Research on Automatic Mapping Method of Reconfigurable Block Cipher Instruction Set Processor
-
摘要: 计算资源与寄存器资源分配是可重构处理器自动并行映射的重要问题,该文针对可重构分组密码指令集处理器的资源分配问题,建立算子调度参数模型和处理器资源参数模型,研究了分组密码并行调度与资源消耗之间的约束关系;在此基础上提出基于贪婪思维、列表调度和线性扫描的自动映射算法,实现了分组密码在可重构分组密码指令集处理器上的自动映射。通过可用资源变化实验验证算法并行映射的有效性,并对AES-128算法的映射效果做了横向对比验证算法的先进性,所提自动映射算法对分组密码在可重构处理中的并行计算研究有一定的指导意义。
-
关键词:
- 可重构分组密码指令集处理器 /
- 自动映射 /
- 资源分配 /
- 列表调度 /
- 线性扫描
Abstract: The allocation of computing resources and register resources is an important issue for automatic parallel mapping of reconfigurable processors. In this paper, for the resource allocation of reconfigurable block cipher instruction set processors, an operator scheduling parameter model and processor resource parameter model are established, and the constraint relationship between the parallel scheduling of block ciphers and resource consumption is studied; Consequently, an automatic mapping algorithm based on greedy thinking, list scheduling and linear scanning is proposed to realize the block cipher atuomatic mapping on the reconfigurable block cipher instruction set processor. The experiment verifies the effect of the algorithm’s parallel scheduling under different resource constraints, and the contrast of AES-128 algorithm’s mapping effect is made to verify the progress of the algorithm, which obtains certain significance for the parallel computing research of block ciphers in reconfigurable processing. -
表 1 自动映射算法
输入:serial_code //分组密码串行程序代码 输出:映射结果 Initial_schdule(list) //对结点进行调度 { for each node vi in list; Sdi = ASAP(vi); Ssi = Sdi – ALAP(vi); Endfor } Select_ReadyQ(list) { for each node vi in list; merge_sort(list,Ssi); //进行归并排序 endfor select the vi with smallest Sdi; vi $ \to $ ready_queue; //将启动时间最早的结点放入就绪队列 } Mapping_sequencing (list) //对就绪队列中的点按照type和order排序,将同类型算子结点排列在一起 { for each node vj in list Spj = TPj–Oj; endfor merge_sort(list, Spj); // 进行归并排序 return list; } BEGIN compiler_infrastructure(serial_code)$ \to $nodelist; //利用编译基础设施预处理串行代码 S_Q = Initial_S(nodelist); //对结点进行初始调度 while (S_Q$ \ne \varnothing $) { R_Q = Select_ReadyQ(S_Q); //生成就绪队列 M_Q = Mapping_sequencing (R_Q); //将同类型结点放一起 for each vk in M_Q if(ORFU(vk)> RFUN or OREG(vk)>REGN); Sdk = Sdk –1; vk$ \to $S_Q; else update lifetime_table; Allocate_RFU(vk); Allocate_Reg (vk,lifetime_table); delete vk in M_Q; endif endfor } END -
[1] WU L, WEAVER C, and AUSTIN T. CryptoManiac: A fast flexible architecture for secure communication[C]. The 28th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Goteborg, Sweden, 2001: 110–119. doi: 10.1109/ISCA.2001.937439. [2] 孟涛, 戴紫彬. 分组密码处理器的可重构分簇式架构[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(2): 453–456. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01586MENG Tao and DAI Zibin. Reconfigurable clustered architecture of block cipher processor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(2): 453–456. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01586 [3] BUCHTY R, HEINTZE N, and OLIVA D. Cryptonite–a programmable crypto processor architecture for high-bandwidth applications[C]. The International Conference on Architecture of Computing Systems, Augsburg, Germany, 2004: 184–198. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-24714-2_15. [4] LI Wei, ZENG Xiaoyang, NAN Longmei, et al. A reconfigurable block cryptographic processor based on VLIW architecture[J]. China Communication, 2016, 13(1): 91–99. doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7405707 [5] 严迎建, 王寿成, 徐进辉, 等. 基于Amdahl定律的分组密码并行处理模型研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(9): 977–984. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.09.017YAN Yingjian, WANG Shoucheng, XU Jinhui, et al. Research on parallel processing model for block cipher based on Amdahl’s law[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(9): 977–984. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.09.017 [6] 刘雷波, 王博, 魏少军. 可重构计算密码处理器[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 167–172.LIU Leibo, WANG Bo, and WEI Shaojun. Reconfigurable Cryptographic Processor[M]. Beijing: Scientific Publisher, 2019: 167–172. [7] 戴紫彬, 曲彤洲. 基于预配置和配置重用的粗粒度动态可重构系统任务调度技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1458–1465. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180831DAI Zibin and QU Tongzhou. Task scheduling technology for coarse-grained dynamic reconfigurable system based on configuration prefetching and reuse[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1458–1465. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180831 [8] 杜怡然, 南龙梅, 戴紫彬, 等. 可重构分组密码逻辑阵列加权度量模型及高能效映射算法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(1): 82–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.01.011DU Yiran, NAN Longmei, DAI Zibin, et al. Reconfigurable block cryptographic logic array weighted metric model and high energy-efficient mapping algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(1): 82–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.01.011 [9] 杜怡然, 杨萱, 戴紫彬, 等. 粗粒度可重构密码逻辑阵列智能映射算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(1): 101–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.012DU Yiran, YANG Xuan, DAI Zibin, et al. Research on coarse-grained reconfigurable cryptographic logic array intelligent mapping algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(1): 101–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.012 [10] LIU Dajiang, YIN Shouyi, LUO Guojie, et al. Data-flow graph mapping optimization for CGRA with deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2019, 38(12): 2271–2283. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2018.2878183 [11] LI Wei, ZENG Xiaoyang, DAI Zibin, et al. A high energy-efficient reconfigurable VLIW symmetric cryptographic processor with loop buffer structure and chain processing mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(6): 1161–1167. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.06.010 [12] 王寿成, 严迎建, 徐进辉. 基于流体系结构的高效能分组密码处理器研究[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(4): 937–943. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112WANG Shoucheng, YAN Yingjian, and XU Jinhui. Research of high-efficient block cipher processor based on stream architecture[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(4): 937–943. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112 [13] 张惠臻, 王超, 李曦, 等. 可重构指令集处理器的代码优化生成算法研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2012, 49(9): 2018–2026.ZHANG Huizhen, WANG Chao, LI Xi, et al. An optimized code-generating algorithm for reconfigurable instruction set processors[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2012, 49(9): 2018–2026. [14] KWOK Y K and AHMAD I. Static scheduling algorithms for allocating directed task graphs to multiprocessors[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 1999, 31(4): 406–471. doi: 10.1145/344588.344618 [15] DU Yiran, LI Wei, DAI Zibin, et al. PVHArray: An energy-efficient reconfigurable cryptographic logic array with intelligent mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2020, 28(5): 1302–1315. doi: 10.1109/tvlsi.2020.2972392 [16] LIU Bin and BAAS B M. Parallel AES encryption engines for many-core processor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(3): 536–547. doi: 10.1109/TC.2011.251 [17] SHAN Weiwei, FU Xingyuan, and XU Zhipeng. A secure reconfigurable crypto IC with countermeasures against SPA, DPA, and EMA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2015, 34(7): 1201–1205. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2419621 -





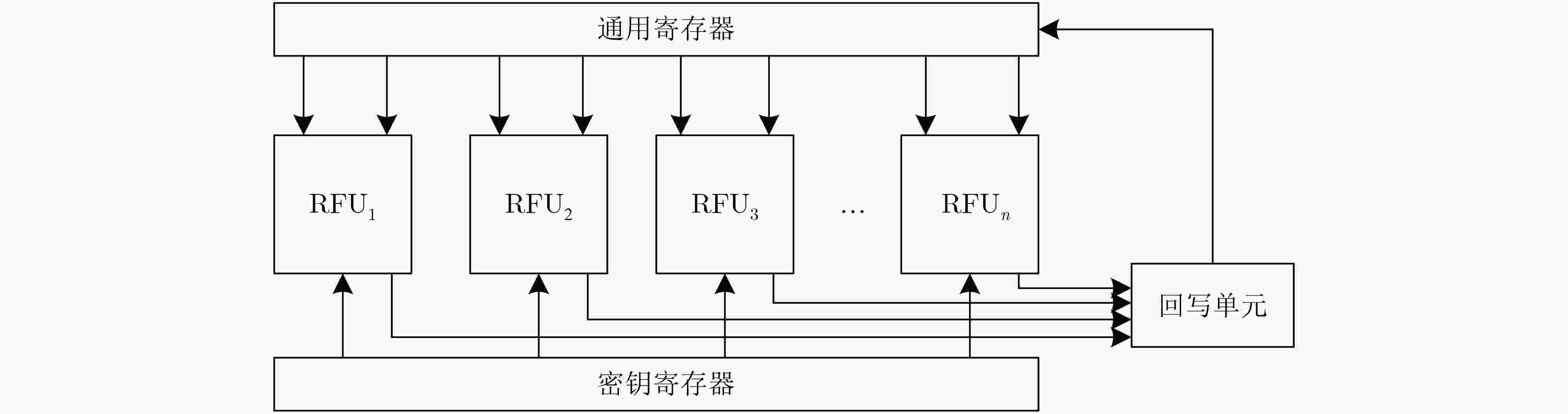
 下载:
下载:
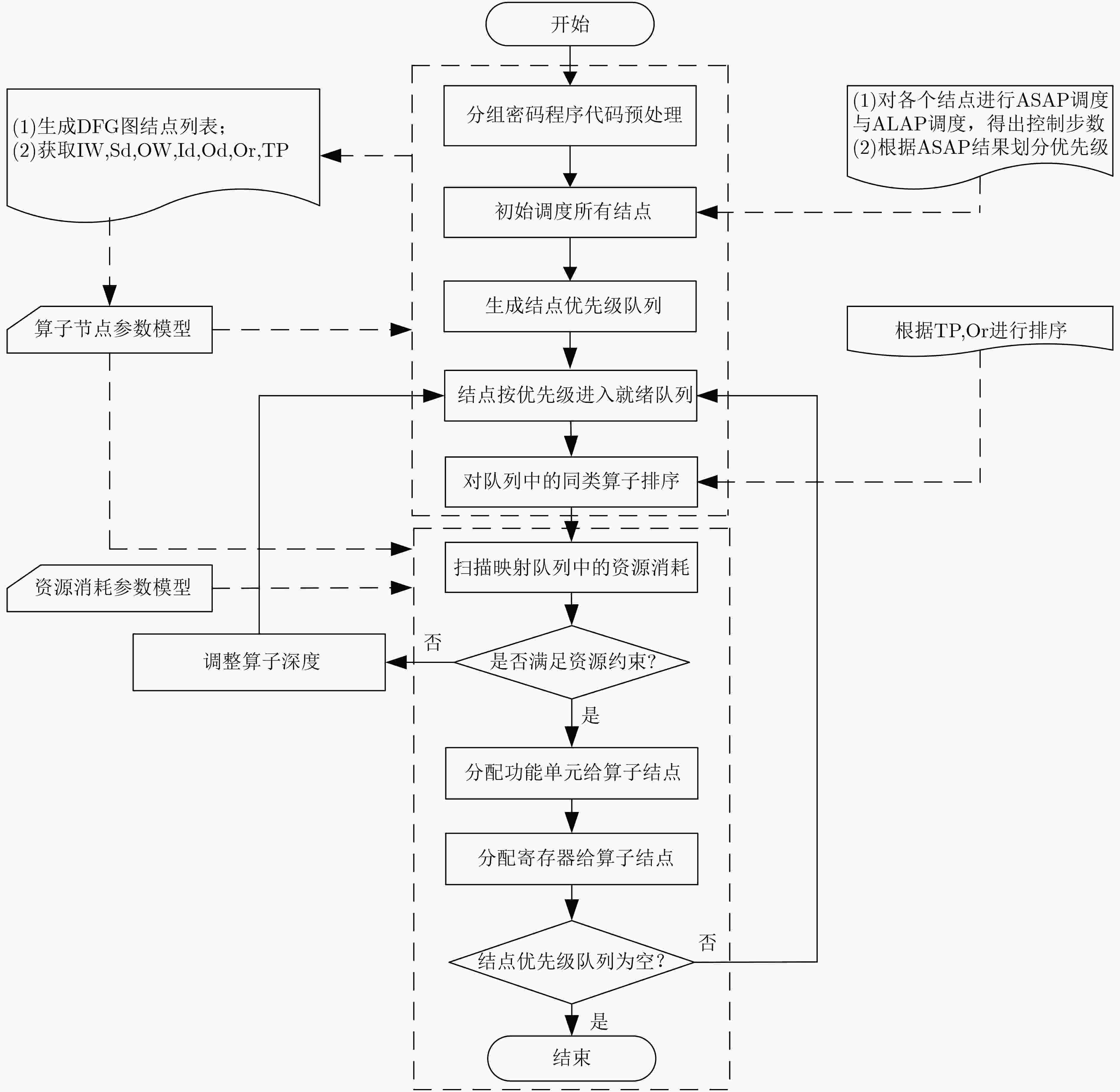
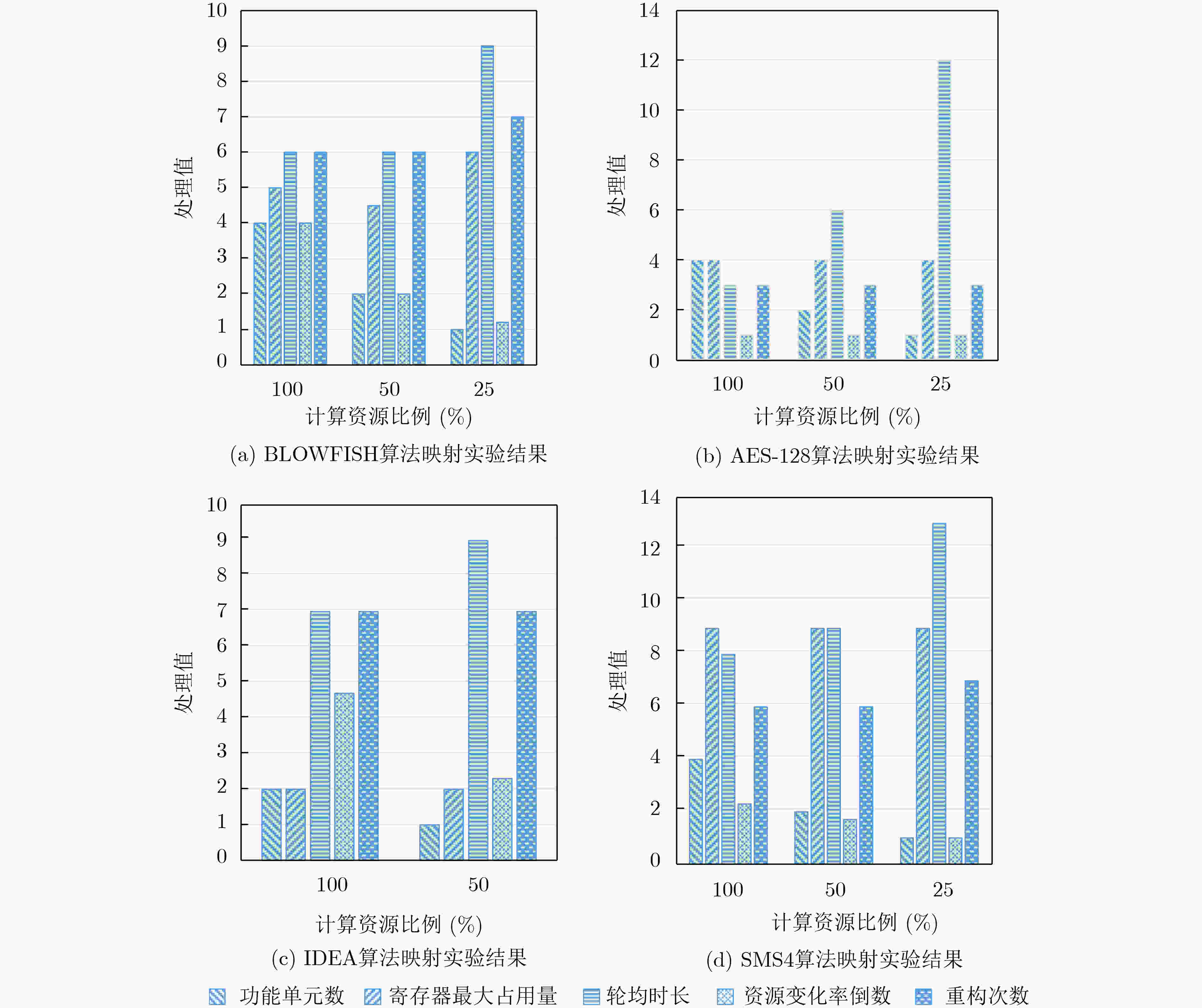
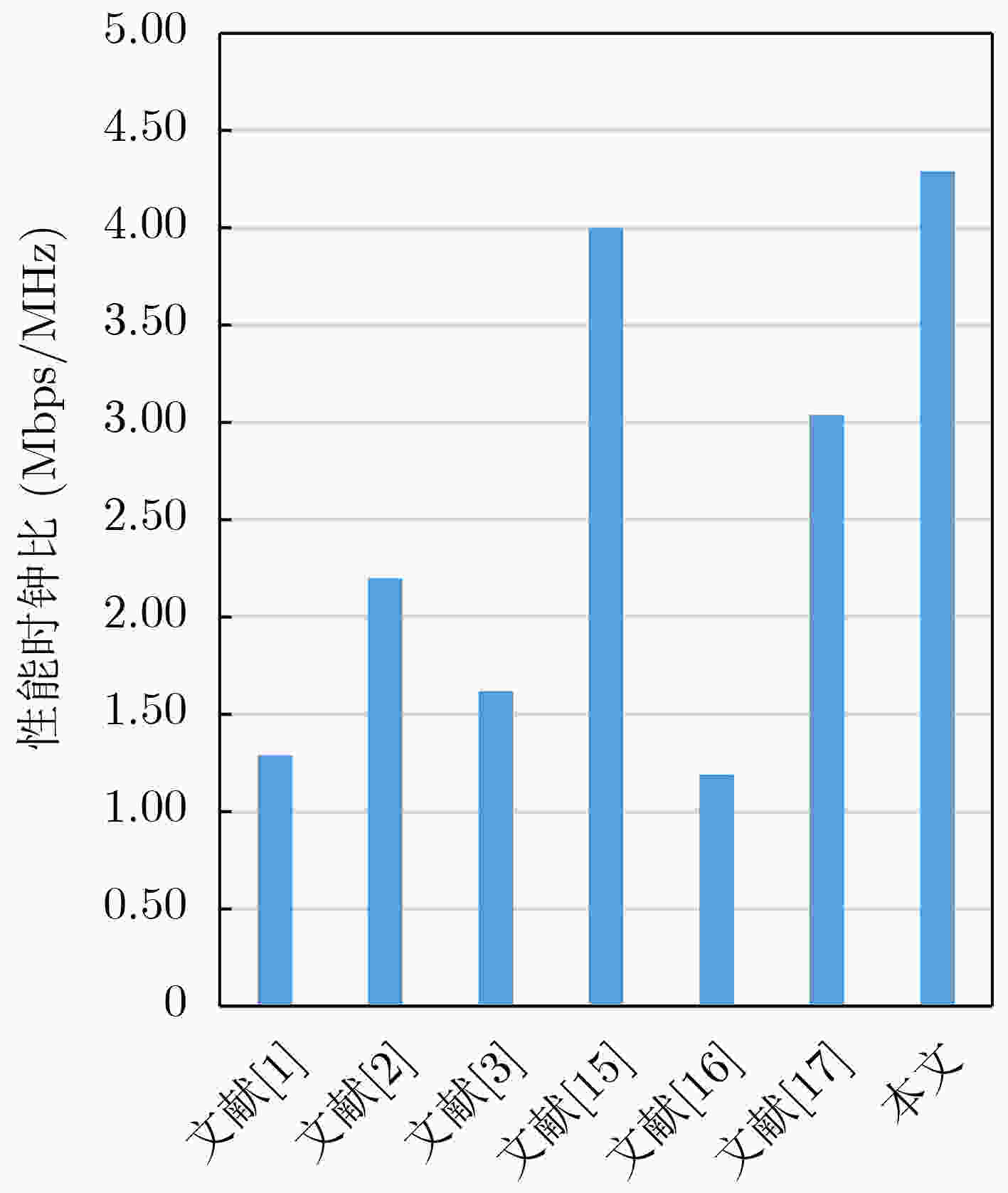


 下载:
下载:
