A Logarithmic Total Least Squares Adaptive Filtering Algorithm for Impulsive Noise Suppression
-
摘要: 在未知系统输入信号和输出信号均含有噪声的环境中,传统的自适应滤波算法,如最小均方(LMS)算法,会产生有偏估计。总体最小二乘(TLS)算法能够同时最小化输入信号与输出信号的噪声干扰,是解决此类问题的重要方法。然而,在许多实际应用中,干扰噪声可能具有冲击特性,这使得传统基于2阶统计量的自适应滤波算法,包括总体最小二乘算法性能严重恶化,以至于不能正常工作。为了解决这个问题,该文在总体最小二乘法的基础上,利用对数函数对其改进,提出了一种能够抗冲击干扰的对数总体最小二乘(L-TLS)算法。最后,通过计算机仿真实验验证了该新算法的有效性。Abstract: In environments where both the input and output signals of the unknown system contain noise, classical adaptive filtering algorithms, such as the Least Mean Square (LMS) algorithm, will produce biased estimates. The Total Least Squares (TLS) method is devised to minimize the perturbation of errors in the input and output signals, which is an important method to solve such problems. However, when the signals are disturbed by impulsive noises, which exist in many practical applications, the performance of traditional adaptive filtering algorithms that only relies on the second-order statistics of the errors, including the TLS algorithm, will deteriorate seriously, so that it can not work properly. In order to solve this problem, based on the TLS method, this paper uses logarithmic function to improve the TLS algorithm, and proposes a Logarithmic Total Least Square (L-TLS) algorithm which can efficiently reduce the effects of impulsive noises. Finally, computer simulation experiments verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Adaptive filtering /
- Impulsive noises /
- Total Least Squares (TLS)
-
表 1 L-TLS算法流程
算法初始化 ${{w}}(0) = 0$ 算法实现 for i=0, 1, 2 $e(n) = \tilde d(n) - {{{w}}^{\rm{T}}}\tilde {{x}}(n)$ $\bar {{w}} = {\left[ {\sqrt \gamma {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} - {{{w}}^{\rm{T}}}} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ $a(n) = \dfrac{ { { {\left\| {\bar {{w} }(n)} \right\|}^2}e(n)\tilde {{x} }(n){\rm{ + } }{e^2}(n){{w} }(n)} }{ { { {\left\| {\bar {{w} }(n)} \right\|}^4} + { {\left\| {\bar {{w} }(n)} \right\|}^2}\alpha {e^2}(n)} }$ ${{w}}(n + 1) = {{w}}(n) + \mu {{a}}(n)$ end 表 2 算法的计算复杂度
算法 加/减法 乘法 除法 LMS $2L$ $2L + 1$ 0 RLMLS $2L + 1$ $2L + 4$ 1 GD-TLS $4L$ $5L + 3$ 1 L-TLS $4L + 1$ $5L + 7$ 1 -
SAYED A H. Fundamentals of Adaptive Filtering[M]. New York: Wiley Interscience, 2003: 72–80. ARABLOUEI R, WERNER S, and DOĞANÇAY K. Analysis of the gradient-descent total least-squares adaptive filtering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(5): 1256–1264. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2301135 DAVILA C E. An efficient recursive total least squares algorithm for FIR adaptive filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(2): 268–280. doi: 10.1109/78.275601 FENG Dazheng, ZHANG Xianda, CHANG Dongxia, et al. A fast recursive total least squares algorithm for adaptive FIR filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(10): 2729–2737. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.834260 FENG Dazheng and ZHENG Weixing. Fast approximate inverse power iteration algorithm for adaptive total least-squares FIR filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(10): 4032–4039. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.880245 ARABLOUEI R, DOĞANÇAY K, and WERNER S. Recursive total least-squares algorithm based on inverse power method and dichotomous coordinate-descent iterations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(8): 1941–1949. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2405492 马济通, 邱天爽, 李蓉, 等. 脉冲噪声下基于Renyi熵的分数低阶双模盲均衡算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(2): 378–385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170366MA Jitong, QIU Tianshuang, LI Rong, et al. Dual-mode blind equalization algorithm based on Renyi entropy and fractional lower order statistics under impulsive noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(2): 378–385. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170366 邱天爽. 相关熵与循环相关熵信号处理研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 105–118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190646QIU Tianshuang. Development in signal processing based on correntropy and cyclic correntropy[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 105–118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190646 SHEN Pengcheng and LI Chunguang. Minimum total error entropy method for parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(15): 4079–4090. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2437836 WANG Fei, HE Yicong, WANG Shiyuan, et al. Maximum total correntropy adaptive filtering against heavy-tailed noises[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141: 84–95. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.05.029 LI Lei and ZHAO Haiquan. A robust total least mean m-estimate adaptive algorithm for impulsive noise suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 67(4): 800–804. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2019.2925626 SAYIN M O, VANLI N D, and KOZAT S S. A novel family of adaptive filtering algorithms based on the logarithmic cost[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(17): 4411–4424. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2333559 XIONG Kui and WANG Shiyuan. Robust least mean logarithmic square adaptive filtering algorithms[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(1): 654–674. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.10.019 SÖDERSTRÖM T. Errors-in-variables methods in system identification[J]. Automatica, 2007, 43(6): 939–958. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.11.025 -





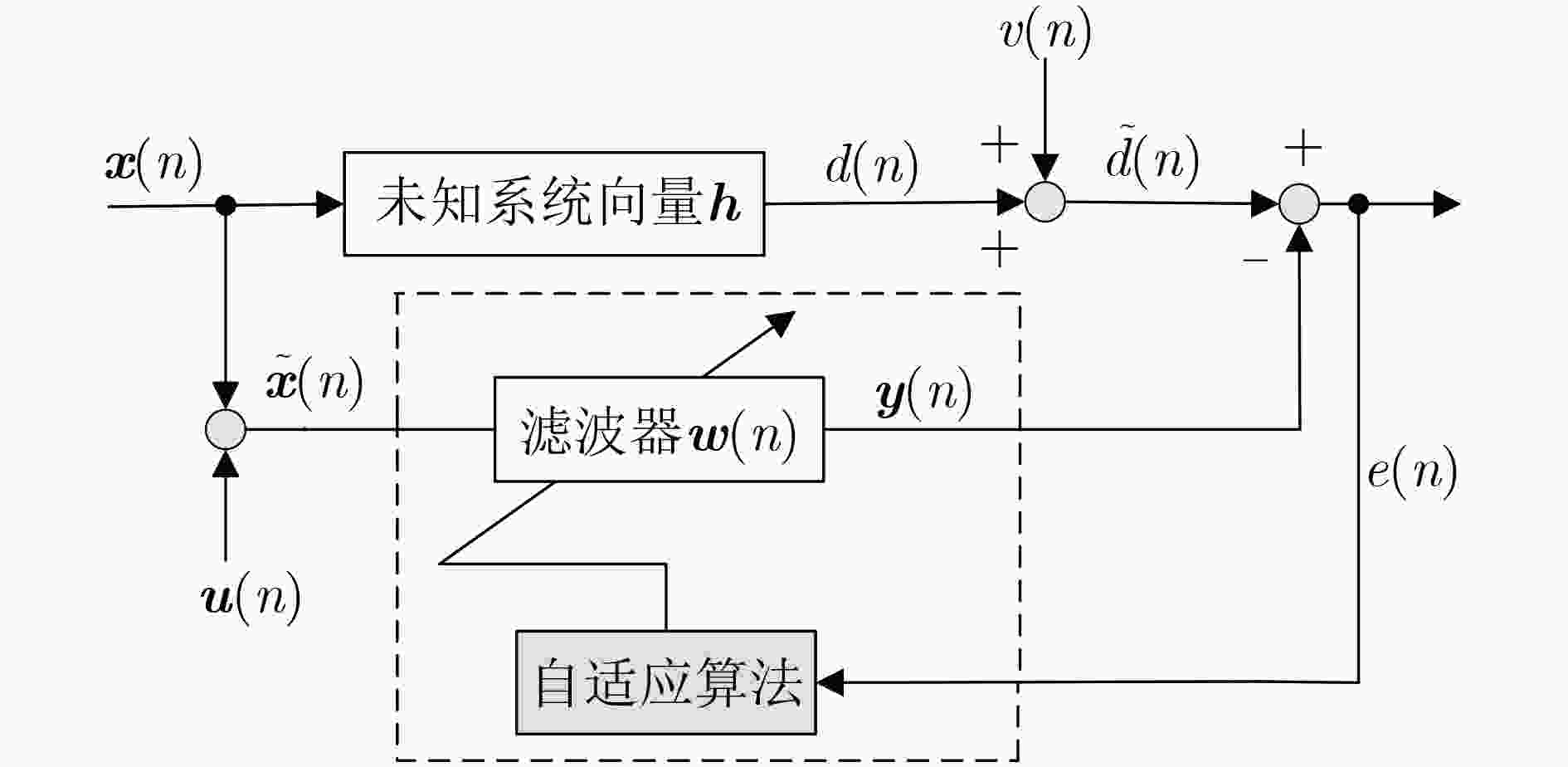
 下载:
下载:
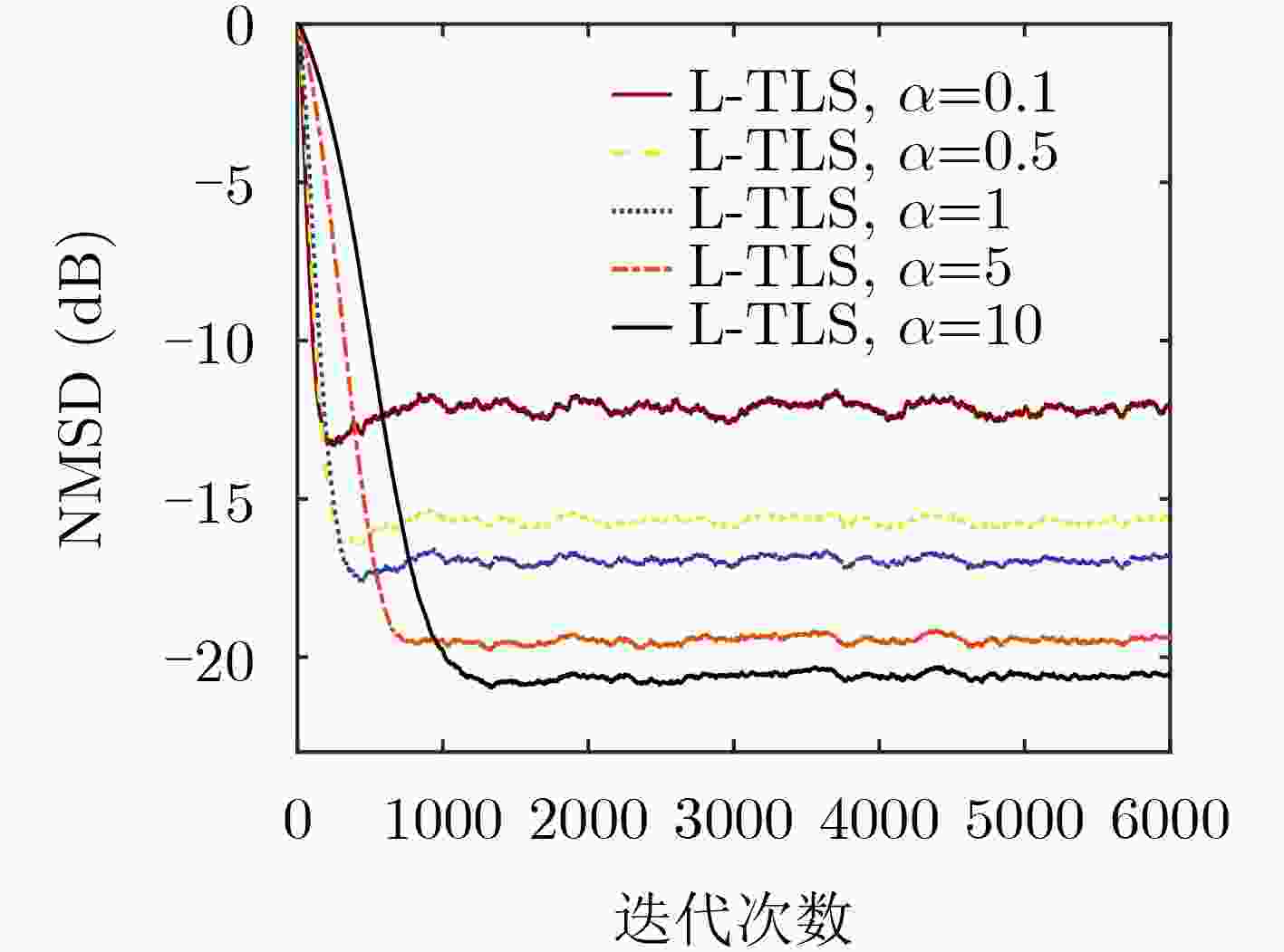

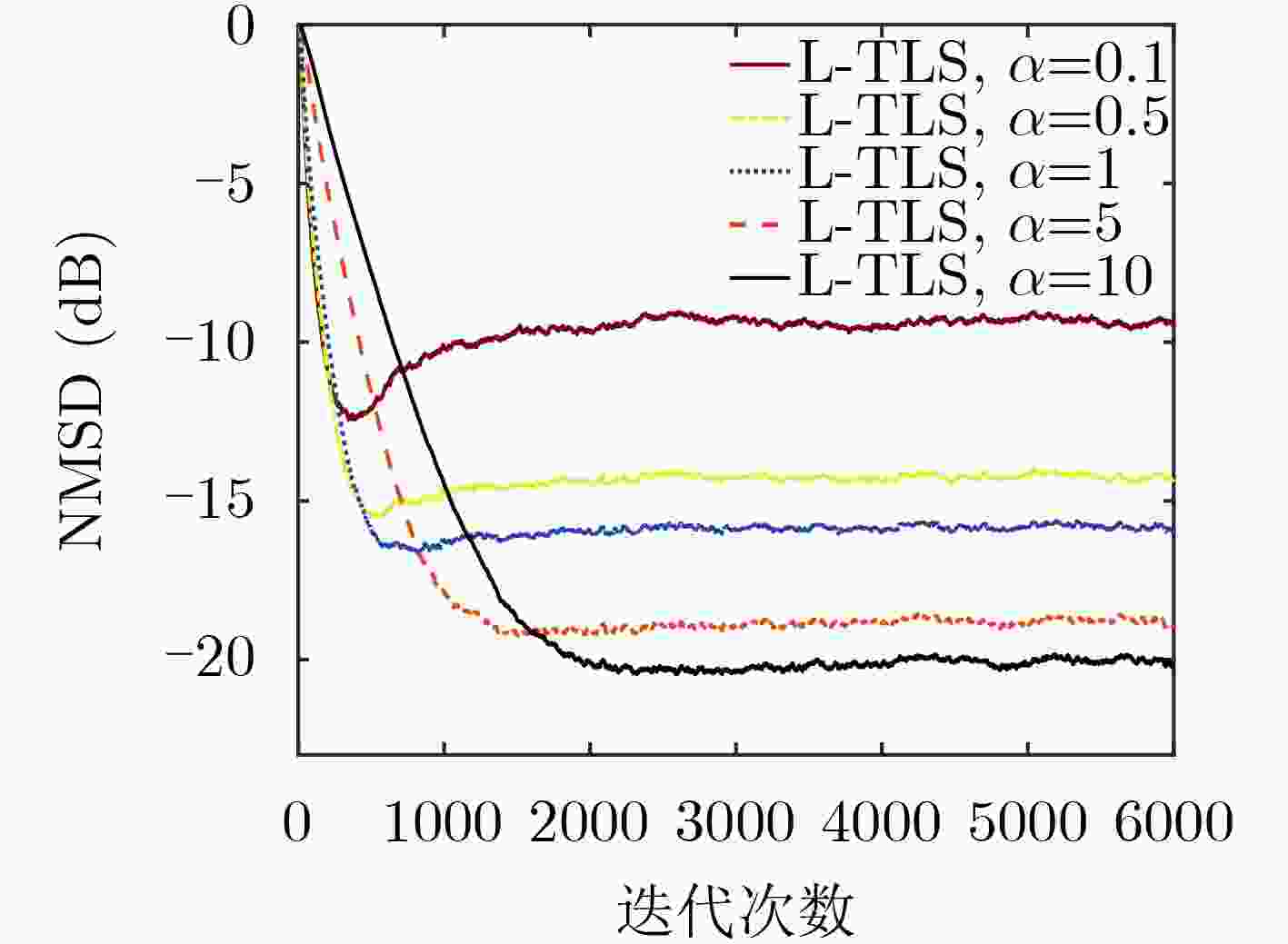


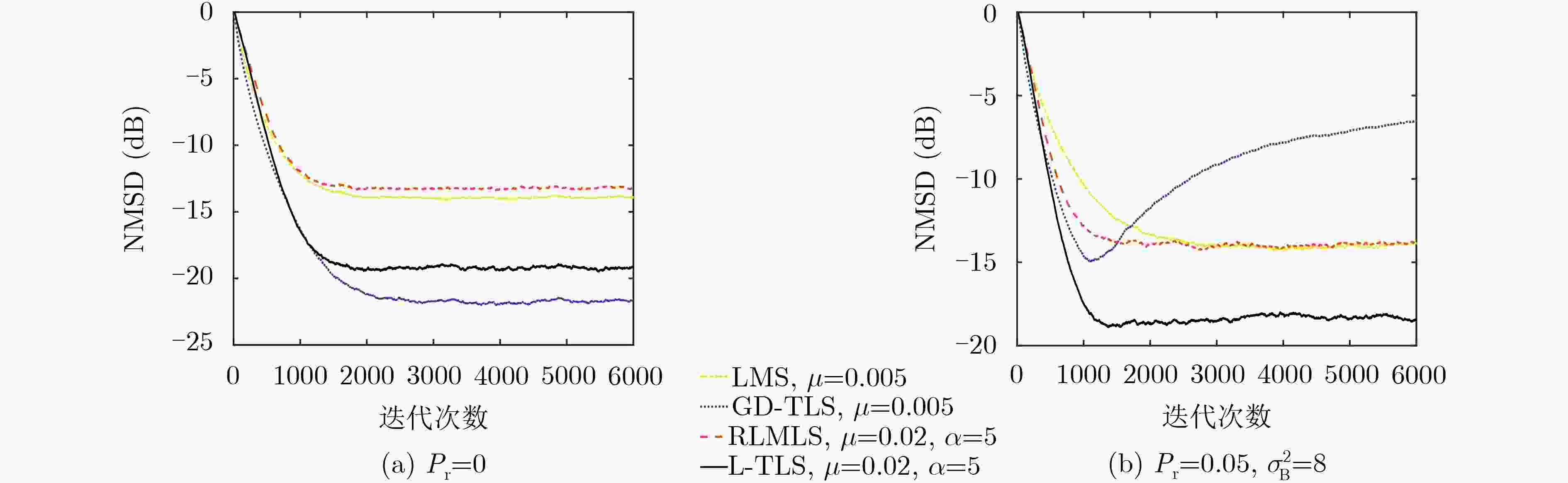


 下载:
下载:
