High Resolution ISAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Robust Two-tier Group LASSO Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
-
摘要: 经典的逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)稀疏成像算法一般通过求解
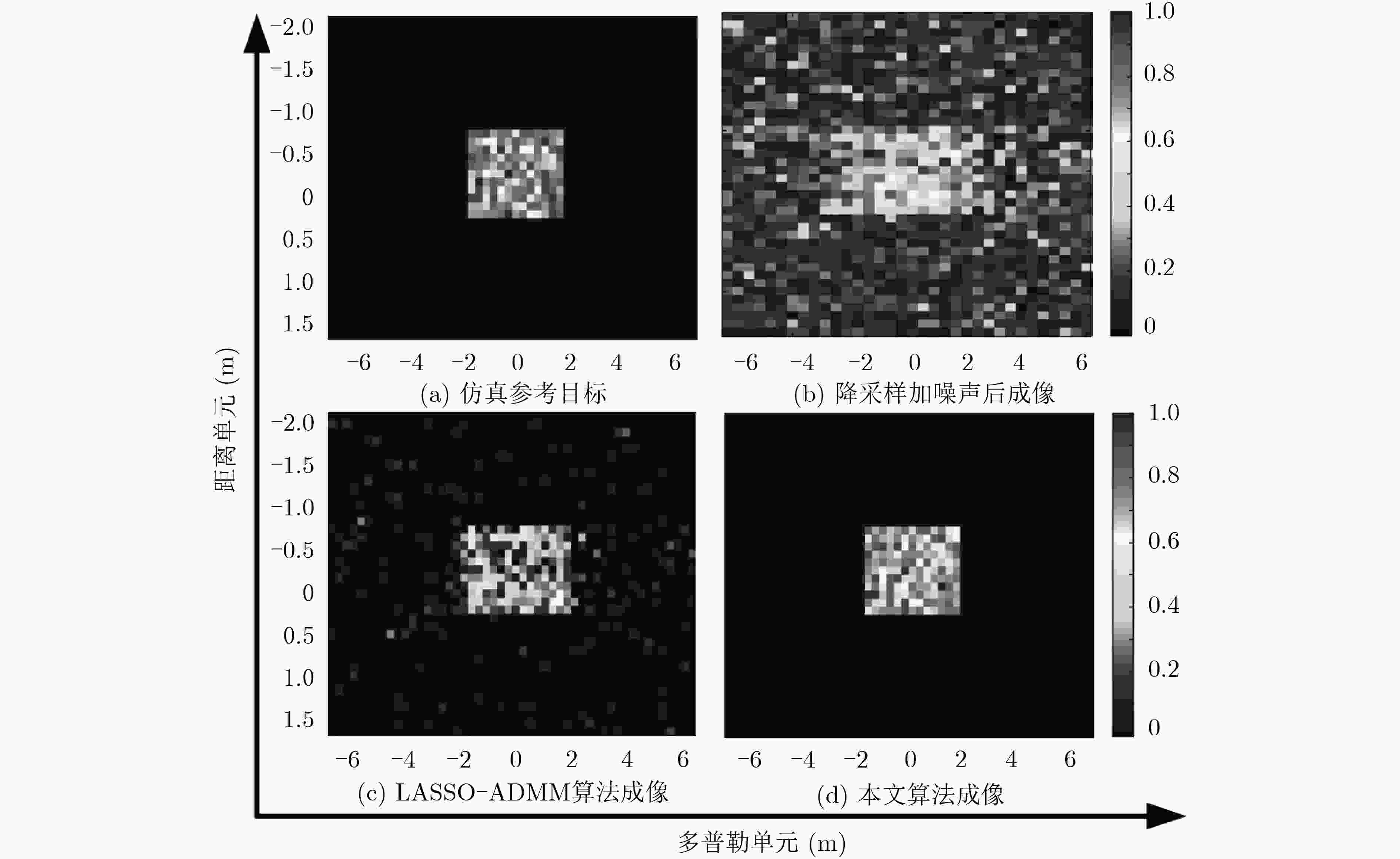
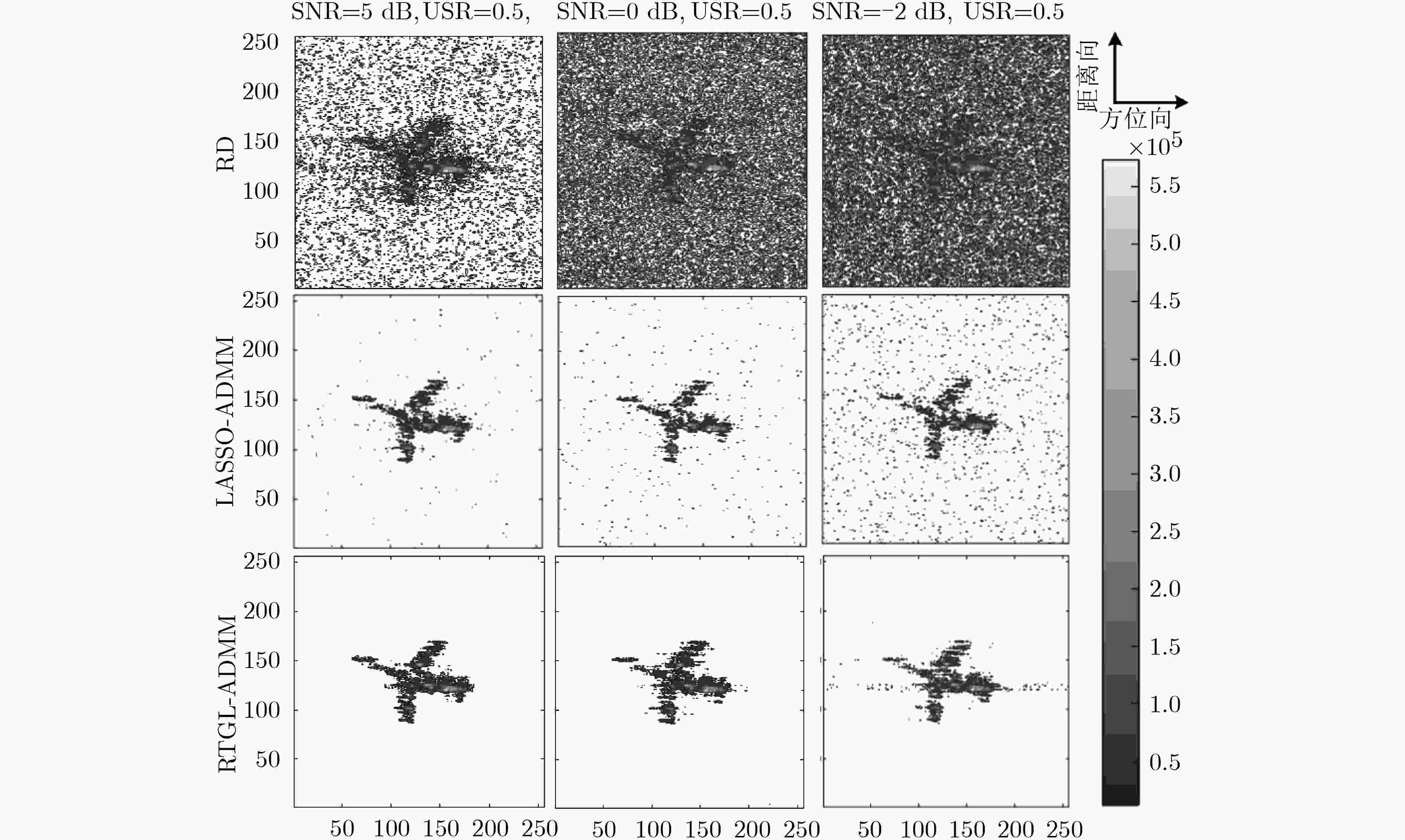
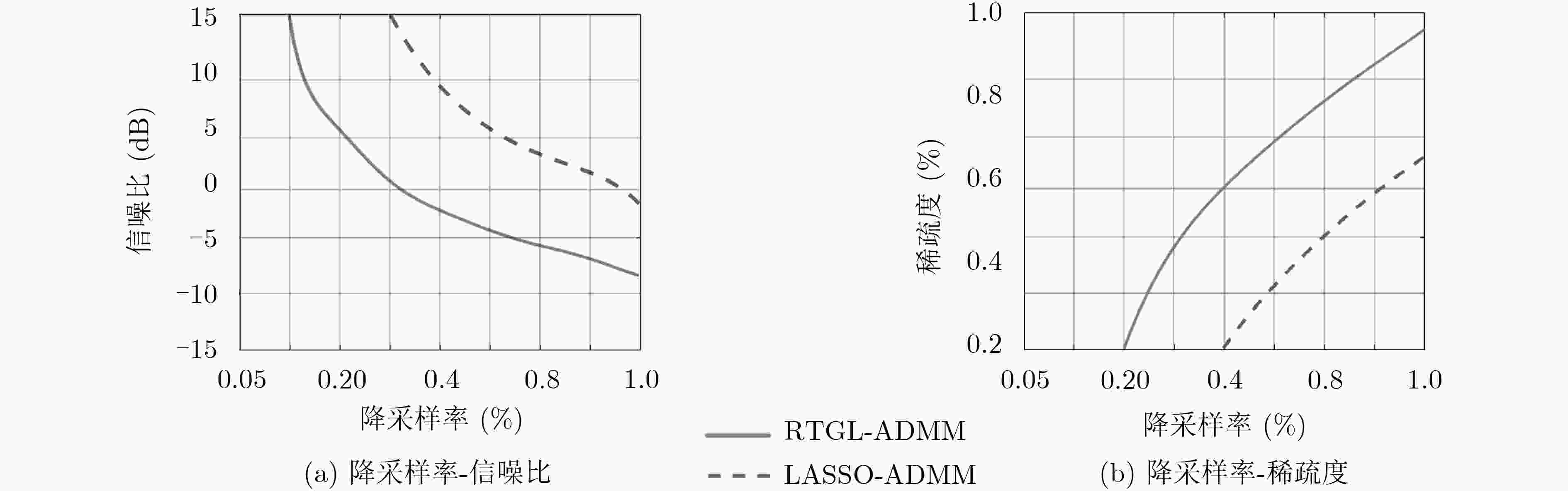
${\ell _{1}}$ 范数约束的最小化问题获取稀疏恢复结果,但此类算法在恢复过程中很容易将某些散射强度较低的分辨单元当作背景噪声一并消除,从而导致目标部分弱散射结构特征丢失。针对这一问题,该文提出一种基于稳健型双层叠组LASSO回归模型的交替方向多乘子算法(RTGL-ADMM)。该算法在ISAR目标稀疏先验的基础上,进一步引入目标散射体空间连续性结构特征先验知识,并应用${{{\ell _{1}}} / {{\ell _{\rm{F}}}}}$ 混合范数进行定量表征。接下来,在ADMM框架下引入非平滑的${{{\ell _{1}}} / {{\ell _{\rm{F}}}}}$ 混合范数惩罚项,并将距离向和方位向雷达回波复数据分别进行分组处理后再使其双层叠加,然后对混合范数对应的邻近算子进行对偶迭代运算,实现“分解-协同”框架下结构与组稀疏特征的有机调和,从而在对ISAR数据稀疏成像的同时实现结构特征增强。实验验证采用ISAR仿真复数据与Yak-42实测数据,针对RTGL-ADMM成像进行定性分析。继而采用相变曲线图定量分析RTGL-ADMM在不同参数调节下的成像能力,从而验证了该文所提算法应用于ISAR高分辨成像时的稳健性与优越性。Abstract: The classical sparse recovery of Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) imagery obtains the ISAR image by solving the constrained problem of${\ell _{1}}$ norm regularization. However, this manner may remove the scattering points in low amplitude, and accordingly, lose the structural features in weak scattering. To this end, a novel and Robust Two-tier Group LASSO-Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (RTGL-ADMM) is proposed in this paper, which is capable of enhancing block sparsity structures of the targets-of-interests. Based on the sparse prior of the target, the proposed algorithm further introduces the prior knowledge of spatial continuity structure of the target’s scatters, and the${\ell _{1}}/{\ell _{\rm{F}}}$ mixed norm is accordingly used to formulate the prior. Next, the non-smooth${\ell _{1}}/{\ell _{\rm{F}}}$ mixed norm penalty term is presented under the ADMM framework, where the scatters in both range and azimuthal directions are grouped and overlapped to enhance the block sparsity outer the groups. According to the theory of ADMM, the proximal mapping of the${\ell _{1}}/{\ell _{\rm{F}}}$ mixed norm is solved and dually iterated to achieve a robust and efficient solution. The proposed algorithm proceeds in the "Decomposition-Coordination" manner, which guarantees superior convergence. In this way, the sparse imaging of ISAR data is combined with the enhancement of structural features. The experiment verifies the adoption of ISAR simulation complex data and YAK-42 measured data, and conducts qualitative analysis against RTGL-ADMM. Then the phase transition curve is used to analyze quantitatively the imaging capability of RTGL-ADMM under different parameters, thus verifying the robustness and superiority of the proposed algorithm in the application of ISAR high-resolution imaging. -
表 1 RTGL-ADMM算法流程
基于稳健型双层叠组LASSO模型的交替方向多乘子(RTGL-
ADMM)算法步骤 1 初始化,令$k = 0$,${{{X}}^{{0}}},{{{Z}}^{{0}}},{{{U}}^{{0}}}$; 步骤 2 设定迭代次数与目标精度,若停止准则不满足,进行循环; 步骤 3 根据式(10)更新${{X}}$变量如: ${{{X}}^{k + 1}} = {\left( {{{{A}}^{\rm{H}}}{{A}} + \rho {{I}}} \right)^{ - 1}}\left[ {{{{A}}^{\rm{H}}}{{Y}} + \rho \left( {{{{Z}}^k} - {{{U}}^k}} \right)} \right]$ 步骤 4 根据式(11)更新方位向分裂变量${{Z}}_1^{k + 1}$如:
${{Z}}_1^{k + 1} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{w = 1}^W {{\rm{pro}}{{\rm{x}}_{{\beta / \rho }}}} } \left[ {{{X}}_{n,w}^{k + 1} + {{U}}_{n,w}^k} \right]$步骤 5 根据式(12)更新距离向分裂变量${{Z}}_2^{k + 1}$如:
${{Z}}_2^{k + 1} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{v = 1}^V {{\rm{pro}}{{\rm{x}}_{{\beta / \rho }}}} } \left[ {{{X}}_{m,v}^{k + 1} + {{U}}_{m,v}^k} \right]$步骤 6 加权层叠后${{{Z}}^{k + 1}} = \left( {{{1} / {2}}} \right)\left( {{{Z}}_1^{k + 1} + {{Z}}_2^{k + 1}} \right)$ 步骤 7 根据式(13)更新对偶变量
${{{U}}^{k + 1}} = {{{U}}^k} + {{{X}}^{k + 1}} - {{{Z}}^{k + 1}}$步骤 8 若不满足停止准则,继续步骤3—步骤7,若满足停止准
则,跳出循环;步骤 9 输出${{X}}$ -
田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. Review of high-resolution imaging techniques of wideband inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060 王天. 机载雷达对海面目标SAR/ISAR成像方法[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019.WANG Tian. The hybrid SAR/ISAR imaging of sea-surface target by airborne radar[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. 朱晓秀, 胡文华, 郭宝锋. 基于压缩感知的ISAR成像技术综述[J]. 飞航导弹, 2018(3): 84–89. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2018.03.20ZHU Xiaoxiu, HU Wenhua, and GUO Baofeng. A review of ISAR imaging techniques based on compressed sensing[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2018(3): 84–89. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2018.03.20 苏潇然. 基于稀疏信号处理的ISAR运动补偿及成像技术[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2019.SU Xiaoran. ISAR motion compensation and imaging technologies based on sparse signal processing[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2019. DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 王伟, 张斌, 李欣. 基于混合匹配追踪算法的MIMO雷达稀疏成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(10): 2415–2422. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151453WANG Wei, ZHANG Bin, and LI Xin. An imaging method for MIMO radar based on hybrid matching pursuit[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(10): 2415–2422. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151453 李瑞, 张群, 苏令华, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的双基雷达关联成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2865–2872. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180933LI Run, ZHANG Qun, SU Linghua, et al. Bistatic radar coincidence imaging based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2865–2872. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180933 BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 杨磊, 李埔丞, 李慧娟, 等. 稳健高效通用SAR图像稀疏特征增强算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2826–2835. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190173YANG Lei, LI Pucheng, LI Huijuan, et al. Robust and efficient sparse-feature Enhancement for generalized SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2826–2835. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190173 YUAN Ming and LIN Yi. Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology) , 2006, 68(1): 49–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00532.x YANG Lei, LI Pucheng, ZHANG Su, et al. Cooperative multitask learning for sparsity-driven SAR imagery and nonsystematic error autocalibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 5132–5147. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2972972 TIBSHIRANI R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological) , 1996, 58(1): 267–288. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x DONOHO D L, MALEKI A, and MONTANARI A. The noise-sensitivity phase transition in compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2011, 57(10): 6920–6941. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2011.2165823 -









 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
