Multi-task Learning of Sparse Autofocusing for High-Resolution SAR Imagery
-
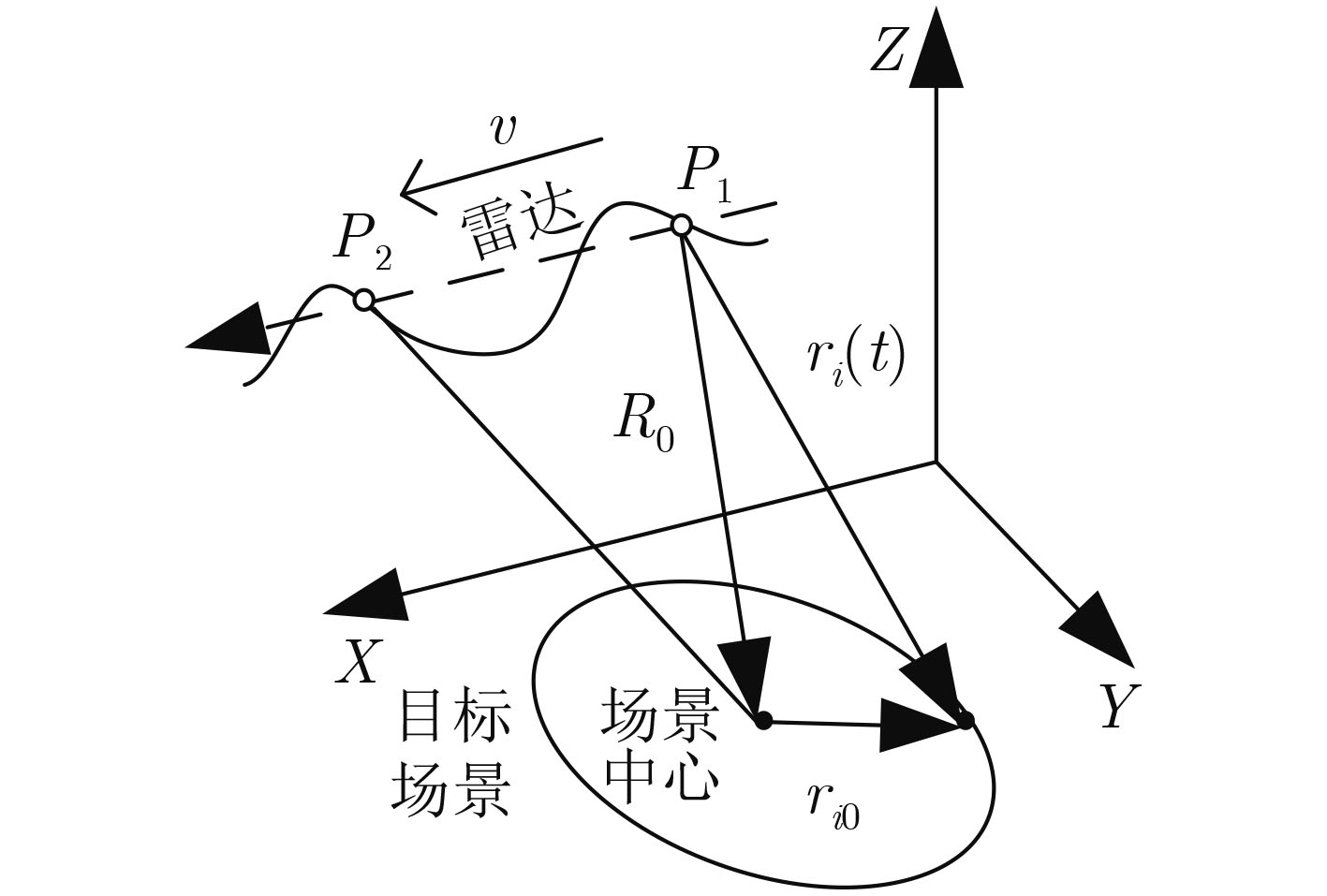
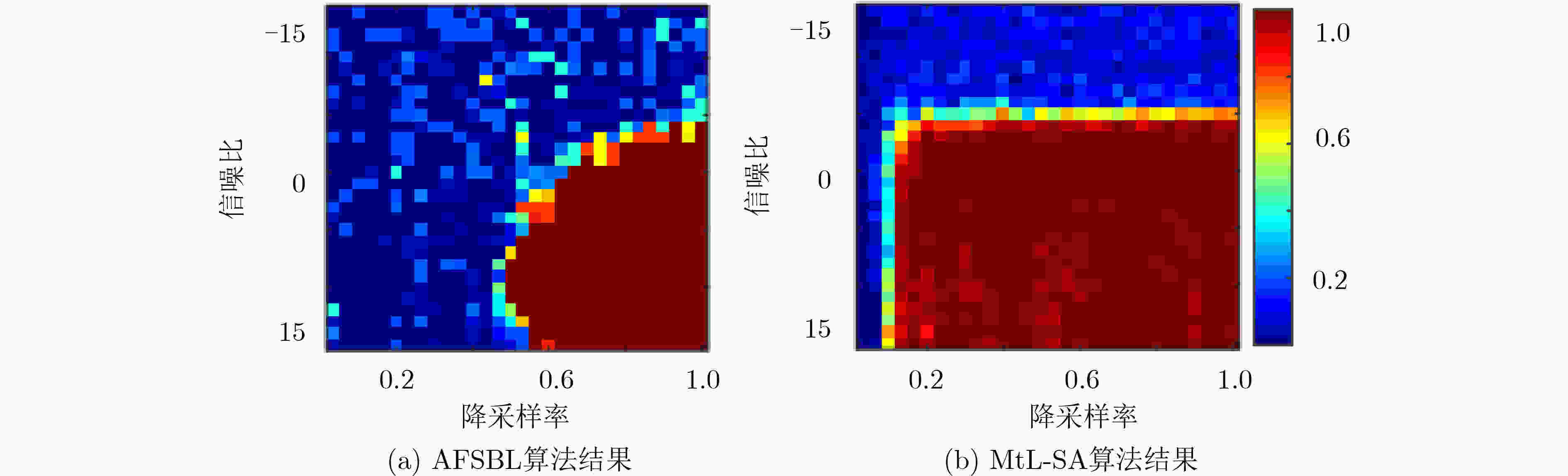
摘要: 针对传统高分辨合成孔径雷达(SAR)稀疏自聚焦成像算法难以有效平衡稀疏与聚焦特征的问题,该文提出一种基于交替方向多乘子方法(ADMM)的多任务协同优化学习稀疏自聚焦(MtL-SA)算法。该算法通过引入熵范数表征SAR成像结果聚焦特征,在ADMM优化框架下,利用近端算法求解聚焦特征解析解。针对原熵范数正则优化目标函数的非凸问题,该文合理设计代价函数,从而保证熵范数近端算子的闭合解析解。同时,应用
$ \ell {_1}$ 范数表征成像结果稀疏特征,并建立面向复数SAR成像数据的复数软阈值近端算子。该文所提MtL-SA成像算法可实现对目标场景后向散射场对应稀疏特征和聚焦特征的解析求解,并有效提升自聚焦算法的可靠性和稳健性。两种特征增强处理相互调和,保证了算法运行过程中有效降低误差传播,进而保证联合特征增强精度。仿真及实测机载SAR成像数据实验,验证了算法的有效性和实用性,同时应用相变分析方法分别定量和定性地分析了该文所提算法相比其他传统算法的优越性。Abstract: As it is difficult to balance the sparse and focusing features for conventional sparse autofocusing algorithm of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), a Multi-task Learning Sparse Autofocusing (MtL-SA) algorithm is proposed under a novel Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) in this paper. The image entropy norm is introduced to model the focusing feature of the SAR imagery, and it is minimized in a regularized manner using the proximal algorithm. To overcome the non-convexity of the original objective function, a surrogate function under the ADMM framework is designed and optimized accordingly. This ensures closed-form solution of the errors and the focusing feature. Besides, the$ \ell {_1}$ -norm is applied to denote the intended sparse feature of the SAR imagery, and a complex-valued proximity operator is derived for the range-compressed SAR data. Due to the cooperative framework, both the features