Crowd Counting Method Based on Multi-Scale Enhanced Network
-
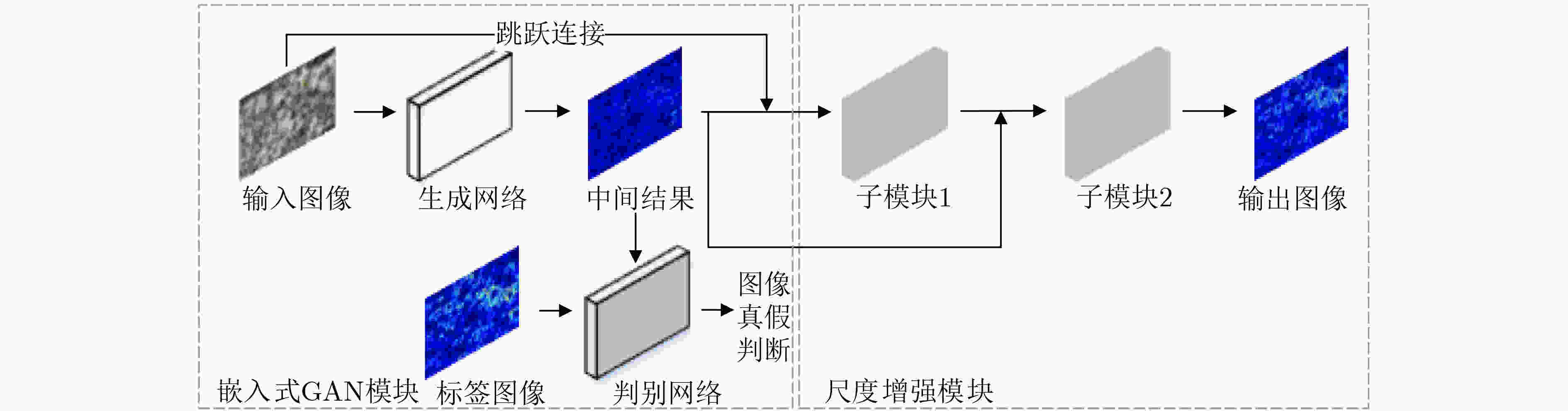
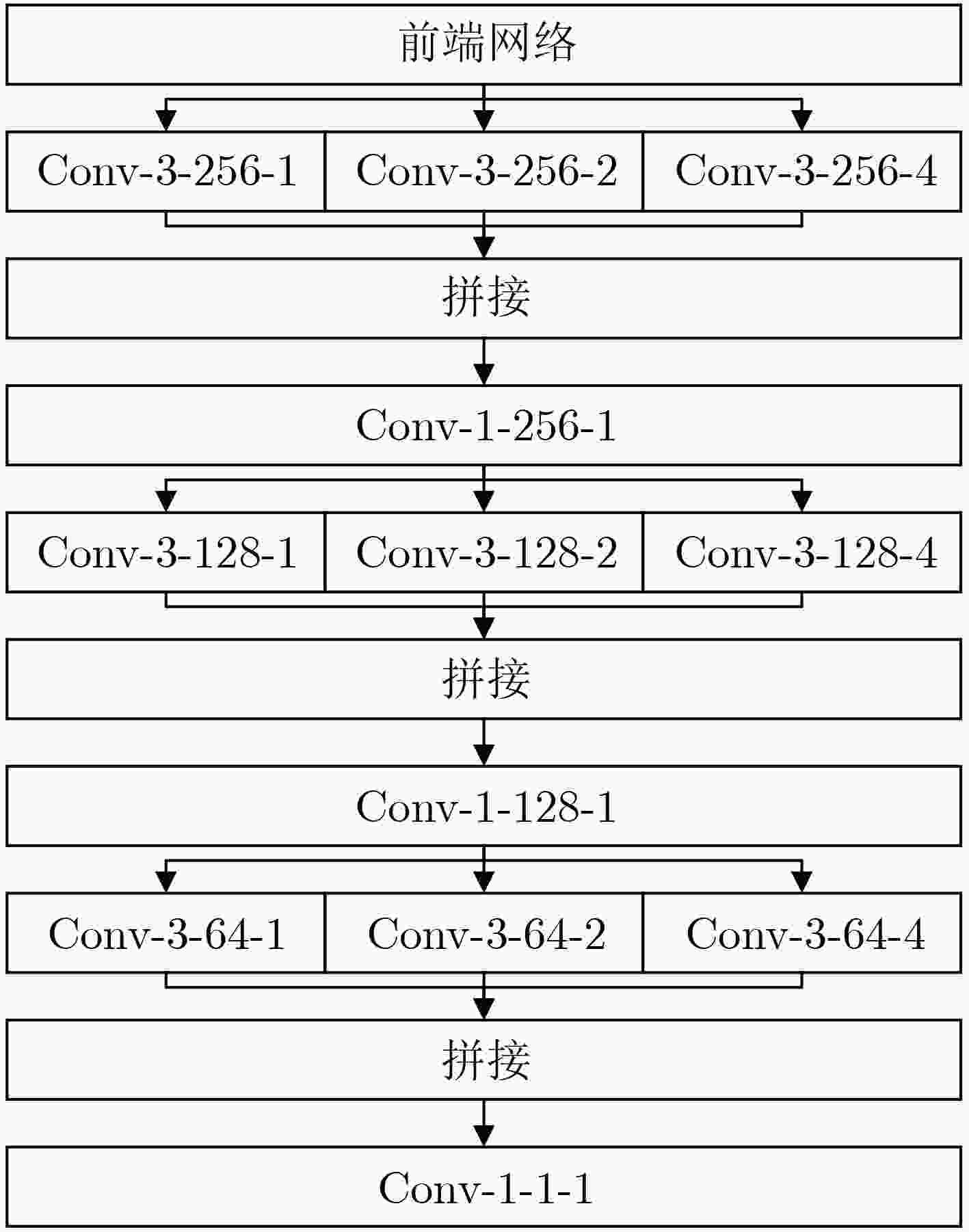
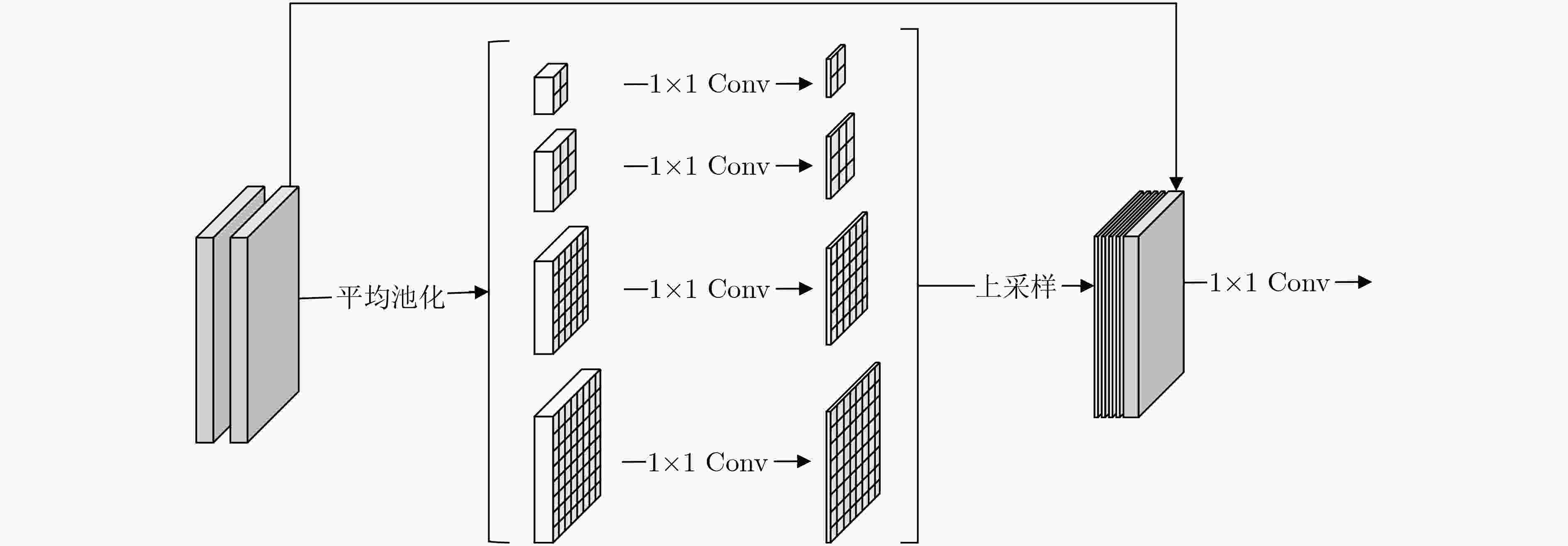
摘要: 人群计数研究普遍使用欧几里得损失函数,易造成图像局部相关性缺失,且现有研究方法未能充分提取人群图像中连续变化的尺度特征,影响了人群计数模型的性能。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于多尺度增强网络的人群计数模型(MSEN)。首先,在多分支结构生成网络中引入区域性判别网络,将二者组合形成嵌入式GAN模块,以增强生成图像的局部相关性;之后,基于金字塔池化结构设计了尺度增强模块,将该模块连接在嵌入式GAN模块之后,进一步从不同区域提取不同尺度的局部特征,以最大程度地应对人群图像局部尺度连续变化的问题,从而增强整体模型的泛化能力。最后,在3个具有挑战性的人群计数公共数据集上进行了广泛的实验。实验结果表明,该文所述模型可有效提升人群计数问题的准确性和鲁棒性。Abstract: The performance of the crowd counting methods is degraded due to the commonly used Euclidean loss ignoring the local correlation of images and the limited ability of the model to cope with multi-scale information. A crowd counting method based on Multi-Scale Enhanced Network(MSEN) is proposed to address the above problems. Firstly, an embedded GAN module with a multi-branch generator and a regional discriminator is designed to initially generate crowd density maps and optimize their local correlation. Then, a well-designed scale enhancement module is connected after the embedded GAN module to extract further local features of different scales from different regions, which will strengthen the generalization ability of the model. Extensive experimental results on three challenging public datasets demonstrate that the performance of the proposed method can effectively improve the accuracy and robustness of the prediction.
-
表 1 数据集基本信息对比
数据集 图像数量 分辨率 最小人数 最大人数 密度水平 ShanghaiTech
Part_A482 不等 33 3139 高 ShanghaiTech
Part_B716 768×1024 9 578 低 UCF_CC_50 50 不等 94 4543 极高 UCF-QNRF 1535 不等 49 12865 极高 表 2 ShanghaiTech数据集实验结果
表 3 UCF_CC_50数据集实验结果
表 4 UCF-QNRF数据集实验结果
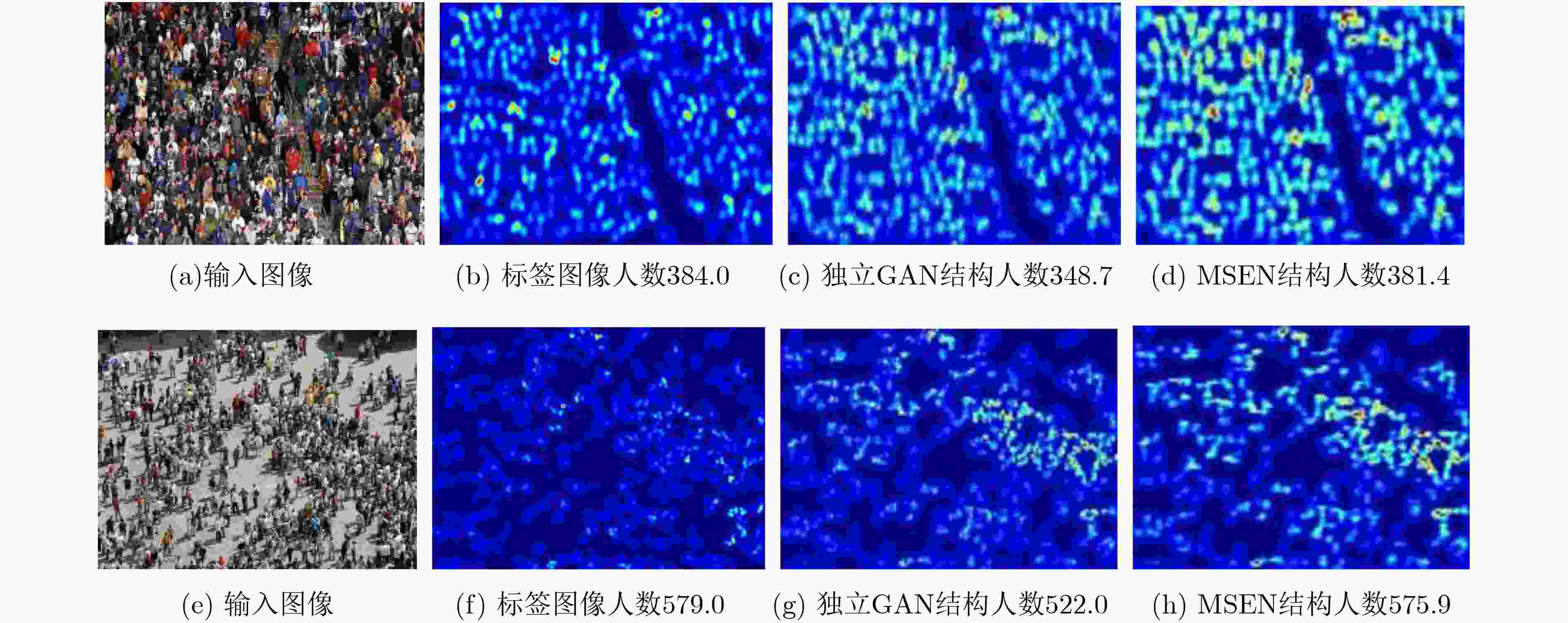
表 5 不同结构的模型及其对应的实验结果
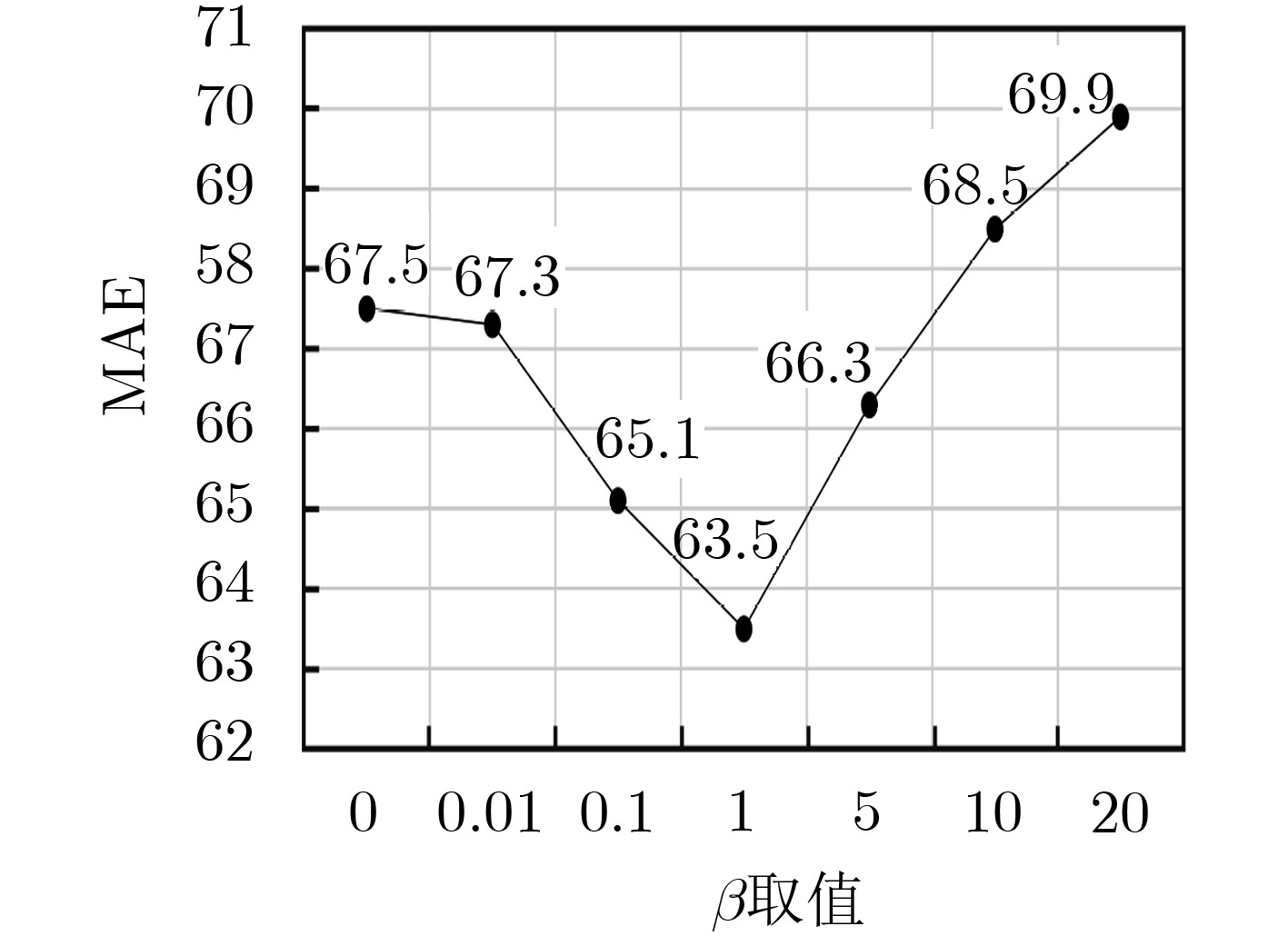
模型序号 结构概述 嵌入式 尺度增强子模块数量 跳跃连接 MAE (1) G – – – 67.5 (2) GAN – – – 65.6 (3) GAN*$ {\mathrm{G}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{N}}^{*} $(E×1) – 1 – 65.3 (4) GAN*$ {\mathrm{G}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{N}}^{*} $(E×1+S) – 1 √ 65.2 (5) GAN*$ {\mathrm{G}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{N}}^{*} $(E×2) – 2 – 66.5 (6) GAN*$ {\mathrm{G}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{N}}^{*} $(E×2+S) – 2 √ 66.4 (7) 嵌入式GAN+ E×1 √ 1 – 65.0 (8) 嵌入式GAN+ E×1+S √ 1 √ 64.7 (9) 嵌入式GAN+ E×2 √ 2 – 64.1 (10) 嵌入式GAN+ E×2+S (MSEN) √ 2 √ 63.5 -
[1] 陈朋, 汤一平, 王丽冉, 等. 多层次特征融合的人群密度估计[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(8): 1181–1192. doi: 10.11834/jig.180017 [2] XIE Weidi, NOBLE J A, and ZISSERMAN A. Microscopy cell counting and detection with fully convolutional regression networks[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering: Imaging & Visualization, 2018, 6(3): 283–292. doi: 10.1080/21681163.2016.1149104 [3] 左静, 窦祥胜. 视频车辆分类与计数的模型与应用[J]. 运筹与管理, 2020, 29(1): 124–130. [4] CUI Kai, HU Cheng, WANG Rui, et al. Deep-learning-based extraction of the animal migration patterns from weather radar images[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(4): 140304. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2800-0 [5] 孙彦景, 石韫开, 云霄, 等. 基于多层卷积特征的自适应决策融合目标跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2464–2470. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180971SUN Yanjing, SHI Yunkai, YUN Xiao, et al. Adaptive strategy fusion target tracking based on multi-layer convolutional features[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2464–2470. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180971 [6] 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 等. 基于空间可靠性约束的鲁棒视觉跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1650–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180780PU Lei, FENG Xinxi, HOU Zhiqiang, et al. Robust visual tracking based on spatial reliability constraint[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1650–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180780 [7] ZHANG Cong, LI Hongshen, WANG Xiaogang, et al. Cross-scene crowd counting via deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 833–841. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298684. [8] ZHANG Yingying, ZHOU Desen, CHEN Siqin, et al. Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 589–597. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.70. [9] SAM D B, SURYA S, and BABU R V. Switching convolutional neural network for crowd counting[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4031–4039. [10] SHEN Zan, XU Yi, NI Bingbing, et al. Crowd counting via adversarial cross-scale consistency pursuit[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 5245–5254. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00550. [11] LI Yuhong, ZHANG Xiaofan, and CHEN Deming. CSRNet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1091–1110. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00120. [12] CAO Xinkun, WANG Zhipeng, ZHAO Yanyun, et al. Scale aggregation network for accurate and efficient crowd counting[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 757–773. [13] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–14. [14] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. [15] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.660. [16] IDREES H, SALEEMI I, SEIBERT C, et al. Multi-source multi-scale counting in extremely dense crowd images[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 2547–2554. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.329 [17] IDREES H, TAYYAB M, ATHREY K, et al. Composition loss for counting, density map estimation and localization in dense crowds[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 544–559. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01216-8_33. [18] QU Yanyun, CHEN Yizi, HUANG Jingying, et al. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 8152–8160. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00835. [19] SHI Miaojing, YANG Zhaohui, XU Chao, et al. Revisiting perspective information for efficient crowd counting[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7271–7280. [20] JIANG Xiaolong, XIAO Zehao, ZHANG Baochang, et al. Crowd counting and density estimation by trellis encoder-decoder networks[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6126–6135. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00629. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
