Research on POI Recommendation Model Based on Spatio-temporal Context Information
-
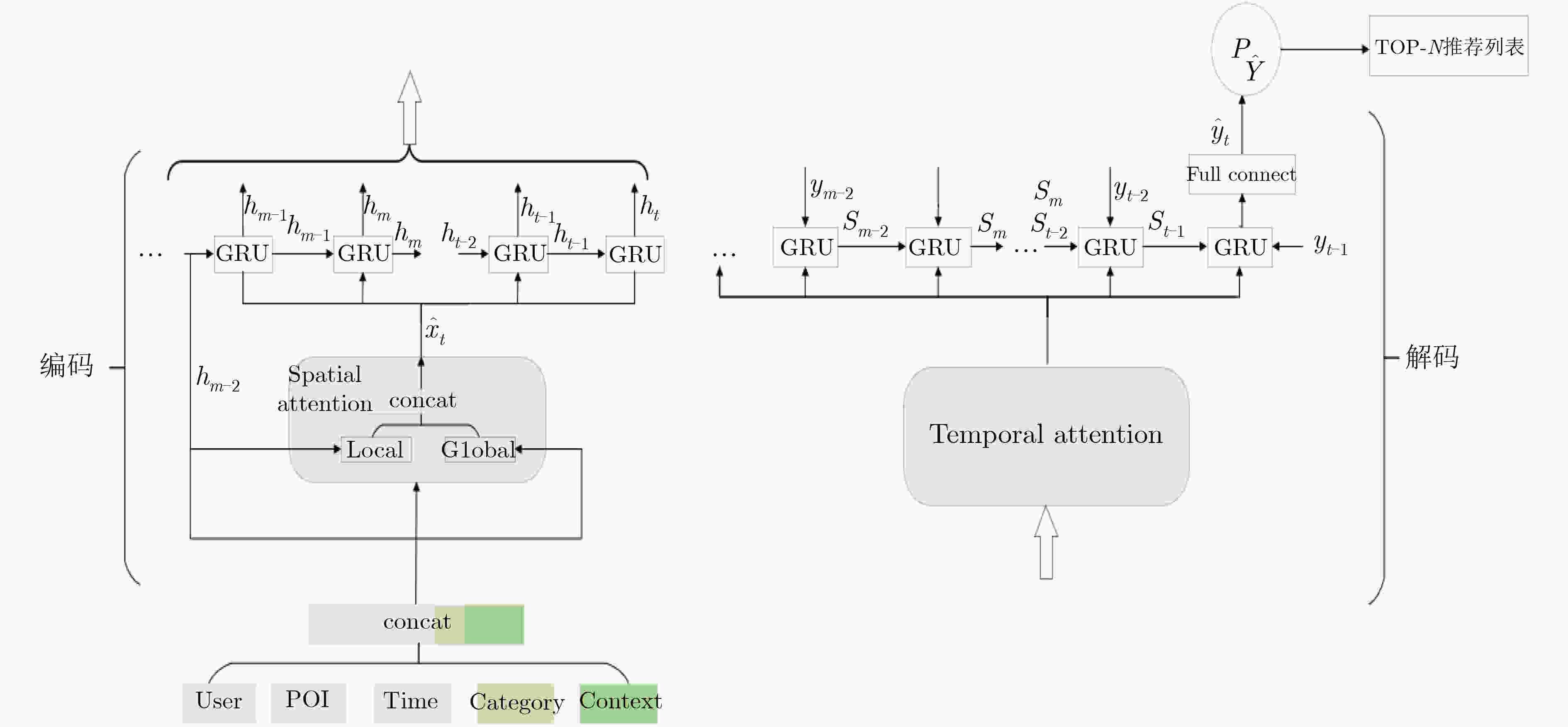
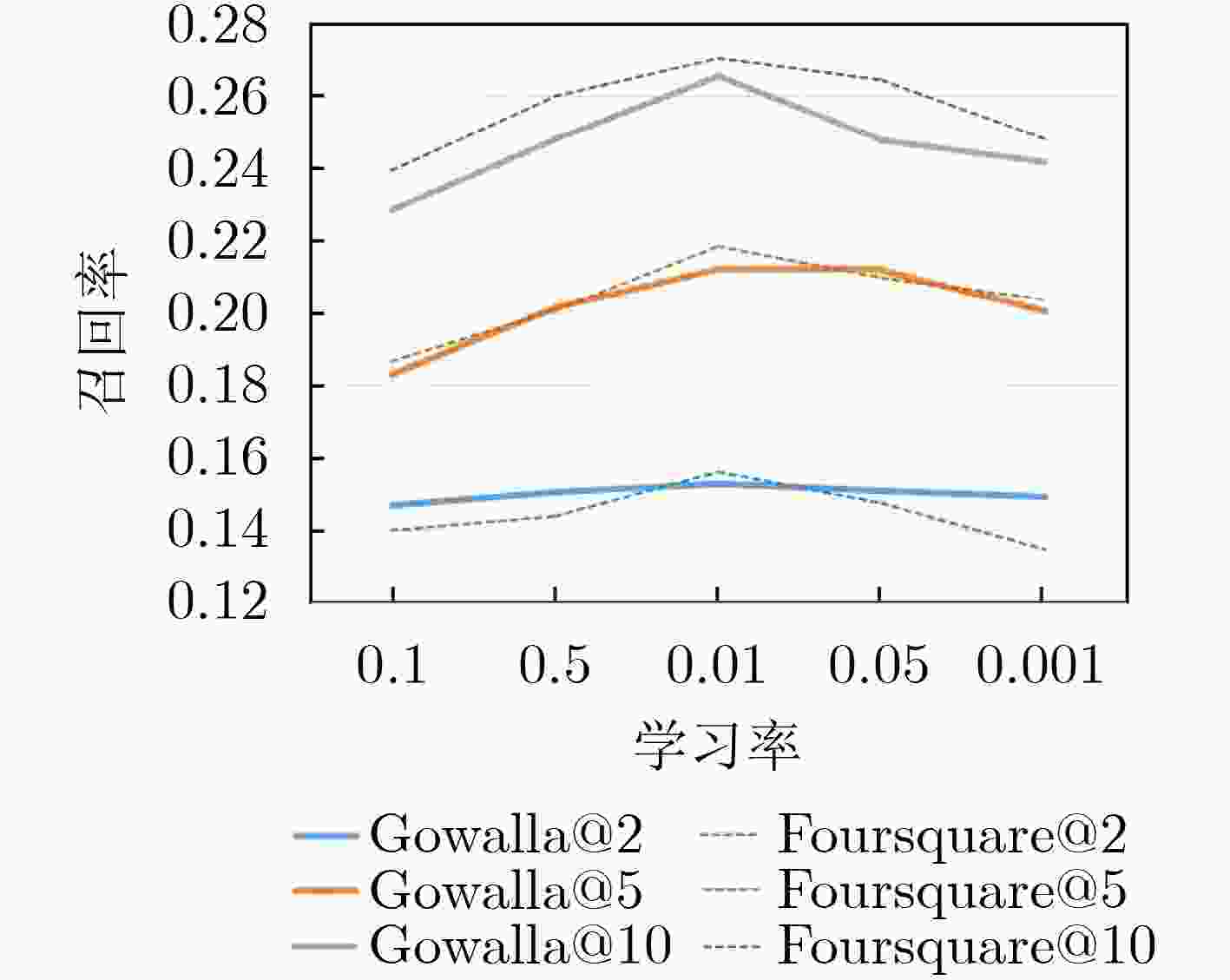
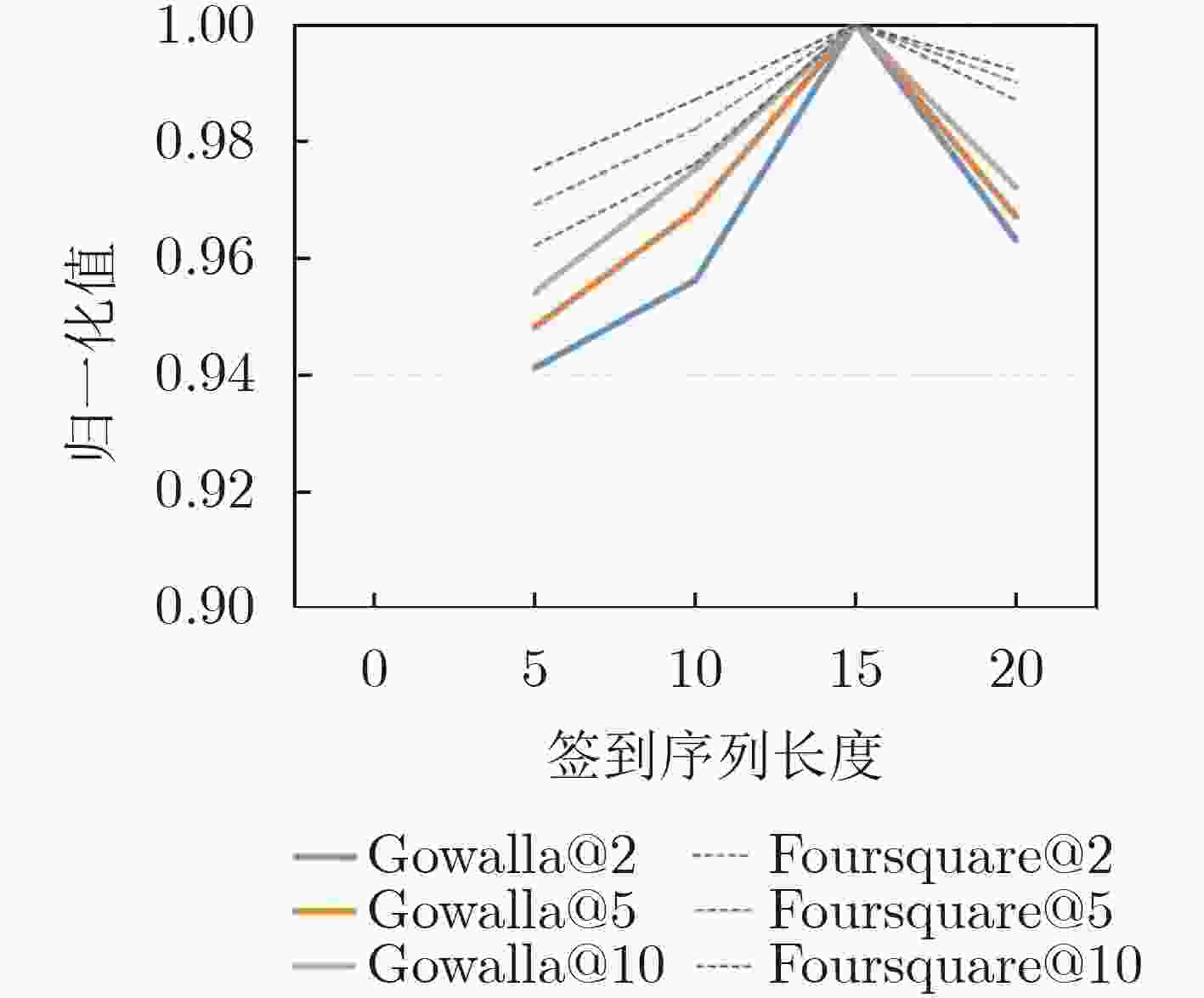
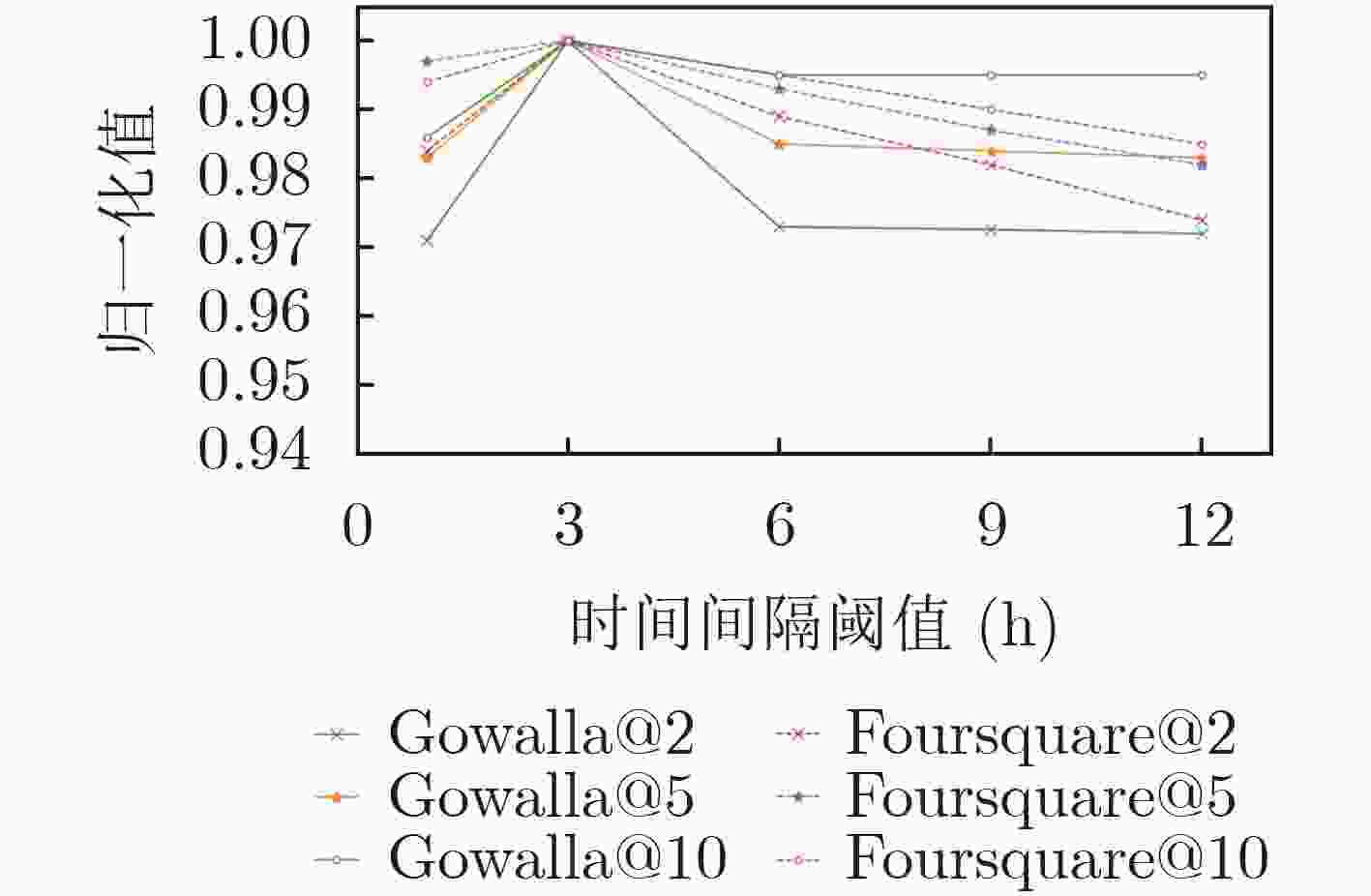
摘要: 随着基于位置的社交网络(LBSN)技术的快速发展,为移动用户提供个性化服务的兴趣点(POI)推荐成为关注重点。由于POI推荐面临着数据稀疏、影响因素多和用户偏好复杂的挑战,因此传统的POI推荐往往只考虑签到频率以及签到时间和地点对用户的影响,而忽略了签到序列中用户前后行为的关联影响。为了解决上述问题,该文通过序列的表示考虑签到数据的时间影响和空间影响,建立了时空上下文信息的POI推荐模型(STCPR),为POI推荐提供了更精准的个性化偏好。该模型基于序列到序列的框架下,将用户信息、POI信息、类别信息和时空上下文信息进行向量化后嵌入GRU网络中,同时利用了时间注意力机制、全局和局部的空间注意力机制来综合考虑用户偏好与变化趋势,从而向用户推荐感兴趣的Top-N的POI。该文通过在两个真实的数据集上实验来验证模型的性能。实验的结果表明,该文所提出的方法在召回率(Recall)和归一化折损累计增益(NDCG)方面优于几种现有的方法。Abstract: With the high-speed development of Location-Based Social Networking (LBSN) technology, Point-Of-Interest(POI) recommendation for providing personalized services to mobile users has become the focus of attention. Because POI recommendation is faced with the challenges of sparse data, multiple influencing factors and complex user preferences, traditional POI recommendation usually only considers the influence of check-in frequency, check-in time and place on users, but ignores the correlation influence of users’ behaviors before and after the check-in sequence. In order to solve the above problems, this paper takes into account the time influence and spatial influence of the check-in data through the representation of the sequence, and establishes a Spatio-Temporal Context information of POI Recommendations (STCPR), provides a more accurate and personalized preference for POI Recommendations. The model based on the framework of sequence to sequence, the user information, POI information, categories and space-time context information are embedded in GRU helped after vectorization network, at the same time the time attention mechanism, the mechanism of spatial attention of the global and local comprehensive are used for consideration of user preferences and trends, and in Top - N POI is recommended to users. In order to verify the performance of the model, experiments on two real data sets show that the proposed method is superior to several existing methods in terms of recall rate (Recall) and Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG).
-
表 1 数据集
数据集 用户数 地点数 签到数 密度 Gowalla 13117 37196 953006 0.0019 Foursquare 5398 27895 864230 0.0021 表 2 不同方法在两个数据集上的实验结果(%)
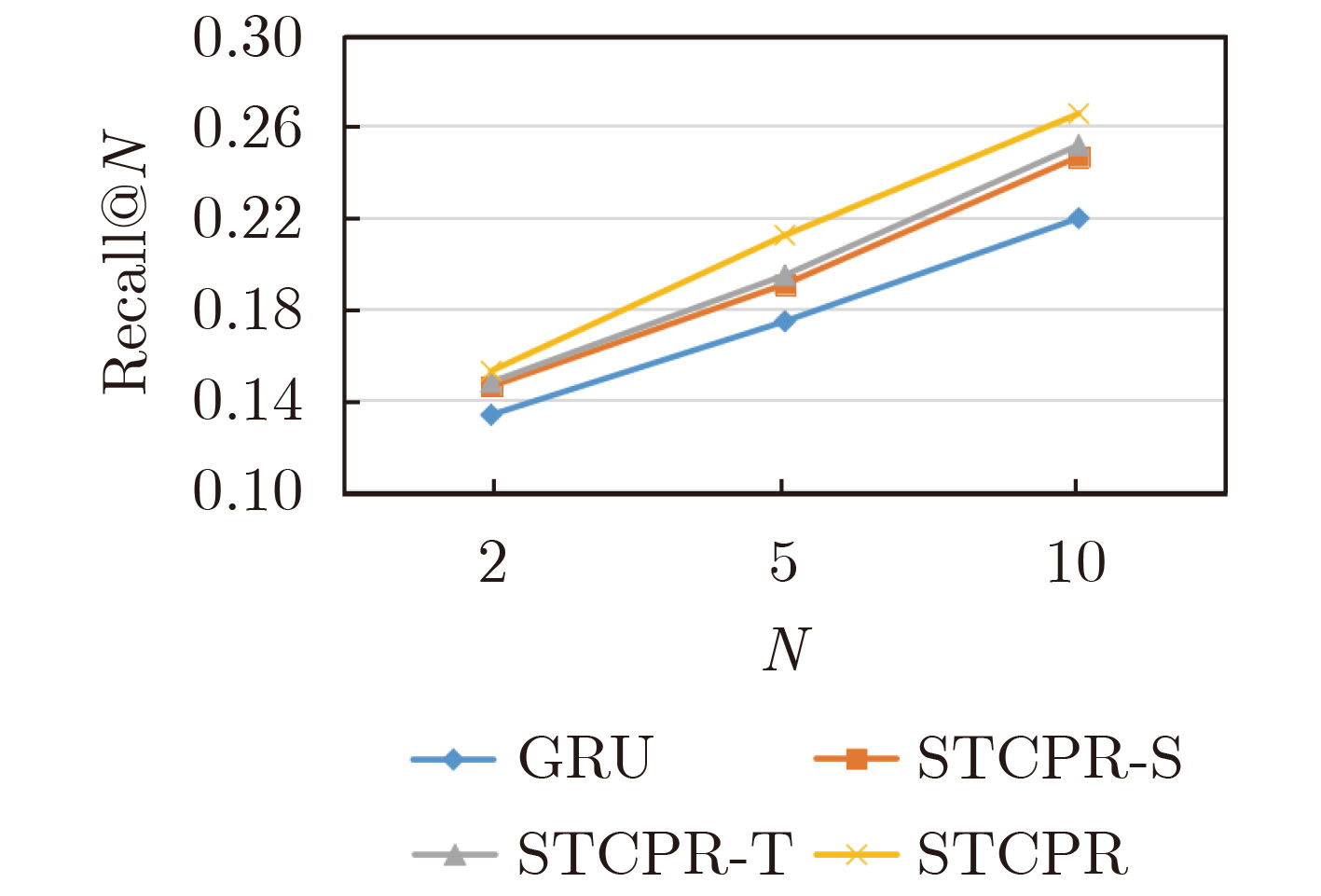
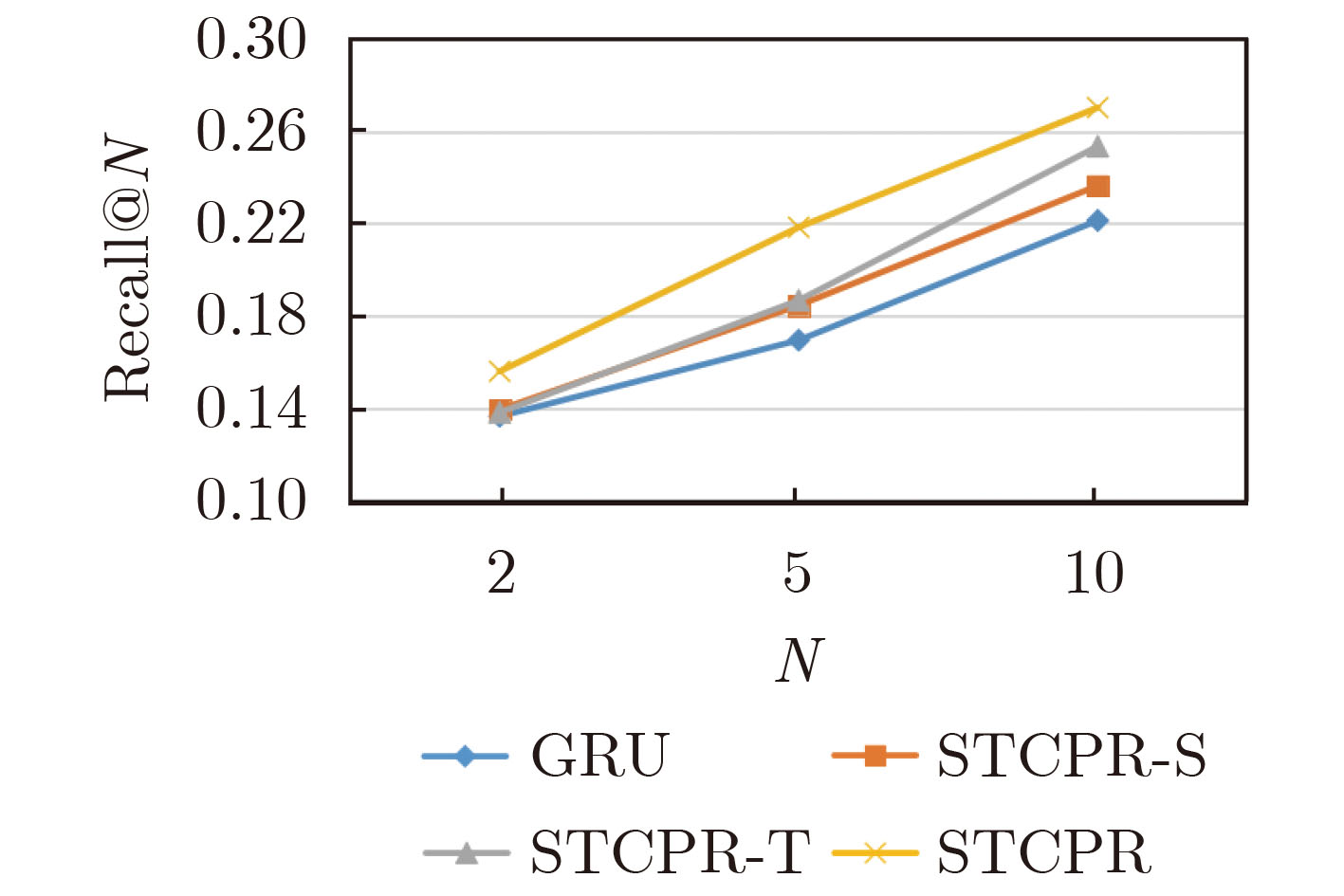
数据集 模型 Recall@N NDCG@N N=2 N=5 N=10 N=2 N=5 N=10 Gowalla FPMC 9.84 14.12 19.28 7.92 9.89 11.51 Distance2Pre 14.27 18.05 23.57 11.73 13.95 15.68 GRU 13.34 17.44 21.96 10.28 13.12 14.74 ST-RNN 13.95 19.04 23.04 10.79 12.54 13.52 UCGSMF_GEN 13.66 18.52 22.66 8.75 10.59 12.49 STCPR 15.26 21.21 26.54 13.56 15.84 17.79 Foursquare FPMC 10.61 15.55 20.87 8.54 10.32 11.67 Distance2Pre 14.36 18.93 24.12 12.11 14.34 15.87 GRU 13.64 16.94 22.13 11.48 13.17 14.98 ST-RNN 13.56 19.32 23.27 10.78 13.08 13.86 UCGSMF_GEN 12.71 17.82 22.97 9.08 11.72 12.8 MFM-HNN 13.95 18.85 23.89 11.76 13.52 14.23 STCPR 15.59 21.84 27.03 13.96 16.37 18.34 -
[1] 司亚利, 张付志, 刘文远. 基于签到活跃度和时空概率模型的自适应兴趣点推荐方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 678–686. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190287SI Yali, ZHANG Fuzhi, and LIU Wenyuan. An adaptive point-of-interest recommendation method based on check-in activity and temporal-spatial probabilistic models[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 678–686. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190287 [2] FENG Shanshan, GAO Cong, AN Bo, et al. POI2Vec: Geographical latent representation for predicting future visitors[C]. Proceedings of the 31th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 102–108. [3] 孟祥福, 张霄雁, 唐延欢, 等. 基于地理-社会关系的多样性与个性化兴趣点推荐[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(11): 2574–2590. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.02574MENG Xiangfu, ZHANG Xiaoyan, TANG Yanhuan, et al. A diversified and personalized recommendation approach based on geo-social relationships[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(11): 2574–2590. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.02574 [4] 任星怡, 宋美娜, 宋俊德. 基于位置社交网络的上下文感知的兴趣点推荐[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(4): 824–841. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.00824REN Xingyi, SONG Meina, and SONG Junde. Context-aware point-of-interest recommendation in location-based social networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(4): 824–841. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.00824 [5] WEI Jian, He Jianhua, CHEN Kai, et al. Collaborative filtering and deep learning based recommendation system for cold start items[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 69: 29–39. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.09.040 [6] 柳天闻. 基于位置社交信息和群组的地点推荐算法研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2018.LIU Tianwen. The research and implementation of location recommendation algorithms based on location-social information and groups[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018. [7] 冯浩, 黄坤, 李晶, 等. 基于深度学习的混合兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 880–887. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180458FENG Hao, HUANG Kun, LI Jing, et al. Hybrid point of interest recommendation algorithm based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 880–887. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180458 [8] WANG Mufan, LU Yishu, HUANG J L, et al. SPENT: A successive POI recommendation method using similarity-based poi embedding and recurrent neural network with temporal influence[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing, Kyoto, Japan, 2019: 1–8. [9] ZHAO Shenglin, LYU M R, KING I, et al. Geo-teaser: Geo-temporal sequential embedding rank for POI recommendation[C]. The 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion, Perth, Australia, 2017: 153–162. [10] WANG Hao, SHEN Huawei, OUYANG Wentao, et al. Exploiting POI-specific geographical influence for point-of-interest recommendation[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Main Track, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3877–3883. [11] ZHAO Shenglin, ZHAO Tong, YANG Haiqing, et al. STELLAR: Spatial-temporal latent ranking for successive point-of-interest recommendation[C]. The 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 2605–2611. [12] CAI Ling, XU Jun, LIU Ju, et al. Integrating spatial and temporal contexts into a factorization model for POI recommendation[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2018, 32(3): 524–546. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2017.1400550 [13] ZHANG Zhiqian, LI Chenliang, WU Zhiyong, et al. Next: A neural network framework for next POI recommendation[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2020, 14(2): 314–333. doi: 10.1007/s11704-018-8011-2 [14] QIAN Tieyun, LIU Bei, NGUYEN Q V H, et al. Spatiotemporal representation learning for translation-based POI recommendation[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2019, 37(2): 18. doi: 10.1145/3295499 [15] RENDLE S, FREUDENTHALER C, and SCHMIDT-THIEME L. Factorizing personalized markov chains for next-basket recommendation[C]. The 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, Raleigh, USA, 2010: 811–820. doi: 10.1145/1772690.1772773. [16] CUI Qiang, TANG Yuyuan, WU Shu, et al. Distance2Pre: Personalized spatial preference for next point-of-interest prediction[C]. The 23rd Pacific-Asia Conference, Macau, China, 2019: 289–301. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-16142-2_23. [17] LIU Qiang, WU Shu, WANG Liang, et al. Predicting the next location: A recurrent model with spatial and temporal contexts[C]. The 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 194–200. [18] CHO K, VAN MERRIËNBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]. The 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1724–1734, doi: 10.3115/v1/D14-1179. [19] 彭宏伟, 靳远远, 吕晓强, 等. 一种基于矩阵分解的上下文感知POI推荐算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(8): 1797–1811. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.01797PENG Hongwei, JIN Yuanyuan, LV Xiaoqiang, et al. Context-Aware POI recommendation based on matrix factorization[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(8): 1797–1811. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.01797 -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