can be solved and achieved with high robustness and acceptable accuracy. Compared with conventions, the computational efficiency improved twice orders in terms of CPU time. The proposed MtL-SA algorithm can realize the analytical solutions of the sparse and focusing features, so as to improve the robustness of the joint enhancement. Experiments using airborne simulated and raw SAR data are performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Phase transition analysis is applied to examine the superiority of the proposed algorithm compared with the conventions in terms of both quantitative and qualitative. -
表 1 MtL-SA算法流程
步骤1 设定初值${ {\boldsymbol{X} } }^{0}={ {\boldsymbol{Z} } }^{0}={ {\boldsymbol{D} } }^{0}={{{\textit{0}}} },\;k=0,\;G{=2}$,设定迭代停止准则,开始循环。 步骤2 全局优化:${\boldsymbol{X}}$更新运算${ {\boldsymbol{X} }^{k + 1} } = \left[ { { {\boldsymbol{A} }^{\rm{H} } }{ {\boldsymbol{E} }^{\rm{H} } }{\boldsymbol{Y} } + {\rho _1}\left( { { {\boldsymbol{Z} }_1}^k + { {\boldsymbol{D} }_1}^k} \right) + {\rho _2}\left( { { {\boldsymbol{Z} }_2}^k + { {\boldsymbol{D} }_2}^k} \right)} \right] \cdot {\left( { { {\boldsymbol{A} }^{\rm{H} } }{\boldsymbol{A} } + \rho G{\boldsymbol{I} } } \right)^{ - 1} }\quad \quad \quad \quad$ 步骤3 局部优化:${{\boldsymbol{Z}}_1}$, ${{\boldsymbol{D}}_1}$, ${{\boldsymbol{Z}}_2}$和${{\boldsymbol{D}}_2}$顺次更新运算 ${\rm{for }}\;\;g = G$ ${\boldsymbol{Z} }_{\rm{1} }^{k + 1} = {\left( { { {\boldsymbol{E} }^{k + 1} } } \right)^{\rm{H} } }{ {\boldsymbol{A} }^{\rm{H} } }{\boldsymbol{Y} },\;{\boldsymbol{D} }_{\rm{1} }^{k + 1} = {\boldsymbol{D} }_{\rm{1} }^k - { {\boldsymbol{X} }^{k + 1} } + {\boldsymbol{Z} }_{\rm{1} }^{k + 1}\quad \quad \quad \quad \quad$ ${\boldsymbol{Z} }_2^{k + 1} = {\rm{pro} }{ {\rm{x} }_{ { { {\lambda _2} } / \rho } } }\left[ { { {\boldsymbol{W} }^{k + 1} } } \right]{\rm{, } }{\boldsymbol{D} }_2^{k + 1} = {\boldsymbol{D} }_2^k - { {\boldsymbol{X} }^{k + 1} } + {\boldsymbol{Z} }_2^{k + 1}\quad \quad \quad \quad$ ${\rm{end}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{Z}}^{k + 1}} = \left[ {{\boldsymbol{Z}}_1^{k + 1}\;{\boldsymbol{Z}}_2^{k + 1}} \right],\;{{\boldsymbol{D}}^{k + 1}} = \left[ {{\boldsymbol{D}}_1^{k + 1}\;{\boldsymbol{D}}_2^{k + 1}} \right],\;k = k + 1$ 步骤4 当残差小于加性噪声方差时,跳至步骤5,迭代结束。否则,跳至步骤2。 步骤5 输出联合稀疏聚焦特征增强后的图像数据${\boldsymbol{X}}$。 -
[1] 闫贺, 王珏, 黄佳, 等. 基于二维速度搜索的星载SAR运动目标聚焦算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1287–1293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180663YAN He, WANG Jue, HUANG Jia, et al. A moving-targets detection algorithm for spaceborne SAR system based on two-dimensional velocity search method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1287–1293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180663 [2] 李煜, 陈杰, 张渊智. 合成孔径雷达海面溢油探测研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 751–762. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180468LI Yu, CHEN Jie, and ZAHNG Yuanzhi. Progress in research on marine oil spills detection using synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 751–762. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180468 [3] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [4] 田鹤, 于海锋, 朱宇, 等. 基于频域稀疏压缩感知的星载SAR稀疏重航过3维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 2021–2028. doi: 10.11999/JEJT190638TIAN He, YU Haifeng, ZHU Yu, et al. Sparse flight 3-D imaging of spaceborne SAR based on frequency domain sparse compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 2021–2028. doi: 10.11999/JEJT190638 [5] YANG Lei, ZHAO Lifan, BI Guoan, et al. SAR ground moving target imaging algorithm based on parametric and dynamic sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 2254–2267. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2498158 [6] ALONSO M T, LOPEZ-DEKKER P, and MALLORQUI J J. A novel strategy for radar imaging based on compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4285–4295. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2051231 [7] ZHAO Lifan, WANG Lu, BI Guoan, et al. An autofocus technique for high-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6392–6403. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2296497 [8] 张群英, 江兆凤, 李超, 等. 太赫兹合成孔径雷达成像运动补偿算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(1): 129–137. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160201ZHANG Qunying, JIANG Zhaofeng, LI Chao, et al. Motion compensation imaging algorithm of terahertz synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(1): 129–137. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160201 [9] ZHOU Song, YANG Lei, ZHAO Lifan, et al. Quasi-polar-based FFBP algorithm for miniature UAV SAR imaging without navigational data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7053–7065. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2739133 [10] LINNEHAN R, MILLER J, and ASADI A. Map-drift autofocus and scene stabilization for video-SAR[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 1401–1405. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378769. [11] MAO Xinhua, HE Xueli, and LI Danqi. Knowledge-aided 2-D autofocus for spotlight SAR range migration algorithm imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5458–5470. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2817507 [12] KRAGH T J and KHARBOUCH A A. Monotonic iterative algorithms for SAR image restoration[C]. 2006 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Atlanta, USA, 2006: 645–648. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2006.312463. [13] 张柘, 张冰尘, 洪文, 等. 结合MD自聚焦算法与回波模拟算子的快速稀疏微波成像误差补偿算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(1): 25–34. doi: 10.12000/JR15055ZHANG Zhe, ZHANG Bingchen, HONG Wen, et al. Accelerated sparse microwave imaging phase error compensation algorithm based on combination of SAR raw data simulator and Map-drift autofocus algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(1): 25–34. doi: 10.12000/JR15055 [14] GÜNGÖR A, ÇETIN M, and GÜVEN H E. Autofocused compressive SAR imaging based on the alternating direction method of multipliers[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 1573–1576. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944458. [15] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [16] GÜVEN H E, GÜNGÖR A, and ÇETIN M. An augmented Lagrangian method for complex-valued compressed SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2016, 2(3): 235–250. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2580498 [17] ÖNHON N Ö and ÆETIN M. A sparsity-driven approach for SAR image formation and space-variant focusing[C]. 2011 IEEE 19th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, Turkey, 2011: 614–617. doi: 10.1109/SIU.2011.5929725. [18] 刘碧丹, 王岩飞, 韩松. 距离徙动校正和斜地变换的实时算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(5): 1099–1102. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00192LIU Bidan, WANG Yanfei, and HAN Song. A real-time associative algorithm of RCMC and SRGR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(5): 1099–1102. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00192 [19] MALEKI A, ANITORI L, YANG Z, et al. Asymptotic analysis of complex LASSO via Complex Approximate Message Passing (CAMP)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(7): 4290–4308. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2252232 [20] DONOHO D L, MALEKI A, and MONTANARI A. The noise-sensitivity phase transition in compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2011, 57(10): 6920–6941. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2011.2165823 -







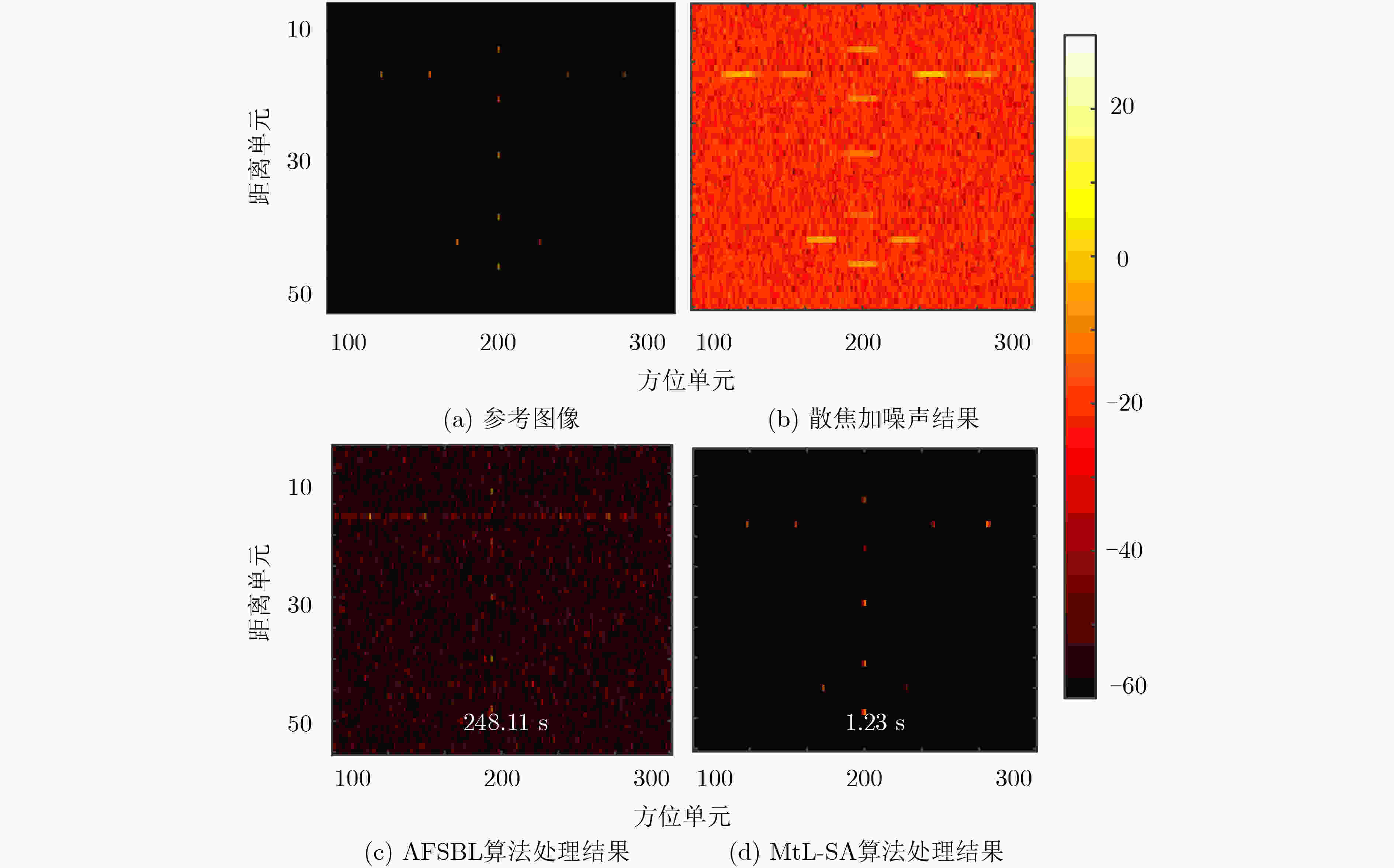
 下载:
下载:
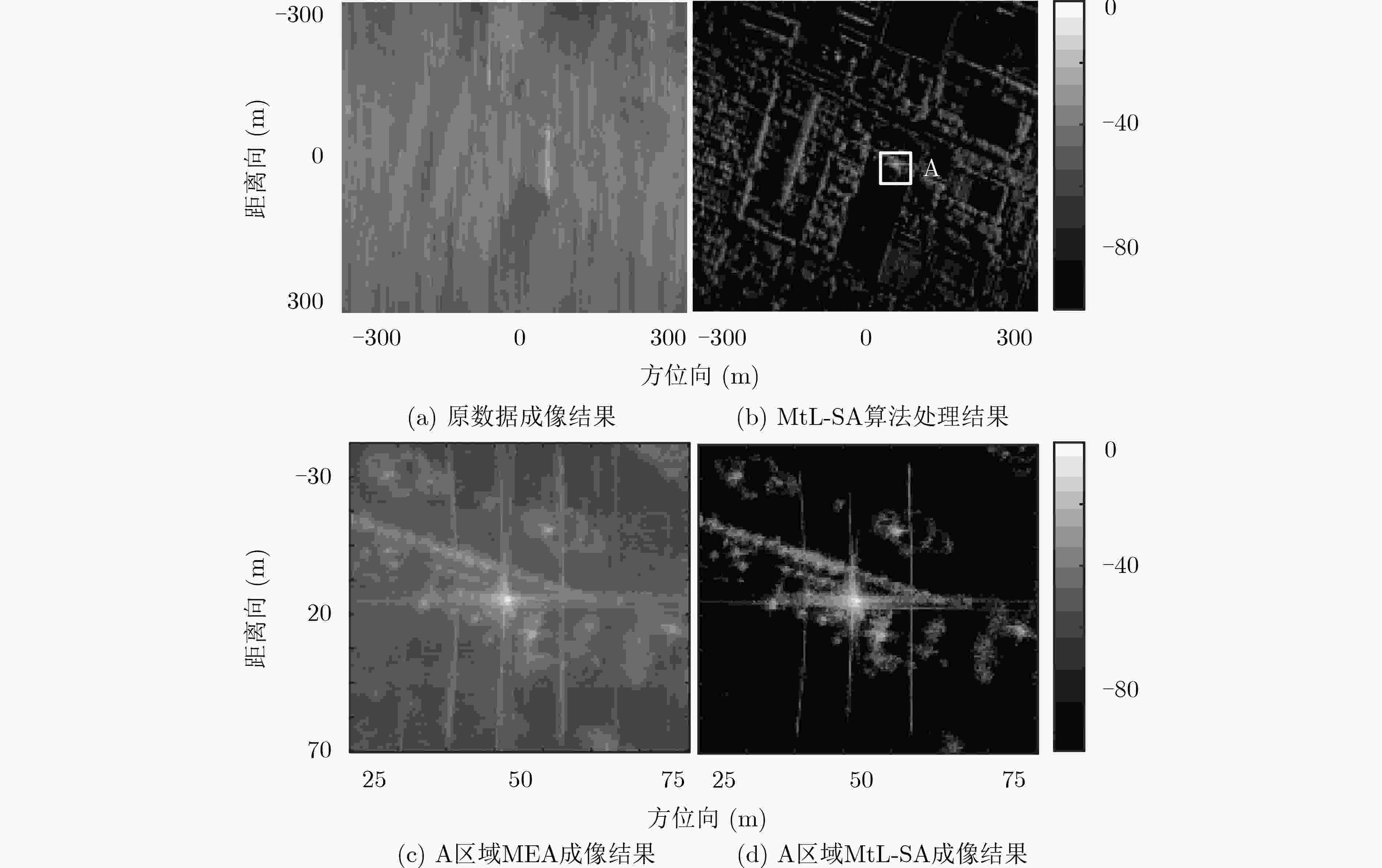
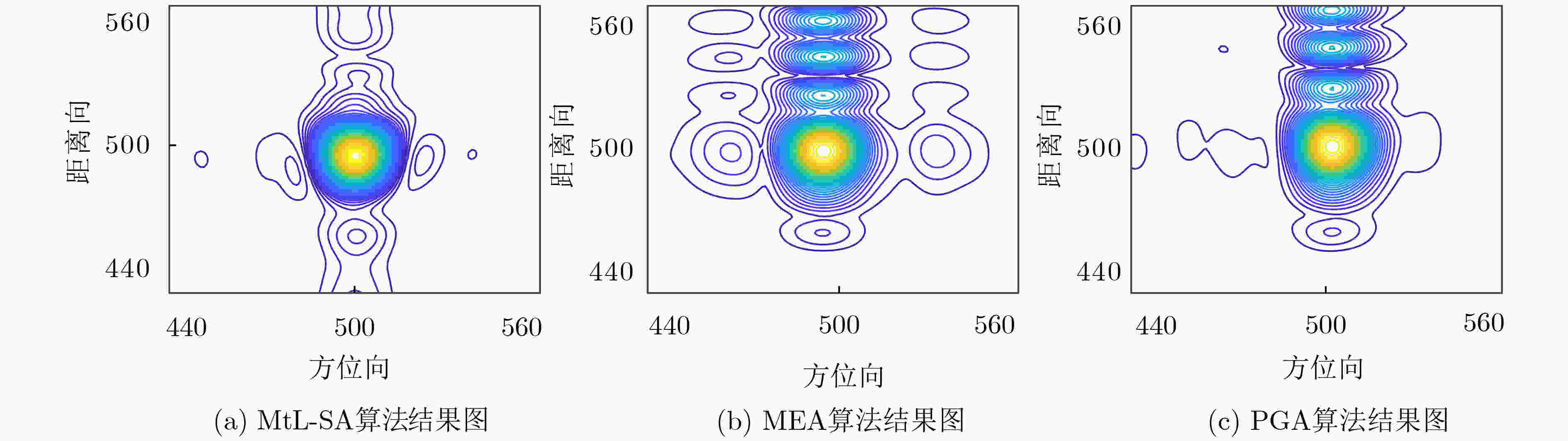


 下载:
下载:
