表 1 系统仿真参数
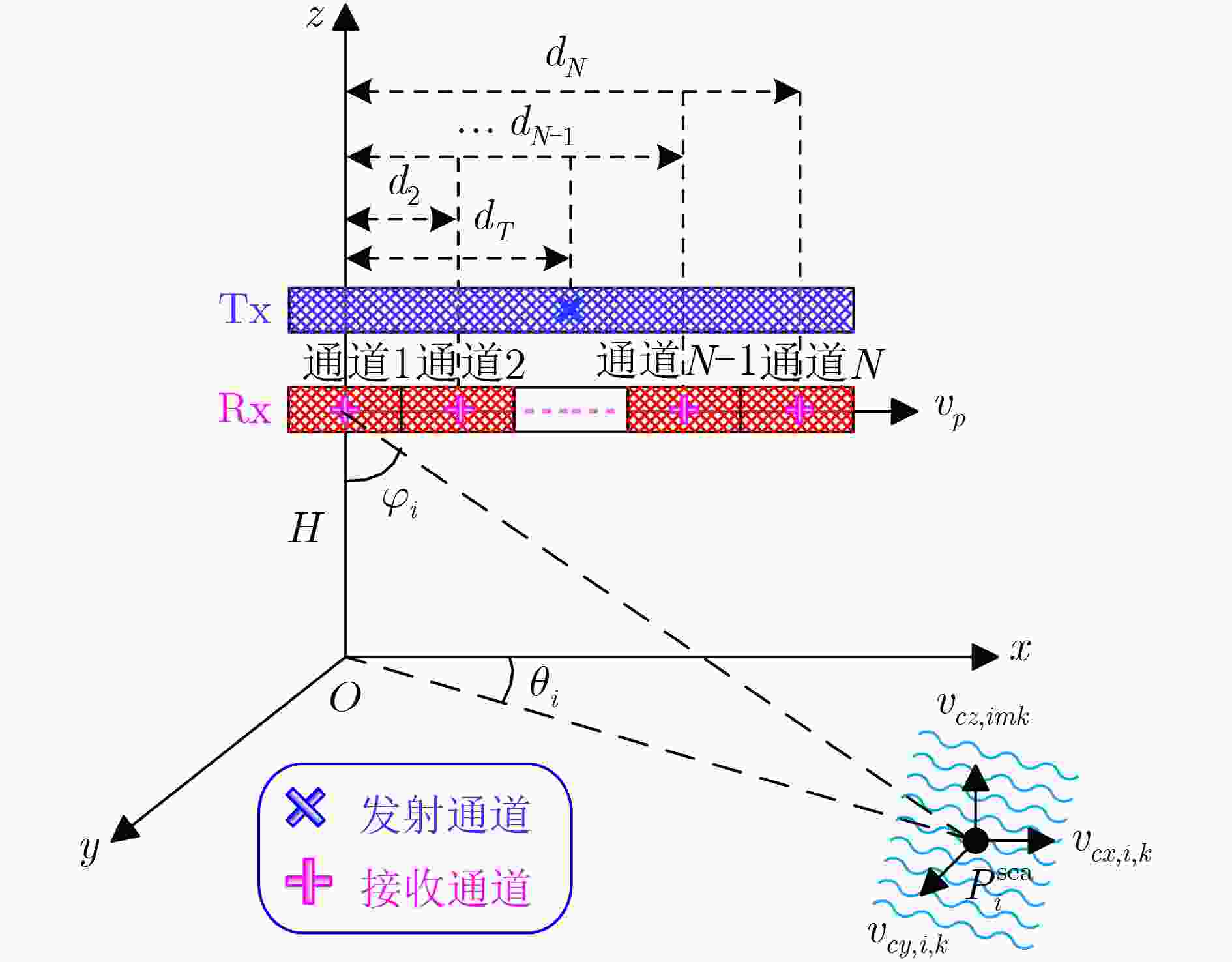
参数 值 平台高度 4000 m 平台运动速度 100 m/s 雷达频率 9.6 GHz 信号带宽 30 MHz 采样频率 36 MHz 接收机噪声带宽 36 MHz 脉冲重复频率 3000 Hz 脉冲数 90 波束中心下视角 60° 波束中心方位角 90° 方位通道数 8 天线方位维长度 1.000 m 天线俯仰维长度 0.125 m 发射增益 42.1 dB 接收增益 42.1 dB 发射天线方位和距离向加权 –13 dB/–13 dB(等幅加权) 接收天线方位和距离向加权 –40 dB/–20 dB(切比雪夫加权) 系统噪声 2 dB 系统损耗 11 dB 表 2 实测数据系统参数
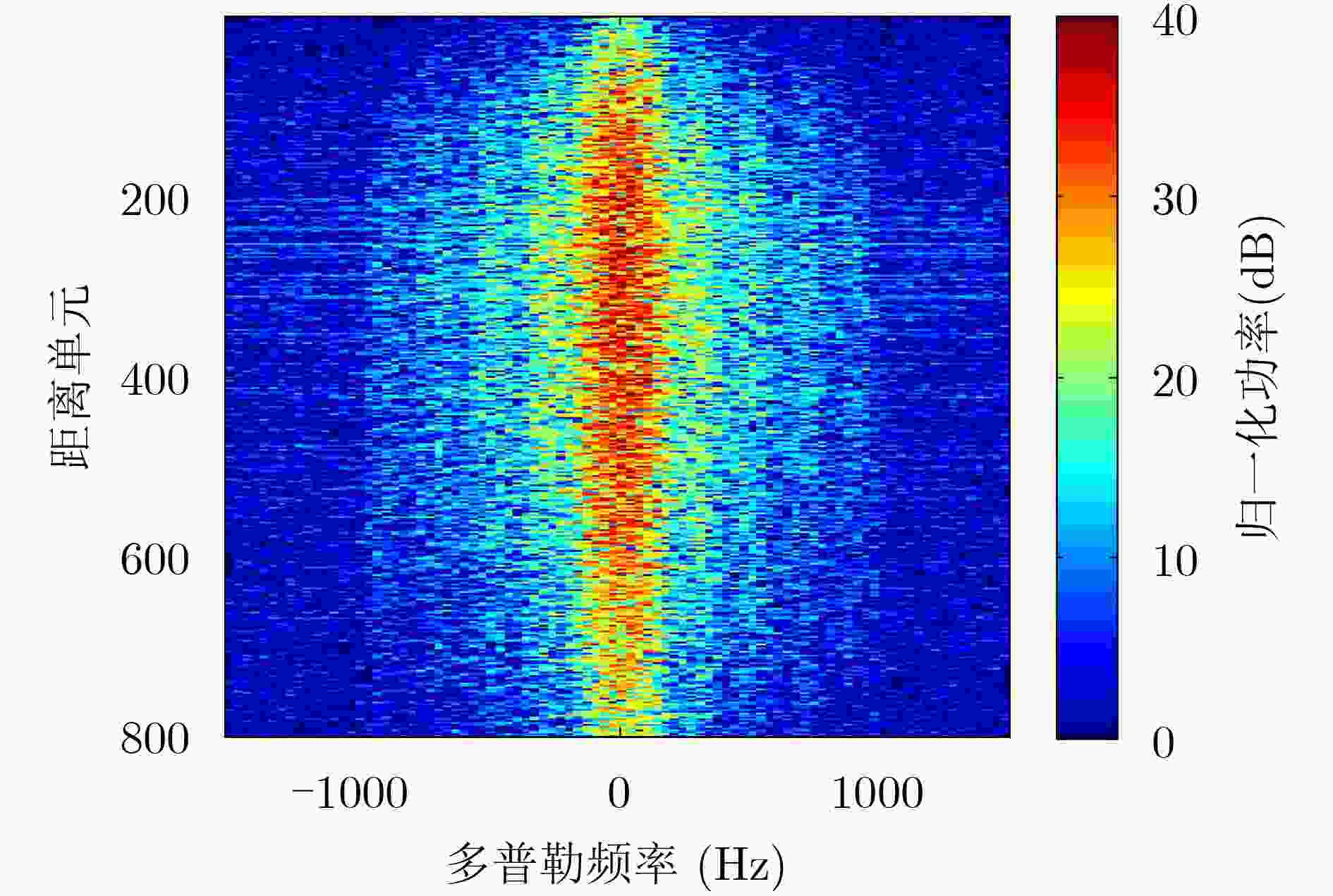
参数 值 平台高度 3100 m 平台运动速度 80 m/s 雷达频率 9.6 GHz 脉冲重复频率 4000 Hz -
[1] 蒋千, 吴昊, 王燕宇. 机载多功能海上监视雷达系统设计与关键技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 303–317. doi: 10.12000/JR19045JIANG Qian, WU Hao, and WANG Yanyu. Airborne multi-functional maritime surveillance radar system design and key techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 303–317. doi: 10.12000/JR19045 [2] GUERCI J R. Space-Time Adaptive Processing for Radar[M]. London: Artech House, 2003: 1–3. [3] 谢文冲, 段克清, 王永良. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, and WANG Yongliang. Space time adaptive processing technique for airborne radar: An overview of its development and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073 [4] DIPIETRO R C. Extended factored space-time processing for airborne radar systems[C]. 1992 Conference Record of the Twenty-Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1992: 425–430. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.1992.269236. [5] BRENNAN L E, PIWINSKI D J, and STAUDAHER F M. Comparison of space-time processing approaches using experimental airborne radar data[C]. The Record of the 1993 IEEE National Radar Conference, Lynnfield, USA, 1993: 176–181. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1993.270470. [6] WANG Hong and CAI Lujing. On adaptive spatial-temporal processing for airborne surveillance radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 660–670. doi: 10.1109/7.303737 [7] BROWN R D, WICKS M C, ZHANG Q, et al. A space-time adaptive processing approach for improved performance and affordability[C]. Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1996: 321–326. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1996.510701. [8] 王永良, 吴志文, 彭应宁. 适于非均匀杂波环境的空时自适应处理方法[J]. 电子学报, 1999, 27(9): 56–58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1999.09.017WANG Yongliang, WU Zhiwen, and PENG Yingning. A STAP approach for the non-homogeneous radar clutter environment[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1999, 27(9): 56–58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1999.09.017 [9] GOLDSTEIN J S and REED I S. Reduced-rank adaptive filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(2): 492–496. doi: 10.1109/78.554317 [10] SARKAR T K, WANG Hong, PARK S, et al. A deterministic least-squares approach to space-time adaptive processing (STAP)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2001, 49(1): 91–103. doi: 10.1109/8.910535 [11] 侯静, 胡孟凯, 王子微. 一种改进的知识辅助MIMO雷达空时自适应处理方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 795–800. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180557HOU Jing, HU Mengkai, and WANG Ziwei. An improved knowledge-aided space-time adaptive signal processing algorithm for MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 795–800. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180557 [12] YANG Zhiwei, SHU Yuxiang, and LIAO Guisheng. Robust ambiguous clutter suppression for the near-shore water areas with spaceborne multichannel SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(2): 319–323. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2337653 [13] LI Boyu, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Clutter suppression via subspace projection for spaceborne HRWS multichannel SAR system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(9): 1538–1542. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2951198 [14] GRACHEVA V and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Multi-channel analysis of sea clutter for STAP applications[C]. EUSAR 2012; The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 195–198. [15] GRACHEVA V and ENDER J. Multichannel analysis of medium grazing angle sea clutter[C]. EUSAR 2014; The 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2014: 1065–1068. [16] GRACHEVA V and ENDER J. Multichannel analysis and suppression of sea clutter for airborne microwave radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 2385–2399. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2500918 [17] XIN Zhihui, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. A deterministic sea-clutter space-time model based on physical sea surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(11): 6659–6673. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2587739 [18] MELVIN W L, WICKS M C, and BROWN R D. Assessment of multichannel airborne radar measurements for analysis and design of space-time processing architectures and algorithms[C]. The 1996 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1996: 130–135. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1996.510669. [19] KOGON S M and ZATMAN M A. STAP adaptive weight training using phase and power selection criteria[C]. Conference Record of Thirty-Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2001: 98–102. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2001.986887. [20] 许华健, 杨志伟, 廖桂生, 等. 一种稳健的非均匀杂波协方差矩阵估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1036–1043. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160747XU Huajian, YANG Zhiwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Robust approach for clutter covariance matrix estimation with STAP in heterogeneous environment[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1036–1043. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160747 [21] 熊绍华. 机载雷达空时二维海杂波特征谱和功率谱研究[D]. [硕士论文], 桂林电子科技大学, 2015. doi: 10.7666/d.D790913.XIONG Shaohua. Research on eigenspectrum and power spectrum of airborne radar spatial-temporal sea clutter[Master dissertation], Guilin University of Electronic Technology, 2015. doi: 10.7666/d.D790913. [22] XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Knowledge-aided space-time adaptive processing based on Morchin model[C]. The 2015 IET International Radar Conference, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1049/cp.2015.1268. [23] WARD K, TOUGH R, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed. London: IET, 2013: 54–55. [24] ZHAO Peng, WU Zhensen, ZHANG Yong, et al. The theoretical and experimental study on backscattering from arable land[C]. The 2012 International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory, Xi’an, China, 2012: 845–848. doi: 10.1109/ISAPE.2012.6408904. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
