A Low-Cost Triple-Node-Upset-Resilient Latch Design
-
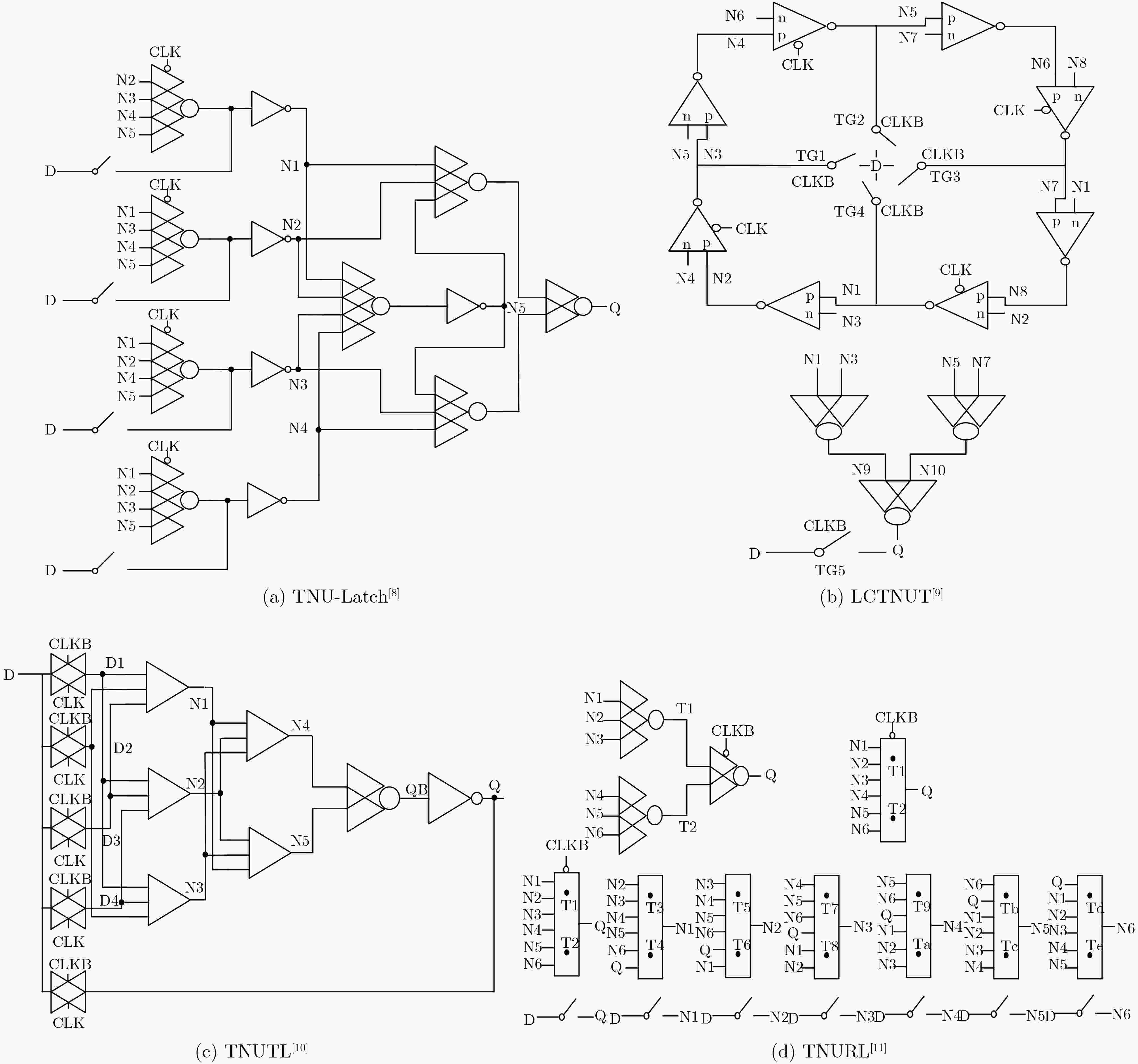
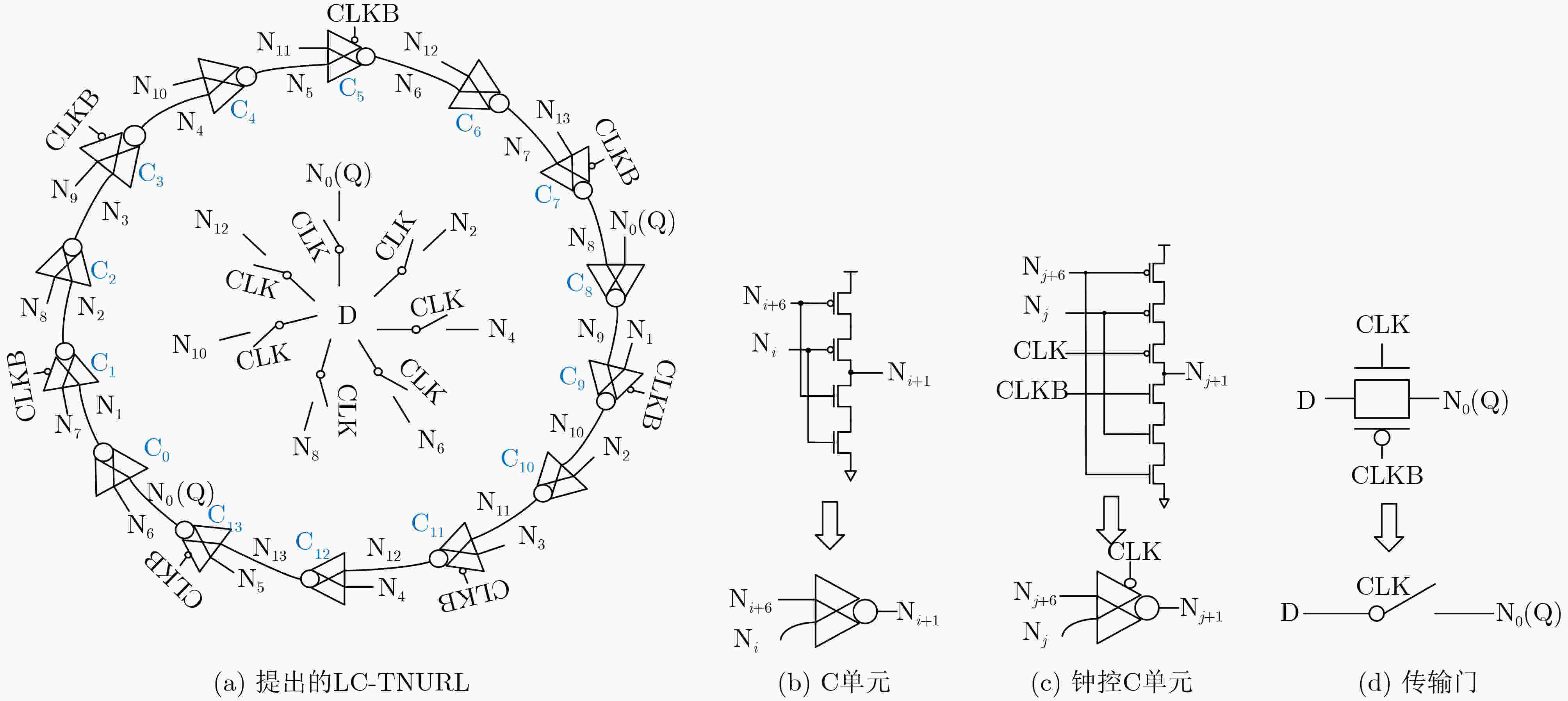
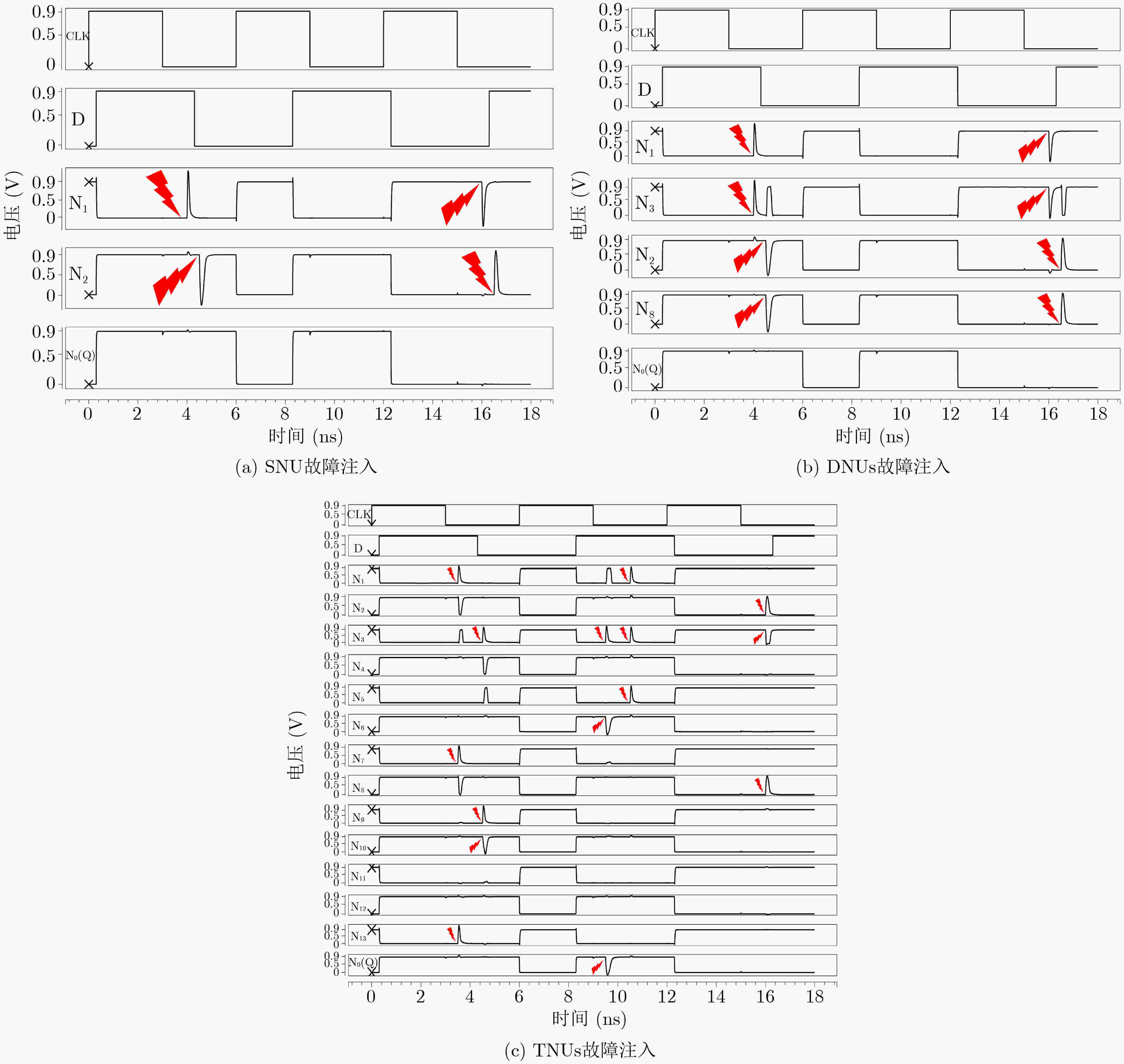
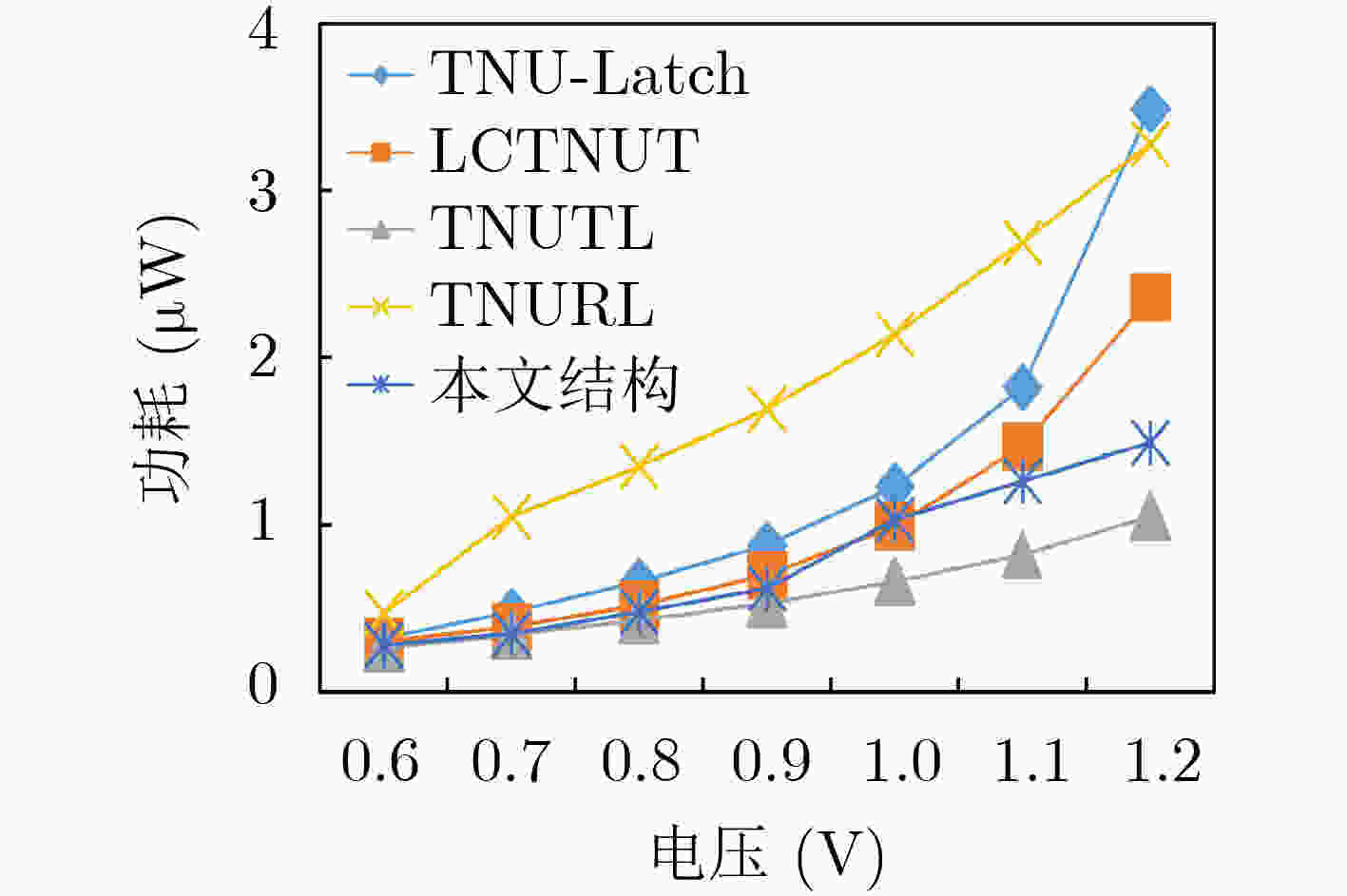
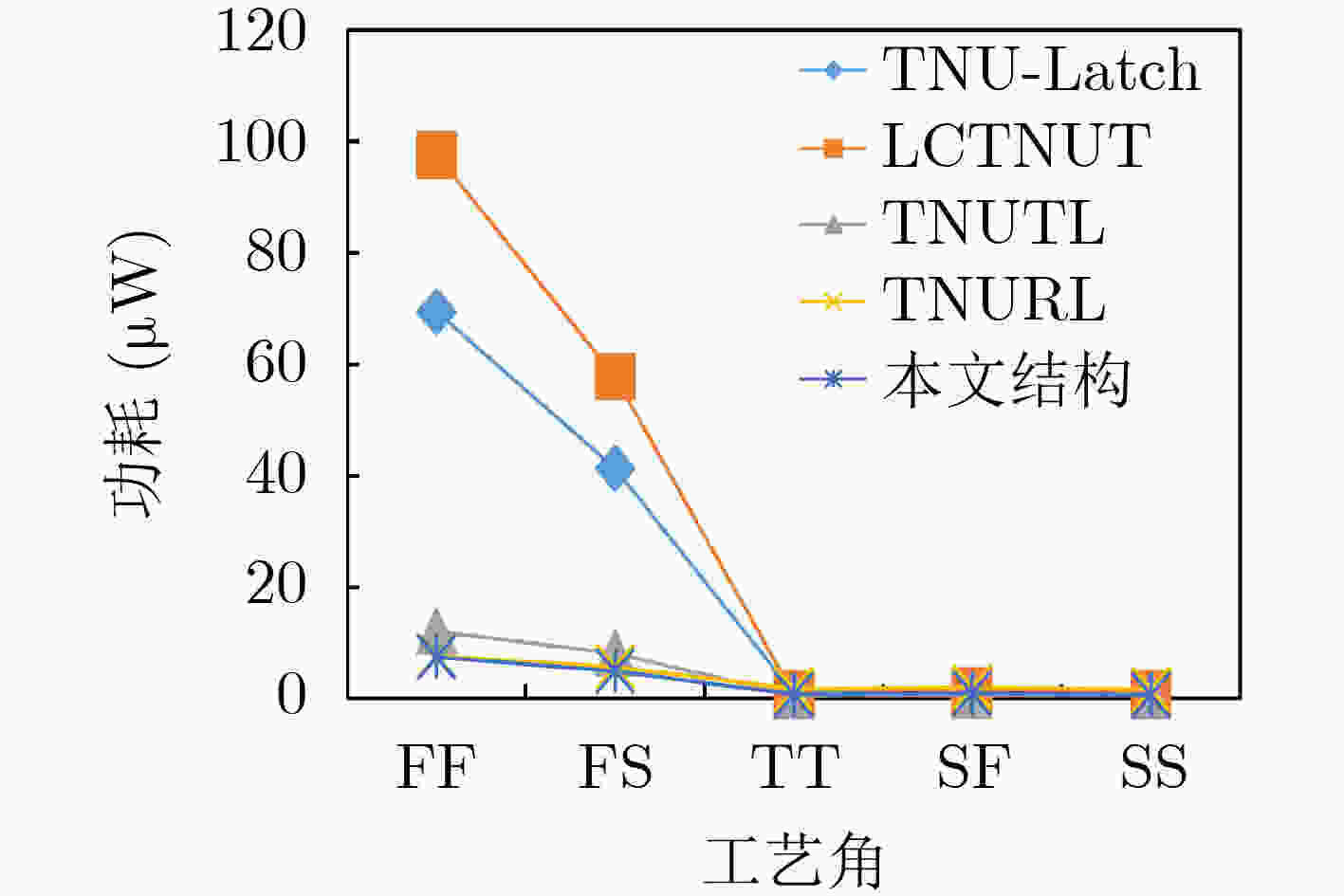
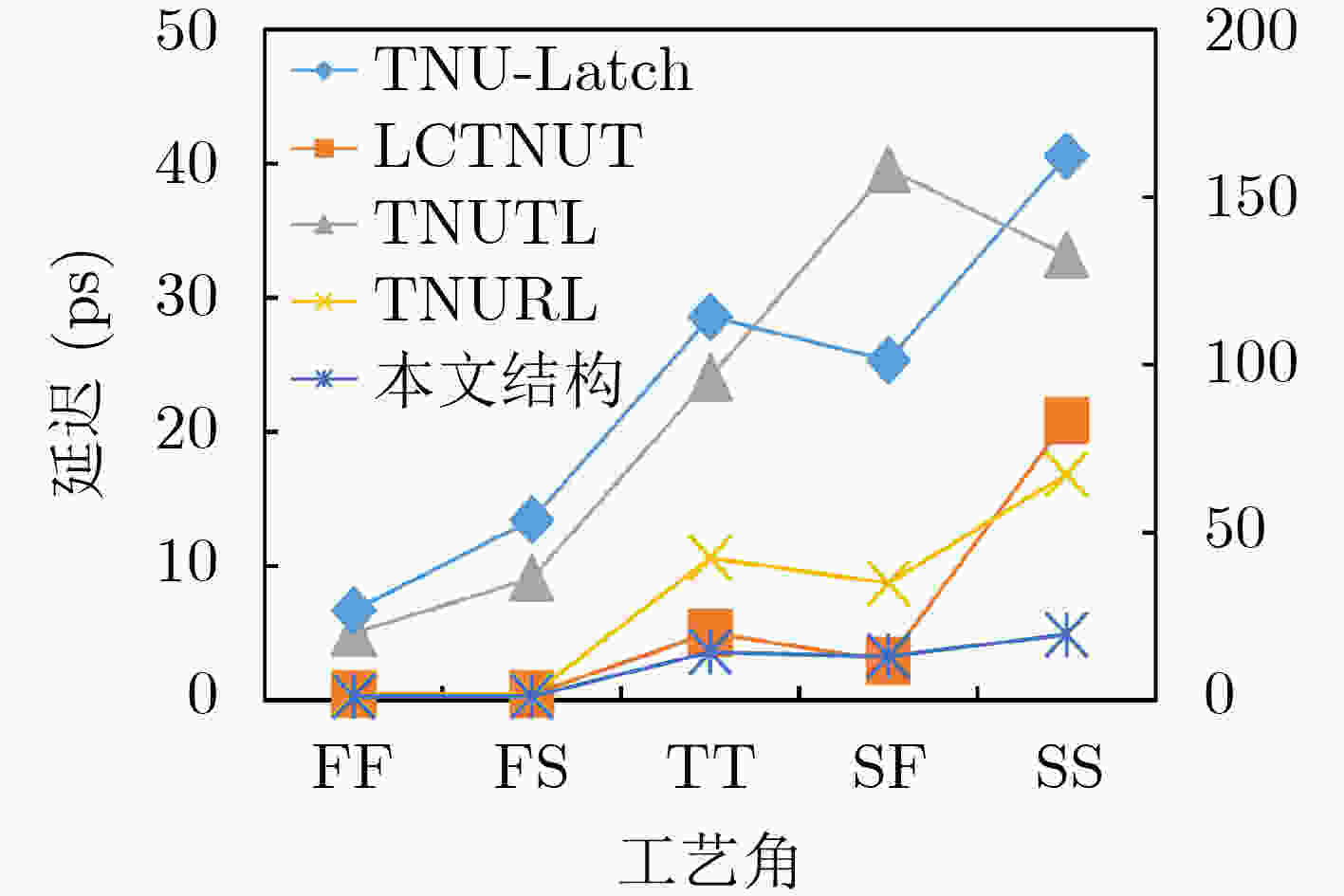
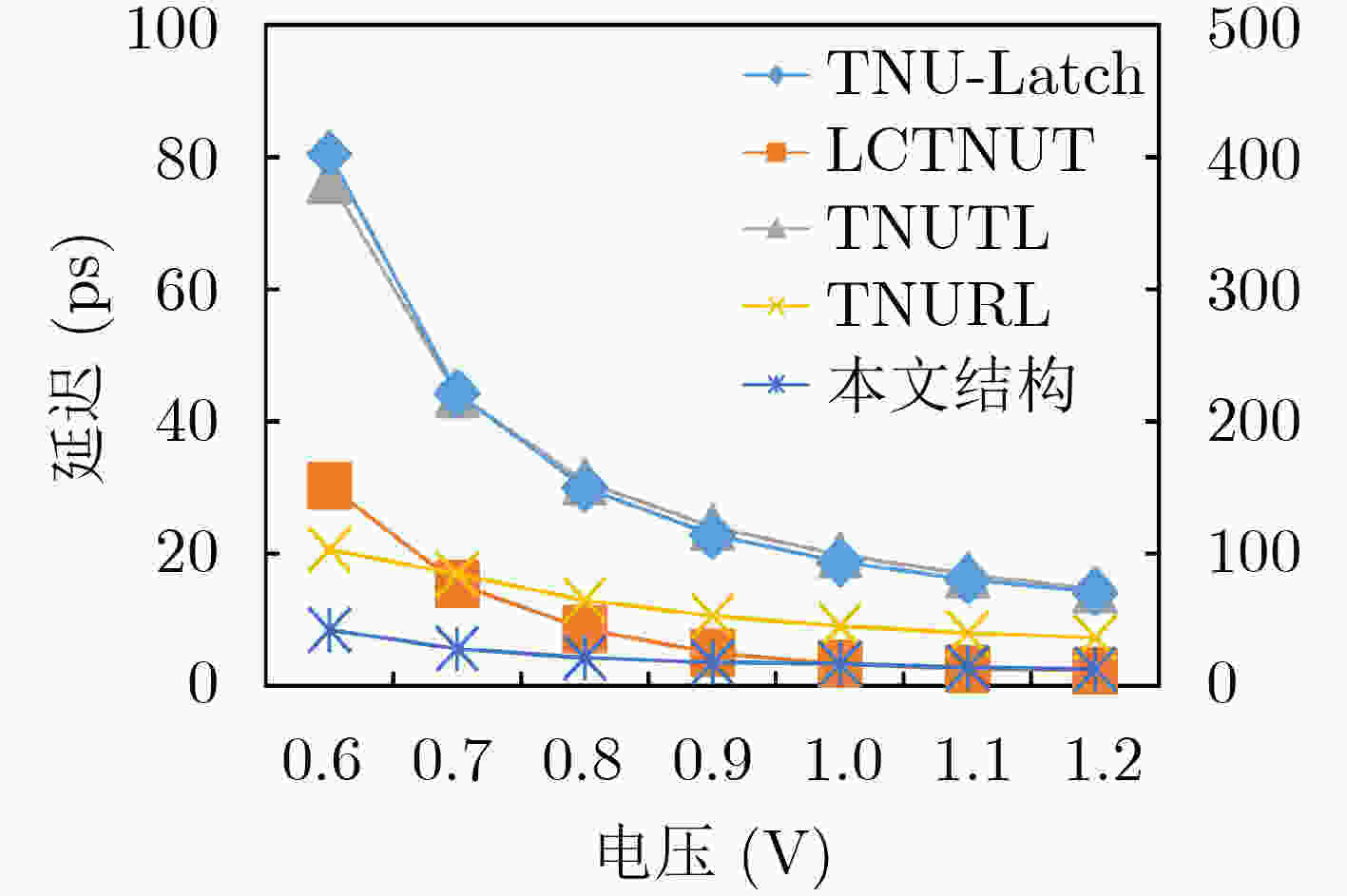
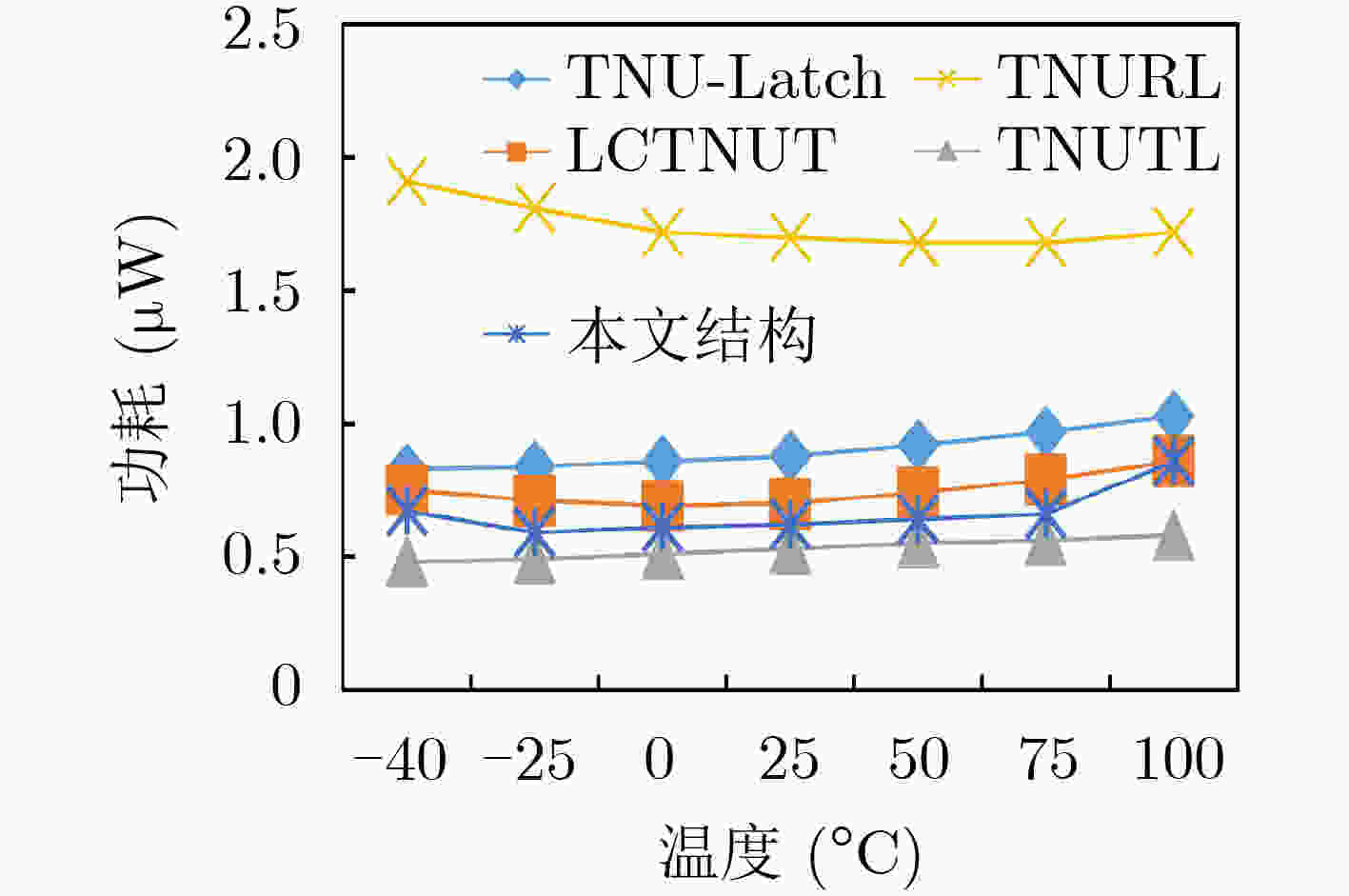
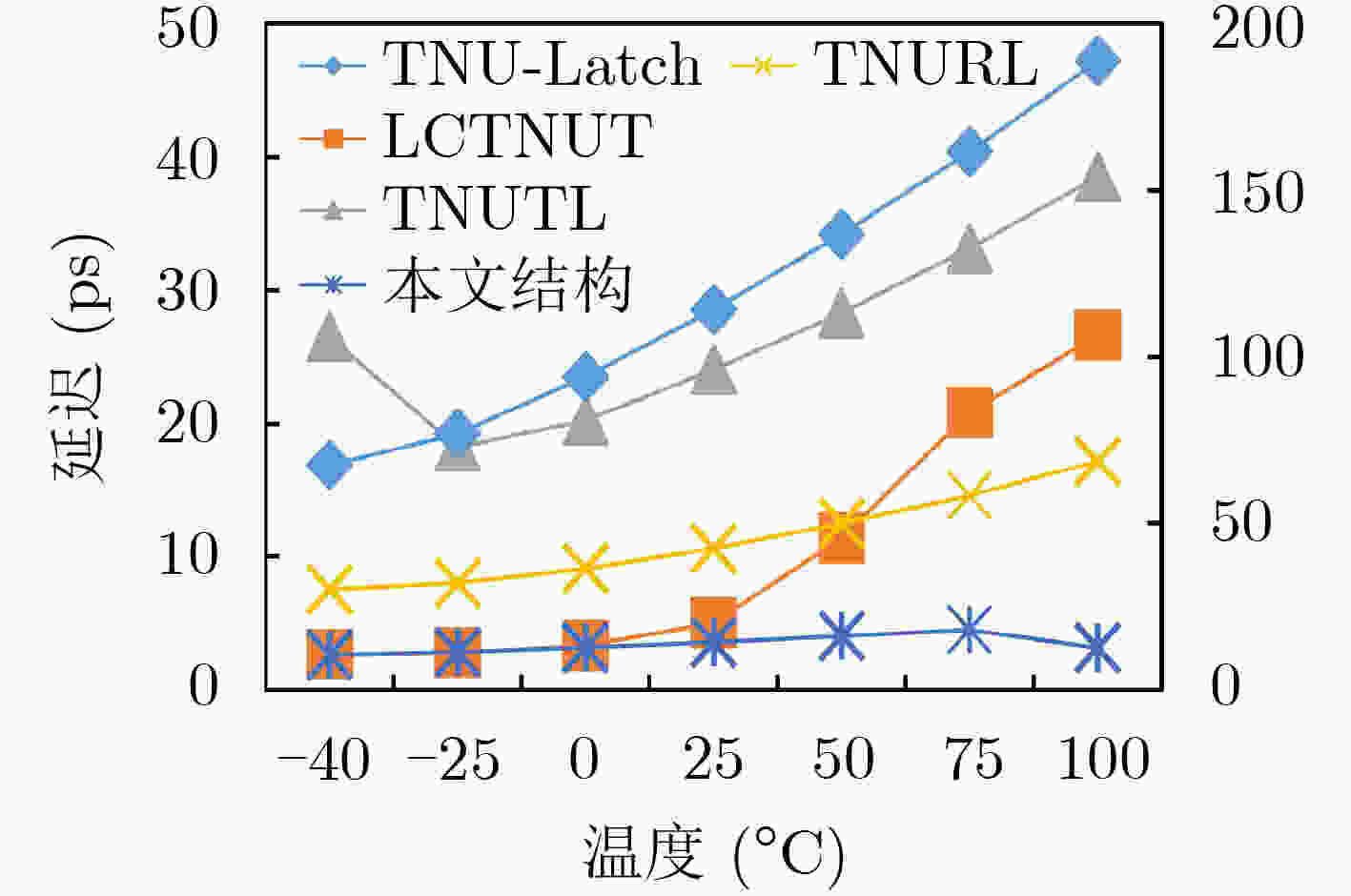
摘要: 随着集成电路特征尺寸的不断缩减,在恶劣辐射环境下,纳米级CMOS集成电路中单粒子三点翻转的几率日益增高,严重影响可靠性。为了实现单粒子三点翻转自恢复,该文提出一种低开销的三点翻转自恢复锁存器(LC-TNURL)。该锁存器由7个C单元和7个钟控C单元组成,具有对称的环状交叉互锁结构。利用C单元的阻塞特性和交叉互锁连接方式,任意3个内部节点发生翻转后,瞬态脉冲在锁存器内部传播,经过C单元多级阻塞后会逐级消失,确保LC-TNURL锁存器能够自行恢复到正确逻辑状态。详细的HSPICE仿真表明,与其他三点翻转加固锁存器(TNU-Latch, LCTNUT, TNUTL, TNURL)相比,LC-TNURL锁存器的功耗平均降低了31.9%,延迟平均降低了87.8%,功耗延迟积平均降低了92.3%,面积开销平均增加了15.4%。相对于参考文献中提出的锁存器,LC-TNURL锁存器的PVT波动敏感性最低,具有较高的可靠性。Abstract: As the feature size of integrated circuits continues to scale down, under the harsh radiation environment, the probability of single event triple node upsets in nano-scale CMOS integrated circuits is increasing, seriously affecting reliability. In order to realize the resilient of single-event triple-node-upsets, a Low-Cost Triple-Node-Upset-Resilient Latch (LC-TNURL) is proposed. The latch is composed of seven C-elements and seven clock-gating C-elements, and has a symmetrical ring-shaped cross-interlock structure. Using the interceptive characteristics of the C-elements and the cross-interlock connection mode, after any three internal nodes are flipped, the transient pulse propagates inside the latch. After the C-elements is blocked in multiple stages, it will disappear step by step to ensure the LC-TNURL latch can self-recover to the correct logic state. Detailed HSPICE simulation shows that the power consumption of the LC-TNURL latch is reduced by an average of 31.9%, the delay is reduced by an average of 87.8%, the power-delay product is reduced by an average of 92.3% and the area overhead is increased by an average of 15.4% compared to other triple-node-upsets hardened latches (TNU-Latch, LCTNUT, TNUTL, TNURL). The LC-TNURL latch proposed in this paper is the least sensitive to PVT fluctuations and has high reliability compared with reference latches.
-
Key words:
- Latch /
- Radiation hardening by design /
- C-elements /
- Resilient /
- Triple node upsets
-
表 1 各锁存器加固能力对比(%)
表 2 性能与开销对比
表 3 性能与开销的相对变化(%)
-
[1] 贾海昆, 池保勇. 硅基毫米波雷达芯片研究现状与发展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 173–190. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190666JIA Haikun and CHI Baoyong. The status and trends of silicon-based millimeter-wave radar SoCs[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 173–190. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190666 [2] 贺成艳, 卢晓春, 郭际. 一种新型卫星导航信号波形畸变特性评估新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1017–1024. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180656HE Chengyan, LU Xiaochun, and GUO Ji. Evil waveform evaluating method for new GNSS signals[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1017–1024. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180656 [3] LIANG Huaguo, Li Xin, HUANG Zhengfeng, et al. Highly robust double node upset resilient hardened latch design[J]. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 2017, E100-C(5): 496–503. doi: 10.1587/transele.E100.C.496 [4] IBE E, TANIGUCHI H, YAHAGI Y, et al. Impact of scaling on neutron-induced soft error in SRAMs from a 250 nm to a 22 nm design rule[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2010, 57(7): 1527–1538. doi: 10.1109/ted.2010.2047907 [5] 冯彦君, 华更新, 刘淑芬. 航天电子抗辐射研究综述[J]. 宇航学报, 2007, 28(5): 1071–1080. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2007.05.001FENG Yanjun, HUA Gengxin, and LIU Shufen. Radiation hardness for space electronics[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2007, 28(5): 1071–1080. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2007.05.001 [6] JIANG Jianwei, XU Yiran, REN Jiangchuan, et al. Low-cost single event double-upset tolerant latch design[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(9): 554–556. doi: 10.1049/el.2018.0558 [7] HUANG Zhengfeng, ZHANG Yangyang, SU Zian, et al. A hybrid DMR latch to tolerate MNU using TDICE and WDICE[C]. 2018 IEEE 27th Asian Test Symposium (ATS), Hefei, China, 2018: 121–126. doi: 10.1109/ats.2018.00033. [8] WATKINS A and TRAGOUDAS S. Radiation hardened latch designs for double and triple node upsets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2020, 8(3): 616–626. doi: 10.1109/tetc.2017.2776285 [9] YAN Aibin, LAI Chaoping, ZHANG Yinlei, et al. Novel low cost, double-and-triple-node-upset-tolerant latch designs for nano-scale CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2021, 9(1): 520–533. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2018.2871861 [10] LIU Xin. Multiple node upset-tolerant latch design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 2019, 19(2): 387–392. doi: 10.1109/TDMR.2019.2912811 [11] YAN Aibin, FENG Xiangfeng, HU Yuanjie, et al. Design of a triple-node-upset self-recoverable latch for aerospace applications in harsh radiation environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1163–1171. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2925448 [12] KUMAR C I and ANAND B. A highly reliable and energy-efficient triple-node-upset-tolerant latch design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2019, 66(10): 2196–2206. doi: 10.1109/tns.2019.2939380 [13] YAN Aibin, XU Zhelong, YANG Kang, et al. A novel low-cost TMR-without-voter based HIS-insensitive and MNU-tolerant latch design for aerospace applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(4): 2666–2676. doi: 10.1109/taes.2019.2951186 [14] LIN Dianpeng, XU Yiran, LI Xiaoyun, et al. A novel self-recoverable and triple nodes upset resilience DICE latch[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2018, 15(19): 20180753. doi: 10.1587/elex.15.20180753 [15] NICOLAIDIS M, PEREZ R, and ALEXANDRESCU D. Low-cost highly-robust hardened cells using blocking feedback transistors[C]. 26th IEEE VLSI Test Symposium (vts 2008), San Diego, USA, 2008: 371–376. doi: 10.1109/vts.2008.15. [16] BLUM D R and DELGADO-FRIAS J G. Schemes for eliminating transient-width clock overhead from SET-tolerant memory-based systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2006, 53(3): 1564–1573. doi: 10.1109/tns.2006.874496 [17] CALIN T, NICOLAIDIS M, and VELAZCO R. Upset hardened memory design for submicron CMOS technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1996, 43(6): 2874–2878. doi: 10.1109/23.556880 [18] 黄正峰, 王世超, 欧阳一鸣, 等. 40 nm CMOS工艺下的低功耗容软错误锁存器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1464–1471. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160889HUANG Zhengfeng, WANG Shichao, OUYANG Yiming, et al. Low power soft error tolerant latch for 40 nm CMOS technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1464–1471. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160889 [19] 黄正峰, 陈凡, 蒋翠云, 等. 基于时序优先的电路容错混合加固方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(1): 234–240. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00449HUANG Zhengfeng, CHEN Fan, JIANG Cuiyun, et al. A hybrid hardening strategy for circuit soft-error-tolerance based on timing priority[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(1): 234–240. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00449 [20] MITRA S, SEIFERT N, ZHANG M, et al. Robust system design with built-in soft-error resilience[J]. Computer, 2005, 38(2): 43–52. doi: 10.1109/mc.2005.70 [21] NEALE A and SACHDEV M. Neutron radiation induced soft error rates for an adjacent-ECC protected SRAM in 28 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2016, 63(3): 1912–1917. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2016.2547963 [22] OMANA M, ROSSI D, and METRA C. Latch susceptibility to transient faults and new hardening approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2007, 56(9): 1255–1268. doi: 10.1109/TC.2007.1070 [23] MESSENGER G C. Collection of charge on junction nodes from ion tracks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1982, 29(6): 2024–2031. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1982.4336490 [24] KATSAROU K and TSIATOUHAS Y. Soft error interception latch: Double node charge sharing SEU tolerant design[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(4): 330–332. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.4374 [25] YAN Aibin, LIANG Huaguo, HUANG Zhengfeng, et al. An SEU resilient, SET filterable and cost effective latch in presence of PVT variations[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2016, 63: 239–250. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2016.06.004 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
