Energy Efficiency Optimization Algorithm Based On PD-NOMA Under Heterogeneous Cloud Radio Access Networks
-
摘要: 针对异构云无线接入网络的频谱效率和能效问题,该文提出一种基于功率域-非正交多址接入(PD-NOMA)的能效优化算法。首先,该算法以队列稳定和前传链路容量为约束,联合优化用户关联、功率分配和资源块分配,并建立网络能效和用户公平的联合优化模型;其次,由于系统的状态空间和动作空间都是高维且具有连续性,研究问题为连续域的NP-hard问题,进而引入置信域策略优化(TRPO)算法,高效地解决连续域问题;最后,针对TRPO算法的标准解法产生的计算量较为庞大,采用近端策略优化(PPO)算法进行优化求解,PPO算法既保证了TRPO算法的可靠性,又有效地降低TRPO的计算复杂度。仿真结果表明,该文所提算法在保证用户公平性约束下,进一步提高了网络能效性能。Abstract: In view of the spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency of Heterogeneous Cloud Radio Access Networks (H-CRAN), an energy efficiency optimization algorithm based on Power Domain Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (PD-NOMA) is proposed. First, the algorithm takes queue stability and forward link capacity as constraints, jointly optimizes user association, power allocation and resource block allocation, and it establishes a joint optimization model of network energy efficiency and user fairness. Secondly, because the state space and action space of the system are both high-dimensional and continuity, the research problem is the NP-hard problem of the continuous domain, and then Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO) algorithm is introduced to solve efficiently the continuous domain issue. Finally, the amount of calculations generated by the standard solution for the TRPO algorithm is too large, and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm is used to optimize the solution. The PPO algorithm not only ensures the reliability of the TRPO algorithm, but also reduces effectively the TRPO calculation complexity. Simulation results show that the algorithm proposed in this paper improves further the energy efficiency performance of the network under the constraint of ensuring user fairness.
-
表 1 近端策略优化PPO训练Actor网络参数算法
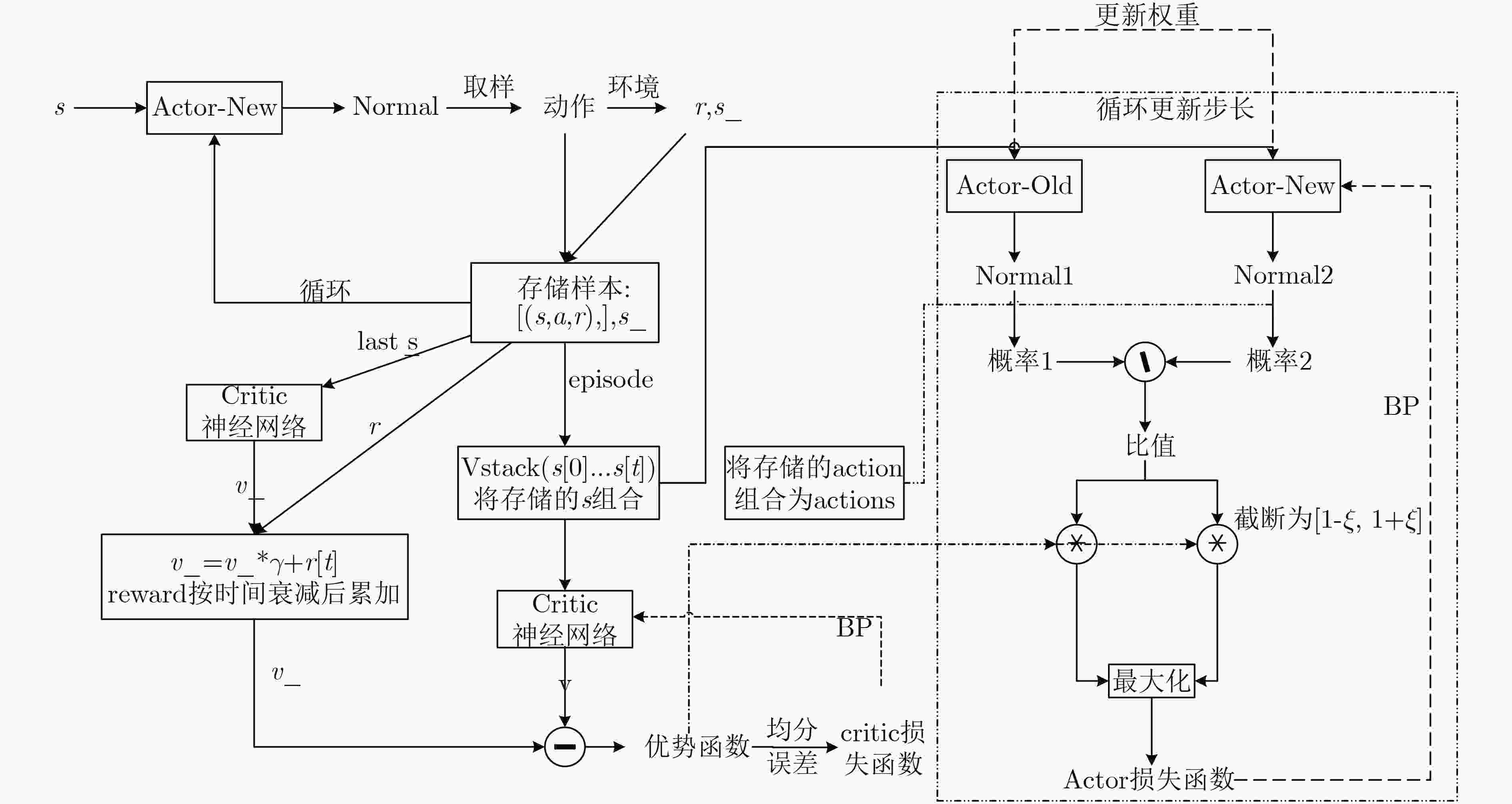
算法1 近端策略优化(PPO)训练Actor网络参数算法 (1) 初始化Actor神经网络参数$\theta $以及Critic的神经网络参数${\kappa _v}$ (2) For episode $G = 1,2,···,1000$ do (3) while经验池D中没有足够的元组do (4) 随机选取一个初始状态${s_0}$ (5) for step=1, 2, ···, n do (6) 定义起始状态$s$,根据策略$\pi (s|\theta )$选取动作$a$ (7) 采取动作$a$与无线网络环境进行交互后,观察下一
状态$s'$并计算出奖励回报$r$.(8) 通过式(15)计算出累计折扣奖励${R_i}$,将元组
$({s_i},{a_i},{s'_i},{R_i})$存入经验池$D$中(9) end for (10) end while (11) ${\theta ^{{\rm{old}}}} \leftarrow \theta $ (12) for 每次更新回合 do (13) 从经验池D中随机采样mini-batch样本 (14 ) 对于Critic网络而言:通过最小Critic网络中的损失函
数来更新Critic的参数${\kappa _v}$(15) 对于Actor网络而言: (16) 根据状态${s_i}$,利用式(17)计算优势函数${A_i}$,通过最大
化actor网络的损失函数来更新Actor的参数$\theta $(17) end for (18) End For -
[1] 张广驰, 曾志超, 崔苗, 等. 无线供电混合多址接入网络的资源分配[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(12): 3013–3019. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180219ZHANG Guangchi, ZENG Zhichao, CUI Miao, et al. Resource allocation for wireless powered hybrid multiple access networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(12): 3013–3019. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180219 [2] MOKDAD A, AZMI P, MOKARI N, et al. Cross-layer energy efficient resource allocation in PD-NOMA based H-CRANs: Implementation via GPU[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(6): 1246–1259. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2860985 [3] ZHANG Yizhong, WU Gang, DENG Lijun, et al. Arrival rate-based average energy-efficient resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous cloud RAN[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 136332–136342. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939348 [4] 陈前斌, 管令进, 李子煜, 等. 基于深度强化学习的异构云无线接入网自适应无线资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1468–1477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190511CHEN Qianbin, GUAN Lingjin, LI Ziyu, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive wireless resource allocation algorithm for heterogeneous cloud wireless access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1468–1477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190511 [5] PENG Mugen, LI Yong, ZHAO Zhongyuan, et al. System architecture and key technologies for 5G heterogeneous cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Network, 2015, 29(2): 6–14. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2015.7064897 [6] HUNG S, HSU H, CHENG S, et al. Delay guaranteed network association for mobile machines in heterogeneous cloud radio access network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(12): 2744–2760. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2815702 [7] TAN Zhongwei, YANG Chuanchuan, and WANG Ziyu. Energy evaluation for cloud RAN employing TDM-PON as front-haul based on a new network traffic modeling[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(13): 2669–2677. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2613095 [8] DHAINI A R, HO P H, SHEN Gangxiang, et al. Energy efficiency in TDMA-based next-generation passive optical access networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2014, 22(3): 850–863. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2013.2259596 [9] WANG Kaiwei, ZHOU Wuyang, and MAO Shiwen. Energy efficient joint resource scheduling for delay-aware traffic in cloud-RAN[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Washington, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7841793. [10] SABELLA D, DE DOMENICO A, KATRANARAS E, et al. Energy efficiency benefits of RAN-as-a-service concept for a cloud-based 5G mobile network infrastructure[J]. IEEE Access, 2014, 2: 1586–1597. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2014.2381215 [11] NEELY M J. Stochastic Network Optimization with Application to Communication and Queueing Systems[M]. Morgan & Claypool, 2010: 1–211. doi: 10.2200/S00271ED1V01Y201006CNT007. [12] NGUYEN K K, DUONG T Q, VIEN N A, et al. Non-cooperative energy efficient power allocation game in D2D communication: A multi-agent deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 100480–100490. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2930115 [13] ARULKUMARAN K, DEISENROTH M P, BRUNDAGE M, et al. Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(6): 26–38. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2743240 [14] NASIR Y S and GUO Dongning. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for dynamic power allocation in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(10): 2239–2250. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933973 -






 下载:
下载:
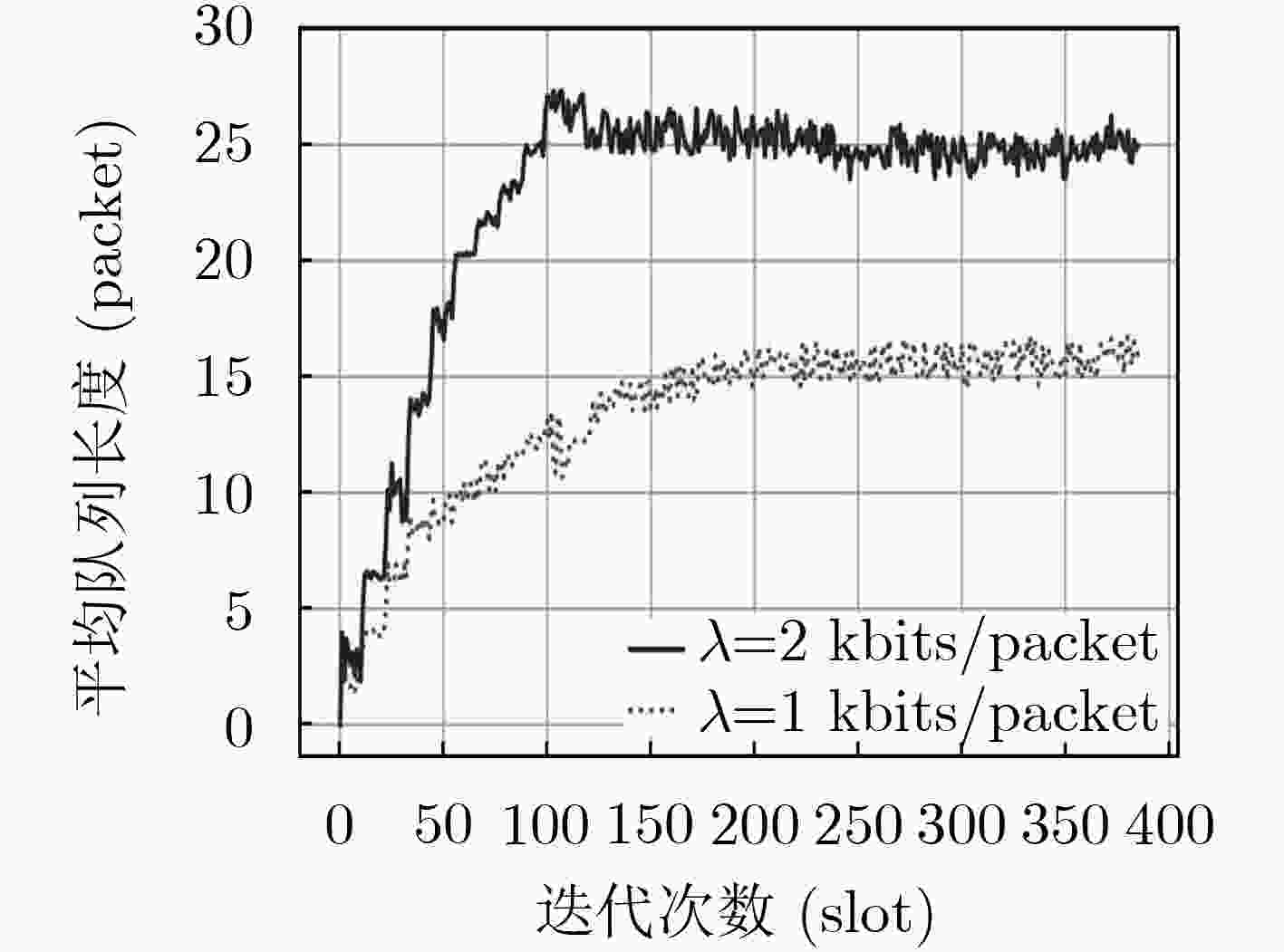
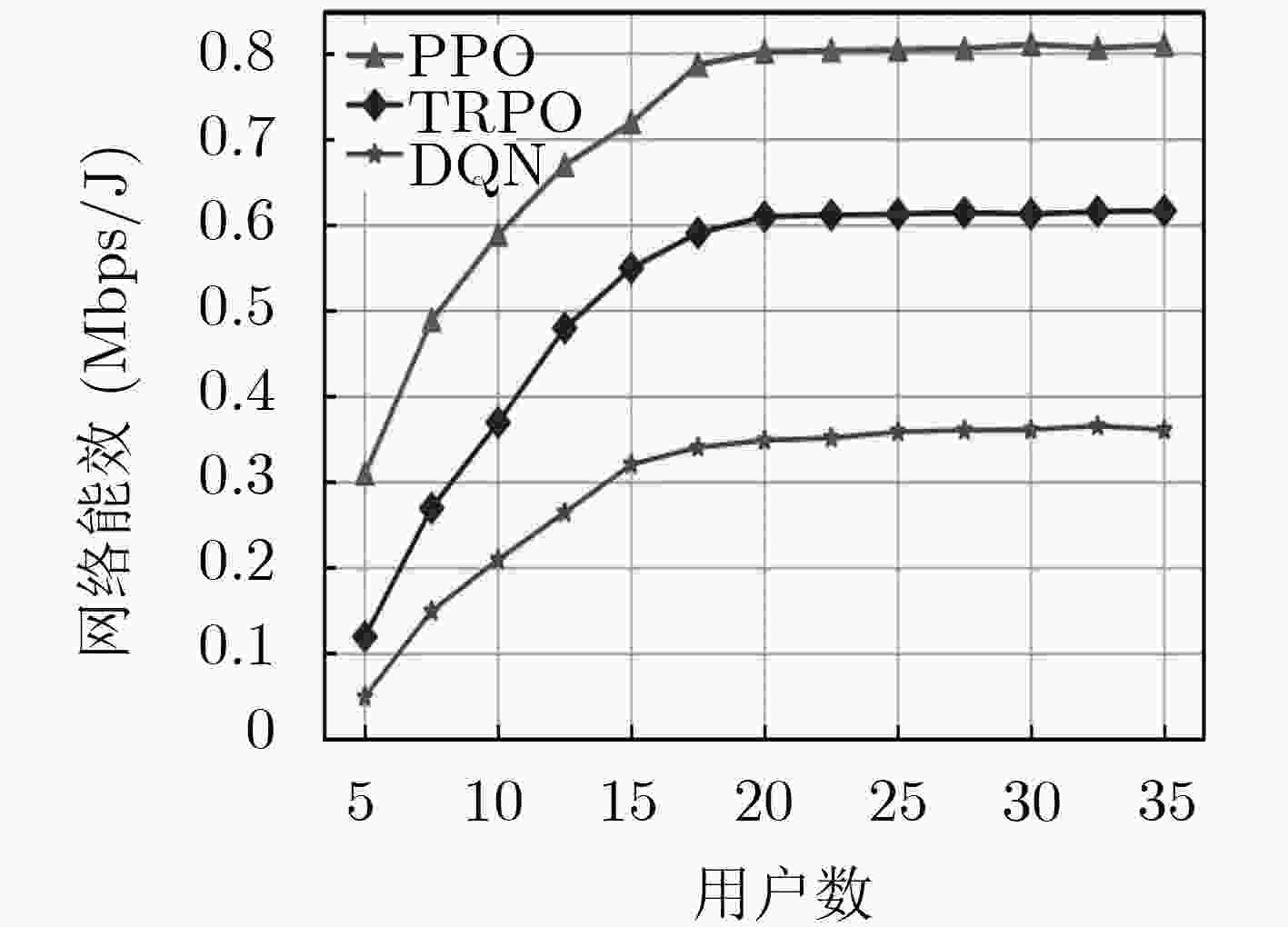
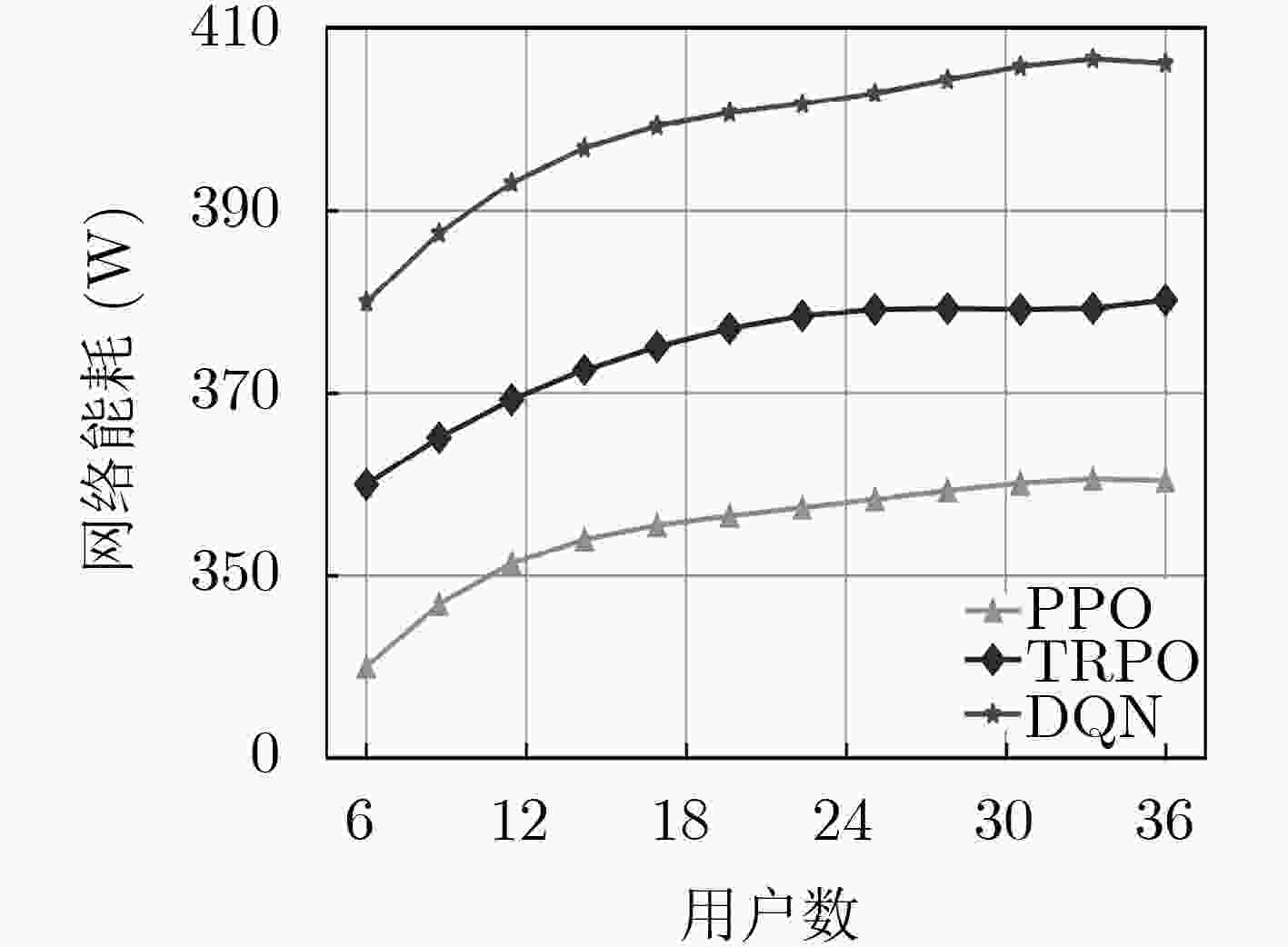


 下载:
下载:
