Anti-Interference Distributed Energy-Efficient Power Allocation for Multi-Carrier Ultra-Dense Networks
-
摘要: 该文研究多载波超密集网络(UDN)上行链路能效最优功率分配方案,基于非合作博弈论提出一种抗干扰分布式功率分配方案,使每个小区独立优化能效的同时抑制邻小区干扰。由于最大传输功率和QoS约束下的能效函数具有不易解决的非凸特性,且小小区间存在严重干扰。针对以上挑战,该文在最佳响应过程中设计了一种高精度低复杂度的阶梯注水算法,基于该算法利用干扰信道增益提出了一种多用户抗干扰功率分配算法。仿真结果和数值分析表明该算法运算复杂度低,且能在保证系统频谱效率的同时大幅度提升系统能效。Abstract: The energy-efficient power allocation is studied in the uplink of the multi-carrier Ultra-Dense Networks (UDN). Based on the non-cooperative game theory, a distributed anti-interference power allocation scheme is proposed so that each cell can independently optimize energy efficiency while suppressing the inter-cell interference. Due to the fact that the energy efficiency problem under the constrains of the Quality of Service(QoS)and the maximum transmitter power is a challenging nonconvex problem and small cells suffer from the severe inter-cell interference, an accurate and low-complexity stair water-filling algorithm is proposed to solve the nonconvex problem in the best response process. Based on this algorithm, a multi-user anti-interference power allocation algorithm is proposed using interference channel gains. Simulation results and numerical analysis show that this algorithm can improve the system energy efficiency with no reduction in spectrum efficiency performance.
-
表 1 阶梯注水算法
(1) 通过遍历搜索获取注水水位和阶梯个数的上下界 (2) for $i = \underline L , ··· ,\bar L$ (3) 根据式(11),求解阶梯区间${C_{k,i}}$内解集${{{T}}_{k,i}}$ (4) end (5) 根据式(13)确定最优注水水位$\mu _k^*$和注水功率
${\rm{WF}}({{{d}}_k}) = {\left[ {\mu _k^* - {{{d}}_k}} \right]^\dagger }$表 2 多用户抗干扰能效功率分配算法
(1) 选择初始点${{p}}(0) = {\rm{(}}{{{p}}_1}(0),{{{p}}_2}(0),···,{{{p}}_K}{\rm{(0)) = }}{\bf{0}}$,设置$v{\rm{ = 0}}$ (2) while $\left| {{{{p}}_k}(v + 1) - {{{p}}_k}(v)} \right| > \varepsilon $ (3) for $k = 1,2,···,K$ (4) 测量${{\gamma }_k}(v + 1)$得到干扰${{{\overset{\frown} {{I}}} }_k}(v)$ (5) if ${{{\overset{\frown} {{I}}} }_k}(v{\rm{ + 1}}) > = {{{\overset{\frown} {{I}}} }_k}(v)$ (6) ${{p}}_k^* = {{{p}}_k}(v)$ (7) ${{{p}}_k}(v + 1) = \alpha \times {{p}}_k^* + (1 - \alpha ) \times {\rm{WF}}({{{p}}_{\backslash k}}(v{\rm{ + }}1))$ (8) else (9)$ {{p}}_{k}(v+1)=\beta \times {{p}}_{k}^{*}+(1-\beta )\times {{p}}_{k}(v)$ (10)end (11) end (12) end while 表 3 仿真参数
变量 含义 取值 $N$ 子载波数目 5 ${N_0}$ 噪声谱密度 $3.98 \times {10^{ - 19}}\;{\rm{ W/Hz}}$ $B$ 总带宽 $1\;{\rm{ MHz}}$ ${p_{\rm{c}}}$ 电路消耗功率 $300\;{\rm{ mW}}$ $a$ 传播指数 3.6 ${\rm{cte}}$ 传播常数 $2.57399 \times {10^{ - 2}}$ ${d_{\min }}$ 最小距离 $35\;{\rm{ m}}$ ${d_{\max }}$ 最大距离 $250\;{\rm{ m}}$ $K$ 用户数 10 $M$ 基站天线数 10 -
[1] The Climate Group. Smart 2020: Enabling the low carbon economy in the information age[R]. The Climate Group London, 2008. [2] BACCI G, BELMEGA E V, MERTIKOPOULOS P, et al. Energy-aware competitive power allocation for heterogeneous networks under QoS constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(9): 4728–4742. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2425397 [3] LAHOUD S, KHAWAM K, MARTIN S, et al. Energy-efficient joint scheduling and power control in multi-cell wireless networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3409–3426. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2611847 [4] CHARAR M A, GUENNOUN Z, and ANIBA G. Assessment of a closed-form iterative water filling energy efficient power control algorithm in multi-carrier context[C]. 2017 International Conference on Wireless Networks And Mobile Communications (Wincom), Rabat, Morocco, 2017: 304–309. doi: 10.1109/WINCOM.2017.8238195. [5] HE P, ZHANG Shan, ZHAO Lian, et al. Multichannel power allocation for maximizing energy efficiency in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 5895–5908. doi: 10.1109/tvt.2018.2803126 [6] HE P and DONG Min. Energy-efficient power allocation maximization with mixed group sum power bound and QoS constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(10): 7139–7151. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2926454 [7] DONG Guannan, ZHANG Haixia, JIN Shi, et al. Energy-efficiency-oriented joint user association and power allocation in distributed massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5794–5808. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2912388 [8] D'ORO S, ZAPPONE A, PALAZZO S, et al. A learning-based approach to energy efficiency maximization in wireless networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Barcelona, Spain, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2018.8377081. [9] LI Yuzhou, ZHANG Yu, LUO Kai, et al. Ultra-dense hetnets meet big data: Green frameworks, techniques, and approaches[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(6): 56–63. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700425 [10] 朱晓荣, 朱蔚然. 超密集小峰窝网中基于干扰协调的小区分簇和功率分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(5): 1173–1178. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150756ZHU Xiaorong and ZHU Weiran. Interference coordination-based cell clustering and power allocation algorithm in dense small cell networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(5): 1173–1178. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150756 [11] PENG Juan, ZENG Jie, SU Xin, et al. A QoS-based cross-tier cooperation resource allocation scheme over ultra-dense HetNets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 27086–27096. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901506 [12] XIN Jincan, GAO Hui, TAN Yuande, et al. Energy-efficient power control for ultra-dense networks with distributed antenna arrays[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCW.2019.8757032. [13] 钱志鸿, 蒙武杰, 王雪, 等. 全负载蜂窝网络下多复用D2D通信功率分配算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 2939–2945. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190974QIAN Zhihong, MENG Wujie, WANG Xue, et al. Research on power allocation algorithm of multi-to-one multiplexing D2D communication underlaying full load cellular networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 2939–2945. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190974 [14] MIAO Guowang, HIMAYAT N, LI G Y, et al. Distributed interference-aware energy-efficient power optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2011, 10(4): 1323–1333. doi: 10.1109/twc.2011.021611.101376 [15] KWON G and PARK H. Joint user association and beamforming design for millimeter wave UDN with wireless backhaul[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(12): 2653–2668. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2947926 [16] KHODMI A, BENREJEB S, and CHOUKAIR Z. Iterative water filling power allocation and relay selection based on two-hop relay in 5G/heterogeneous ultra dense network[C]. The 7th International Conference on Communications and Networking (ComNet), Hammamet, Tunisia, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/COMNET.2018.8622298. [17] ZENG Ming, NGUYEN N P, DOBRE O A, et al. Spectral-and energy-efficient resource allocation for multi-carrier uplink NOMA systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(9): 9293–9296. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2926701 [18] JIANG Yanxiang, LU Ningning, CHEN Yan, et al. Energy-efficient noncooperative power control in small-cell networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(8): 7540–7547. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2673245 [19] FACCHINEI F and KANZOW C. Generalized Nash equilibrium problems[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2010, 175(1): 177–211. doi: 10.1007/s10479-009-0653-x -





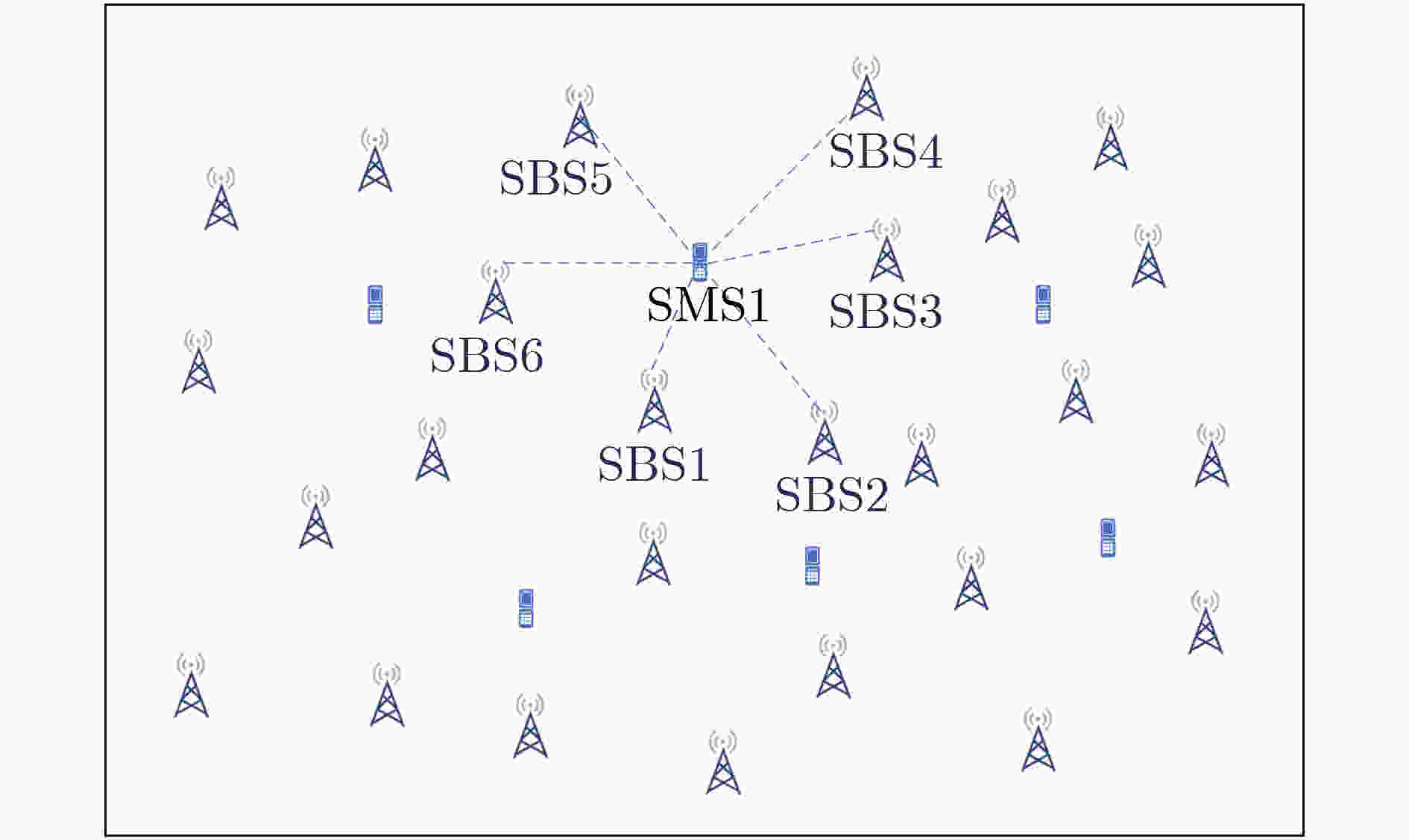
 下载:
下载:
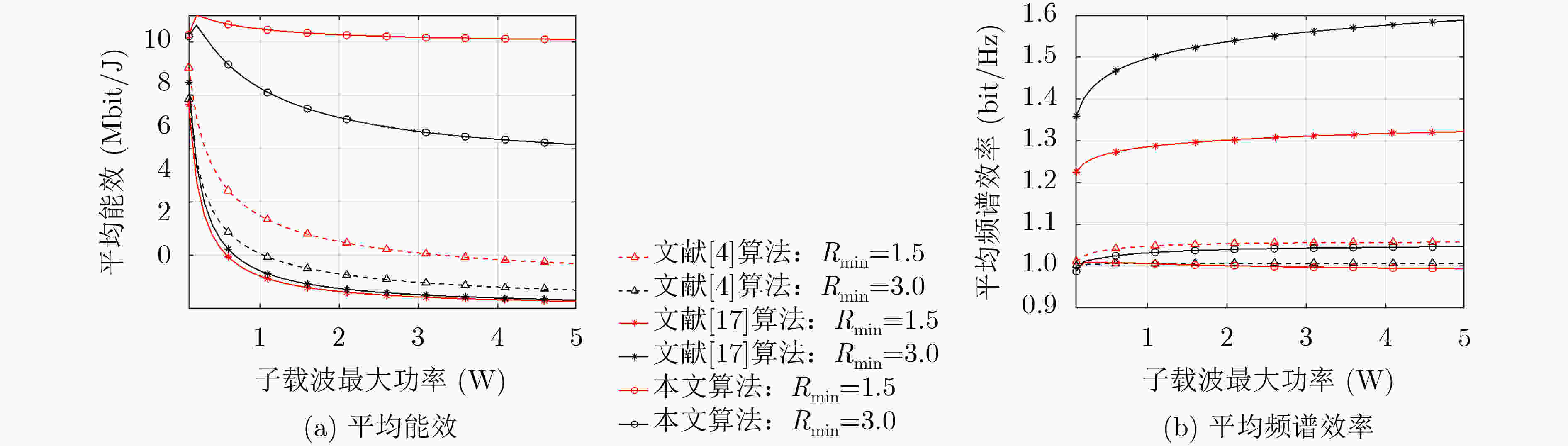
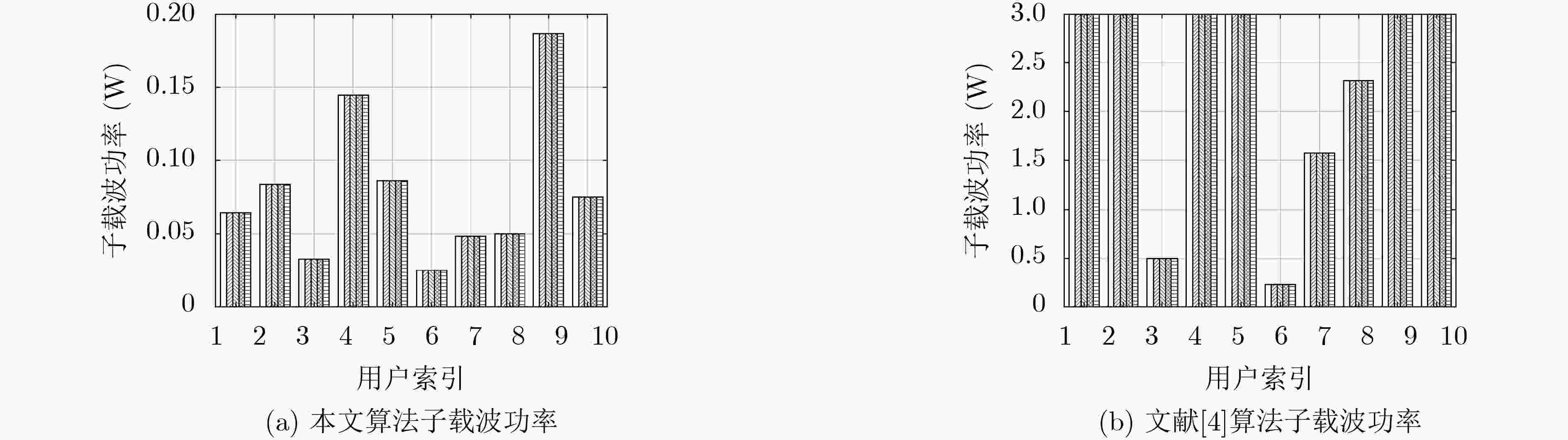


 下载:
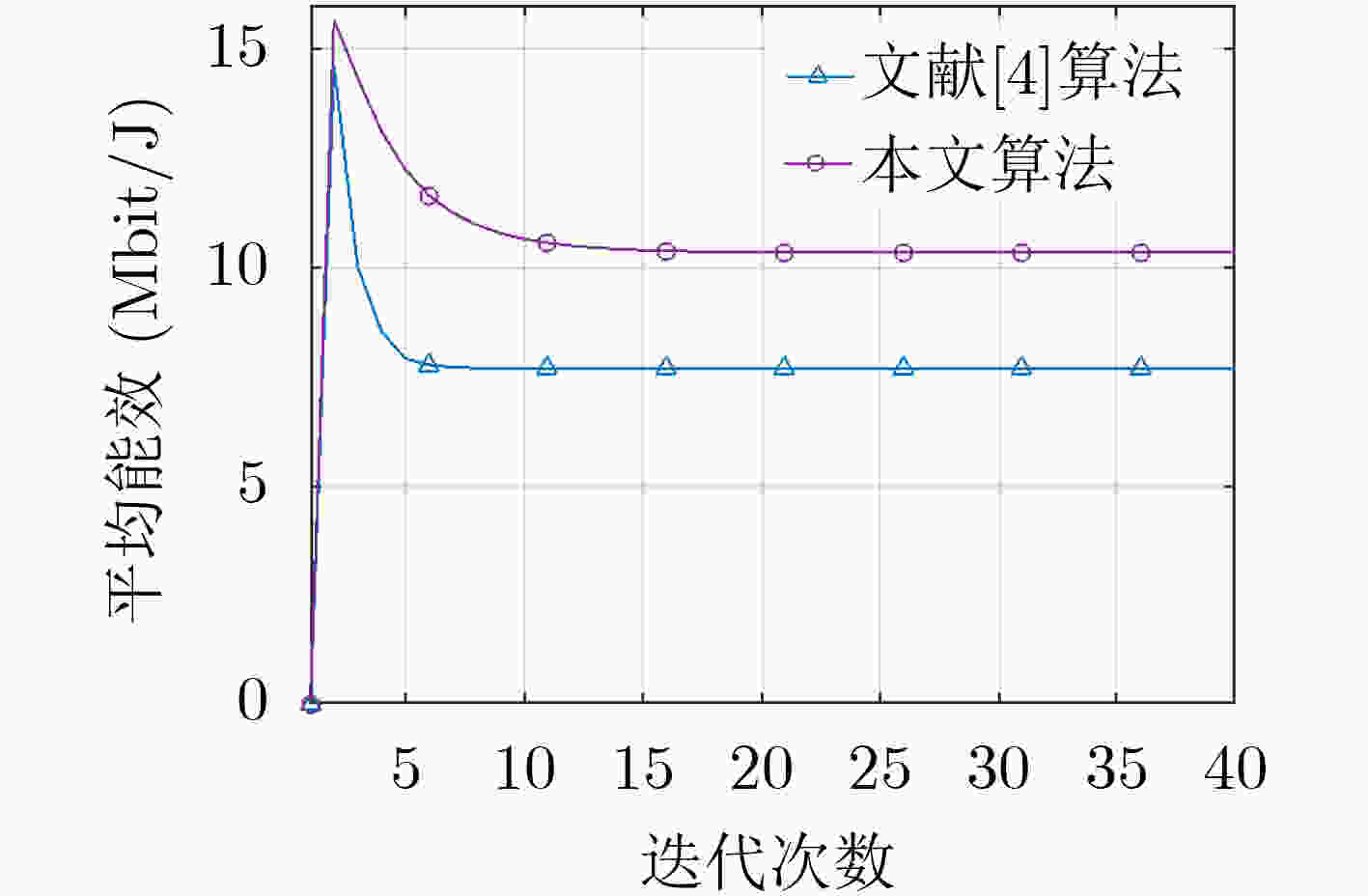
下载:
