Image Reconstruction Based on Gaussian Smooth Compressed Sensing Fractional Order Total Variation Algorithm
-
摘要: 针对全变分(TV)算法梯度效应造成图像纹理细节丢失和单像素成像系统中的环境噪声问题,该文给出基于高斯平滑压缩感知分数阶全变分(FOTVGS)算法的图像重构。分数阶微分损失图像低频分量的同时增加了图像的高频分量,达到增强图像细节的目的,高斯平滑滤波算子更新拉格朗日梯度算子滤除了微分算子导致的加性高斯白噪声高频分量的增加。仿真结果表明,对比其他4种同类算法,在相同的采样率和噪声水平下,该算法能取得最大的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似度(SSIM)。采样率为0.2时,对比分数阶全变分(FOTV)算法,在无噪声(测量值
${\rm{SNR}} = \infty $ )和有噪声(测量值${\rm{SNR}} = 25\;{\rm{dB}}$ )情况下提高的最大峰值信噪比和结构相似度分别是1.39 dB(0.035)和3.91 dB(0.098)。可见,此算法在无噪声和有噪声情况下均能提高图像的重构质量,尤其是在有噪声情况下对图像重构质量有较大提高。该算法为单像素成像等计算成像系统中由于环境造成的噪声的图像重构提供了可行的解决方案。Abstract: In view of the gradient effect caused by the gradient effect of the Total Variation (TV) algorithm and the environmental noise in the single pixel imaging system, an image reconstruction based on the Gaussian Smooth compressed sensing Fractional Order Total Variation algorithm (FOTVGS) is proposed. Fractional differential loss of low-frequency components of the image increases the high-frequency components of the image to achieve the purpose of enhancing image details. The Gaussian smoothing filter operator updates the Lagrangian gradient operator to filter out the additive white Gaussian noise caused by the differential operator. Simulation results show that, compared with other four similar algorithms, the algorithm can achieve the maximum Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural SIMilarity(SSIM) at the same sampling rate and noise level. When the sampling rate is 0.2, compared with the Fractional Order Total Variation (FOTV) algorithm, the maximum PSNR and SSIM increase by 1.39 dB (0.035) and 3.91 dB (0.098) respectively. It can be proved that this algorithm can improve the reconstruction quality of the image in the absence of noise and noise, especially in the case of noise, the quality of image reconstruction is greatly improved. The proposed algorithm provides a feasible solution for image reconstruction of noise caused by environment in single-pixel imaging and other computing imaging system.-
Key words:
- Image reconstruction /
- Compressive sensing /
- Fractional differential /
- Total variation /
- Gaussian smooth
-
表 1 改进算法流程
输入:测量矩阵${{A}}$,测量值${{y}}$,相关参数${{\nu}} $, ${{\lambda}} $, $\beta $, $\gamma $, $\alpha $ 初始化:${{u}} = {{{A}}^{\rm T}}{{y}}$, ${{\nu}} = {\bf{0}}$, ${{\lambda}} = {\bf{0}}$, $\beta = {2^6}$, $\gamma = {2^7}$, $\alpha = {2^7}$ While (目标函数式(8)未达到最优解) do While ${\left\| { { {{u} }^{(k + 1)} } - { {{u} }^k} } \right\|_2} \ge \varepsilon$ do 利用式(12)求解${{w}}$子问题 利用式(13)求解${{u}}$子问题 End while 利用式(10),使用高斯平滑滤波算子$G$更新拉格朗日梯度算子 使用式(4),将输入图像的像素值作为权重,乘以相关核 将上面各步得到的结果相加后输出 End while 输出:恢复的图像${{u}}$ 表 2 在无噪声(测量值SNR=
${{ \infty }}$ )和有噪声情况下5种算法图像重构峰值信噪比(PSNR: dB)采样率 0.1 0.2 SNR (dB) 10 20 25 30 35 $\infty $ 10 20 25 30 35 $\infty $ Barbara TV 12.53 16.26 18.77 19.39 20.43 22.06 13.62 17.25 19.83 20.48 21.66 24.12 TVNR 13.50 16.73 18.92 19.83 21.53 23.06 14.54 17.82 20.23 21.56 22.23 25.05 FOTV 10.83 15.55 16.39 18.28 19.86 24.35 12.91 16.77 18.10 19.24 20.04 25.56 TVGS 13.10 16.57 18.43 18.76 20.04 21.53 14.12 17.73 19.94 19.52 20.62 23.21 FOTVGS 14.32 17.93 19.17 20.36 22.30 25.28 15.25 18.37 20.77 22.10 23.31 26.35 Lena TV 16.65 20.48 22.53 23.96 24.03 25.29 18.33 22.10 23.43 25.24 26.94 28.42 TVNR 17.87 21.42 23.10 24.40 25.15 26.34 19.54 23.03 24.93 26.94 27.55 28.93 FOTV 15.93 19.40 21.58 22.78 23.44 27.81 17.21 21.22 22.30 24.19 25.12 29.38 TVGS 17.28 20.98 22.78 23.52 23.87 24.72 18.88 22.74 24.23 25.14 26.21 28.02 FOTVGS 18.69 22.59 24.41 25.42 26.46 27.93 20.39 24.47 25.38 27.58 28.20 30.77 Boats TV 14.75 18.58 20.13 21.30 22.51 23.21 15.57 19.38 21.00 22.91 24.28 26.66 TVNR 15.93 19.74 20.99 21.94 23.01 23.75 16.55 20.34 22.88 23.65 24.87 27.12 FOTV 13.51 17.37 18.89 20.86 21.39 24.60 14.21 18.75 20.78 21.93 23.93 27.86 TVGS 15.33 19.00 20.23 21.02 22.06 23.01 16.02 19.93 21.21 22.82 24.01 26.03 FOTVGS 17.10 20.86 22.37 23.55 24.37 25.46 17.82 23.26 24.69 25.15 26.84 28.69 Peppers TV 16.66 20.51 21.19 22.54 23.53 24.03 17.89 21.75 23.24 24.65 25.30 26.06 TVNR 17.52 21.79 22.36 23.11 24.00 24.78 18.77 23.23 24.88 25.94 26.23 27.83 FOTV 15.75 19.13 20.23 21.47 22.72 25.66 16.51 20.96 22.41 23.71 24.51 28.41 TVGS 17.21 21.55 21.24 22.31 23.17 23.84 18.25 22.55 23.94 24.71 25.02 25.87 FOTVGS 18.63 22.35 23.79 24.47 25.32 26.33 19.54 24.77 25.44 26.11 27.32 28.88 采样率 0.3 0.4 SNR (dB) 10 20 25 30 35 $\infty $ 10 20 25 30 35 $\infty $ Barbara TV 14.69 18.55 21.05 22.50 23.40 26.33 16.55 20.45 23.64 24.98 25.90 28.11 TVNR 15.77 19.49 21.97 23.87 24.58 27.33 17.63 22.37 24.53 25.78 26.45 29.49 FOTV 13.93 18.56 19.04 21.51 22.54 27.95 15.34 19.24 22.21 23.48 24.24 29.98 TVGS 15.43 19.03 21.24 22.47 23.21 26.00 17.21 21.23 24.01 25.07 25.79 27.91 FOTVGS 16.83 20.36 22.45 24.34 25.14 28.57 18.56 23.66 25.49 26.03 27.86 30.47 Lena TV 19.41 23.90 25.72 27.42 28.01 31.14 21.31 25.80 27.86 29.73 30.01 32.62 TVNR 21.32 25.45 26.11 28.01 29.21 31.95 22.41 26.97 28.99 30.01 31.52 33.43 FOTV 18.33 22.97 24.50 25.93 27.18 32.66 20.45 24.85 25.06 27.11 29.99 34.53 TVGS 20.78 24.35 25.96 27.51 27.94 30.99 22.17 26.65 27.99 29.70 29.88 32.39 FOTVGS 22.45 26.36 27.69 29.02 30.03 33.10 23.58 27.51 29.73 31.48 32.89 35.36 Boats TV 17.88 23.01 24.19 25.27 26.55 28.35 19.23 25.36 26.00 27.41 28.28 29.87 TVNR 19.53 24.94 25.24 26.45 27.14 28.83 20.82 26.65 27.21 28.77 29.56 30.29 FOTV 17.02 22.94 23.12 24.56 25.51 29.25 18.88 24.16 25.78 26.03 27.64 30.68 TVGS 18.77 24.68 24.23 25.10 26.35 28.01 20.59 26.18 26.55 27.46 28.00 29.51 FOTVGS 20.45 25.49 26.22 27.18 28.03 29.67 21.96 27.42 28.69 29.15 30.24 31.43 Peppers TV 18.61 23.40 24.22 25.04 26.74 27.96 19.97 24.06 25.61 26.97 28.16 29.71 TVNR 19.93 24.82 25.96 26.92 27.71 28.32 21.32 25.36 26.99 27.98 28.72 29.92 FOTV 17.44 20.67 22.58 24.23 25.35 29.11 18.54 23.66 24.97 26.05 27.14 30.51 TVGS 19.66 24.54 24.42 25.02 26.45 27.31 20.86 25.88 25.97 26.87 29.03 29.41 FOTVGS 21.23 25.35 26.79 27.47 28.89 29.42 22.39 26.77 27.44 28.35 29.11 30.89 -
[1] CANDES E J. Compressive sampling[J]. Marta Sanz Solé, 2006, 17(2): 1433–1452. [2] TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108 [3] BLUMENSATH T and DAVIES M E. Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 27(3): 265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2009.04.002 [4] SELESNICK I. Total variation denoising via the Moreau envelope[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(2): 216–220. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2647948 [5] ZHANG Jian, LIU Shaohui, XIONG Ruiqin, et al. Improved total variation based image compressive sensing recovery by nonlocal regularization[C]. 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Beijing, China, 2013: 2836–2839. [6] 刘亚男, 杨晓梅, 陈超楠. 基于分数阶全变分正则化的超分辨率图像重建[J]. 计算机科学, 2016, 43(5): 274–278, 307. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.5.052LIU Ya’nan, YANG Xiaomei, and CHEN Chaonan. Super-resolution image reconstruction based on fractional order total variation regularization[J]. Computer Science, 2016, 43(5): 274–278, 307. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.5.052 [7] MA Liyan, MOISAN L, YU Jian, et al. A stable method solving the total variation dictionary model with L∞constraints[J]. Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2014, 8(2): 507–535. doi: 10.3934/ipi.2014.8.507 [8] QU Shuai, CHANG Jun, CONG Zhenhua, et al. Data compression and SNR enhancement with compressive sensing method in phase-sensitive OTDR[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 433: 97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.09.064 [9] LI Yunhui, WANG Xiaodong, WANG Zhi, et al. Modeling and image motion analysis of parallel complementary compressive sensing imaging system[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 423: 100–110. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.04.018 [10] HONG Tao and ZHU Zhihui. Online learning sensing matrix and sparsifying dictionary simultaneously for compressive sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 153: 188–196. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.05.021 [11] 李如春, 程云霄, 覃亚丽. 稀疏信号结构性噪声干扰下的感知矩阵优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 911–916. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180513LI Ruchun, CHENG Yunxiao, and QIN Yali. Sensing matrix optimization for sparse signal under structured noise interference[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 911–916. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180513 [12] 赵辉, 张静, 张乐, 等. 基于非局部低秩和加权全变分的图像压缩感知重构算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 2025–2032. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180828ZHAO Hui, ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Le, et al. Compressed sensing image restoration based on non-local low rank and weighted total variation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 2025–2032. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180828 [13] PARTHASARATHY G and ABHILASH G. Entropy-based learning of sensing matrices[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2019, 13(7): 650–660. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2018.5078 [14] LEINONEN M, CODREANU M, and JUNTTI M. Signal reconstruction performance under quantized noisy compressed sensing[C]. 2019 Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, USA, 2019: 586. [15] LI Chengbo, YIN Wotao, JIANG Hong, et al. An efficient augmented lagrangian method with applications to total variation minimization[J]. Computational Optimization and Applications, 2013, 56(3): 507–530. doi: 10.1007/s10589-013-9576-1 [16] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [17] XIAO Yunhai, YANG Junfeng, and YUAN Xiaoming. Alternating algorithms for total variation image reconstruction from random projections[J]. Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2012, 6(3): 547–563. doi: 10.3934/ipi.2012.6.547 -







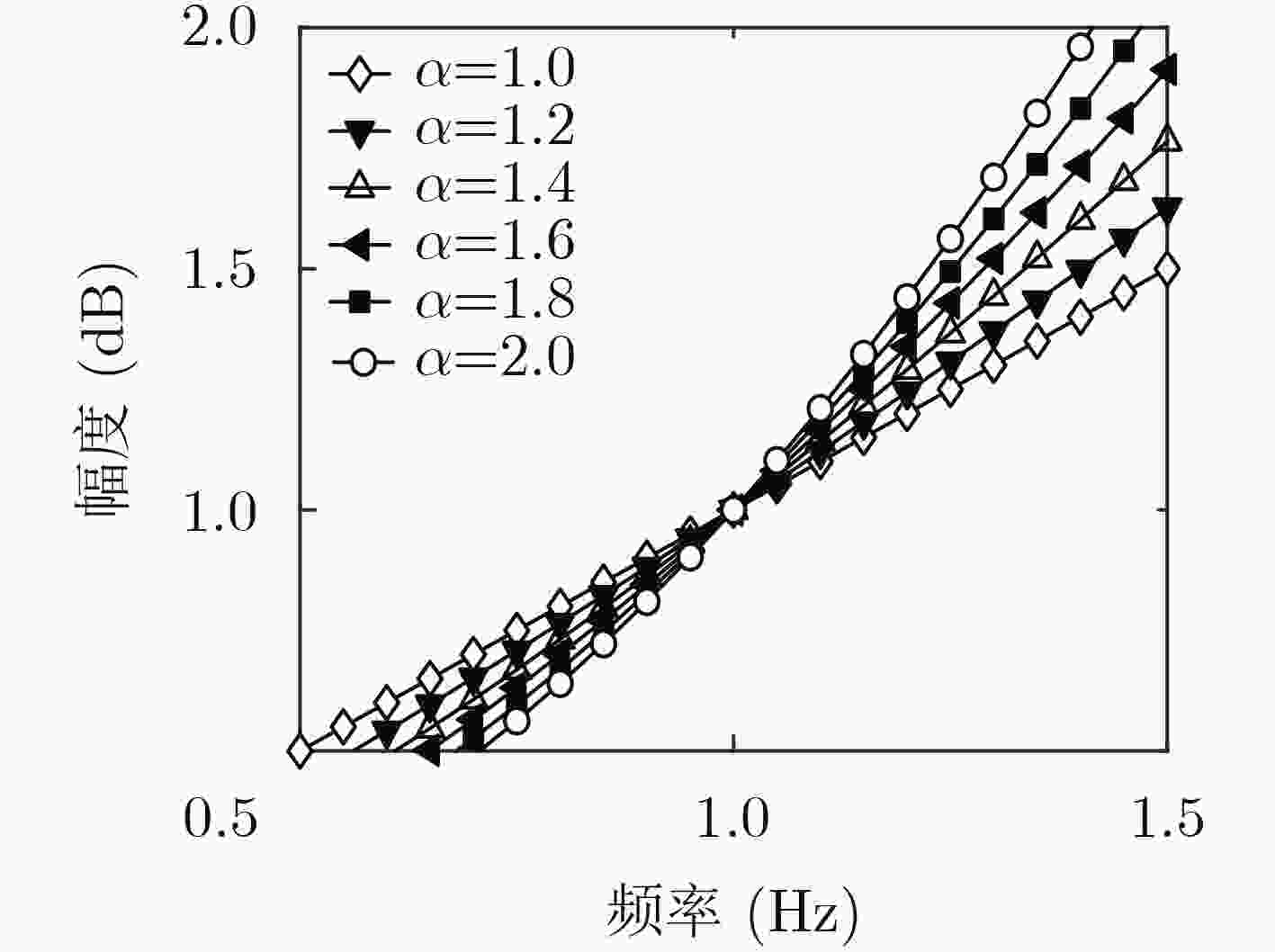

 下载:
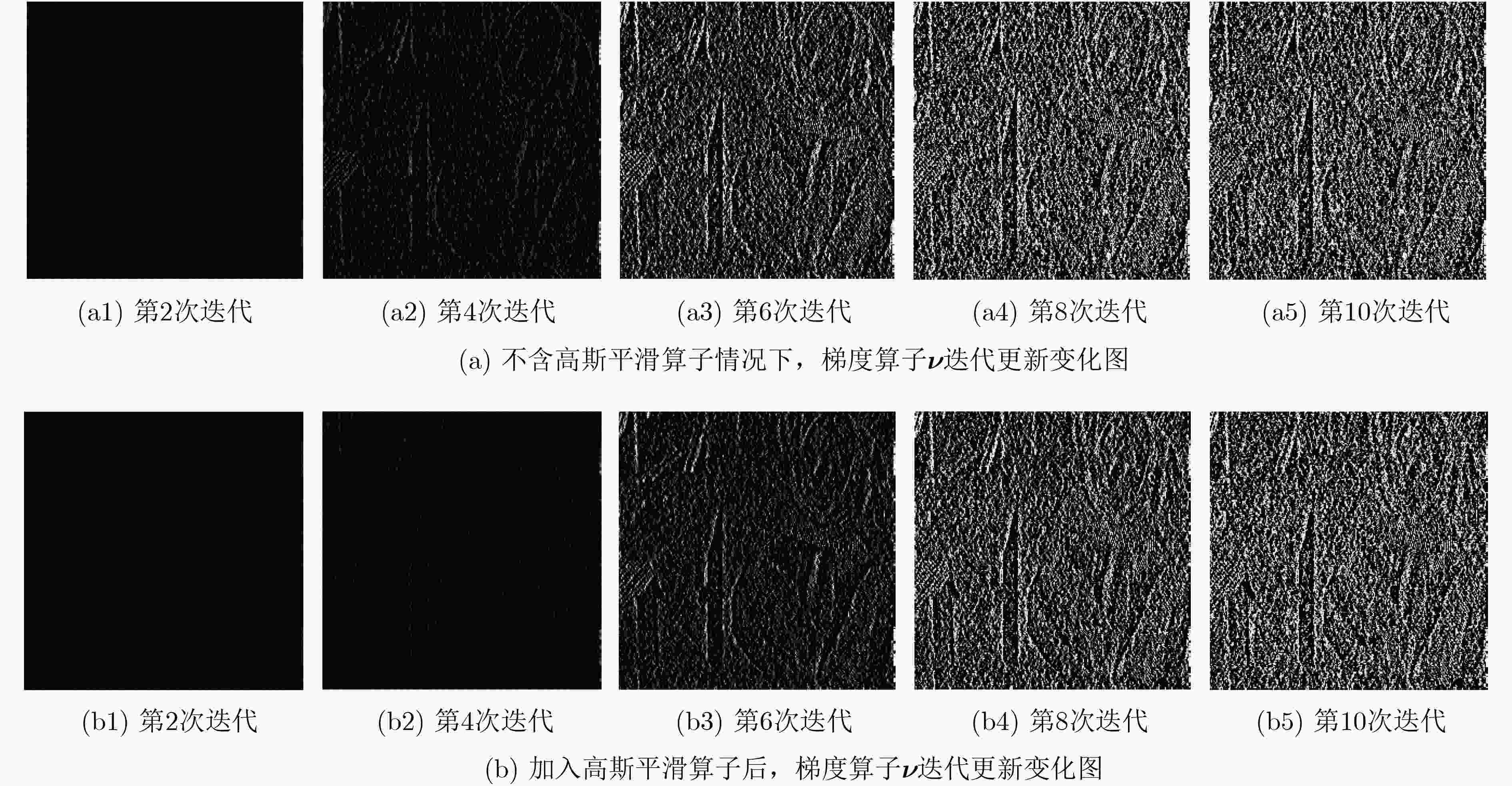
下载:


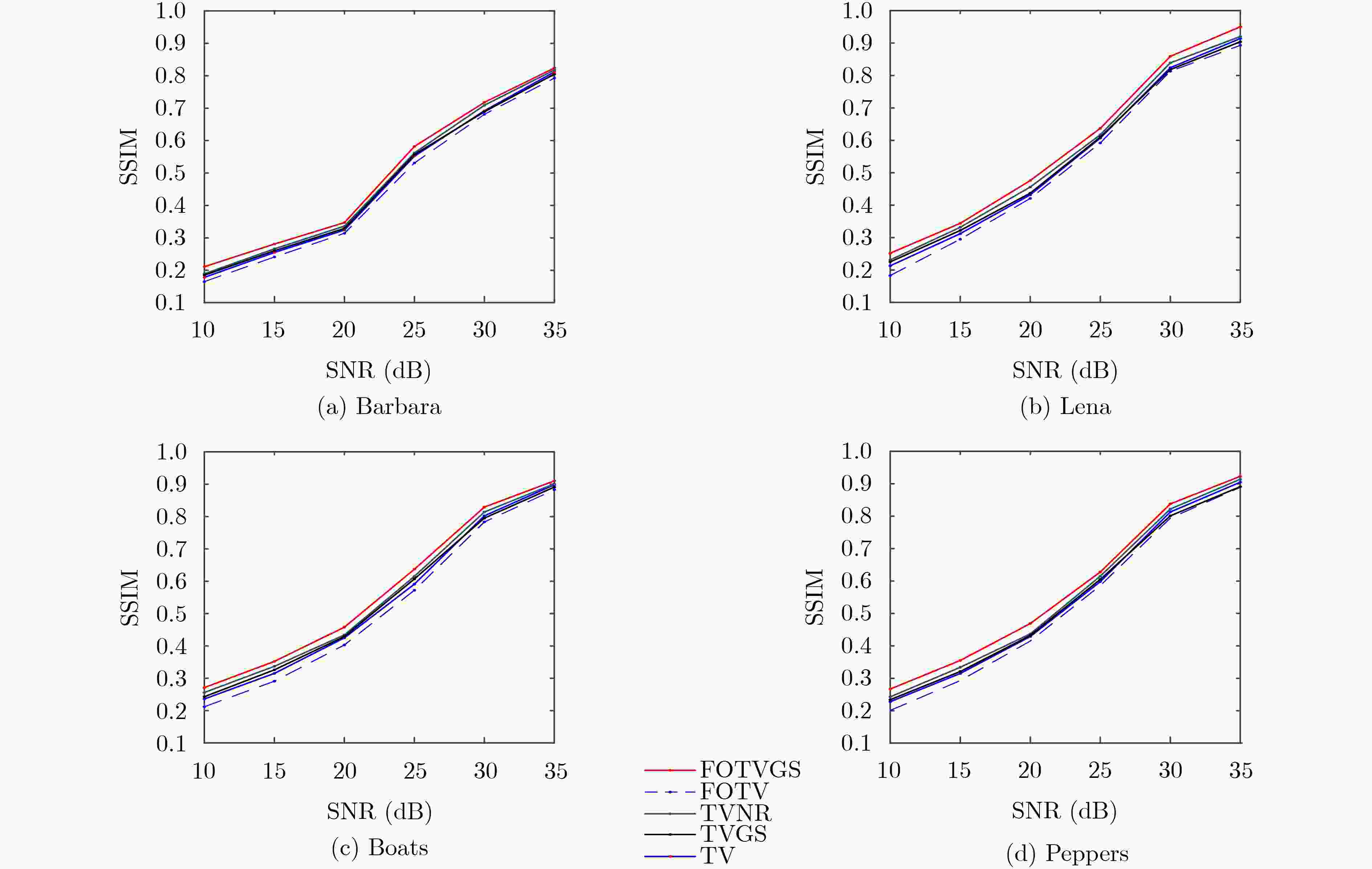



 下载:
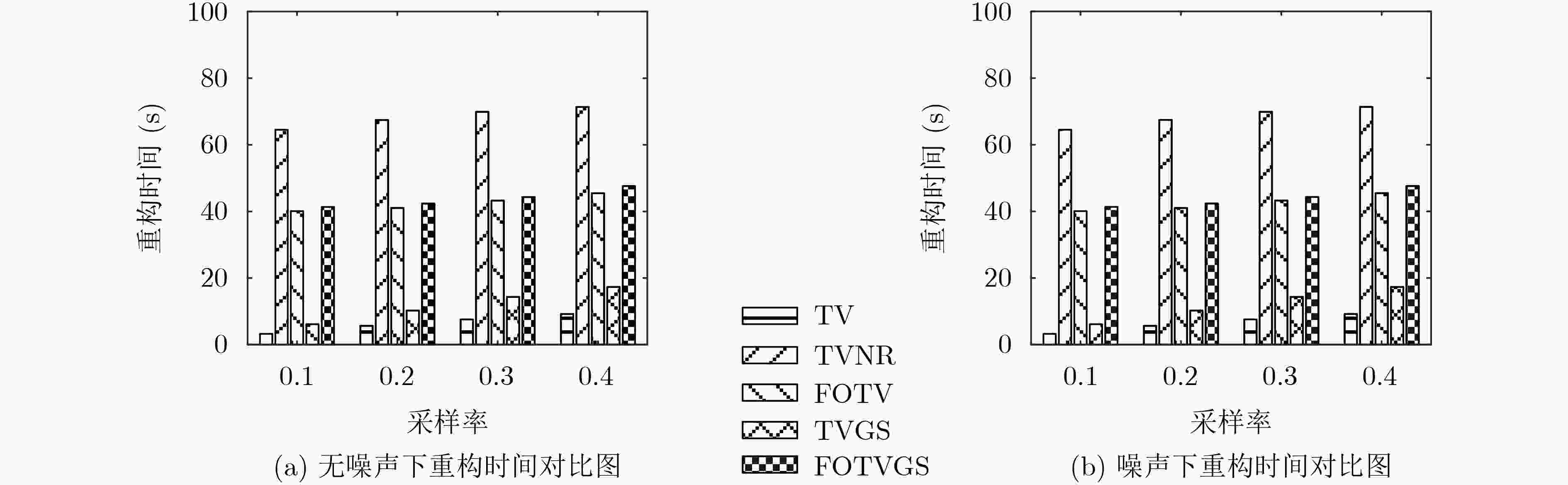
下载:
