Convex Combination of Multiple Adaptive Filters under the Maximum Correntropy Criterion
-
摘要: 基于最大互相关熵准则(MCC)的自适应滤波算法在非高斯噪声环境下具有强鲁棒性,得到了广泛应用。然而,传统MCC滤波算法在选择参数时依然受到收敛速度与稳态精度之间固有矛盾的困扰。为解决这一问题,该文提出一类多凸组合MCC算法,能够充分发挥不同参数组合下滤波算法的性能优势,从而获得更好的信道跟踪能力。理论分析得出了所提算法的均值收敛条件和稳态均方误差,同时,仿真实验表明所提算法在对抗高斯和非高斯噪声时均具有收敛快、稳态精度高的特点。Abstract: The adaptive filtering algorithms under the Maximum Correntropy Criterion (MCC) show strong robustness against impulsive noises. The original MCC adaptive filter, however, still suffers from a compromise between convergence rate and misadjustment when choosing parameters. To address this issue, a convex combination approach is proposed in this paper, where multiple MCC adaptive filters with different step-sizes and kernel widths are combined together to yield fast convergence speed and lower misadjustment. Theoretical analysis on convergence of the new approach demonstrates that it can achieve more desirable performance than the original MCC adaptive filter as well as convex combination of two MCC adaptive filers with different step-sizes or kernel widths. Simulation results confirm the excellent performance of the new method.
-
表 1 算法参数设置
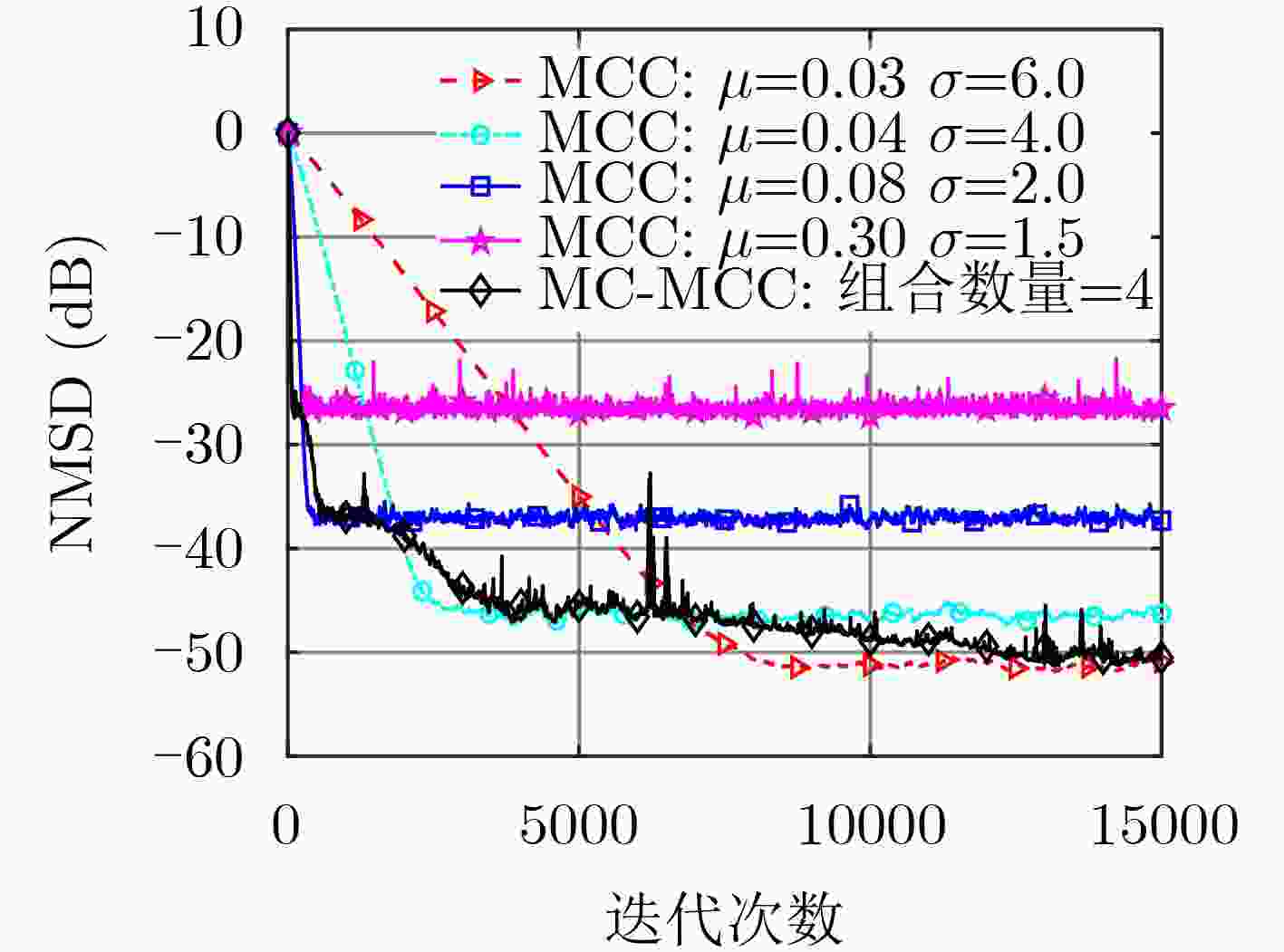
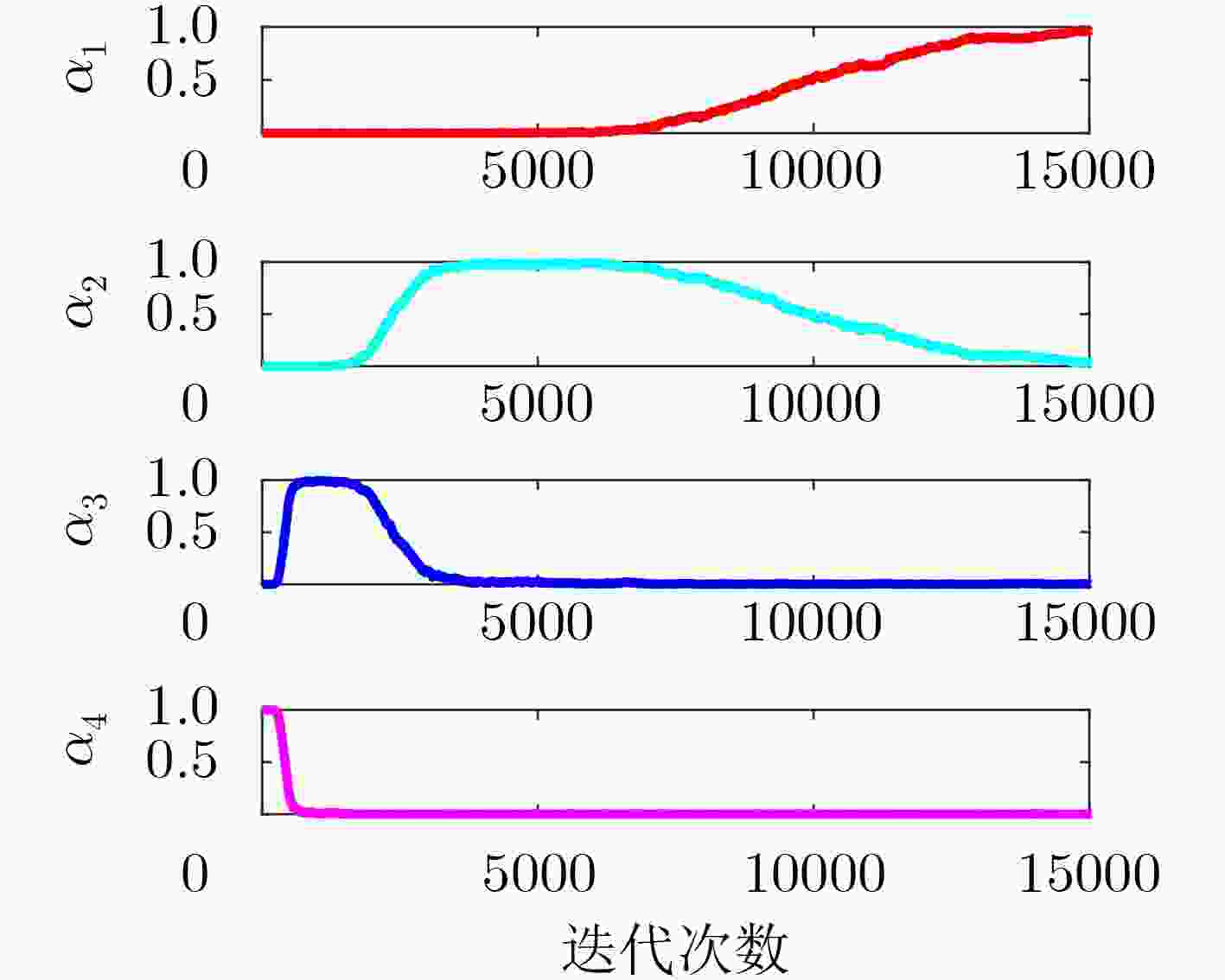
名称 ${\mu _1}$/${\sigma _1}$ ${\mu _2}$/${\sigma _2}$ ${\mu _3}$/${\sigma _3}$ ${\mu _4}$/${\sigma _4}$ ${\mu _\xi }$/${\sigma _\xi }$ 数值 0.03/6.0 0.04/4.0 0.08/2.0 0.3/1.5 4.5/1.0 表 2 算法参数设置
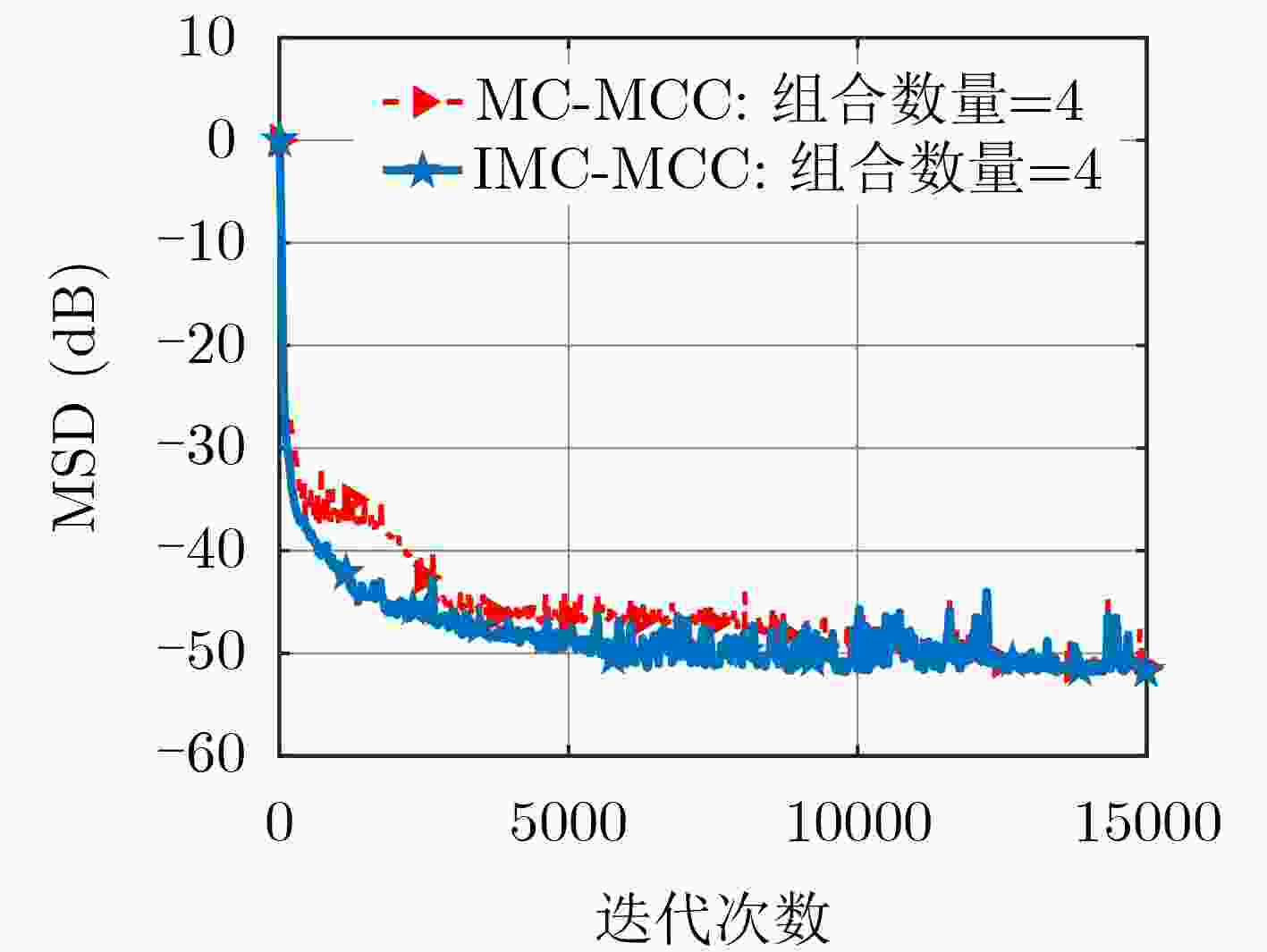
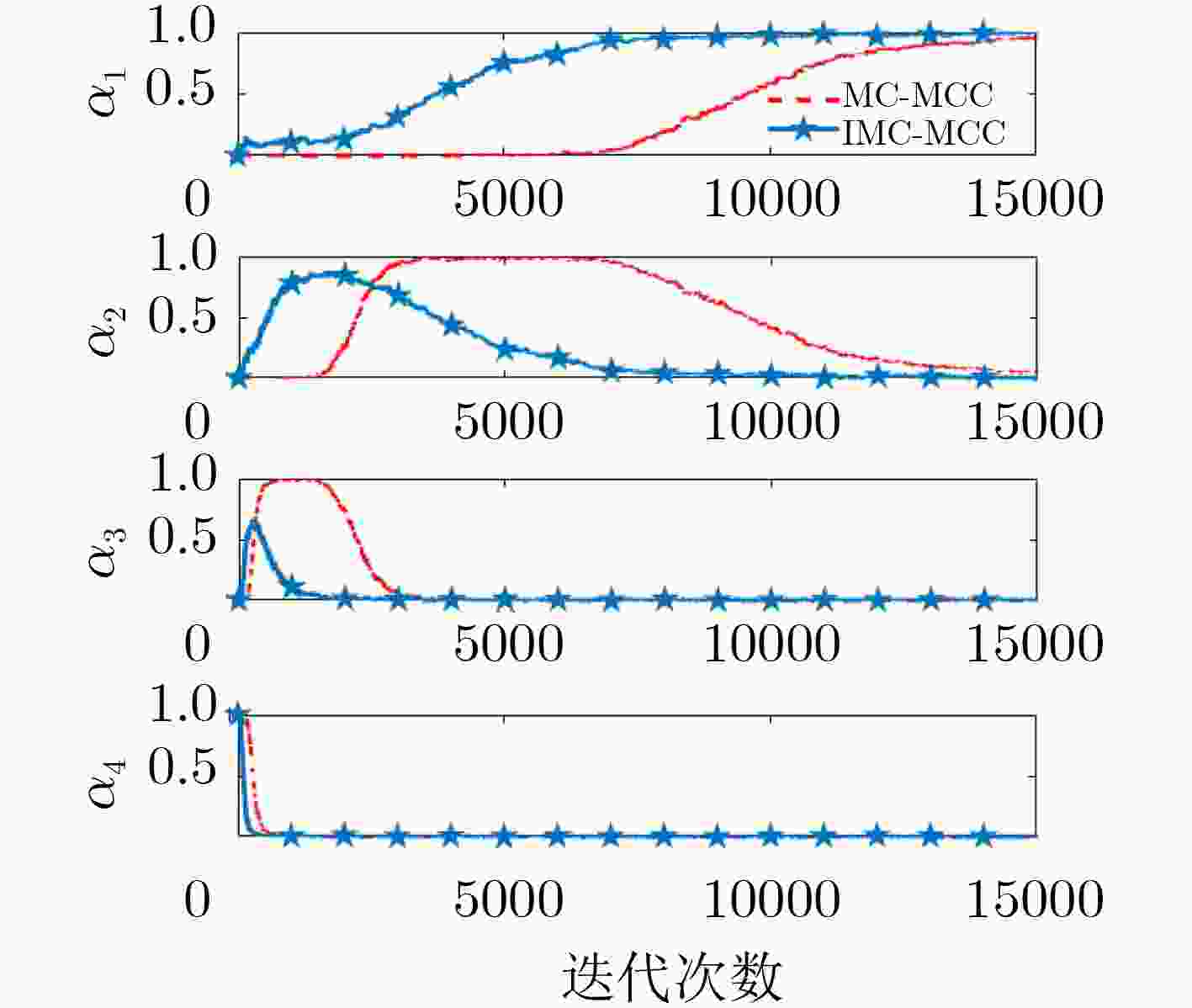
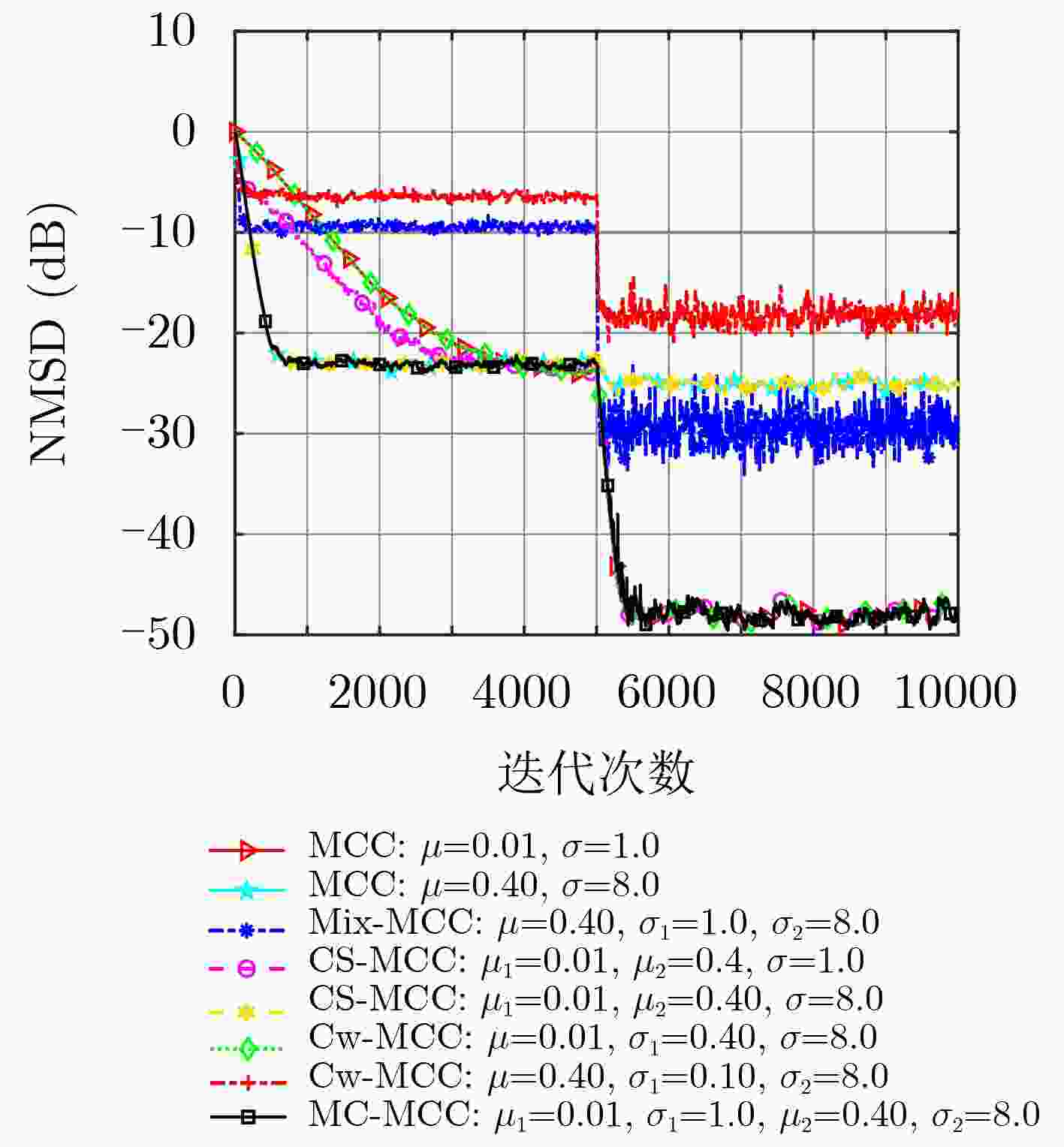
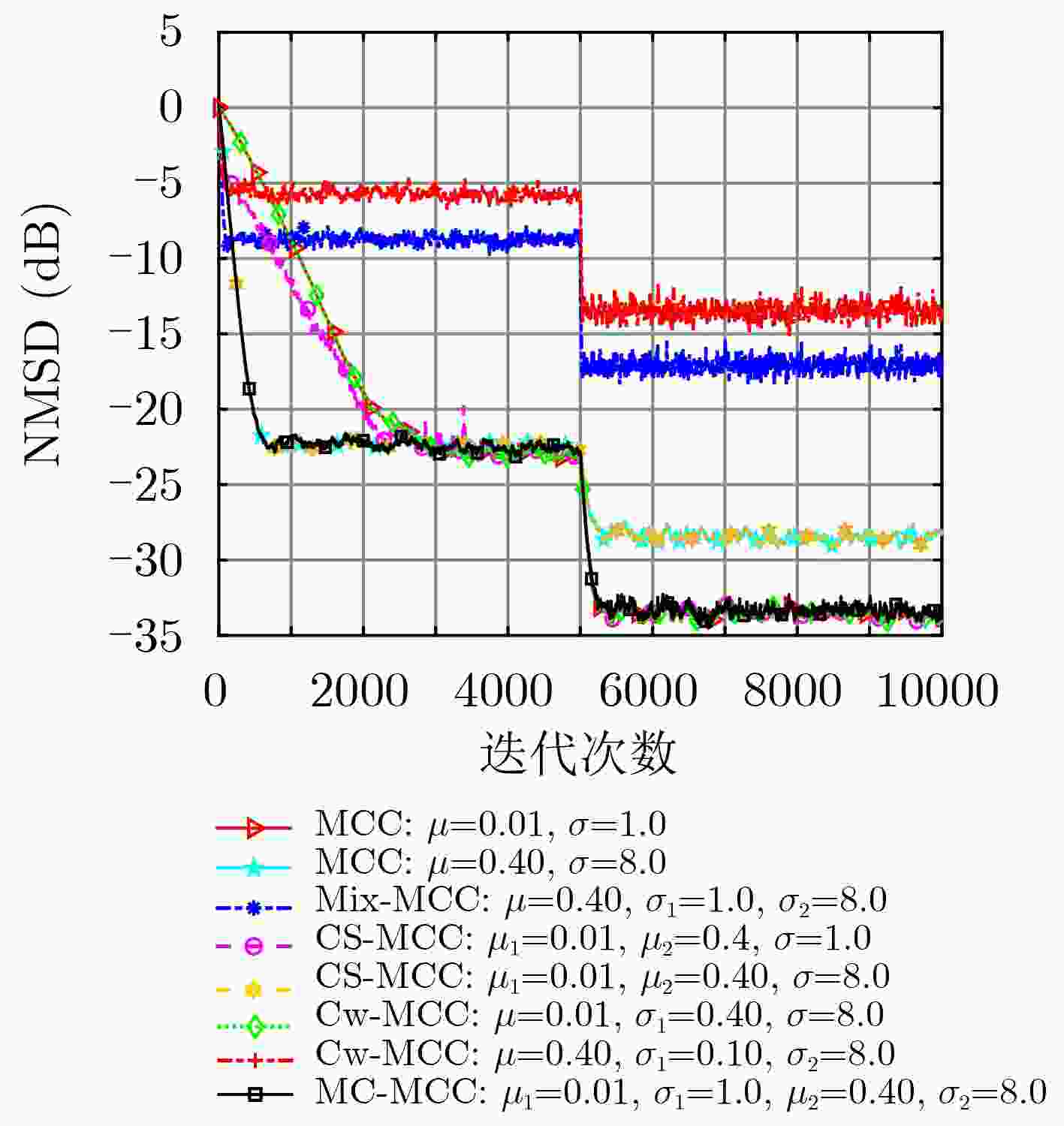
名称 ${\mu _1}$ ${\mu _2}$ ${\sigma _1}$ ${\sigma _2}$ 数值 0.01 0.4 1.0 8.0 -
PRINCIPE J C. Information Theoretic Learning: Renyi’s Entropy and Kernel Perspectives[M]. New York: Springer, 2010: 385–388, 415–424. CHEN Badong, ZHU Yu, HU Jinchun, et al. System Parameter Identification: Information Criteria and Algorithms[M]. London: Elsevier, 2013: 32–40. HE Ran, ZHENG Weishi, and HU Baogang. Maximum correntropy criterion for robust face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(8): 1561–1576. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.220 SINGH A and PRÍNCIPE J C. A loss function for classification based on a robust similarity metric[C]. 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Barcelona, Spain, 2010: 1–6. ZHAO Songlin, CHEN Badong, and PRÍNCIPE J C. An adaptive kernel width update for correntropy[C]. 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Brisbane, Australia, 2012: 1–5. CHEN Badong and PRINCIPE J C. Maximum correntropy estimation is a smoothed MAP estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 19(8): 491–494. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2204435 CHEN Badong, XING Lei, LIANG Junli, et al. Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(7): 880–884. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2319308 SAYED A H. Adaptive Filters[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008: 163–200. WIDROW B and STEARNS S D. Adaptive Signal Processing[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1985. 邱天爽. 相关熵与循环相关熵信号处理研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 105–118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190646QIU Tianshuang. Development in signal processing based on correntropy and cyclic correntropy[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 105–118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190646 ZHIDKOV S V. Impulsive noise suppression in OFDM-based communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2003, 49(4): 944–948. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2003.1261179 WANG Ren, CHEN Badong, ZHENG Nanning, et al. A variable step-size adaptive algorithm under maximum correntropy criterion[C]. 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Killarney, Ireland, 2015: 1–5. ZHAO Haiquan, LIU Bing, and SONG Pucha. Variable step-size affine projection maximum correntropy criterion adaptive filter with correntropy induced metric for sparse system identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 67(11): 2782–2786. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.2973764 WANG Weihua, ZHAO Jihong, QU Hua, et al. An adaptive kernel width update method of correntropy for channel estimation[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Singapore, 2015: 916–920. HUANG Fuyi, ZHANG Jiashu, and ZHANG Sheng. Adaptive filtering under a variable kernel width maximum correntropy criterion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2017, 64(10): 1247–1251. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2017.2671339 李群生, 赵剡, 寇磊, 等. 一种基于多尺度核学习的仿射投影滤波算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 924–931. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190023LI Qunsheng, ZHAO Yan, KOU Lei, et al. An affine projection algorithm with multi-scale kernels learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 924–931. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190023 CHEN Badong, WANG Xin, LU Na, et al. Mixture correntropy for robust learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 79: 318–327. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.02.010 ARENAS-GARCÍA J, GÓMEZ-VERDEJO V, and FIGUEIRAS-VIDAL A R. New algorithms for improved adaptive convex combination of LMS transversal filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2005, 54(6): 2239–2249. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2005.858823 SILVA M T M and NASCIMENTO V H. Improving the tracking capability of adaptive filters via convex combination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(7): 3137–3149. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.919105 ARENAS-GARCIA J, FIGUEIRAS-VIDAL A R, and SAYED A H. Mean-square performance of a convex combination of two adaptive filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 1078–1090. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.863126 SHI Liming and LIN Yun. Convex combination of adaptive filters under the maximum correntropy criterion in impulsive interference[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(11): 1385–1388. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2337899 ARENAS-GARCIA J, MARTINEZ-RAMON M, GOMEZ-VERDEJO V, et al. Multiple plant identifier via adaptive LMS convex combination[C]. 2003 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing, Budapest, Hungary, 2003: 137–142. MA Wentao, QU Hua, GUI Guan, et al. Maximum correntropy criterion based sparse adaptive filtering algorithms for robust channel estimation under non-Gaussian environments[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2015, 352(7): 2708–2727. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2015.03.039 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
