Construction of Low-rank Circulant Matrices and Their Associated Nonbinary LDPC Codes
-
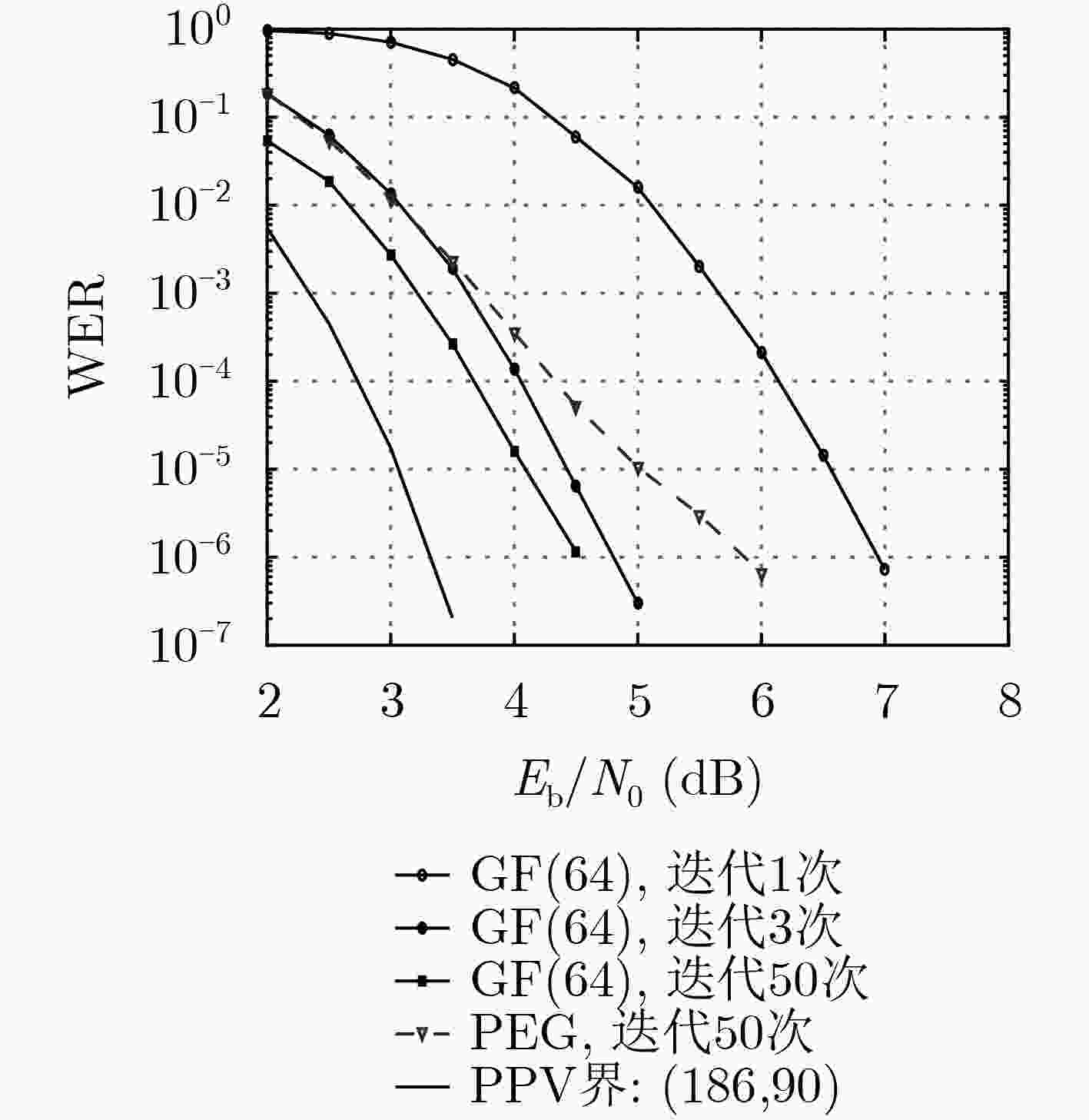
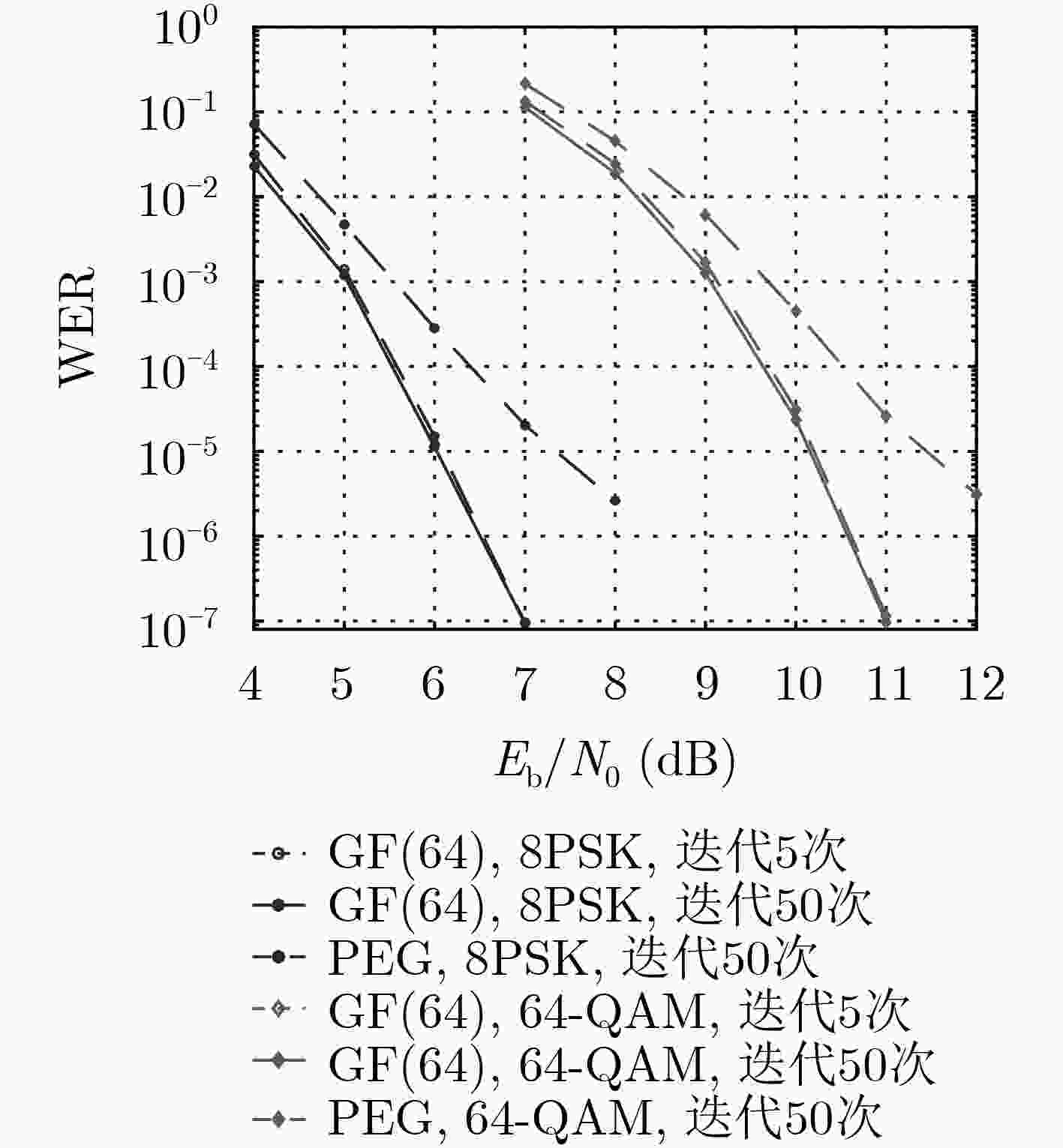
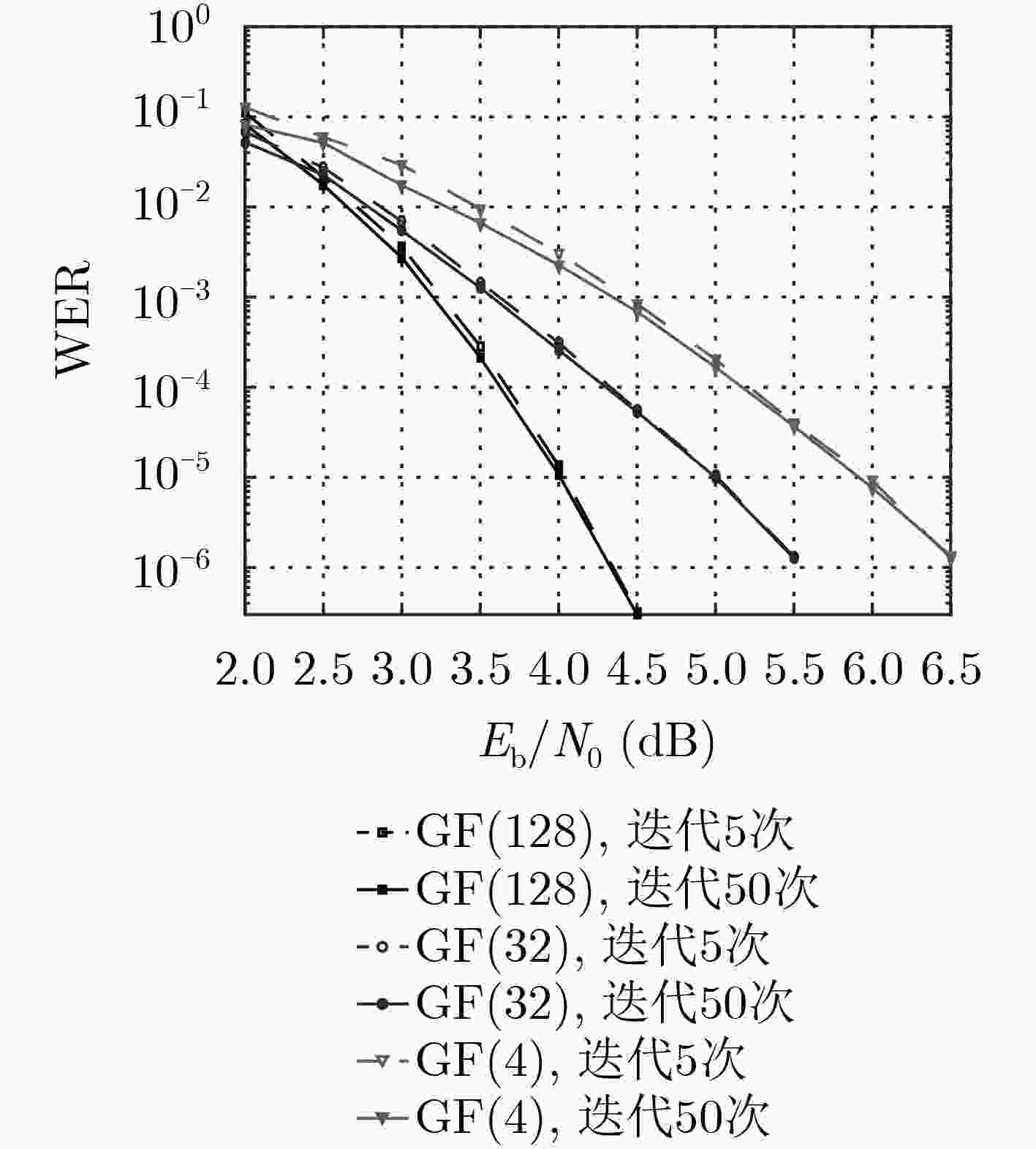
摘要: 在图像处理中,低秩矩阵的冗余信息可用于图像恢复和图像特征提取,而在迭代译码中,校验矩阵的冗余行可以加快译码收敛速度。该文研究一类易于硬件实现的低秩循环矩阵。首先将循环矩阵转换为位置集合,并基于同构理论简化了位置集合的搜索空间,从而基于比特移位方法提出了循环矩阵的构造方法。考虑非零域元素的列赋值与矩阵秩之间的关系,选取Tanner图中没有长度为4的环的循环矩阵,基于非零域元素的列赋值思想提出了不同阶数、不同码率的多元LDPC码构造方法。数值仿真结果表明,与基于PEG算法构造的二元LDPC码比较,所构造的多元LDPC码在BPSK调制方式下在误码字率10–5附近有0.9 dB的增益;在与高阶调制相结合时,有更大的性能提升。此外,所构造的多元LDPC码在迭代5次与50次下的性能几乎一致,这为低时延高可靠通信提供了一种有效的候选编码方案。Abstract: In image processing, the redundant information of low-rank matrices can be used for image recovery and image feature extraction, and redundant rows of the parity-check matrices can accelerate the convergence rate in iterative decoding. A class of low-rank circulant matrices with easy hardware implementation is studied. Circulant matrices are first converted into position sets, the search space of position sets is pruned based on isomorphism theory, and then construction of circulant matrices is proposed based on the bit shift method. Considering the relationship between the column assignment of non-zero field elements and the matrix rank, circulant matrices whose Tanner graphs have no cycles of length 4 are chosen, and according to the column assignment of non-zero field elements, construction of nonbinary LDPC codes over various finite fields and with different code rates is presented. Numerical simulation results show that, compared with binary LDPC codes constructed based on the PEG algorithm, the proposed nonbinary LDPC codes have 0.9 dB gain at Word Error Rate (WER) of 10-5 when the modulation is BPSK, and the performance gap becomes large by combining with high order modulations. Furthermore, the performance gap of the proposed codes between 5 iterations and 50 iterations is negligible, and it provides a promising coding scheme for low-latency and high-reliability communications.
-
Key words:
- LDPC code /
- Low-rank matrix /
- Circulant matrix /
- Isomorphism theory /
- Girth
-
表 1 算法1:秩小于R的循环矩阵搜索算法
输入:阈值R,循环矩阵的行(或列)数L,行(或列)重m。 输出:位置集合S及其秩。 (1) repeat (2) 基于比特移位方法按照组合顺序产生位置集合$S = \left\{ {{s_1}\left( { = 0} \right),{s_2},{s_3}, ··· ,{s_m}} \right\}$,其中对于$1 < l \le m$,${s_{l - 1}} < {s_l}$和$0 < {s_l} < L$; (3) 根据位置集合S生成大小为$L \times L$的二元循环矩阵C; (4) 计算循环矩阵C的秩r; (5) 如果r小于R,存储位置集合S,并记录它的秩为r,并打印输出集合S和秩r(注意,如果多个位置集合的秩相同,则只存储第1个位置集
合,其他不再存储);(6) until (全部找到秩从1到R的位置集合,或${s_m} - {s_1} = m - 2$) 表 2 基于算法1搜索的部分循环矩阵
行/列数 行/列重 秩 位置集合 行/列数 行/列重 秩 位置集合 9 3 3 {0, 3, 6} 30 4 10 {0, 5, 15, 20} 12 3 4 {0, 4, 8} 32 4 8 {0, 8, 16, 24} 15 3 5 {0, 5, 10} 36 4 9 {0, 9, 18, 27} 18 3 6 {0, 6, 12} 40 4 10 {0, 10, 20, 30} 21 3 7 {0, 7, 14} 42 4 14 {0, 7, 21, 28} 24 3 8 {0, 8, 16} 44 4 11 {0, 11, 22, 33} 27 3 9 {0, 9, 18} 48 4 12 {0, 12, 24, 36} 30 3 10 {0, 10, 20} 25 5 5 {0, 5, 10, 15, 20} 33 3 11 {0, 11, 22} 30 5 6 {0, 6, 12, 18, 24} 39 3 13 {0, 13, 26} 35 5 7 {0, 7, 14, 21, 28} 42 3 14 {0, 14, 28} 40 5 8 {0, 8, 16, 24, 32} 45 3 15 {0, 15, 30} 45 5 9 {0, 9, 18, 27, 36} 48 3 16 {0, 16, 32} 50 5 10 {0, 10, 20, 30, 40} 8 4 2 {0, 2, 4, 6} 39 6 12 {0, 1, 13, 14, 26, 27} 12 4 3 {0, 3, 6, 9} 42 6 7 {0, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35} 16 4 4 {0, 4, 8, 12} 42 6 12 {0, 2, 14, 16, 28, 30} 18 4 6 {0, 3, 9, 12} 45 6 10 {0, 5, 15, 20, 30, 35} 20 4 5 {0, 5, 10, 15} 45 6 12 {0, 3, 15, 18, 30, 33} 24 4 6 {0, 6, 12, 18} 48 6 8 {0, 8, 16, 24, 32, 40} 27 4 7 {0, 7, 14, 21} 48 6 12 {0, 4, 16, 20, 32, 36} 表 3 算法2:检验循环矩阵C中是否存在4-环的算法
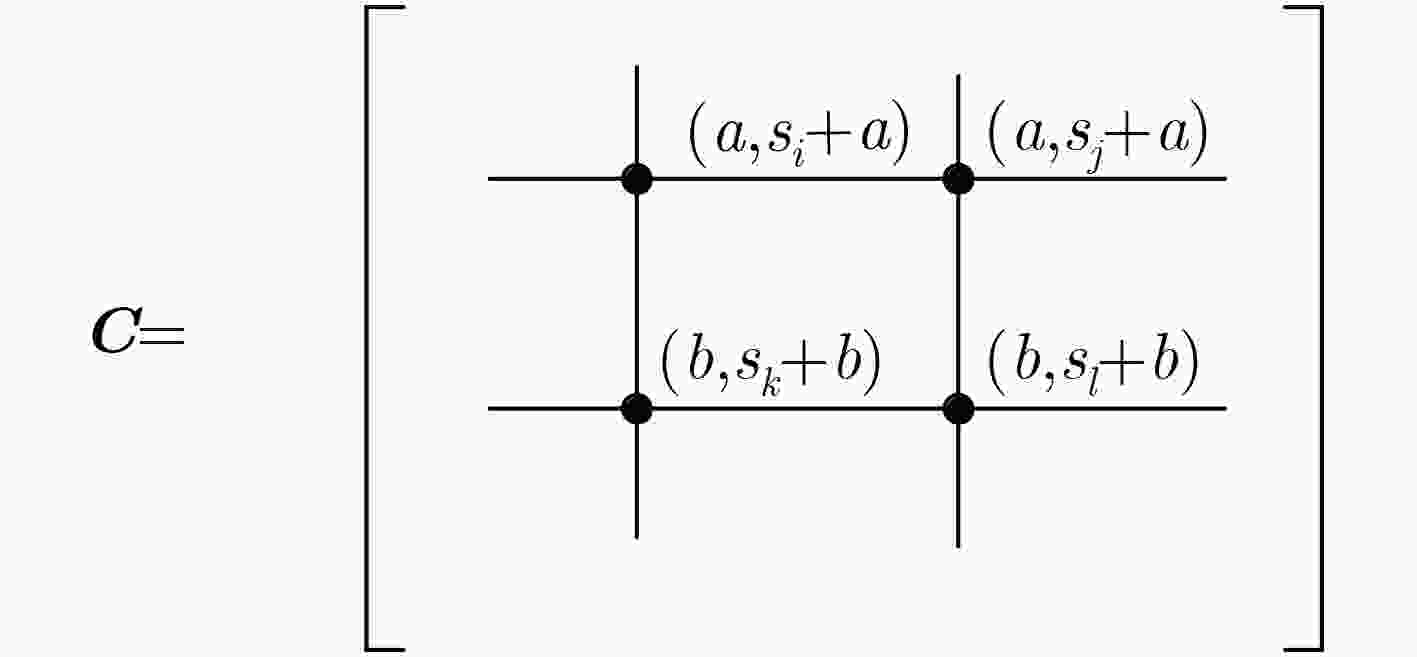
输入:循环矩阵C的位置集合$S = \left\{ {{s_1},{s_2}, ··· ,{s_m}} \right\}$,循环矩阵的行(或列)数L; 输出:是否存在4-环。 (1) 根据位置集合$S = \left\{ {{s_1},{s_2}, ··· ,{s_m}} \right\}$得到差集$D = \left\{ {d \in {Z_L}|d = {s_i} - {s_j}\left( {{\rm{mod}} \; L} \right),1 \le i \le m,1 \le j \le m,i \ne j} \right\}$; (2) 计算差集D中元素的个数,或者检查集合$E = \left\{ {e|e = {d_i} + {d_j}\left( {{\rm{mod}} \; L} \right),i \ne j,{d_i} \in D,{d_j} \in D,} \right\}$中是否有零元素; (3) 如果差集D中元素的个数小于$C_m^2$,或者集合E中有零元素,直接输出“存在4-环”;否则,输出“不存在4-环”。 表 4 不包含4-环的循环矩阵位置集合
行/列数 行/列重 秩 位置集合 行/列数 行/列重 秩 位置集合 7 3 4 {0, 1, 3} 39 5 27 {0, 1, 5, 8, 25} 14 3 8 {0, 2, 6} 42 5 20 {0, 2, 8, 28, 32} 21 3 12 {0, 3, 9} 45 5 35 {0, 1, 3, 10, 15} 49 3 28 {0, 7, 21} 63 5 30 {0, 3, 12, 42, 48} 56 3 32 {0, 8, 24} 93 5 48 {0, 3, 9, 21, 45} 60 3 44 {0, 4, 16} 45 6 28 {0, 1, 3, 12, 19, 40} 63 3 36 {0, 9, 27} 48 6 39 {0, 1, 3, 7, 12, 33} 70 3 40 {0, 10, 30} 60 6 39 {0, 1, 5, 28, 49, 52} 84 3 48 {0, 12, 36} 63 6 32 {0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 31} 91 3 52 {0, 13, 39} 65 6 48 {0, 1, 3, 30, 43, 51} 15 4 8 {0, 1, 3, 7} 84 6 60 {0, 1, 5, 8, 21, 40} 21 4 14 {0, 1, 3, 8} 85 6 60 {0, 1, 5, 21, 62, 79} 30 4 16 {0, 2, 6, 14} 90 6 56 {0, 2, 6, 24, 38, 80} 45 4 24 {0, 3, 9, 21} 51 7 43 {0, 1, 3, 9, 21, 37, 47} 75 4 40 {0, 5, 15, 35} 57 7 39 {0, 1, 3, 13, 36, 43, 52} 90 4 48 {0, 6, 18, 42} 62 7 47 {0, 1, 3, 10, 14, 39, 57} 91 4 75 {0, 1, 6, 17} 63 7 39 {0, 1, 3, 18, 34, 54, 58} 21 5 10 {0, 1, 4, 14, 16} 63 8 26 {0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 20, 31, 41} 31 5 16 {0, 1, 3, 7, 15} 85 8 48 {0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 42, 63} -
赵亚军, 郁光辉, 徐汉青. 6G移动通信网络: 愿景、挑战与关键技术[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(8): 963–987. doi: 10.1360/N112019-00033ZHAO Yajun, YU Guanghui, and XU Hanqing. 6G mobile communication networks: Vision, challenges, and key technologies[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(8): 963–987. doi: 10.1360/N112019-00033 LIU Yanfang, OLMOS P M, and MITCHELL D G M. Generalized LDPC codes for ultra reliable low latency communication in 5G and beyond[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 72002–72014. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2880997 CHEN Chao, BAI Baoming, SHI Guangming, et al. Nonbinary LDPC codes on cages: Structural property and code optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2015, 63(2): 364–375. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2014.2387341 ZHU Min, GUO Quan, BAI Baoming, et al. Reliability-based joint detection-decoding algorithm for nonbinary LDPC-coded modulation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2487454 WANG Shuai, HUANG Qin, and WANG Zulin. Symbol flipping decoding algorithms based on prediction for non-binary LDPC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(5): 1913–1924. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2677438 HUANG Qin, SONG Liyuan, and WANG Zulin. Set message-passing decoding algorithms for regular non-binary LDPC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(12): 5110–5122. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2746101 ZHANG Mu, CAI Kui, HUANG Qin, et al. On bit-level decoding of nonbinary LDPC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(9): 3736–3748. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2827994 WIJEKOON V B, VITERBO E, HONG Yi, et al. A novel graph expansion and a decoding algorithm for NB-LDPC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1358–1369. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2961884 HUANG Qin, LIU Keke, and WANG Zulin. Low-density arrays of circulant matrices: Rank and row-redundancy, and QC-LDPC codes[C]. 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Cambridge, USA, 2012: 3073–3077. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2012.6284127. 李骜, 刘鑫, 陈德运, 等. 基于低秩表示的鲁棒判别特征子空间学习模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1223–1230. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190164LI Ao, LIU Xin, CHEN Deyun, et al. Robust discriminative feature subspace learning based on low rank representation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1223–1230. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190164 彭义刚, 索津莉, 戴琼海, 等. 从压缩传感到低秩矩阵恢复: 理论与应用[J]. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(7): 981–994. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00981PENG Yigang, SUO Jinli, DAI Qionghai, et al. From compressed sensing to low-rank matrix recovery: Theory and applications[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 981–994. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00981 陈容, 陈岚, WAHLA A H. 基于公式递推法的可变计算位宽的循环冗余校验设计与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1261–1267. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190503CHEN Rong, CHEN Lan, and WAHLA A H. Design and implementation of cyclic redundancy check with variable computing width based on formula recursive algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1261–1267. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190503 RYAN W E and LIN Shu. Channel Codes: Classical and Modern[M]. New York, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 448–578. CHEN Chao, BAI Baoming, and WANG Xinmei. Construction of quasi-cyclic LDPC codes based on a two-dimensional MDS code[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2010, 14(5): 447–449. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2010.05.100008 XU Hengzhou, BAI Baoming, ZHU Min, et al. Construction of short-block nonbinary LDPC codes based on cyclic codes[J]. China Communications, 2017, 14(8): 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CC.2017.8014342 陈智雄, 苑津莎. 基于多重置换阵的满秩结构化LDPC码构造方法[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(2): 313–318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.02.017CHEN Zhixiong and YUAN Jinsha. Construction of structure LDPC codes with full rank based on multi-permutation matrix[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(2): 313–318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.02.017 TANNER R. A recursive approach to low complexity codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1981, 27(5): 533–547. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1981.1056404 XIAO Xin, VASIĆ B, LIN Shu, et al. Reed-Solomon based quasi-cyclic LDPC codes: Designs, girth, cycle structure, and reduction of short cycles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(8): 5275–5286. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2916605 XU Hengzhou, FENG Dan, SUN Cheng, et al. Algebraic-based nonbinary ldpc codes with flexible field orders and code rates[J]. China Communications, 2017, 14(4): 111–119. doi: 10.1109/CC.2017.7927569 HU Xiaoyu, ELEFTHERIOU E, and ARNOLD D M. Regular and irregular progressive edge-growth tanner graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(1): 386–398. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2004.839541 POLYANSKIY Y, POOR H V, and VERDU S. Channel coding rate in the finite blocklength regime[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(5): 2307–2359. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2043769 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
